- How to calculate pump power
- Internal sewerage
Sewage systems for a private home or summer cottage differ from urban ones in their autonomy. And while some country villages have central water supply, they do not have sewerage. Therefore, it is important to think through all the nuances of pipeline installation.
How does a typical sewer system work?
“Amenities in the yard” can only be satisfied if we are talking about a summer cottage without running water, where the owners appear occasionally and for a short time.
Work on improvement of a residential building primarily involves the installation of water supply and sewerage. They are designed simultaneously. If the water is already connected, then the sewerage system is “adjusted” to the existing network.
There should be no mistakes when choosing a sewerage scheme for a residential building. An incorrectly assembled network will not work or problems will arise during its operation (+)
The development of a sewer system layout option is usually carried out at the building design stage and constructed during the construction process.
If necessary, you can, of course, carry out this work in an already built house and on a developed site, but this will be more troublesome and costly.
Image gallery
Photo from
Sewer hatch in a suburban area
Internal part of independent sewerage
External treatment facilities
Ground treatment system
You need to know that the system consists of two interrelated elements:
- External sewerage. It is located outside the building and includes a pipeline connecting to a centralized sewerage system or a wastewater treatment plant. The latter can be of any type.
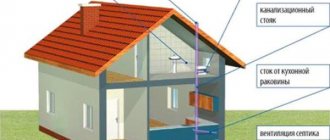
- Internal sewerage . This is a structure made of pipes connecting the outlets of all plumbing fixtures located inside the building into a single system.
Both parts of the sewer system perform a common task and function in harmony.
An autonomous sewer system consists of internal and external interconnected parts, each of which must clearly perform its own function
Biological treatment station: packaged solution
A compact biological treatment station is a two-in-one solution, that is, an anaerobic septic tank and aerobic treatment devices assembled in a compact housing. The designs of different developers differ in detail, but the essence does not change: all of these are “boxed” solutions with sludge settling tanks, anaerobic and aerobic treatment zones with forced aeration, as well as the subsequent removal of water, purified up to 95%, to the terrain - into the drainage system , filter well or nearest ditch (also by gravity or forced, due to a drainage pump).
Stations offered on the market may differ in the materials from which the housings are made (most are made of polypropylene), the quantity, the ratio of the volumes of primary and secondary chambers, the presence and design of control automation systems, built-in biofilters, pumps, and models of compressors for aerating wastewater.
Principles of designing a sewer system for a private house
A local sewerage project for a country house should be as simple as possible in order to minimize the number of errors that are possible during installation. You can develop such a scheme yourself, based on drawings on the Internet. But it is better to entrust a complex project to specialists.
A simple sewer system for a private house consists of standard elements: pipes connected to plumbing fixtures, a riser, an external pipeline and a storage or treatment facility into which all wastewater from the house is drained.
When choosing the location of inspection wells and treatment facilities, as well as when choosing the depth of the trenches, you should carefully adhere to SNiP and regulatory documents (+)
When developing a sewer system plan, we are guided by several principles:
- In a one-story house, it is reasonable to place nearby rooms in which plumbing fixtures are installed (kitchen, bathroom, toilet).
- It is better to place blocks with plumbing fixtures closer to the point where the pipes exit to the street.
- In a two- or three-story residential building, rooms with plumbing are planned one above the other in order to connect all equipment to a common riser.
- The internal sewage system of the house should be designed so that the number of connections is minimal. This will have a positive effect on the efficiency of the sewer system, and the likelihood of blockages and problems will be reduced. The main rule: simple is more reliable.
- Sometimes the layout of the house is such that it is necessary to develop a complex communications scheme. An alternative is to install several simple systems with separate external pipelines and treatment facilities.
There are houses where it is necessary to use a sewer pumping station in the drainage system. In such cases, it is better not to skimp on technology, but to entrust the design and installation of a complex sewer system for a country house to professionals.
Standard sewage hose is 25 m. If the distance from the machine to the treatment plant is greater, the wastewater will have to be pumped out with a vacuum pump, which will be more expensive
When developing a sewerage project, several important factors should be taken into account:
- Water supply system arrangement diagram . It can operate from a private hydraulic structure (well or borehole with a pump) or a centralized network.
- The number and type of plumbing fixtures that will be installed, as well as how much water each one uses on average.
- Distance from the house to the septic tank , volume and number of chambers, total length of the pipeline.
- The method of cleaning the storage tank, the presence/absence of access roads for sewage disposal equipment.
- Climate and hydrogeological features of the area : level of soil freezing, groundwater level, terrain of the area.
During the design process, all the nuances are taken into account: sewerage layout (internal and external), type and quantity of materials, turns, joints and connections.
If the local sewerage scheme provides for the installation of additional equipment (pumps, compressors or aerators for septic tanks), then the locations of the devices are also indicated in the drawings.
Let us examine in more detail the features of the design and arrangement of external and internal sewer systems.
Filtration field: where does the water go?
As we have already noted, an anaerobic septic tank is capable of purifying wastewater by a little more than half, but this is not enough for drainage onto the terrain or discharge into a drainage ditch. In most cases, septic tanks are used with so-called filtration fields.
If the terrain of the site allows, wastewater should flow into the septic tank and onto the filtration field by gravity. At high groundwater levels, crushed stone fields in which perforated drainage pipes are laid must be made in bulk. If the drainage of wastewater from the septic tank is located below the filtration field, a storage well is installed between them, water from which is periodically pumped upward by a drainage pump with a float switch. This solution, however, is not without its drawbacks, because in this case such advantages as “bury and forget” and energy independence are lost.
Arrangement of an external sewer system
The external sewerage project is developed so that it is as close as possible to the septic tank, and the pipeline section is straight. As for pipes, the choice in favor of polymers is rational.
Selection of required materials
Most homeowners choose sewer pipes made from synthetic materials. They are suitable for both indoor and outdoor wiring. These are durable products that are corrosion resistant. Under strong mechanical stress, they are capable of deformation, but rarely crack.
Thus, deposits accumulate less on the smooth inner walls of PVC and HDPE sewer pipes than on metal surfaces. Thanks to this, the line is less prone to blockages.
Polymer pipes are environmentally friendly. When heated, the materials do not release toxic substances into the atmosphere, water or soil
Products made from polymers are resistant to acids and alkalis. Chemically active wastewater does not harm pipes, which has a positive effect on their service life. Also, polypropylene and polyvinyl chloride tolerate high temperatures (up to 60-100°C).
Expert in the field of arrangement of sewerage systems and water supply systems
An important nuance. Professionals strongly advise not to choose pipes made of different materials for external sewerage in a private house. The risk of joint destruction due to different rates of thermal expansion is too great.
To install the pipeline, you will need connecting parts, tees, and fittings. To make it convenient to inspect and repair the sewer system, it is necessary to ensure the presence of inspection niches, inspection wells and hatches for them.
It is also necessary to select a suitable sealant for processing joints. It is best to give preference to a special silicone composition with antiseptic additives.
Features of laying external networks
In general, the process of installing sewerage is not much different from laying water pipes, but there are differences. First of all, sewerage does not always need insulation. This is explained by the fact that the liquid passes through the pipes without stopping and, theoretically, they stand empty most of the time.
In addition, the wastewater leaves the internal system with a temperature of at least 15 ° C; while moving through the pipeline, it simply does not have time to freeze.
Therefore, sewer pipes can be laid approximately 0.5 m above the freezing line of soil layers. But in areas with cold winters, it is better to insulate them to be on the safe side. This can be done in any suitable way, similar to plumbing.
Do not use mineral wool, which gets wet and loses its insulating properties. A good option is polystyrene foam, polyethylene foam with a foil outer shell.
If severe frosts are possible, then pipes laid underground and in unheated areas of the house are insulated with heat-insulating material
External sewer pipes are laid at a slope, which allows the drains to move by gravity. For plastic parts, the minimum slope is 0.8 cm per meter of pipeline.
The optimal option is 1.5 cm per meter. For asbestos pipes, these figures are 1.5 and 3 cm per meter, respectively. It is not recommended to make a larger slope, otherwise the liquid will quickly drain, and large inclusions may be deposited on the walls and clog the pipe. We provided detailed calculations of the slope of a sewer pipe with formulas in this article.
External network pipes are laid at a certain slope. The recommended values for the inclination of the elements should not be neglected, otherwise the risk of clogging increases.
Experts remind you that work on laying external sewerage pipes begins from the point of insertion into the centralized sewerage system or from the septic tank and moves towards the house.
Installation includes several stages:
- A trench of pre-calculated depth is dug. It is advisable to immediately maintain the desired slope. It is not advisable to backfill a finished trench. This is quite labor-intensive, given the need for additional compaction of the bottom.
- A sand cushion is poured. The height of the structure is 0.1-0.15 m. The sand is well shed with water, after which it is thoroughly compacted.
- Pipes are placed on the prepared base. The presence of a specified slope is checked.
- A layer of sand about 0.1 m high is poured in. The backfill is again spilled and compacted.
- The soil is being backfilled.
When laying external sewerage, you need to remember the need to install inspection wells. They are placed at all turns and in areas where there are differences in depth. In addition, such structures are also installed on straight sections every 25 m.
Image gallery
Photo from
Trench for laying sewer pipe
The starting stage of the construction of a sewer main
Sewer pipe slope
Sewer pipe insertion height
3) Water sources of drinking water and sanitary areas
3.1 Consideration of the issue regarding the installation of a sewerage system on a site involves taking into account such factors as the presence of a water well or drinking well. In this case, it is necessary to determine the depth of water in the well and the depth of the well. Such information will allow us to approximately determine the depth of the drinking water level in this area.
3.2 When considering the option for water drainage, one should take into account the presence of devices for water intake not only directly on the site, but also in the territories adjacent to it (neighbors, water protection zones). It is necessary to take into account the location of the site on the general scale of the area, and also determine the area of adjacent sites.
3.3 If the neighbors’ plots are located close to the water drainage point, then the sanitary zones of the neighbors’ plots should be taken into account, and also determine whether they have devices for collecting drinking water.
3.4 If the site is located in the water protection zone of a fishery reservoir, then this implies additional restrictions regarding the use of wastewater treatment facilities, as well as their additional disinfection using special equipment. Chlorine cartridges, ultraviolet lamps, ozonation, etc. are used to carry out the disinfection process. At the design stage, all this is agreed upon by the supervisory authorities in accordance with the existing scheme within the framework of regulatory documents.
3.5 When carrying out work on the project, the supervisory authorities agree on the type of treatment facility, its necessary indicators and quality characteristics of wastewater treatment. All the above factors are carefully taken into account, sanitary zones are also determined, and the final point of wastewater discharge is agreed upon. The most important thing when agreeing on the water discharge point is to take into account the level of protection of the aquifer for drinking water.
9) Maintenance
9.1 The necessary consultations of our specialists are free of charge. The company provides the necessary support in selecting the type of treatment facility, which happens right in the company’s office, where they also provide all the necessary information regarding the treatment facility.
9.2 Our company also informs you about the existence of related organizations engaged in dealer activities, and also provides information about the location of an authorized representative of the company in your area, performing the entire range of services from the purchase of equipment to its installation.
You should be guided by the Product Data Sheet, as well as the installation and operating instructions when considering a possible scheme for installing an autonomous sewer system .
The following are the meanings of some terms that will help you better understand the operating technology of various treatment facilities.
Activated sludge is sludge located in a biological treatment structure (aeration tank), which is formed from solid particles suspended in domestic wastewater. A variety of microorganisms (bacteria and protozoa) serve as the basis for activated sludge. The process involves the decomposition of organic pollutants by bacteria, which in turn are eaten by protozoan single-celled organisms. Activated sludge is an accelerator of the process of wastewater purification and oxidation.
Anaerobic bacteria are microorganisms that can exist in an environment without oxygen.
Aeration - This is the artificial saturation of the medium in water with air to oxidize the organic substances contained in it. Aeration is the basis of the process of biological wastewater treatment in aeration tanks and biofilters, as well as in other treatment facilities.
Aerobic bacteria are microorganisms that require oxygen to function. Aerobic bacteria are divided into conditional and unconditional (the former can live on a small amount of oxygen, while the latter live without it at all - in this case they receive oxygen from sulfates, nitrates, etc.). Denitrifying bacteria, for example, are a type of conditional bacteria.
Aerotank (aero - air, tank - container) - This is a container for purifying wastewater from organic contaminants due to their oxidation by various kinds of microorganisms that are found in activated sludge. Using a pneumatic or mechanical aerator, air is introduced into the aeration tank, mixing the waste water with activated sludge and saturating it with the oxygen necessary for the life of bacteria. The continuous supply of oxygen and the strong saturation of wastewater with activated sludge provide a high degree of intensity of the oxidation process of organic substances and make it possible to achieve a high degree of purification.
Aerofilter - This is a device for biological wastewater treatment, which differs from a biofilter in that it has a larger filtration layer area, and also in that it contains an air supply device to guarantee a high degree of oxidation intensity.
Biological wastewater treatment - This is one of the methods for removing unfavorable substances and microorganisms from industrial wastewater, based on the ability inherent in microorganisms to use pollutants of organic origin as food.
Biofilter - This is a device for artificial biological wastewater treatment, which is made in the form of a container with a double bottom and coarse-grained material for filtration inside (crushed stone, slag, expanded clay, gravel, etc.). Accumulations of microorganisms form a biological film as a result of wastewater passing through the filter material. Microorganisms mineralize and oxidize organic substances.
Biological oxygen demand (BOD) - This is the amount of oxygen that is necessary for the final decomposition of organic matter contained in runoff waters. An indicator of the degree of water pollution, which is characterized by the amount of oxygen spent over a set time on the oxidation of pollutants (5 days - BOD 5) contained in one unit volume of water.
Nitrification - This is the purification of wastewater from ammonia nitrogen. Chemical Oxygen Demand (COD) This is the amount of oxygen required for the final oxidation of wastewater.