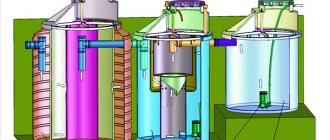
Treatment facilities are a set of special structures designed to purify wastewater from the contaminants it contains.
Purified water is either used further or discharged into natural reservoirs (Great Soviet Encyclopedia). Every settlement needs effective wastewater treatment plants. The operation of these complexes determines what water will enter the environment and how this will subsequently affect the ecosystem. If liquid waste is not cleaned up at all, not only will plants and animals die, but the soil will also be poisoned, and harmful bacteria can enter the human body and cause serious consequences.
Every enterprise that has toxic liquid waste is required to operate a treatment plant system. Thus, this will affect the state of nature and improve human living conditions. If treatment systems work effectively, wastewater will become harmless when it enters the ground and water bodies. The size of treatment facilities (hereinafter - OS) and the complexity of treatment strongly depend on the contamination of wastewater and its volume. More details about the stages of wastewater treatment and types of O.S. read on.
- Bioreactors for deep purification
- City wastewater treatment plants
Stages of wastewater treatment
The most indicative in terms of the presence of water purification stages are urban or local OS, designed for large populated areas. It is household wastewater that is most difficult to treat, as it contains various pollutants.
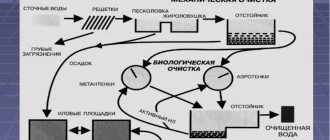
It is typical for sewerage water treatment facilities that they are built in a certain sequence. Such a complex is called a treatment plant line. The scheme begins with mechanical cleaning. Grates and sand traps are most often used here. This is the initial stage of the entire water treatment process.
This could be leftover paper, rags, cotton wool, bags and other debris. After the grates, sand traps come into operation. They are necessary in order to retain sand, including large sizes.
Mechanical stage of wastewater treatment
Initially, all water from the sewer enters the main pumping station into a special reservoir.
This reservoir is designed to compensate for the increased load during peak hours. A powerful pump evenly pumps the appropriate volume of water to pass through all stages of cleaning. Next, the water enters the mechanical cleaning shop. Up to 75% of contaminants are eliminated at this stage. There are several devices for removing large debris and insoluble impurities:
1. Grids and sieves catch large debris larger than 16 mm - cans, bottles, rags, bags, food, plastic, etc. Subsequently, this waste is either processed on site or transported to sites for processing solid household and industrial waste. The gratings are a type of transverse metal beams, the distance between which is several centimeters.
2. Sand traps. In fact, they catch not only sand, but also small pebbles, glass fragments, slag, etc. Sand settles to the bottom quite quickly under the influence of gravity. Then the settled particles are raked by a special device into a recess at the bottom, from where they are pumped out. The sand is washed and disposed of.
3. Grease traps . Here all impurities that float to the surface of the water (fats, oils, petroleum products, etc.) are removed. By analogy with a sand trap, they are also removed with a special scraper, only from the surface of the water.
4. Settling tanks are an important element of any treatment plant line. In them, water is freed from suspended substances, including helminth eggs. They can be vertical and horizontal, single-tier and two-tier. The latter are the most optimal, since in this case the water from the sewer in the first tier is purified, and the sediment (silt) that has formed there is discharged through a special hole into the lower tier. How does the process of releasing suspended solids from sewer water take place in such structures? The mechanism is quite simple. Sedimentation tanks are large, round or rectangular shaped tanks where substances settle under the influence of gravity.
To speed up this process, you can use special additives - coagulants or flocculants. They promote the sticking together of small particles due to a change in charge; larger substances settle faster. Thus, sedimentation tanks are indispensable structures for purifying water from sewers. It is important to take into account that they are also actively used in simple water treatment. The principle of operation is based on the fact that water enters from one end of the device, while the diameter of the pipe at the exit becomes larger and the flow of liquid slows down. All this contributes to the sedimentation of particles.
5. Other elements of mechanical wastewater treatment can be used depending on the degree of water contamination and the design of a particular treatment facility. These include: membranes, filters, septic tanks, etc.
If we compare this stage with conventional water treatment for drinking purposes, then in the latter version such structures are not used and there is no need for them. Instead, processes of water clarification and discoloration occur. Mechanical cleaning is very important, since in the future it will allow for more effective biological treatment.
Biological wastewater treatment plants
Biological treatment can be either an independent treatment facility or an important stage in a multi-stage system of large urban treatment complexes.
The essence of biological treatment is to remove various pollutants (organics, nitrogen, phosphorus, etc.) from water using special microorganisms (bacteria and protozoa). These microorganisms feed on harmful contaminants contained in the water, thereby purifying it.
From a technical point of view, biological treatment is carried out in several stages:
1. Aerotank is a rectangular reservoir where water after mechanical purification is mixed with activated sludge (special microorganisms), which purifies it. There are 2 types of microorganisms:
- Aerobic – using oxygen to purify water. When using these microorganisms, the water must be enriched with oxygen before entering the aeration tank.
- Anaerobic – NOT using oxygen to purify water.
2. An air purification workshop is necessary to remove unpleasantly smelling air and then clean it. This workshop is necessary when the volume of wastewater is large enough and/or treatment facilities are located near populated areas.
3. Secondary settling tanks. Here the water is purified from activated sludge by settling it. Microorganisms settle to the bottom, where they are transported to the pit using a bottom scraper. A surface scraper mechanism is provided to remove floating sludge.
4. Sludge treatment. The purification scheme also includes sludge digestion. The most important treatment facility is the digester. It is a reservoir for the fermentation of sludge, which is formed during settling in two-tier primary settling tanks. During the fermentation process, methane is produced, which can be used in other technological operations. The resulting sludge is collected and transported to special sites for thorough drying. Sludge beds and vacuum filters are widely used for sludge dewatering. After this, it can be disposed of or used for other needs. Fermentation occurs under the influence of active bacteria, algae, and oxygen. The sewer water purification scheme may also include biofilters.
It is best to place them before the secondary settling tanks, so that substances that are carried away with the flow of water from the filters can settle in the settling tanks. It is advisable to use so-called pre-aerators to speed up cleaning. These are devices that help saturate water with oxygen to accelerate aerobic processes of oxidation of substances and biological treatment. It should be noted that sewerage water purification is conventionally divided into 2 stages: preliminary and final.
The treatment plant system may include biofilters instead of filtration and irrigation fields.
Biofilters are devices where wastewater is purified by passing through a filter containing active bacteria. It consists of solid substances, which can be granite chips, polyurethane foam, polystyrene foam and other substances. A biological film consisting of microorganisms forms on the surface of these particles. They decompose organic matter. As biofilters become dirty, they need to be cleaned periodically.
Wastewater is fed into the filter in doses, otherwise high pressure can destroy beneficial bacteria. After biofilters, secondary settling tanks are used. The sludge formed in them goes partly into the aeration tank, and the rest of it goes to the sludge compactors. The choice of one or another biological treatment method and type of treatment facility largely depends on the required degree of wastewater treatment, topography, soil type and economic indicators.
Underground networks
Wastewater travels a long way to treatment plants. First, from residential areas and industrial enterprises they flow through internal and yard networks into the city sewerage system.
Basically, water moves by gravity because the pipes underground have a certain slope. Where it is impossible to provide it, pumping stations operate to create the required pressure. As Moscow continues to be actively developed, the length of sewer networks is constantly growing - on average, up to 50 kilometers are added per year.
Clean water for 36 districts of the capital: how the Western water treatment plant will change
Water flows from sewers and sewers to pumping stations. There are many foreign objects in wastewater - these can be rags, solid household waste and other debris. It happens that pumps become clogged because of this. To avoid breakdowns, water is passed through grates before entering pumping stations. The garbage they retain is then removed.
Wastewater tertiary treatment
After passing through the main stages of treatment, 90-95% of all contaminants are removed from wastewater. But the remaining pollutants, as well as residual microorganisms and their metabolic products, do not allow this water to be discharged into natural reservoirs. In this regard, various wastewater treatment systems were introduced at wastewater treatment plants.
Bioreactors for deep purification
In bioreactors the process of oxidation of the following pollutants occurs:
- organic compounds that were too tough for microorganisms,
- these microorganisms themselves,
- ammonium nitrogen.
This happens by creating conditions for the development of autotrophic microorganisms, i.e. converting inorganic compounds into organic ones. For this purpose, special plastic backfill discs with a high specific surface area are used. Simply put, these are disks with a hole in the center. To speed up processes in the bioreactor, intensive aeration is used.
Filters for wastewater treatment
Filters purify water using sand. The sand is continuously updated automatically. Filtration is carried out in several installations by supplying water to them from the bottom up. In order to avoid using pumps and not wasting electricity, these filters are installed at a level lower than other systems. Filter washing is designed in such a way that it does not require a large amount of water. Therefore, they do not occupy such a large area.
Ultraviolet water disinfection
Disinfection or disinfection of water is an important component that ensures its safety for the body of water into which it will be discharged. Disinfection, that is, the destruction of microorganisms, is the final stage of sewerage wastewater treatment. A wide variety of methods can be used for disinfection: ultraviolet irradiation, alternating current, ultrasound, gamma irradiation, chlorination.
Ural irradiation is a very effective method that destroys approximately 99% of all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, protozoa, and helminth eggs. It is based on the ability to destroy the membrane of bacteria. But this method is not used so widely. In addition, its effectiveness depends on the turbidity of the water and the content of suspended substances in it. And UV lamps quickly become covered with a coating of mineral and biological substances. To prevent this, special emitters of ultrasonic waves are provided.
The most commonly used method after treatment facilities is chlorination. Chlorination can be different: double, superchlorination, with preammonization. The latter is necessary to prevent unpleasant odors. Superchlorination involves exposure to very large doses of chlorine. Double action means that chlorination is carried out in 2 stages. This is more typical for water treatment. The method of chlorinating sewer water is very effective, in addition, chlorine has an aftereffect that other cleaning methods cannot boast of. After disinfection, the wastewater is discharged into a reservoir.
Phosphate removal
Phosphates are salts of phosphoric acids. They are widely used in synthetic detergents (washing powders, dishwashing detergents, etc.). Phosphates entering water bodies lead to their eutrophication, i.e. turning into a swamp.
Purification of wastewater from phosphates is carried out by dosed addition of special coagulants to the water before biological treatment facilities and before sand filters.
Principle of operation
During operation, the treatment station frees water from the following types of contaminants:
- organic (feces, food residues);
- mineral (sand, stones, glass);
- biological;
- bacteriological.
The greatest danger is posed by bacteriological and biological impurities. As they decompose, they release dangerous toxins and unpleasant odors. If the level of purification is insufficient, an epidemic of dysentery or typhoid fever may occur. To prevent such situations, water after a full cleaning cycle is checked for the presence of pathogenic flora, and only after examination is discharged into reservoirs.
The principle of operation of treatment facilities is the gradual separation of garbage, sand, organic components, and fat. The semi-purified liquid is then sent to settling tanks containing bacteria, which digest the smallest particles. These colonies of microorganisms are called activated sludge. Bacteria also release their waste products into the water, so after they have disposed of organic matter, the water is cleared of bacteria and their waste.
In the most modern equipment, almost waste-free production occurs - sand is caught and used for construction work, bacteria are compressed and sent to the fields as fertilizer. The water goes back to consumers or into the river.
Auxiliary premises of treatment facilities
- Aeration
- Disposal of excess activated sludge
- Air cleaning
- Laboratory
- Administrative and amenity complex
- Electrical substation
Aeration shop
Aeration is the active process of saturating water with air, in this case by passing air bubbles through the water. Aeration is used in many processes in wastewater treatment plants. Air supply is carried out by one or more blowers with frequency converters. Special oxygen sensors regulate the amount of air supplied so that its content in the water is optimal.
Disposal of excess activated sludge (microorganisms)
At the biological stage of wastewater treatment, excess sludge is formed, as microorganisms actively multiply in aeration tanks. Excess sludge is dewatered and disposed of.
The dehydration process takes place in several stages:
- Special reagents are added to excess sludge , which stop the activity of microorganisms and promote their thickening
- In the sludge compactor , the sludge is compacted and partially dewatered.
- In a centrifuge , the sludge is squeezed out and any remaining moisture is removed from it.
- Flow dryers use continuous circulation of warm air to completely dry the sludge. The dried sludge has a residual moisture content of 20-30%.
- The sludge is then packed into sealed containers and disposed of
- The water removed from the sludge is sent back to the beginning of the cleaning cycle.
Air cleaning
Unfortunately, wastewater treatment plants don't smell the best. The biological wastewater treatment stage is especially smelly. Therefore, if the treatment plant is located near populated areas or the volume of wastewater is so large that a lot of bad-smelling air is generated, you need to think about cleaning not only the water, but also the air.
Air purification usually takes place in 2 stages:
- Initially, polluted air is supplied to bioreactors, where it comes into contact with specialized microflora adapted for recycling organic substances contained in the air. It is these organic substances that cause bad odors.
- The air goes through a disinfection stage with ultraviolet light to prevent these microorganisms from entering the atmosphere.
Laboratory at wastewater treatment plants
All water that leaves treatment plants must be systematically monitored in the laboratory. The laboratory determines the presence of harmful impurities in water and whether their concentrations comply with established standards. If one or another indicator is exceeded, treatment plant workers conduct a thorough inspection of the corresponding treatment stage. And if a malfunction is detected, it is eliminated.
Administrative and amenity complex
The personnel servicing the treatment plant can reach several dozen people. For their comfortable work, an administrative and amenity complex is being created, which includes:
- Equipment repair workshops
- Laboratory
- Control room
- Offices of administrative and management personnel (accounting, human resources, engineering, etc.)
- Head office.
Electrical substation
Power supply O.S. performed according to the first reliability category. Since a long shutdown of O.S. due to lack of electricity may cause O.S. output. out of service.
To prevent emergency situations, power supply O.S. carried out from several independent sources. The branch of the transformer substation provides for the input of a power cable from the city power supply system. As well as the introduction of an independent source of electric current, for example, from a diesel generator, in case of an emergency in the city power grid.
Conclusion
Based on all of the above, we can conclude that the design of treatment facilities is very complex and includes various stages of treating wastewater from sewers. First of all, you need to know that this scheme applies only to domestic wastewater. If industrial wastewater occurs, then in this case special methods are additionally included that will be aimed at reducing the concentration of hazardous chemicals. In our case, the cleaning scheme includes the following main stages: mechanical, biological cleaning and disinfection (disinfection).
Mechanical cleaning begins with the use of grates and sand traps, which trap large debris (rags, paper, cotton wool). Sand traps are needed to sediment excess sand, especially coarse sand. This is of great importance for subsequent stages. After screens and sand traps, the sewer water treatment plant scheme includes the use of primary settling tanks. Suspended substances settle in them under the force of gravity. To speed up this process, coagulants are often used.
After settling tanks, the filtration process begins, which is carried out mainly in biofilters. The mechanism of action of the biofilter is based on the action of bacteria that destroy organic substances.
The next stage is secondary settling tanks. The silt that was carried away by the current of liquid settles in them. After them, it is advisable to use a digester, in which the sludge is fermented and transported to sludge sites.
The next stage is biological treatment using an aeration tank, filtration fields or irrigation fields. The final stage is disinfection.
Types of treatment facilities
A variety of structures are used for water treatment. If it is planned to carry out this work on surface water immediately before its supply to the city’s distribution network, then the following structures are used: settling tanks, filters. For wastewater, a wider range of devices can be used: septic tanks, aeration tanks, digesters, biological ponds, irrigation fields, filtration fields, and so on. There are several types of treatment plants depending on their purpose. They differ not only in the volume of water being purified, but also in the presence of stages of its purification.
City wastewater treatment plants
Data from O.S. are the largest of all, they are used in large cities and towns. In such systems, particularly effective methods of liquid purification are used, for example, chemical treatment, methane tanks, flotation units. They are designed for the treatment of municipal wastewater. These waters are a mixture of domestic and industrial wastewater. Therefore, there are a lot of pollutants in them, and they are very diverse. The water is purified to meet the standards for discharge into a fishery reservoir. The standards are regulated by Order of the Ministry of Agriculture of Russia dated December 13, 2016 No. 552 “On approval of water quality standards for water bodies of fishery importance, including standards for maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances in the waters of water bodies of fishery importance.”
In OS data, as a rule, all stages of water purification described above are used. The most illustrative example is the Kuryanovsky wastewater treatment plant.
Kuryanovsky O.S. are the largest in Europe. Its capacity is 2.2 million m3/day. They serve 60% of Moscow's wastewater. The history of these objects goes back to 1939.
Local treatment facilities
Local treatment facilities are structures and devices designed to treat the subscriber's wastewater before discharging it into the public sewerage system (defined by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of February 12, 1999 No. 167).
There are several classifications of local OS, for example, there are local OS. connected to the central sewerage and autonomous. Local O.S. can be used on the following objects:
- In small towns
- In the villages
- In sanatoriums and boarding houses
- At car washes
- On personal plots
- At manufacturing plants
- And at other objects.
Local O.S. can vary greatly from small units to capital structures that are maintained daily by qualified personnel.
Treatment facilities for a private home.
Several solutions are used to dispose of wastewater from a private home. They all have their advantages and disadvantages. However, the choice always remains with the home owner.
1. Cesspool . In truth, this is not even a treatment facility, but simply a tank for temporary storage of wastewater. When the pit is filled, a sewage disposal truck is called, which pumps out the contents and takes it away for further processing.
This archaic technology is still used today due to its cheapness and simplicity. However, it also has significant disadvantages, which sometimes negate all its advantages. Wastewater can enter the environment and groundwater, thereby polluting it. It is necessary to provide a normal entrance for the sewer truck, since it will have to be called quite often.
2. Storage . It is a container made of plastic, fiberglass, metal or concrete into which wastewater is drained and stored. They are then pumped out and disposed of by a sewer truck. The technology is similar to a cesspool, but the water does not pollute the environment. The disadvantage of such a system is the fact that in the spring, when there is a large amount of water in the ground, the storage tank can be squeezed out to the surface of the earth.
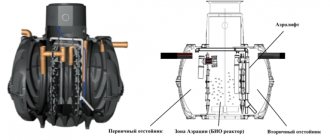
3. Septic tank - is a large container, in which substances such as coarse dirt, organic compounds, stones and sand precipitate, and elements such as various oils, fats and petroleum products remain on the surface of the liquid. The bacteria that live inside the septic tank extract oxygen for life from the fallen sediment, while reducing the level of nitrogen in the wastewater. When the liquid leaves the sump, it becomes clarified. It is then purified using bacteria. However, it is important to understand that phosphorus remains in such water. For final biological treatment, irrigation fields, filtration fields or filter wells can be used, the operation of which is also based on the action of bacteria and activated sludge. Plants with a deep root system cannot be grown in this area.
A septic tank is very expensive and can take up a large area. It should be borne in mind that this is a structure that is designed to treat small amounts of domestic wastewater from the sewer system. However, the result is worth the money spent. The structure of a septic tank is shown more clearly in the figure below.
4. Deep biological treatment stations are already a more serious treatment facility, unlike a septic tank. This device requires electricity to operate. However, the quality of water purification is up to 98%. The design is quite compact and durable (up to 50 years of operation). To service the station, there is a special hatch at the top, above the ground surface.
Stormwater treatment plants
Despite the fact that rainwater is considered quite clean, it collects various harmful elements from asphalt, roofs and lawns. Garbage, sand and petroleum products. To ensure that all this does not end up in nearby water bodies, stormwater treatment facilities are being created.
In them, water undergoes mechanical purification in several stages:
- Sump. Here, under the influence of the Earth's gravity, large particles - pebbles, glass fragments, metal parts, etc. - settle to the bottom.
- Thin layer module. Here, oils and petroleum products collect on the surface of the water, where they are collected on special hydrophobic plates.
- Sorption fiber filter. It catches everything that the thin-layer filter missed.
- Coalescent module. It helps to separate oil particles that float to the surface and are larger than 0.2 mm in size.
- Carbon filter after purification. It finally rids the water of all petroleum products that remain in it after passing through the previous stages of purification.
Design of wastewater treatment plants
Design of O.S. determine their cost, choose the right treatment technology, ensure reliable operation of the structure, and bring wastewater to quality standards. Experienced specialists will help you find effective installations and reagents, draw up a wastewater treatment plan and put the installation into operation. Another important point is drawing up an estimate that will allow you to plan and control expenses, as well as make adjustments if necessary.
For the project O.S. The following factors greatly influence:
- Wastewater volumes. Designing structures for a personal plot is one thing, but designing structures for treating wastewater in a cottage community is another. Moreover, it must be taken into account that the capabilities of O.S. must be greater than the current amount of wastewater.
- Terrain. Wastewater treatment facilities require access to special vehicles. It is also necessary to provide for the power supply of the facility, the removal of purified water, and the location of the sewage system. O.S. may occupy a large area, but they should not interfere with neighboring buildings, structures, roads and other structures.
- Wastewater pollution. The technology for treating storm water is very different from treating domestic water.
- Required level of cleaning. If the customer wants to save on the quality of purified water, then it is necessary to use simple technologies. However, if you need to discharge water into natural reservoirs, then the quality of treatment must be appropriate.
- Competence of the performer. If you order O.S. from inexperienced companies, then get ready for unpleasant surprises in the form of an increase in construction estimates or a septic tank floating in the spring. This happens because they forget to include quite critical points in the project.
- Technological features. The technologies used, the presence or absence of treatment stages, the need to construct systems servicing the treatment facility - all this must be reflected in the project.
- Other. It is impossible to foresee everything in advance. As the treatment plant is designed and installed, various changes may be made to the design plan that could not be foreseen at the initial stage.
Stages of designing a treatment plant:
- Preliminary work. They include studying the site, clarifying the customer’s wishes, analyzing wastewater, etc.
- Collection of permits. This point is usually relevant for the construction of large and complex structures. For their construction, it is necessary to obtain and approve the relevant documentation from the supervisory authorities: MOBVU, MOSRYBVOD, Rosprirodnadzor, SES, Hydromet, etc.
- Choice of technology. Based on paragraphs 1 and 2, the necessary technologies used for water purification are selected.
- Drawing up an estimate. Construction costs O.S. must be transparent. The customer must know exactly how much the materials cost, what the price of the installed equipment is, what the workers' wage fund is, etc. You should also consider the costs of subsequent system maintenance.
- Cleaning efficiency. Despite all the calculations, the cleaning results may be far from desired. Therefore, already at the planning stage O.S. it is necessary to conduct experiments and laboratory studies that will help avoid unpleasant surprises after construction is completed.
- Development and approval of project documentation. To begin construction of treatment facilities, it is necessary to develop and agree on the following documents: a draft sanitary protection zone, a draft standards for permissible discharges, a draft maximum permissible emissions.
Installation of treatment facilities
After the O.S. project has been prepared and all necessary permits have been obtained, the installation stage begins. Although the installation of a country septic tank is very different from the construction of a sewage treatment plant in a cottage community, they still go through several stages.
First, the area is prepared. A pit is being dug to install a treatment plant. The floor of the pit is filled with sand and compacted or concreted. If a treatment plant is designed for a large amount of wastewater, then, as a rule, it is built on the surface of the earth. In this case, the foundation is poured and a building or structure is already installed on it.
Secondly, the installation of equipment is carried out. It is installed, connected to the sewerage and drainage system, and to the electrical network. This stage is very important because it requires personnel to know the specifics of the operation of the equipment being configured. It is incorrect installation that most often causes equipment failure.
Thirdly, inspection and delivery of the object. After installation, the finished treatment facility is tested for the quality of water treatment, as well as for its ability to operate under high load conditions. After checking O.S. is handed over to the customer or his representative, and also, if necessary, undergoes a state control procedure.
Definition and purpose
Treatment facilities are complex equipment that is designed to solve the most important problems - ecology and human health. The amount of waste is constantly increasing, new types of detergents are appearing, which are difficult to remove from water so that it is suitable for further use.
The system is designed to receive a certain volume of wastewater from a city or local sewerage system, purify it from all kinds of impurities and organic substances and then send it to natural reservoirs using pumping equipment or the gravity method.