Choice screwdriver
by voltage and other parameters
When choosing a screwdriver suitable for certain tasks, you should pay special attention to different properties. Among them, not only the power of the device and the capacity of its battery are important, but also the battery voltage, and sometimes the torque
.
When carrying out construction and repair work, a screwdriver is an indispensable tool that simplifies the tightening of various types of fasteners, and sometimes even drilling holes. And, despite the fact that there are two versions of this device - mains and battery-powered, more often the latter option is chosen to perform household tasks. At the same time, attention is paid to the parameters of the power tool itself and to such characteristics as the voltage in the screwdriver, its power, torque and battery capacity . Each of these indicators is important for evaluating and choosing the correct device. Whereas it’s not worth buying based on suitable power or voltage alone.
Selecting a screwdriver
In this article, we would like to touch upon the topic of choosing a screwdriver, take a closer look at their types and, naturally, the technical properties that you should pay attention to when purchasing this type of tool, in order to answer in detail the question that is appearing more and more often in the near future, and specifically. How to choose a screwdriver for your home, cottage or work.
Screwdriver application areas
- Tightening/unscrewing screws, self-tapping screws, bolts and other fasteners;
- Drilling holes in wood, metal and brick.
- Stirring consistency and paints;
- Drilling holes for winter ice fishing.
There is an unlimited number of screwdrivers on the market, varying in characteristics and manufacturers. They are divided into professional and household depending on the nutrient element, cartridge size, power, a number of additional functions, delivery set and price. This division, in general, is inherent in virtually any instrument.
First, let's look at the division by nutrient element. There are two types: rechargeable (Li-Ion, Ni-Cd, Ni-Mh) and electronic, we will talk about each of them in more detail below.
The most modern and common type of rechargeable battery today, not only in screwdrivers, but also in almost all other tools (also in portable devices that we all use). Modern Li-Ion batteries are designed for three thousand charge-discharge cycles. The rechargeable battery is light in weight and charges quite quickly, in addition, it has no memory for charging.
The main disadvantages are: the shelf life of the battery, which is three years, the need for constant use to obtain the greatest return, and a significant price.
They have appeared on the market for quite a long time and are used in almost all tools, not only in screwdrivers. Designed for one and a half thousand charge-discharge cycles. The shelf life of such batteries is 5 years, it is also possible to work in the cold, at temperatures up to 15 degrees and, very important for the average buyer, the lowest cost of all types of batteries.
The negative aspects of this type of battery are the rather long charging process (an hour in the best case), the presence of memory for charging and the significant weight of the battery.
In essence, it is a cross between Li-Ion and Ni-Cd batteries. They are found in screwdrivers much less frequently than the above types of batteries. The number of charge-discharge cycles varies about a thousand. In fact, it has no memory to charge, and has the lowest self-discharge among all types of batteries. One of the downsides is the weight.
All batteries vary in capacity and battery voltage.
Capacity is measured in amperes times hour (Ah). The higher this indicator, the more the battery can carry a charge inside itself; accordingly, the greater amount of work will be done on a one hundred percent charged battery.
Battery voltage is measured in V (Volts). The power that can be obtained from a screwdriver running on these batteries depends on this indicator. Simply put, battery voltage directly affects the very likely characteristics of soft and hard torque, which we will discuss below.
They are very similar to drills (don’t miss the article “How to choose a drill”), the main difference is the presence of torque adjustment. Models of screwdrivers of this type are represented by only a few manufacturers of household-grade tools. Famous manufacturers focus on professional screwdrivers for work on drywall, the chuck of which begins to rotate the bit only after it is “sunk” into the material.
Corded screwdrivers are suitable for one-time work around the house or for professional use in repairs and construction. Based on the situation, the lack of need for charging can be considered a plus. The limitations created by the need for an electronic network, low mobility and wires getting tangled underfoot are definitely the main disadvantages of this tool.
Chucks and reducers
Screwdrivers come with a quick-release three-jaw chuck (clamping range of the equipment from 0.5 to thirteen mm) and with a hexagonal seat for equipment with a 1/4-inch shank. A quick-release chuck is more convenient and allows you to use any equipment of suitable diameter. Obviously, the larger the diameter of the chuck, the more versatile the screwdriver.
The hexagonal chuck is comfortable for frequent changes of equipment and when working in inaccessible places. To drill with such a screwdriver, you need to use drills with a hex shank. It is possible to install a conventional chuck with a hex shank.
Rotation from the motor to the chuck is transmitted by means of a gearbox. The gears inside the gearbox can be made of metal or plastic. Iron gears are more typical for massive professional models of screwdrivers.
Reflect two parameters measured in Nm (Newtonometer), these are soft and hard torques:
- A soft torque is an indicator of the greatest effort of a screwdriver in terms of tightening/unscrewing; the rotation speed in this mode for most screwdrivers varies from zero to three hundred and 50 rpm.
- The hard torque, in turn, reflects the greatest force in the drilling mode, in this case the rotation speed is usually calculated from zero to one thousand or more rpm.
The greater these characteristics, the stronger, more productive and practical the screwdriver. For example, a screwdriver with a torque of 20 5 to 30 Nm can easily screw a screw up to 70 mm long into wood. To tighten screws from 70 to 100 mm, you will need a torque of 40 Nm. Longer screws require pre-drilling the hole.
Additional abilities of some screwdrivers:
- The presence of an impact mechanism is, without a doubt, a fairly necessary function, especially when working with socket heads or when drilling holes in brick and stone.
- The presence of an impulse, sometimes an increased torque, will be needed to more easily sink the fastener into the material when unscrewing a stuck screw or even a drill if the hammer drill cannot control itself. It is especially useful when there is no ability to brace yourself in order to press the screwdriver firmly.
- The presence of three speeds will allow you to completely change the corded drill at home, because the rotation speed of the chuck in this mode can be more than three thousand rpm, and the first speed will produce a significant torque.
- The presence of backlighting is very important when working in inaccessible places or with poor or even completely absent lighting. A more successful option for placing the backlight above the battery pack is that there are models with a backlight located above the start button, which is almost always the least effective.
Summing up the result of all of the above, I would like to note that it is unrealistic to recommend a universal screwdriver for everyone, since many components of the choice depend on your goals and tasks that you are going to perform with this equipment, but in the end, I will still share my views on the choice , using some examples.
Screwdriver for home/dacha
For the most part, the network version will be enough, due to its availability, low weight and lack of need for special mobility. If we consider rechargeable versions, then it is worth paying attention to Ni-Cd and Ni-Mh, if you plan to use them rarely, this way you will save money and get a longer battery life.
In cases where frequent implementation is planned, requiring continuity of the work process, without any hesitation, the choice of a Li-Ion battery will be 100% justified. Why don’t I recommend using more modern batteries for rare jobs? It’s simple, they are more expensive and designed for measured use; you should also not forget that their shelf life is two years less, and therefore, in this case there will be even more lost capabilities.
For home needs, the highest torque of 25-35 Nm will be completely sufficient; naturally, you can take a more powerful one, here everything depends on your desire and financial abilities. The battery capacity is not so important for repeated use at home, so 1.5-2 Ah will be just right.
READ Converting a Screwdriver to a 220V Network
Screwdriver for professional use
When working in inaccessible places, it would be wise to choose a smaller model. The features of frequent and long continuous use in almost all cases will justifiably lead to the purchase of a Li-Ion screwdriver with the highest torque of 40 Nm and above, depending on the type of materials that will be worked with in the future.
Li-Ion batteries, in this case, are vital because of the continuity of the work process provided by the fast charging of the batteries, and they are also simply lighter, which is important for your hand during prolonged use.
The choice of additional screwdriver capabilities directly depends on your needs. Try to find out exactly what needs you will use it for, and decide on a budget. Last but not least, the presence of other tools, such as a drill or a hammer drill; with rare use, these points will allow you to weed out unnecessary functions and highlight the ones that are obviously necessary.
In conclusion, I would like to note that the screwdriver market is saturated with different options and choosing exactly what is right for you will not be very difficult. We hope that we were able to help you decide on the choice of a screwdriver. We want you to get the most out of your instrument and more positive feelings!
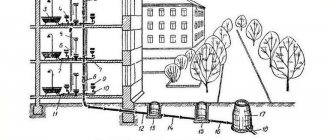
Screwdriver battery: design and types
It should be seen that regardless of the brand of screwdriver and the country of manufacture, the batteries have a similar structure. The assembled battery pack looks like this.
If we take it apart, we will see that it is assembled from small parts that are assembled one by one. And from the school physics course we know that elements that are connected in series balance their potentials.
Set-up parts or “cans” usually have a standard size and voltage; they differ only in capacity. The battery capacity is measured in Ah and is indicated on the element (shown below).
To assemble screwdriver batteries, the following types of parts are used:
- Nickel – cadmium (Ni – Cd) batteries, with a nominal voltage on the “banks” of 1.2V;
- Nickel-metal hydride (Ni-MH), element voltage – 1.2V;
- Lithium-ion (Li-Ion), with a voltage of 3.6V.
Let's take a closer look at the pros and cons of each type.
- The most common type due to its low price;
- Low temperatures are not terrible, for example, like Li-Ion batteries;
- It is stored in a discharged state, but retains its properties.
- Made exclusively in third world countries due to toxicity during production;
- Memory effect;
- Self-discharge;
- Small capacity;
- A small number of charge/discharge cycles means they do not “live” for a long time under heavy use.
- An environmentally friendly creation, it is possible to purchase a high-quality branded battery;
- Small memory effect;
- Small self-discharge;
- Large capacity compared to Ni – Cd;
- More charge/discharge cycles.
- Price;
- Loses some of its features when stored for a long time in a discharged state;
- At low temperatures it does not “live” for a long time.
- No memory effect;
- There is virtually no self-discharge;
- Highest battery capacity;
- The number of charge/discharge cycles is many times greater than with previous types of batteries;
- To set the required voltage, you need the smallest number of “cans,” which significantly reduces the weight and dimensions of the battery.
- The highest cost, almost three times in comparison with nickel-cadmium;
- After three years, a significant loss of capacity occurs, because Li decomposes.
We have become familiar with the elements, let's move on to the remaining elements of the screwdriver battery pack. Disassembling the unit, for example, to repair the battery of a Hitachi screwdriver (shown below), is very simple - unscrew the screws around the perimeter and disconnect the housing.
The housing has four contacts:
- Two power ones, “” and “-”, for charge/discharge;
- The upper control is switched on via a temperature sensor (thermistor). The thermistor is needed to protect the batteries; it turns off or limits the charging current when a certain temperature of the parts is exceeded (usually in the range of 50 - 600C). Heating occurs due to huge currents during forced charging, so-called “fast” charging;
- The so-called “service” contact, which is connected through a 9Kohm resistance. It is used for complex charging stations that smooth out the charge on all battery elements. In everyday life, such stations are of no use, due to their high price.
That's actually the entire design of the battery. Below is how to disassemble the block.
Is it possible to “reanimate” elements and how?
Let's proceed to Part 3 of screwdriver battery repair and immediately make a reservation that the concept of “reanimation” for lithium-ion batteries is not applicable. There is no memory effect in them; most likely, lithium decomposed, and nothing can be done about it. In such batteries, you need to find out what the cause of the malfunction is: the element itself or the control circuit. There are two options:
- We change the control circuit from another, but similar to ours, battery, if it helps, we find a replacement and change it;
- Apply 4V to the element with a current of approximately 200mA, for this you need a regulated charger. If the voltage on the element rises to 3.6V, the element is working properly, there is a problem in other elements, or in the control circuit.
Refurbishment of a screwdriver battery is available mostly for Ni-Cd batteries, but they are usually the most common in household screwdrivers.
So, how to revive a screwdriver battery? There are two types of “reanimation” for these types of batteries:
- The method of compaction or compression (it will work in cases where the electrolyte is still available, but the volume is lost);
- “Firmware” with voltage and current that is huge from the nominal one. This method allows you to remove the memory effect, and although not completely, return the lost capacity.
This method is given below.
This method, if its outcome is positive, will not solve the problem of parts failure. Rather, it will only delay the replacement of those that have become unusable, and in the future it will still be useful to repair the battery of a Makita screwdriver or any other.
Troubleshooting
We have figured out the purpose of the battery design parts, now let’s look at how to find the fault, this is part 2 of repairing the screwdriver battery. Let us immediately note that all the elements cannot fail at once, and since our circuit is alternate, when the 1st element fails, the entire circuit does not work. This means our task is to find where the weakest link in our chain is.
For this we will need a multimeter, and for the second method of troubleshooting a 12V lamp, if your battery for the screwdriver is also twelve volt. The procedure is as follows:
Thus, we found candidates for “reanimation” or “amputation” and replacement with new elements.
If your screwdriver operates on a voltage of twelve or 13V, you can search in a more conventional way. We disassemble the fully charged battery and connect a twelve-volt lamp to the “” and “-” contacts. The lamp will be a load and will drain the battery. Next, we take measurements on the battery elements, where the voltage drop is greatest, there is a weak link.
There are other methods, instead of a lamp you can select a resistance, but this already requires the basics of electrical engineering, and it is not clear that a resistor with the required resistance would be at hand.
Other malfunctions occur very rarely. For example, loss of contact in the places where batteries are soldered or power contacts of the unit, failure of the thermistor. This problem is more common with fakes. Due to its rarity, we will not focus on the battery elements.
The “problematic” elements have been dealt with and need to be fixed. How to repair a screwdriver battery? In general, there are two methods available for repair, so to speak. This is the restoration and replacement of parts that have become unusable.
Basic parameters of the battery and the tool itself
The main parameter that characterizes the operation of a screwdriver is the battery voltage, which, in turn, determines the power of the electric motor and torque . For household models, the difference in voltage between screwdrivers is small - on average, it is in the range of 10.8–14.4 V. More productive options intended for constant use can be equipped with 24–36 volt batteries.
The battery voltage of a screwdriver also depends on the type of battery - you can answer what the difference is by knowing what metals were used to make it. For nickel-cadmium batteries, large in size with a similar capacity, the value of the indicator is a multiple of 1.2 V (this is exactly the voltage of one element that makes up the battery pack), for lithium-ion batteries - 3.6 V.
Other equally important characteristics include:
- torque, the value of which can be one of the main answers to the question of what the voltage of the screwdriver battery affects. Using this characteristic, you can determine both the diameter and the length of the screw or self-tapping screw being screwed. Large fasteners, as well as drilling deep and wide holes and hard materials, require significant torque. Torque – 12-15 Nm (maximum up to 30 Nm) is enough for home models, and from 30 Nm for professional models. This parameter is important, pay attention to it.
- If the maximum speed is below 1000 rpm, the tool will be convenient for tightening screws and drilling soft materials (wood, metal, plastic). If you are going to drill metal, choose models with speeds above 1500 rpm. They will have two speeds: the first is for fastening, the second is for drilling.
- For serial work (installation of drywall sheets, clapboard paneling), choose corded screwdrivers with a depth limiter. Both mains-powered and battery-powered models are suitable for working at home, so choose what you like best.
There are two types of torque for screwdrivers - starting (larger in magnitude and required to put the device into operation) and constant, that is, working. The parameter value for modern equipment models can be adjusted - you can find out how many modes can be selected for a particular device in the documentation available for it. Moreover, tools with a pulse mode of operation (turning on the rotating part in jerks) have more screwing capabilities - allowing them to periodically increase the torque, they can screw in a larger screw.
The output torque value of electric motors is not constant and depends, first of all, on the speed of the motor; the higher the speed, the lower the torque on the shaft.
In addition to the voltage of the screwdriver and its power, the battery capacity should also be assessed. The characteristic is measured in ampere-hours or milliamp-hours. The higher the indicator, the longer the screwdriver can work without recharging.
The average battery capacity of a household model is 1300 mAh, which is enough for 2–3 hours of operation. Professional equipment requires more time to complete the work - and a master who uses a screwdriver throughout the whole working day should purchase a model with a battery of 1.5–2.0 Ah or more.
Tools
The price of a new screwdriver is approximately 70% the price of its battery. Therefore, it is not mind-blowing when, faced with a battery failure, we ask ourselves the question - what next? Should I take a new battery or a screwdriver, or maybe there is an opportunity to repair the screwdriver battery with my own hands and continue working with regular equipment?
In this article, which we will conditionally divide into three parts, we will look at: the types of batteries that are used in screwdrivers (part 1), their probable causes of failure (part 2) and available repair methods (part 3).
- Screwdriver battery: design and types
- Troubleshooting
- Is it possible to “reanimate” elements and how?
- Repair and replacement of screwdriver battery parts
READ Do-it-yourself power supply for a screwdriver
Repair and replacement of screwdriver battery elements
A more effective method of repairing screwdriver batteries is to replace parts that we have identified as faulty.
We will also need a soldering iron, low-corrosive flux (preferably alcohol flux based on rosin) and tin. We are not talking about spot welding, because for a one-time battery repair there is hardly a need to obtain or assemble it...
There is nothing complicated in the substitution itself, especially if there is any kind of it. I have experience in soldering. The photo shows everything quite carefully; we cut off the faulty element and solder a new one in its place.
Several aspects are worth noting:
- When soldering with a soldering iron, try to solder quickly, so that the battery does not heat up, because You risk spoiling it;
- If possible, make the connection using original plates, or use copper plates of the same size, this is important because the charging currents are huge and if the cross-section of the connecting wires is incorrect, they will heat up, and accordingly the thermistor protection will be triggered;
- Under no circumstances should you confuse the plus of the battery with the minus - the connection is in series, which means that the minus of the previous bank goes to the plus of the newest bank, and the minus of the newest bank. On plus the next one.
After the new elements have been soldered, it is necessary to equalize the potentials on the “banks”, since they are different. We carry out a charge/discharge cycle: set it to charge overnight, give it a day to cool down and measure the voltage on the elements. If we did everything correctly, the picture will be approximately as follows: all elements have the same multimeter reading, within 1.3V.
Next, we proceed to the battery level, insert the battery into the screwdriver and load it “to its fullest.” The main thing is to spare the screwdriver itself, otherwise you will have to repair it too. We bring it to full discharge. We repeat this function twice more, i.e. We charge and fully discharge.
It must be emphasized that the function of erasing the “memory effect” should be performed once every three months. It is carried out in a similar way to the above training.
This not-so-tricky procedure will prolong the operation of your screwdriver, at least until it has to be replaced with a new one.
Features of choice
As you know, professional screwdrivers are more expensive, but this is no coincidence. They are made with a large margin of safety, for which higher quality and more expensive materials are used. In addition, they have more power, which makes it possible to screw in longer screws and/or work with tougher materials.
The internal gears of the gearbox can be made of plastic or metal. The difference between a professional and household screwdriver will be in the resource
To decide whether you need a household or professional screwdriver, assess the amount of work that will need to be done. If you are starting construction or major renovations, you probably need a professional or semi-professional model. If you need a tool periodically to unscrew/tighten something from time to time, a household tool is more than enough. With such work, the professional tool resource simply will not be in demand. So choosing a screwdriver based on this criterion is not very difficult.
When choosing power, you should take into account not only what power of the screwdriver is indicated in the information from the manufacturer. Due to too much productivity, the device may tighten the screws too tightly, pressing their heads into the surface. As a result, the appearance of the coating deteriorates, and the fasteners, if necessary, are almost impossible to unscrew.
When choosing which voltage is best for a screwdriver, you should take into account that voltage is the main parameter of the device. For example, the motor power of the Makita DDF343SHE screwdriver is 700 W, with a voltage of 14.4 V and a battery capacity of 1300 mAh and a torque of 36 Nm. Whereas the other model Hammer ACD182 has a weaker engine (22 Nm) and a less capacious battery (1200 mAh) - and it seems that this device is about 40% weaker. However, due to the 18 V voltage, the Hummer is able to tighten more fasteners without recharging, even being inferior to its competitor in terms of battery capacity.
You can understand why a screwdriver that seems less productive at first glance is inferior to a more powerful one by doing a little calculation:
- the amount of energy stored by the first model is 1.2 x 1.8 = 21.6 Wh;
- the second indicator is only 1.3 x 14.4 = 18.72 Wh, i.e. 15.4% less.
When choosing a screwdriver, it is advisable to take into account the presence of a spare battery included with it. Some models even have 2 additional batteries. On the one hand, such equipment will cost more (especially since the cost of the battery is up to 80% of the price of the equipment), but it will be much more convenient to work with it. At the same time, an additional battery is not needed to perform household tasks - the time of work performed with its help rarely exceeds 1–2 hours. While in the process of constant use of a screwdriver (for example, for repair work or furniture assembly), the second battery allows you to not interrupt the work for longer than a few minutes. The discharged battery is charged, and a spare battery is installed in the device.
If there is no need for long-term work, which may require a screwdriver, it is not recommended to buy a model with additional batteries, not only because of its increased cost. It’s just that the service life of such a battery is short, and after a couple of years the user will have to buy a new part without using up even half of the life of the old one.
What does the battery voltage of a screwdriver affect?
Let me start with the fact that there is a lot on the Internet about restoring batteries from screwdrivers, and they are all similar as a mirror, a short description of the restoration process that these people offer is that we take the battery, push it with a power supply or another battery, then charge and use , and it’s surprising that no one looks at what kind of tension there will be on him when he lies down for a week or two. I propose a completely different recovery method
Which doesn’t just charge and use until the battery dies again. And what you have done is to use it as a new battery until the need arises. This method was filmed in a preliminary version about a month ago, but I never dared to post it on the website, I just didn’t want to re-shoot it for a more correct explanation. Well, to be honest, I have very little free time in the near future.
But now time has passed, which has shown that the recovery option that many people on the Internet offer to use is not destined to live for more than a certain period of time. And my version, even after 2-1 months of inactivity, as if nothing had happened, it works relaxed and charges, I still tried to shoot a new video, where I will try to tell everything in a nutshell.
In fact, everything turned out to be painfully simple, and in this I was helped by the NI-CAD 1.2V battery I disassembled, which showed me that even with all zeros on the outside of the device, inside the patient is faster alive than dead and feels very good.
An attempt to regenerate the tire relative to the slip plate was made using distilled water, and the process was quite successful, as a result of which I came up with the most common method for restoring them, even without disassembling the batteries!
Just drill a hole in the battery in the place behind the rolling, and pour 20.40 ml of distilled water into it. After a couple of cycles, cover the hole with a little silicone.
Before repeating, I recommend watching where I tried to explain the process more thoroughly.
If you are not convinced or are afraid of spoiling a damaged battery, for example, you can do this with one battery.
If your batteries have voltage and it is in the operating spectrum, then you may have a problem with the following:
- charger faulty
— the thermal protection of the battery pack worked
— in the battery pack there is one battery drained to zero volts.
Also, if you see that the drill has become somewhat sluggish and still works for the same long time after charging, then you most likely have a problem with one or more batteries that are at zero!
A very interesting effect on the battery capacity; it was equal to or slightly greater than the indicated battery capacity after restoration in this way.
What does the car battery voltage indicate?
First, you should understand the concepts of voltage and electromotive force (EMF) of a car battery. EMF ensures the flow of current through the circuit and provides a potential difference at the terminals of the power source. In our case, this is a car battery. The battery voltage is determined by the potential difference.
Both quantities, EMF and car battery voltage, are measured in volts. It is also worth adding that the electromotive force in a car battery appears as a result of chemical reactions occurring within it. The relationship between EMF and battery voltage can be expressed by the following formula:
E – electromotive force;
U – voltage at the battery terminals;
R – internal resistance of the battery.
As you can understand from this formula, the EMF is greater than the battery voltage by the amount of voltage drop inside it. So as not to fill your head with unnecessary information, let’s put it simply. The electromotive force of the battery is the voltage at the battery terminals without taking into account leakage current and external load. In other words, if you remove the battery from the car and measure the voltage, then in such an open circuit it will be equal to the EMF.
You can use a multimeter to measure voltage
What should a screwdriver be? Power
Do you think that the larger it is and the more watts, the better? Not certainly in that way. I bought it on pila.prom.ua.
The output torque value of electric motors is not constant and depends, first of all, on the speed of the motor; the higher the speed, the lower the torque on the shaft.
In addition to the voltage of the screwdriver and its power, you should also evaluate the battery capacity
. The characteristic is measured in ampere-hours or milliamp-hours. The higher the indicator, the longer the screwdriver can work without recharging.
battery capacity of a household model is 1300 mAh, which is enough for 2–3 hours of operation. Professional equipment requires more time to complete the work - and a master who uses a screwdriver throughout the whole working day should purchase a model with 1.5–2.0 Ah batteries.
Normal car battery voltage
The voltage on the car battery should be 12.6-12.9 volts if it is 100% charged. The frozen voltage of the battery allows you to quickly assess the state of charge. But the actual condition and wear of the battery cannot be determined by voltage. To obtain reliable data on the condition of the battery, you need to check its actual capacity and conduct a load test, which will be discussed below. We recommend reading the material on how to check the performance of a car battery.
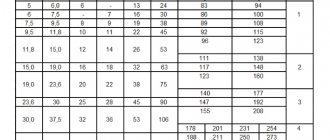
But with the help of voltage you can always find out the degree of charge of the battery. Below is a table of the degree of charge of the battery, which shows the values of voltage, density and freezing temperature of the electrolyte depending on the battery charge.
| Electrolyte density, g/cm. Cube (15 degrees Celsius) | Voltage, V (no load) | Voltage, V (with load 100 A) | Battery charge level, % | Electrolyte freezing temperature, gr. Celsius |
| Electrolyte density, g/cm. Cube (15 degrees Celsius) | Voltage, V (no load) | Voltage, V (with load 100 A) | Battery charge level, % | Electrolyte freezing temperature, gr. Celsius |
| 1,11 | 11,7 | 8,4 | -7 | |
| 1,12 | 11,76 | 8,54 | 6 | -8 |
| 1,13 | 11,82 | 8,68 | 12,56 | -9 |
| 1,14 | 11,88 | 8,84 | 19 | -11 |
| 1,15 | 11,94 | 9 | 25 | -13 |
| 1,16 | 12 | 9,14 | 31 | -14 |
| 1,17 | 12,06 | 9,3 | 37,5 | -16 |
| 1,18 | 12,12 | 9,46 | 44 | -18 |
| 1,19 | 12,18 | 9,6 | 50 | -24 |
| 1,2 | 12,24 | 9,74 | 56 | -27 |
| 1,21 | 12,3 | 9,9 | 62,5 | -32 |
| 1,22 | 12,36 | 10,06 | 69 | -37 |
| 1,23 | 12,42 | 10,2 | 75 | -42 |
| 1,24 | 12,48 | 10,34 | 81 | -46 |
| 1,25 | 12,54 | 10,5 | 87,5 | -50 |
| 1,26 | 12,6 | 10,66 | 94 | -55 |
| 1,27 | 12,66 | 10,8 | 100 | -60 |
Operating the battery in a discharged state leads to increased sulfation of the plates and, as a result, a decrease in capacity. In addition, this can lead to a deep level, which is like death for calcium batteries. For their 2-3 deepest categories, this is a direct path to the landfill.
Voltage will also help diagnose shorted cans. The voltage of the 1st charged battery cell is 2.1-2.15 volts. If one of the banks is short-circuited, then by measuring the total battery voltage at the terminals, you can immediately realize this. True, it will still be necessary to find out which element is shorted. Serviceable batteries that were produced earlier had terminals for each of the parts. By measuring the voltage from them, it was possible to determine where exactly the short circuit was. In modern low-maintenance batteries, a closed cell can be installed when measuring the density of the electrolyte. In a closed element, the density will differ significantly from the average value for the banks. We also recommend reading about the reasons for battery overcharging.
READ How to Convert a Screwdriver to Lithium Batteries
Well, now about what tool a car owner needs to monitor the voltage and condition of the battery.
How to check a screwdriver battery with a multimeter
Many home craftsmen have to face the need to check the battery health of a drill or screwdriver. Over time, the battery runs out, and in order to assess the possibility of its continued performance, you need to know how to check the battery of a screwdriver with a multimeter or tester. A multimeter is a device with the functions of a voltmeter and an ammeter.
What does the battery consist of?
The internal structure of the battery of any screwdriver, regardless of the country of origin, is absolutely identical. If you disassemble a plastic block, there are always “cans” inside, assembled in a certain sequence.
The battery voltage indicator as a whole is added up based on the U level that each battery has individually.
The battery also has four contacts, two of which provide charge-discharge cycles, the third is connected to a temperature sensor, and the fourth, which has a service purpose, is responsible for equalizing the charge potential in all batteries.
So, the interconnected “banks” of a power tool battery are nothing more than a constant current source in which chemical reactions are constantly converted into electricity. This is how the battery releases its accumulated energy into the circuit. And when it charges, the process occurs in the opposite direction: the battery simply takes energy from the network.
General recommendations before checking the battery
Before you check the screwdriver battery with a multimeter for possible faults, you should remind yourself that the nickel-cadmium batteries installed in most power tools have a so-called “memory effect”. Briefly, its essence is that due to frequent and irregular recharging, the capacity of the battery “cans” decreases, and the battery does not use its resource to its fullest.
Before testing the battery, it should be fully charged so that the readings taken by the tester are as accurate as possible. Keep in mind that testing will be optimally accurate if it is carried out under load. It is for this that the battery will need a sufficient amount of charge.
The set of tools you will need is simple:
- tester (or multimeter);
- screwdriver;
- knife;
- soldering iron;
- pliers.
First stage of testing
Checking the screwdriver battery at the first stage is the simplest; current and voltage readings are taken from the battery while it is charging.
Readings are taken several times, at certain time intervals:
- 30 minutes after charging has started, U will be about 13 volts ;
- another 30 minutes U will increase to 13.5 volts ;
- two hours after the start of the process - 14 volts ;
- a fully charged battery will produce a voltage of 17 volts .
As for the increase in current (amperage) during charging, if the operating condition of the battery is in order, then the current increases steadily during the first hour. In addition to the voltage, measure the current an hour after the start of the process. If the indicator has passed the “mark” of 1 ampere, your battery is in good health and does not need to be disassembled and repaired.
Express testing method: measure U at the battery poles
This method is even simpler, but with its help you can get an initial idea of whether the battery is ok. If we measure U without connecting a load, we get an indicator equal to the “idle speed” of the tool.
For example, if we have 12 cells in the battery with a voltage of 1.2 volts each, and the operating U is 14.4 volts, the “idle” U will increase to 17 volts.
If the “idle” voltage is less than specified, this means that there are “banks” in the combination that have failed and need to be replaced.
Also, a decrease in idle voltage may mean that the battery is not fully charged.
Checking performance under load
This means that we will check how long it will take for the screwdriver battery to be completely discharged if an additional load is connected to it - for example, a light bulb.
The load level must be selected based on the power of the battery. If it is not indicated in the operating instructions, it should be calculated independently.
It will be equal to half the current supplied by the battery during operation, multiplied by U of the current source.
Typically this figure is from 35 to 40 Watts, which means that the load can be a headlight from a 35 Watt car, or a 12-volt light bulb.
To take readings, the battery must be connected to the lamp via an ammeter, and the readings themselves must be taken with a voltmeter. The connection time is two to three minutes, after which we measure U.
If it is less than 12.4 volts, some “can” is definitely out of order. A significant decrease in the brightness of the light bulb may also indicate a battery malfunction.
If it goes out quickly within two to three minutes, the battery is clearly not in order and its capacity is very low.
Checking the elements in a disassembled battery
So, if preliminary testing has shown that the screwdriver may have faulty elements, the battery should be carefully disassembled and the batteries unsuitable for operation should be identified.
As already mentioned, the normal voltage of each battery individually should be 1.2 volts. If this indicator is less, the “can” is carefully removed from the chain using pliers.
It also doesn’t hurt to carefully inspect the entire bunch for external damage: rust, leakage of electrolyte.
If the voltage on all “banks individually” is within normal limits, you need to use load testing again, checking the level of internal resistance. This value is determined as follows: the voltage is divided by the current, and then the load resistance is subtracted from it.
To find out the voltage, immediately connect the load.
This time you should use a resistor with a power of 25 watts and a resistance of 10 ohms .
We check each battery, measuring the operating current and U. The calculations should be something like this: let’s say, when taking measurements under load, we got the operating voltage of one element to be 1.19 volts and the current to be 112 milliamps. Before calculating, it is necessary to convert milliamps to amperes. It turns out 0.112 amperes, therefore: divide 1.19 by 0.112 and subtract the resistance of 10 ohms. The result is a value of 0.63 Ohm - this means that the indicator is normal.
Checking the performance of a screwdriver battery yourself using a multimeter is a useful skill that allows you to find out whether the battery needs repair or complete replacement of the batteries.
Measurements of voltage indicators in general, without disassembling the battery pack, should be carried out from time to time. This will help to avoid sudden failure of the tool and eliminate the malfunction in time.
Also, to avoid the accumulation of “memory effect”, do not neglect to fully charge your battery. This will help avoid premature loss of its capacity.
Source: https://batteryk.com/kak-proverit-akkumulyator-shurupoverta-multimetrom
Tools for monitoring car battery voltage
Now that you understand what the usual car battery voltage is, let's talk about measuring it. To monitor the voltage, you will need a multimeter (also called a tester) or an ordinary voltmeter.
Battery voltage measurement
There is also a device called a load fork. It can also measure voltage. For this purpose, the load plug has an integrated voltmeter. But what’s even more interesting for us is that the load plug allows us to determine the battery voltage in a closed circuit with resistance. Based on this evidence, you can judge the condition of the battery. In practice, the load fork creates an imitation of starting a car engine.
To measure voltage under load, connect the terminals of the load plug to the battery terminals and turn on the load for 5 seconds. At the fifth second, watch the readings of the built-in voltmeter. If the voltage drops below nine volts, then the battery has already lost its functionality and should be replaced. Naturally, provided that the battery is one hundred percent charged and in an open circuit it produces a voltage of 12.6-12.9 volts. On a working battery, when a load is applied, the voltage will first drop here and there to 10-10.5 volts, and then begin to rise slightly.
You see, the battery voltage may be normal, but its condition is unsatisfactory. Therefore, one cannot judge the performance of a battery only by the voltage value, but only the degree of its charge. You can also read about the reasons for a low battery in a car. Return to content
What do you need to remember?
In conclusion, here are some tips that will protect you from mistakes when operating the battery:
- Measure the battery voltage from time to time and often (once every three months) recharge it from the mains charger;
- Keep your car's alternator, wiring, and voltage regulator in good condition for routine battery charging when traveling. It is necessary to frequently inspect the leakage current value. The leakage current of the car battery, the norm and its measurement are described in the article at the link;
- Inspect the electrolyte density after charging and refer to the table above;
- Keep the battery clean. This will reduce the leakage current.
Making a homemade power supply
If you are familiar with the principles of constructing electronic circuits, you can make a power supply without the help of others. A diagram giving general concepts is shown in the illustration.
The transformer can be picked up from an old tube TV or other home appliances. Power of two hundred 20 volts 250-350W. The main thing is the power supply - the donor should not be pulsed.
The voltage on the secondary winding is 24-30 volts. The secondary winding is made from wire of the appropriate cross-section.
In general, if the output winding current is more than fifteen amperes (see Transformer Specification), there is nothing to worry about.
After losses on the diode bridge (1-1.5 V on the diode), you will get the required output value.
If you have an electrical engineering education, make the calculation without the help of others. Or by a practical method: by connecting a two hundred 20 volt 100W incandescent lamp as a load, measure the voltage at the output. E
If it exceeds the needs of the screwdriver, reduce the number of turns of the secondary winding of the transformer.
What batteries can be used for screwdrivers
Manufacturers of power tools always indicate in the characteristics of screwdrivers which batteries are recommended for working with them. The battery type is written in several English letters. To know which battery to choose a screwdriver with, you need to understand the abbreviation and know the advantages and disadvantages of each type of battery.
Nickel-cadmium (NiCd)
This type of battery appeared in the middle of the twentieth century. The cathode in it is nickel oxide hydrate supplemented with graphite powder. To create the movement of ions from the cathode, an electrolyte is used - potassium hydroxide. The last key element is the anode, which here is made of cadmium oxide hydrate. The second version is cadmium metal, used in powder form.
Nickel metal hydride (NiMh)
This type is most often used in AA batteries. They began to be developed in the late 1970s. The main substances for accumulating charge and releasing it are nickel-lanthanum, which serves as the anode, and nickel oxide, which is the opposite side - the cathode. The transfer of ions is provided by potassium hydroxide.
Lithium-ion (Li-Ion)
One of the new generations of batteries, which first appeared in 1991. Japanese radio engineering companies began to actively use them, and subsequently they managed to increase their power and use them with power tools.
This type is used in mobile phones, laptops and electric cars. Their cathode and anode are made of aluminum and copper foil, between which a perforated separator is installed. A valve may be present to release internal pressure.
There is a solution - converting the screwdriver into a network one
Yes, with all this, one of the advantages of a cordless tool disappears - mobility. But for work in rooms with access to a network of two hundred and 20 volts, this is a good solution. Moreover, you are giving new life to a broken instrument.
There are two concepts on how to turn a cordless screwdriver into a corded one:
Using a car battery charger
The principle is the same as with the introduction of a computer power supply. You need to purchase an old charger for starter batteries. The modern fashion for small-sized pulse chargers has left behind analog linear devices with manual adjustment of voltage and charge current. Therefore, such a device can be purchased on the auto market for a symbolic price.
Charger MAX INTER
It’s great if the voltage can be adjusted smoothly - in this case, your improvised power supply will fit any screwdriver.
Converting it to a network tool comes down to connecting the electric motor input to the power terminals of the charger.
Using a power supply from a personal computer
On the radio market you can buy an old computer power supply for a small price. We needed a variant of the “AT” format, which had to be turned off with a button after exiting the operating system.
Experienced users remember such system units. The advantage of such a power supply is that it indicates the correct power. If it says 300W, it means you can safely remove 15-16 amperes from the 12-volt output (again, we turn to Ohm’s law). This is completely enough to power an average screwdriver.
Such blocks are equipped with a power button. Another advantage is the presence of a cooling fan and an advanced overload protection system.
If you hide the power source in a beautiful case, don’t forget to include a hole for ventilation.
The connection is very basic. Dark wire (-), yellowish wire (12V).
Limitations - a screwdriver with a supply voltage higher than fourteen volts will not work.
Battery Disadvantages
- Needs constant recharging. At some point, batteries will run out of charge cycles.
- The cheaper the tool, the sooner the time for rework will come.
There is nothing shameful in this, but you should be aware: the manufacturer saves just like you. As follows, the most expensive unit (and this is specifically the battery) will be the cheapest when completed.
As a result, we get a good tool with a working engine and a non-worn gearbox, which does not work due to a bad battery.
There is an option to purchase a new set of batteries, or replace faulty batteries in the unit. But this is an economical exercise. The price is comparable to buying a new screwdriver.
The second option is to use a spare or old battery from the car (if you have one). But the starter battery is heavy, and using such a tandem is not very comfortable.
External power supply
The idea is not as absurd as it might seem. Even a large and heavy step-down rectifier can simply sit near the outlet.
You are identically tied to the power supply and to the plugged-in power plug. And the low-voltage cord can be made of any length.
Fundamentally! Ohm's law says - with the same power, lowering the voltage, we increase the current! Accordingly, the power cord for 12-19 volts must have a larger cross-section than for two hundred and 20 volts.
Power supply in a battery case
Mobility is maintained, you are limited only by the length of the network cable. The only problem is how to squeeze a fairly powerful transformer into a small case.
Let us again remember Ohm's law, and realize that a powerful two hundred and twenty-volt electric motor can be small in size.
Sources:
https://strport.ru/instrumenty/remont-akkumulyatora-shurupoverta-svoimi-rukami https://peling.ru/2014/07/09/realnyiy-sposob-vosstanovit-na-100-akkumulyator-shurupoverta-po-moey -metodike-ni-cad-1-2v/ https://akbinfo.ru/ustrojstvo/naprjazhenie-akkumuljatora-avtomobilja.html https://obinstrumente.ru/elektroinstrument/shurupovert/peredelka-shurupoverta-na-setevoe-pitanie. html
Which battery is better: lithium or nickel-cadmium?
This question about which battery is best for a screwdriver is not posed entirely correctly. It all depends on the situation and the length of time the tool will be used.
types of batteries
The diversity of rechargeable batteries is due to the fact that various chemical elements can be used as electrodes and electrolytes. The quality of operation of the power tool used depends on the correct choice of energy storage device. The following 3 types are most widespread in the field of electrical appliances:
- nickel-cadmium (Ni-Cd);
- nickel metal hydride (Ni-MH);
- lithium-ion (Li-Ion); lithium polymer (Li-Pol).
A lithium battery pack weighs less with the same capacity as cadmium. But this is not the main indicator on the basis of which you should choose a battery for a screwdriver.
Of course, the number of charge-discharge cycles for cadmium cells is several times less than for lithium cells. The standard for Ni-Cd is 500 and for Li it is 1500, which certainly initially makes one think that lithium batteries are much better and lighter in weight.
When choosing batteries, it is important to take into account the fact that the aging of nickel-cadmium batteries depends solely on the cycles they operate, and not on their actual age!
The service life of lithium-ion batteries, unlike cadmium, directly depends on age over the years. After 3 years they will already fail, even if they have not been used.
Nickel-cadmium batteries, on the other hand, will last a long time even if they are rarely used.
For example, when buying a used screwdriver, you should not take it with lithium batteries. There is a high probability that if the tool has not been used for a long time, or has been frozen frequently, its battery pack is no longer suitable for use.
If a used Shurik is sold with cadmium batteries, they can retain up to 60% of the charge, regardless of whether the tool was used or not.
If the screwdriver is not used very often, lithium batteries are more likely to “grow old” than to serve their required 1500 cycles. Therefore, for periodic household use there is no point in buying a tool with lithium batteries.
Cadmium can last 3 to 5 years, whether batteries are used or not. It can also easily lie in a warehouse, maintaining its properties, unlike lithium. If you do not plan to use a screwdriver often, the answer to the question of how to choose a battery will be short and truthful: choose cadmium.
By the way, in temperatures down to -20°C, cadmium “behaves” better than lithium batteries, which do not like extreme frosts. Lithium must be stored at least 60% charged. They need constant recharging when not in use. Otherwise, they begin to collapse.
Thus, it becomes clear that nickel-cadmium batteries are, in fact, no worse than lithium batteries. The main question is only the scope of application of both types of chemical batteries.
When used at the right time and in the right place, both can be equally useful and good.
Ni-MH batteries
Nickel-metal hydride batteries are less common than nickel-cadmium batteries for screwdrivers.
Their advantages include the absence of toxic components, environmentally friendly production, a slight “memory effect” and lower self-discharge than nickel-cadmium batteries.
In addition, when compared with Ni-Cd batteries, nickel-metal hydride batteries have a larger capacity and can withstand a greater number of charge-discharge cycles.
Ni-MH battery has the following advantages:
- they have virtually no memory effect;
- no toxic components are used in their production;
- ease of disposal; capacity is 30% greater than that of nickel-cadmium; light and compact; are not afraid of mechanical damage.
- takes a long time to charge; 500-600 charge-discharge cycles;
- after 300 cycles, a decrease in capacity can be observed;
- cannot be used at sub-zero temperatures;
- cannot be completely discharged; higher cost compared to the previous type.