Hello dear reader!
Back in 1270, the French king Ludwig IX issued a law that prohibited residents of the upper floors from pouring sewage on the heads of passers-by. Instead, they had to go outside and carefully dump all the waste at their feet. The French tried to mask the unbearable stench with perfume.
Can you imagine the amber that permeated the air of medieval Paris?
It is not surprising that the average life expectancy then was about 35-40 years. And there was no need for any poisoned gloves or other cunning methods - people in such an atmosphere were already dying like flies.
Therefore, a well-equipped sewer system is not only a convenience, but also one of the most important factors in a healthy atmosphere at home.
In today's article I will talk in detail about sewer pipes. We will find out what modern pipelines are made of and try to calculate the sewerage parameters ourselves.
Sewage requirements
Requirements for the sewerage system of an apartment and individual residential building are established by SNIP 2.04.01-85. 2.04.03-85 and SNiP 31-02.
I will list the most important ones:
- For sewage systems, the following types of pipes must be used:
- for gravity systems - concrete, cast iron, reinforced concrete, plastic, glass;
- for pressure - cast iron, plastic, reinforced concrete, asbestos-cement;
- It is not allowed to lay sewerage in the floor of living rooms, under the ceiling, in hospital wards and child care institutions, canteens, classrooms, libraries, electrical panels, transformer rooms;
- It is not allowed to connect the exhaust part of sewer risers with chimneys and ventilation systems and to cross the sewer with a gas pipeline.
- The diameter of the outlet hole is determined by calculation. It cannot be smaller than the diameter of the largest drain;
- Pipelines located outside the house must have a diameter of at least 150mm;
- To clean and maintain networks, wells must be installed;
- The outlets are connected to the external network at an angle of at least 90 degrees;
- The length of the pipeline from the plumbing fixture to the riser should not exceed 12 m;
- The diameter of all utilities should be calculated based on their special formulas and standards, according to the planned volume of sewerage and the operating conditions of the sewerage system.
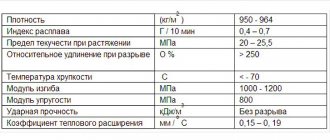
Sewage pipes, regardless of material, must be:
- Durable;
- With a long service life;
- Resistant to external climate and temperatures of transported liquids;
- Frost-resistant;
- With smooth walls;
- Wear-resistant;
Internal pipeline
Pipes for internal sewerage
This does not require the use of powerful pipelines, as for laying under highways or roads where there is constant traffic.
Since there is no intense load on the structure, it is possible to lay a pipeline in the internal section directly inside the building and even place it separately from the building.
There is only one rule for creating this type of pipeline: all structural elements must be covered with wooden, plastic or metal decorative elements. But which pipes are better for sewerage in a private house?
A pipeline that is laid in the private sector or in another territory must have a number of the following functions:
- be resistant to mechanical, biological, and chemical influences
- the material of the products must withstand huge temperature changes in the external environment (for example, in winter, the water in the pipes should not freeze)
- the pipeline must be compatible with the pipes of the external sewerage system (this is required for connection to the central water supply lines)
- it must also be compatible with all sanitary facilities in the house.
In the modern world, most owners of private houses prefer to buy pipes made of metal-plastic or simply plastic. The advantage of these products is ease of transportation and installation.
Their installation does not require special knowledge, and even an owner inexperienced in such work can handle the installation. The main advantages also include the fact that if a breakdown occurs, the entire pipeline network can be easily replaced.
A plastic product can be purchased at any hardware, construction or plumbing store. You can watch the video about installing sewer pipes:
What types of sewer pipes are there?
The choice of material for pipelines should be based on the type of sewage disposal installed in the room - gravity or pressure. Moreover, some types of sewer pipes are universal. Let's look at the most popular:
Cast iron
Despite the increasing popularity of plastic, cast iron products are still in demand. Durable and unpretentious material has long become the standard of reliability. Cast iron products are suitable for both types of systems. They are made from material grade SCh (gray cast iron). In its pure form, gray cast iron is brittle and brittle. To improve performance properties, various impurities are added to the metal. It is by the presence and type of impurities that cast iron pipelines are classified.
Types of cast iron pipes:
- Ductile iron is a high-strength cast iron with the addition of granite granules. The product made from it is frost-resistant and is as strong as carbon steel. Ductile iron pipes are commonly used in industrial systems and are reliable and durable. They are produced only with a socket (technological expansion at one end of the pipe).
- CHK - non-pressure pipes. Flake graphite is added to gray cast iron. They are fragile and only suitable for lightly loaded networks. Due to low ductility, you should not install pipes with your own hands. After dismantling it can be used again.
- ChNR - cast iron pressure products. Suitable for transporting wastewater under pressure. They are used in the same places as ductile iron; they are less durable, but also have a long service life.
- SML - cast pipes made of cast iron and graphite. They have an anti-corrosion coating made of epoxy resins. Available without bell. They are connected using clamps, and such connections do not require additional protection. Sewage from SML pipes is very reliable, can withstand heavy loads and will serve you for many years.
Polypropylene
Polypropylene parts for drainage systems are produced by extrusion. The advantages of this product include light weight, smooth surface, non-corrosion, resistance to sudden temperature changes, increased wear resistance and low cost. Pipes are white, orange, black.
The pipe is marked with the abbreviation PNxx, where XX is the value of the maximum permissible pressure in kg per cm2.
Classification of polypropylene pipes:
- PN 25 - reinforced with glass fiber or aluminum foil. These products have high strength, resistance to mechanical stress and a low coefficient of thermal expansion. Used for external networks.
- PN20 - products with increased impact strength. Used in internal sewer networks;
- PN16 - for internal gravity pipelines;
- PN10 is the most inexpensive and popular product. Suitable for indoor systems.
To increase strength and wear resistance, various impurities and additives are often added to polypropylene.
Polyethylene
Polyethylene pipes are produced by squeezing molten plastic through a round mold, followed by calibration.
Types of products:
- LDPE - high-density polyethylene. They are characterized by high mechanical stability and elasticity. Consist of three layers. Used for pressure sewerage;
- HDPE is low-density polyethylene, durable, withstands temperatures down to −50C.
- Corrugated. Produced from material grade PE-80 and PE-10. They are highly resistant to chemical influences.
Polyvinyl chloride
Made from PVC thermoplastic. They are used for both internal and external sewer networks. Wear-resistant, inexpensive and accessible.
Corrugated
Popular products for sewerage and drainage systems
Classification:
- Lungs. They have low resistance to mechanical stress. Used for laying external sewer systems;
- Heavy. Average level of mechanical stability. Used for installation of underground pipelines;
- Super heavy. They are used for laying communications under highways and railway tracks.
Corrugated plastic pipes can be single-layer or double-layer. Made from PVC, polypropylene, and low-density polyethylene. They combine the advantages of the above materials with increased flexibility and ease of installation. Can transport liquids with high and low temperatures.
Other materials
In addition to metal and plastic, they are ceramic, reinforced concrete, asbestos-cement and fiberglass.
- Ceramics is a material that is resistant to abrasion, but very fragile. It must be installed with extreme caution.
- Reinforced concrete is strong, waterproof, frost-resistant, but very heavy.
- Asbestos cement is a cheap, but fragile and inconvenient material to work with;
- Fiberglass is plastic with the addition of fiberglass. More expensive than regular plastic sewer pipes, but not much better.
Size tables and pipe specifications
After choosing the material, special attention is needed to the size of communications.
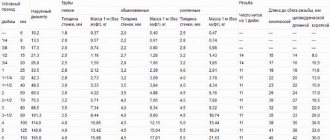
We summarize the diameters for internal and external gaskets in a general table:
| Network type | Outer diameter, mm | Inner diameter with minimum wall thickness, mm | Minimum wall thickness, mm | Inner diameter at maximum wall thickness, mm | Maximum wall thickness, mm |
| Internal | 32 | 30 | 1,0 | 28,40 | 1,80 |
| 40 | 38 | 1,0 | 36,40 | 1,80 | |
| 50 | 47,4 | 1,30 | 46,40 | 1,80 | |
| 75 | 71,2 | 1,90 | 70,40 | 2,30 | |
| 90 | 85,6 | 2,20 | 84,40 | 2,80 | |
| 110 | 104,6 | 2,70 | 103,20 | 3,40 | |
| Outdoor | 125 | 118,6 | 3,20 | 117,20 | 3,90 |
| 160 | 153,6 | 3,20 | 150,20 | 4,90 | |
| 200 | 192,2 | 3,90 | 187,60 | 6,20 | |
| 250 | 240,2 | 4,90 | 234,60 | 7,70 | |
| 315 | 302,6 | 6,20 | 295,60 | 9,70 | |
| 400 | 384,6 | 7,70 | 375,40 | 12,30 | |
| 500 | 480,4 | 9,80 | 469,40 | 15,30 | |
| 630 | 605,4 | 12,30 | 591,40 | 19,30 | |
| 800 | 769,2 | 15,40 | 751,0 | 24,50 | |
| 1000 | 960,8 | 19,60 | 938,80 | 30,60 | |
| 1200 | 1151 | 24,50 | 1126,80 | 36,60 |
For external sewer networks, the optimal diameter is from 160 to 500 mm, for internal ones - from 32 to 110 mm.
GOST standards:
- GOST 22689.2-89 - polyethylene pipes and fittings;
- GOST 18599, GOST 32413, 51613 - PVC pipes;
- GOST 6942-98 - cast iron products;
- GOST 32414-2013 - polypropylene.
How to choose the right diameter?
But now it’s time to figure out the most important thing - how to choose the right diameters for the external and internal networks?
There are 2 methods - non-calculated (according to SNiP) and calculated.
- Non-settlement method:
According to GOST No. 21.604 “Water supply and sewerage”, for laying internal sewerage it is necessary to use the following sizes of plastic pipes:
- bathtub drain pipe - diameter (d) = 40 mm;
- shower - d=40 mm;
- toilet -d=110-150mm mm;
- sink -d=40 mm;
- bidet —d=40 mm;
- sink, washbasin -d=40 mm;
- combined drain for shower, sink and bath—d=50 mm (
- central riser - d= 110 mm;
- bends from the central riser d=60 mm.
In addition to the pipe diameter, it is necessary to select the correct slope.
- Calculation method:
SNiP 2.04.01-85 describes methods for calculating diameters for sewerage in an apartment and a private house. They are complex, taking into account the slope of the pipeline on horizontal sections of the main line, the angle of connection of the leads and other nuances.
To calculate the outer diameter of a sewer pipe, there is a special formula:
D = V ( √ h / d) ≥ K, where:
- D—pipe outer diameter
- V is the speed of movement of wastewater (must be at least 0.7 m/s);
- K is a coefficient depending on the type of material (selected according to SNiP);
- h/d - pipeline filling indicator - the ratio of the flow height h (maximum) to the internal diameter less than 0.6. If clean wastewater moves through the pipeline, this value can reach 0.8
Advice: You should not do the calculations yourself, the probability of error is too high. Use the services of a professional.
Smallest permissible pipe diameters:
- For external networks inside the block −150mm;
- For external street network - 200mm;
- For an external stormwater drainage network −220mm;
- For pressure networks - 150mm.
When constructing a private residential building, the internal diameters are taken from SNiPs or calculated based on all the parameters listed above. For an external network, in any case, a pipe of 150mm-200mm will be sufficient.
Correspondence between the diameter of the pipe and the plumbing fixture (toilet, sink, etc.)
The size of the sewer pipe does not always correspond to the size of the pipes of the plumbing fixtures. For example, the sink corrugation usually has a diameter of 30mm, and the waste pipe has a diameter of 50mm. What to do?
The answer is simple - you need to use connecting fittings.
Connecting elements
The range of fittings is very wide. They are made of cast iron, PVC, polyethylene, polypropylene, as well as the pipes themselves.
When installing pressure systems, tees, bends, pipes, sockets (double and single), O-rings, and saddles are used.
Plastic types of fittings are distinguished by their light weight, long service life, resistance to temperature fluctuations and a wide range of types.
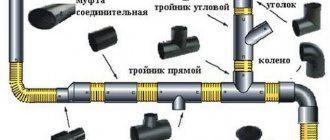
Let's look at some types of shaped products:
- Tee - used to connect 2 or more pipes at an angle of 45, 60, 90 degrees;
- Coupling - connects two parallel sections of the pipeline;
- Retraction - allows you to rotate 90 degrees when laying;
- Reduction - connects two different diameters and materials;
- Cross - performs perpendicular branches;
- Branch pipe - used when replacing a damaged or cut section of a pipeline;
- Plug - blocks the movement of fluid during repairs.
How to choose sewer pipes for an apartment
There are no difficulties in choosing sewer pipes, just a few tips to help you:
Firstly, choose (buy) pipes from the same manufacturer for the entire apartment. Wall thickness may vary from manufacturer to manufacturer, which may cause connection problems.
Secondly, when purchasing, check for the presence of a gasket in the socket. A gasket purchased separately may not fit.
Thirdly, the diameter and markings of the pipes are written on them at the factory.
Fourthly, try not to use 90º shaped corners in the apartment. Replace them with 2 45º angles or 3 30º angles. This way you will reduce the likelihood of operational blockages.
Connection methods
Depending on the type of sewer pipe selected and connecting fittings, the following connections are classified:
- Bell-shaped - the pipe socket is put on a fitting or other part. Fixed with an O-ring. For socket joints of cast iron pipes, cement is used instead of an O-ring;
- For gluing (usually used for assemblies made of plastic pipes). The installation adhesive is made from a mixture of PVC and tetrahydrofuran;
- Using clamps and levers. This method allows you to increase the mechanical force;
- Threaded. Quite rarely used to connect cast iron parts.
The connection method should be carefully considered - the operation of the entire network depends on the correct connection of the nodes.
Installation nuances
There are a number of nuances in the installation of sewerage systems, which, if ignored, can result in not a good drainage and drainage system, but, in Russian speaking, large hemorrhoids. So I will list as much as possible:
- When cutting pipes, the cut must be strictly perpendicular to the axis and must be processed with sandpaper;
- The elements to be glued must be degreased;
- Fittings with a rubber seal must be coated with silicone sealant;
- The cross-section of the horizontal pipeline should not exceed the diameter of the sewer riser;
- In places where the pipeline turns, it is necessary to install revisions - cleaning holes with a cover;
- Horizontal connections must be made from angles and oblique tees;
- Sewerage is secured at intervals equal to 10 x pipe diameter;
- The slope of horizontal sections should not exceed 1-2cm/1m;9. The bell is positioned towards the moving liquid.
Silent sewer pipes
The sewer pipes described above are standard. They are gray in color and unfortunately they are very noisy, especially the sewer risers.
To reduce noise, sewer pipes of a noise-absorbing design are produced. They are white. The diameters are the same, the connection is the same.
Companies that produce “quiet” sewer pipes:
- Rehau: white, two stripes red and green;
- Ostendorf Skolan color light gray, wall thickness 5.3 mm, noise absorption up to 20 dB;
- Wavin: up to 12.3 dB;
- Equation: white.