We are talking about cables for welding machines. Its structure and, most importantly, the choice of a specific type for specific metal welding work is much more important than it might seem at first glance. Let's start with its functional purpose. The main and only function is the effective supply of electric current to the electrode.
You know that we always prioritize the efficiency of welding work, which is determined by many parameters. One of the most important parameters of this kind relates to the characteristics of a special wire - its cross-sectional area.
This indicator must be kept in mind when choosing a suitable option without fail, as well as several other parameters: total length, characteristics of the local network in terms of possible voltage drop, and much more, which we will talk about now.
Types of cables
Naturally, the main determining factors in choosing a welding cable will be the properties of the machine itself for which it is purchased. The first thing is the current strength in the device. If, for example, it is 189A as close as possible, then the correct choice of wire to the inverter will be a KG 1x16 cable.
Such products are produced in a whole line with different sections. There are many tables on the network outlining exactly what cross-section should be taken at different current values in the devices.
Types of welding cables KG.
It should be noted that all cables that are suitable for welding equipment are not cheap. Therefore, it makes a lot of sense to stop and think about what exactly you are going to do, and what kind of product you will need. There are a great variety of them on offer.
The structural varieties are as follows:
Single-core
This welding cable is made from copper wire, which is distinguished by its elasticity and flexibility. In addition, the distinctive quality of copper as a metal is known - it is an excellent conductor of electric current.
These types are usually used for compact portable inverter devices with low power and corresponding parameters of current strength and other technical indicators.
Twin-core
This configuration has a cathode and anode, which are excellent at conducting electrical current during pulse welding.
Most often, these wires consist of pure copper wire, although there are products made of copper alloys with the addition of other metals that conduct current well. But the base is copper in any case, this is an important condition.
Three-core
This type is produced for complex automatic welding equipment, for example, powerful pipelines for transporting oil, gas or their products.
Such work is considered highly responsible with mandatory requirements for the formation of ideal welding seams.
The marking of wires contains all the technical characteristics of welding work, which greatly simplifies their selection for specific work:
- KS - the product can be used in various types of welding work.
- P - the product is covered with an additional layer of polymer material for additional protection of the conductor. If there is a number next to it, it shows the number of cores in the cable.
- HF – the product can be used at high frequency voltage.
Welding cable marking.
There are other useful properties of welding wires. They have excellent resistance to high and low ambient temperatures with a wide range from -50°C to +50°C, they are resistant to moisture and other aggressive external factors.
Most often, welding wires for an inverter come together as part of a common package in modern welding equipment. But they can be purchased separately as consumables. In this case, you need to look for products with the same markings as they were originally.
Modern braids of copper conductors are produced taking into account a wide variety of requirements and a variety of climatic conditions.
According to their resistance to environmental conditions, all products are divided into two large groups:
- Tropical or antiseptic under the KG-T marking can withstand temperatures up to +50°C in combination with high humidity. In such conditions, there is a high risk of fungal mold or the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms. If the braid is not specialized, it can easily become exposed in the heat of the desert or in the tropics.
- Cold-resistant or cold-resistant under the marking KG-HL. The polymer braiding in them is absolutely resistant to frost, so the wire does not freeze or crack in the cold down to -60°C, that is, in the harshest climates.
Welding cable brands and their characteristics
First of all, it should be understood that the welding cable experiences loads not only from the inverter, but also from external conditions. Friction against the surface (including asphalt, concrete, etc.), high and low temperatures, falling objects are common and inevitable unfavorable factors. Therefore, when choosing a cable, it is necessary to take into account the operating parameters of the equipment and its operating conditions. First you need to decide what cables exist and how they differ.
Flexible welding cable KG
One of the most common cable brands. It is explained very simply - the cable is flexible. It performed well in working with direct current up to 1000V or alternating current up to 600V and frequency up to 400 Hz. The wire is intended for switching welding equipment to a 220 or 380 volt network, connecting to ground or a holder.
Welding wire KOG1
This cable differs from its previous analogue in having a smaller core diameter. Because of this, it is more flexible and has a smaller turning radius. This feature is in demand for working in hard-to-reach places or in cases where you need to bring the electrode at an unusual angle—too sharp or, conversely, too wide. Also, a flexible cable is practical during work at heights, during ceiling welding, when a specialist wraps the cord around his hand to make it easier to hold. The wiring is designed to operate from a 220 volt network with a current frequency of 50 Hz.
Safety requirements
Like any other device designed to work with electricity, welding wires are subject to strict requirements and mandatory high safety standards.
The main safety requirements can be divided as follows:
- The cross-section of the core must be able to withstand the required electrical load, that is, the cross-sectional area must be adequate.
- The body of the wire must withstand mechanical stress, as well as the influence of an aggressive chemical environment. These conditions are met using the correct braid made of polymer materials.
- Usually the wires are twisted many times. This fact should not affect the integrity of the braid - it should be elastic and resilient.
Requirements for welding cables
Cables are used when working with electric current, so the wires are subject to several technological requirements and safety standards:
- resistance to impacts, ruptures and exposure to aggressive chemical environments;
- high flexibility ensures a quick change in its position without any consequences for both the performer and the wire itself;
- repeated winding and unwinding should not affect the elasticity and resilience of the cord covering;
- resistance to sunlight, moisture and oil ;
- resistance to various stains .
Selecting the cross-section of the welding cable
The cross-sectional area of the wire for welding is one of the most important parameters for the efficient operation of the entire device: such key indicators as the maximum maximum current strength and conductivity will depend on the cross-sectional area.
The quality of overall welding work depends on these key indicators - the strength and aesthetics of the formed seam and the speed of operational work.
Wire brand and permissible load.
The cross-sectional area, which refers to small calibers, is approximately 7 mm². These products are designed for inverter devices of compact dimensions, which operate when connected to household electrical networks with a voltage level of 220V.
If you are dealing with industrial automatic welding equipment, you will have to deal with conductive cables with large cross-sectional areas - about 47 - 49 mm².
The line of this kind of products with a wide variety of cross-sections and braids is presented in numerous catalogs and tables that will help you choose the most suitable cable cross-section accurate to the millimeter.
In such catalogs, additional markings and maximum current strength with voltage, cord length and calculated weight of the equipment are indicated.
If you make a mistake and choose a wire with the wrong number of strands and inadequate cross-sectional area, you will get into trouble: at a minimum, it will be an inefficient job in terms of time and energy. And most likely, you will have a short circuit with a breakdown of the rheostat, all equipment and other troubles.
What happens if the cross-sectional area of your wire is smaller than the required size and does not fit the programmed power of the equipment in any way: the electric current will be generated in excess, as a result it will begin to concentrate on the fuse of the device.
You will not be able to work in such conditions, because at the slightest ignition of an electric arc, the device will instantly turn off to relieve the voltage.
Characteristics of the cable for the welding machine
Neither domestic nor foreign manufacturers produce a universal welding cable suitable for all working conditions, but they produce a sufficient number of its types to satisfy all possible needs.
Products with similar characteristics, but with different markings, are used as a cable for a welding machine:
- KS is actually purely welding.
- KG – stands for “flexible”. The properties are almost identical to the first.
In addition to these two designations, several more markings are used; we will consider them in more detail.
Any cable is marked according to the same pattern: “A” “B” “C”x”D”
It means:
- "A" is the class to which it belongs. As mentioned above, there are several of them - KS, CG and there is also its version KOG (especially flexible)
- “B” - this place indicates the operating temperature range. If they are in the range from -40 to +50 degrees, then nothing is written, if from -60 , then the marking is CL (cold-resistant); if there are special antifungal and moisture-resistant additives, it is considered tropical and is designated as “T”. It can withstand up to +50 heat. When it does not burn at all, it is marked as non-flammable - “NG”.
- “B” - a number equal to the number of working cores from 1 to 3 .
- “G” - this last position indicates the cross-sectional area of the cable for the welding machine in square millimeters.
Rules for connection and use
When connecting cables to inverter devices, there are a number of rules that you need to know and follow without fail:
- To connect the device at its end there are welding connectors and special tips attached by soldering - plugs for the welding cable. The product should only be connected through them.
- The wires can be connected to each other. This should only be done using special crimping. The main rule here is the mandatory isolation of connections between each other.
- The cable is connected to power type connectors and electrodes through their holders. In this case, it is necessary to remember the polarity, which cannot be changed, except in cases where all current parameters are changed.
- The welding cable for the inverter cannot be used for any other purposes - to pull the device towards you, for example.
- A mandatory requirement is full technical compliance of the cable and the corresponding equipment in terms of rated power and all other parameters.
Requirements
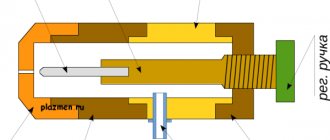
The inverter welding machine is equipped with two cables. One of them supplies current to the electrode, and the other (ground) is connected to the part being welded.
Any cable for a welding machine must meet four requirements:
- Conduct current to the surfaces being welded with minimal losses (for this it is made either entirely of copper or copper-based. In this case, aluminum wire is added to it)
- Be of the required length, thickness and weight (these requirements ensure the possibility of convenient operation without unnecessary movement of the device itself and minimal heating of the cable itself when a high frequency and current current passes through it)
- Reliably isolate the conductive part from contact with the environment (here we are talking not only about obvious moisture, but also about metal surfaces on which welding work is often carried out)
- Have high wear resistance (for an inverter welding machine, it should minimally change its properties under the influence of high or low temperatures, chemical reagents, and mechanical stress).
Cable extension: yes or no
This question most surprisingly continues to excite the minds of professionals and has been a hot topic of discussion for a long time.
Some believe that extension should never be carried out, because too long wires with connectors for the welding cable will lead to a decrease in the efficiency and quality of work.
Manufacturers of inverter welding machines prefer not to speak out on this issue. This means that the wires can be extended and the equipment can be used with very long wires, reducing movement of the machine to a minimum.
On the other hand, if the wire is too long, voltage loss may occur. In this case, the arc will become shorter, it will be much more difficult to control, and the overall quality of welding will decrease significantly.
Types of conductors used in cables
There are three types of conductors used as a base:
- With one core - it is a set of copper wires twisted in a special way, covered with durable and flexible insulation. For example, this is the cable for the Resanta welding machine, popular among garage workers.
- With two cores - in this option, both the cathode and the anode are combined side by side. Each of the cores is similar in design to the first type. The meaning of this design is the convenience of carrying high-frequency currents or alternating current.
- With three cores - these are used in automatic welding machines for large-sized metal parts (for example, bridges, pipelines, tanks). The number of cores gives a high-quality and uniform seam.
Criteria for selecting a cable for welding
The main criterion for selection is the stability of the welding process. This stability is influenced by many things - not only the indicators of the current and the mains voltage source, but also many parameters of the welding and mains wire.
Therefore, when choosing, we think about the correct length, the correct cross-sectional area and braid material - all three parameters are of serious importance. If, for example, the welding current reaches high values, the wire must be selected according to a certain type and material.
We have already said that all wires for welding machines have their own electrical resistance values. It can be calculated using tables, this is not a problem. For example, an aluminum conductor has a higher resistance coefficient than a copper conductor.
As a result of this difference, the aluminum wire for a power extension cord will require many more kilograms than copper wire. And the cross-sectional area of aluminum should also be larger.
Current load table.
Taking into account such facts, the extension of network wires is carried out using copper products in two versions: two- or three-core, with a length not exceeding forty meters. As for the cross-sectional area, it should be greater than 2.5 mm².
Choosing welding wires is a little different from choosing network wires. Products for welding are selected taking into account the strength of the output current; here, stranded copper grades with highly flexible braiding and improved insulation have a huge advantage.
The most popular wires for inverter welding are sold under the marking KG, which means flexible braid, or KOG, which means very flexible braid. These brands are distinguished by excellent insulation in several layers with an outer braid made of rubber materials.
The standard wire length is approximately 2 - 3 meters and rarely longer. This is explained by the fact that every extra meter of wire length will lead to an increase in cross-sectional area by about one and a half times, since the resistance increases significantly and the wire begins to heat up.
The conditions of future work must be taken into account in advance without fail, because it is necessary to choose the most adequate type of insulation and resistance to mechanical damage, temperature conditions or aggressive chemical external environment.
The ability to read and understand welding cable markings can help you in this difficult matter:
- If the marking looks like KG T 1x16, then this means a single-core product with a core cross-sectional area of 16 mm², in a tropical design with resistance to temperatures from -10 to +55°C.
- Marking KOG HL 1x50: single-core product with a cross-section of 50 mm², frost-resistant and heat-resistant to temperatures from -40 to +50°C. In this case, the heat resistance index is not present.
The length of the wire and cross-sectional area must be consistent with the strength of the electric current and other parameters.
How to choose a cable for welding
It's time to move on to practical advice on choosing the best cable option. It must fully correspond to the welding machine with which it will interact. In addition, there are a number of other parameters that must be taken into account when choosing.
What should a vein be like?
The welding cable can be single-core. For example, it is marked 1x16. The value of the first digit is one undivided core. Thanks to this device, the conductor heats up less and transfers voltage from the power source to the holder faster. Another example - 11x30 - is a multi-core cable, where in the marking the first digit indicates the number of insulated cores. This option will be optimal for industrial installations with voltages of 500V or more.
The core is made of copper or aluminum. Aluminum versions are more often found in retail chains, since such products are much cheaper. When the welding machine is rarely used, this is quite enough. For professional use, you need a copper cable: its resistivity is 5-7 times less than its aluminum counterpart. In addition to reducing current losses, copper has other advantages: it heats up less and bends better.
When choosing, you should pay special attention to Chinese copper conductors. Because, as practice shows, the copper content in them is no more than 70%. You can verify this by cutting the cable - the cores with impurities look dull. This cable is suitable for household needs, but for professional use it is rather weak.
Section
To perform the work safely, as well as to eliminate the possibility of equipment breakdown, you should select the correct cable cross-section for welding.
Important! A conductor with too small a cross-section can cause equipment malfunction. If the cross-section is less than the required value, then the current will not flow through the wires and the unit will turn off or burn out. It is very important to correctly correlate two parameters: the cross-section and currents of the welding cable, since they are closely related
Thus, it is important for each performer to know what cross-section of welding cable should be chosen when working with different current loads
It is very important to correctly correlate two parameters: cross-section and currents of the welding cable, since they are closely related. Thus, it is important for each performer to know what cross-section of welding cable should be chosen when working with different current loads
Section selection
Calculating the current cross-section of a welding cable is the simplest and fastest way to select the optimal conductor option.
Many performers have inverter-type welding equipment. Its numerous technical advantages and affordable cost make this equipment popular. Therefore, it is necessary to determine the cross-section of the welding cable for the inverter.
To carry out work at home, performers use units whose maximum current value is about 180-200 A. Let us next consider in more detail the welding cable for the inverter, what cross-section is necessary for certain current values.
- The cable cross-section for an inverter welding machine delivering a maximum current of 80-100 A should be 6 mm2.
- For devices with a maximum current output of 120 A, a wire with a cross-section of 10 mm2 is intended.
- Welding cable with a cross-section of 16 mm2 is designed for inverters that support a maximum current of up to 180 A.
- A 200 Ampere welding cable with a cross-section of 25 mm2 is in demand among welders.
- A welding cable with a cross-section of 35 mm2 can withstand a current of 289 A, therefore, most often it is used to equip transformers. However, manufacturers offer inverters that are capable of delivering current up to 300 A. In such cases, a welding cable with a cross-section of 50 mm2 should be used.
To perform work at a professional level, in most cases the previously mentioned transformers are used.
A very important factor is the certainty of what cable cross-section is needed for a welding machine of this type. Transformer-type equipment is capable of delivering current up to 500 A. Therefore, for this equipment, wires with a cross-section of 70 and 95 mm2 should be used. The first is capable of conducting up to 437 A, the second - up to 522 A.
Welding rectifiers produce current that can reach 600 A
Therefore, performers with this type of equipment should pay attention to wires with a cross-section of 120 mm2
The table of welding cable sections and current loads for wires allows you to find out the optimal conductor option for equipping all the necessary equipment: inverters, transformers, rectifiers, holder, ground terminals.
Having determined two important parameters: the maximum current value and the wire cross-section, you can calculate another important characteristic - the cable length. More information here.
This article will help any contractor determine what cross-section the welding cable should be at certain current values.
Types and markings
By marking the cable for the welding machine, you can determine all the characteristics necessary for operation. The letters indicate the cable class and its design features . Then there are the operating temperature conditions:
- normal mode assumes a range from –40⁰ to +50⁰;
- T – the cable is suitable for use in the tropics, temperature –10⁰ – +55⁰ and increased moisture resistance;
- HL – cold-resistant from –60⁰;
- NG – non-combustible insulation.
In addition, other letters may appear additionally.
For example, an additional H in the marking indicates non-flammable wires. Their outer hose sheath is highly resistant to heat, is non-flammable and allows work in areas with a high fire hazard or in workshops with thermal operating equipment. P – polymer coating. One of the insulation layers is made of polymer. This partially reduces the reliability of the shell. These wires are cheaper. They can be used with household currents up to 120A.
The digital designation reveals the number of cores. There are always 1 of them on welding cables. The cross-sectional area of the copper core is indicated through the “×” sign. For example, KG 1×35. The welding cable is selected according to the operating current value . The specifications for the wires indicate the cross-sectional size for each limit and rated current. For example, 16 mm2 - works with equipment delivering up to 189A.
KRPT
At enterprises with mass production of large welded structures, the welding wire of the KRPT series has shown its reliability . Its abbreviation stands for: rubber-coated cable, type – portable, heavy. A classic cable, the production of which our industry mastered back in the last century.
The "portable" characteristic means that the equipment to which the cable is attached can be moved during operation without twisting all the wires. The cable just pulls freely
The definition of “heavy” does not refer to the specific gravity of the wire, but to its increased protection from external damage. The insulation will not be damaged if a cart or even a car wheel hits the cable, or a hammer or other tool falls. The outer insulation hose is extra strong.
Chief technologist of the plant for the production of insulated wires and cables for HF networks Kostyushenko P.I.: “Currently, the number of welding and suspension cables for connecting to energy-intensive equipment of the KRPT series has decreased. It is being replaced by KG and KGN wires, which are more flexible and lighter. New technologies for the manufacture of insulating coating have significantly increased the strength of the shell, bringing the rubber insulation to a particularly strong state. The production of KRPT series products is done only to order in large quantities for enterprises with old equipment.”
KG
Welding wires of the KG series - a flexible cable with a copper core - replaced mainly the outdated KRPT . The core has wires twisted into 16 diameters along the length of one spiral. The wires are protected from sticking together with talc. Tropical cables have copper cores covered with tin solder for additional protection from moisture.
KG series cables have excellent electrical conductivity and resistance characteristics. The outer hose insulation is strong enough to withstand constant floor friction while being dragged.
Welding wire KG is available in various versions. Each welder can choose which cable cross-section and climatic version he needs or fire-resistant. The weight of the wire is small and the hand holding the holder will not feel it:
- KG1×16 weighs 310 kg/km;
- KG1×95 weighs 1400kg/km.
It is customary to indicate the weight of cables and wires in kg per length of 1 km, therefore: a meter of the smallest and largest widely used cables weighs 0.3 kg and 1.4 kg.
COG
The especially flexible cable is used for manual and semi-automatic welding in hard-to-reach places . The weight of the wire is the same as that of the KG, only the insulation is made of rubber, which is more plastic than rubber. The difference in cost is insignificant, since the copper core of the same cross-section differs in the winding pitch. The choice remains with the performer.
The KOG series cable is made in climatic variants and is non-flammable. Not with increased strength.