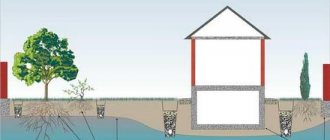
Excess water has a bad effect on the durability of things. It is highly undesirable for water to impact your home, roof, walls, or foundation. There are different types of drains. Protection from large volumes of precipitation is necessary. Simply waterproofing the foundation will not help here; water will still penetrate through micro-cracks into the basement, wood and other materials, and most importantly, load-bearing structures will deteriorate. It is necessary to divert water flows from the building and other places where people live and move. The system of drainage ducts is called the drainage system.
All structures on the surface of the earth can suffer from excess moisture in winter. The expansion force of freezing can lift any structure, tearing away foundations and breaking apart long structures.
And the vegetation suffers from high water: slugs, death of roots and washout of microelements and the soil itself.
Reducing the groundwater level is the main task of the drainage system.
Types of drainage
There are different types of drainage systems.
- The cheapest option is to dig channels for water drainage along the perimeter of the house and the paths of your site with slopes in the right directions. The channel cross-section is up to a meter deep and up to half a meter wide. They are designed to collect water not only from the surface, but also from the lower layers of the soil. Such systems reinforced with concrete save from rain and melt water runoff in mountain settlements.
Disadvantages: Without constant cleaning, such a system becomes clogged after every rainfall or snow melt. On a personal plot, the entire fertile layer will be washed away.
- A more modern solution is closed drainage. After digging, the same trenches are filled with broken bricks and stones, crushed stone, etc., generally loose, insoluble material. The whole thing is sprinkled with sand on top. Due to water permeability, water flows through such channels, being cleared of large fractions. And the main thing is that the appearance of the site does not change much because of this.
Flaws. The main disadvantage is that in this option, silting sharply reduces the service life, the water level rises and floods everything again.
- The most long-lasting option is to lay special drainage pipes at the bottom of the trench. More recently, ceramic pipes or asbestos-cement pipes were used for these purposes. They even used half pipes. Currently, polymer pipes with a perforated surface have become widespread. They have sufficient flexibility, do not crack in the cold and are easily deformed by ice, and in the spring, after the ice melts, they return to their previous sizes. Such pipes are usually made with stiffeners, which gives them additional strength. Typically, drainage pipes 10 cm in diameter are installed.
Flaws. Again, silting of the drainage holes.
However, in the latter option, geotextile filters are used. In this case, you can extend the operating time of the system for a long time.
Different types of drains are suitable for different climate conditions and durability requirements. The choice is yours.
Classification by design
Both surface and underground drainage can have different designs. Surface ones are of this type:
- Linear;
- Spot.
In most modern houses linear drainages ; they are as efficient as possible. In them, drains help remove flood waters from the foundation, trees, and utility rooms through earthen channels. These channels can go into a septic tank or remove excess liquid simply outside the site.
Photo - superficial
Point or local ones are easier to create. They are located only in low-lying areas of the site, so they do not require large expenditures of money and effort for arrangement. They are not the usual drainages, but rather separately installed wells, which can be open or closed. In addition, many experts recommend creating artificial depressions along retaining walls, external sewers and water pipes, etc.
Types of underground systems:
- Vertical;
- Horizontal;
- Combined.
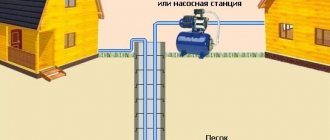
Vertical ones are considered the most complex of all described types. They are a complex structure in which vertical shafts are installed as storm drains. From them, water enters the main line, from where it is discharged into the septic tank.
Photo - vertical diagram
Horizontal drainage is a simple system similar to surface drainage, but installed at a higher depth. It can be backfilled, closed with paths or equipped with special pipes with holes. All these types are often used to create natural drainage of the earth.
Photo - combined
Video: How to drain soil in a dacha https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=rgEwEd4AtHU
Modern materials
The latest materials make it possible to achieve high-quality drainage and long-term service life of drainage systems. These materials are absolutely safe from an environmental point of view. Geotextiles are used as a filter element, preventing sand from entering drainage pipes, allowing only water to pass through.
Despite its thickness, geotextiles can withstand significant dynamic loads with sharply increasing water flows and have great tensile strength.
Geotextiles protect the insulation on pipes and other building structures, increasing their stability and durability.
Thanks to the use of geotextiles, it is ensured that the layers of crushed stone, soil or sand do not mix, since they perform different functions. In this case, water easily enters all layers.
The layers do not wash out or move, maintaining the functional properties of the entire system, because the drainage system pattern does not change.
There are various brands of geotextiles on the market. Basically, polypropylene with the addition of special stabilizers is used in production. The quality of the material depends, among other things, on the number and size of filter pores.
At a certain ratio, fabric and soil form a complementary system. This ensures that dirt stops and stabilizes filtration parameters.
You should not skimp on the quality of the canvas. Having spent a lot of money on drainage of a site with insufficient quality of geotextiles, the results of such “savings” soon become visible. Clogging the pores of cheap fabric with small particles disables the system or dramatically reduces efficiency.
Expensive fabrics have a so-called “pre-compressed” state of the material.
Design features and options for linear drainage
The supply of components for the installation of linear drains is very large. Ready-made water pipelines can have different designs and standard sizes, and different designs. The permissible load, installation methods, as well as connection to the sewer system, the choice of main and additional structural elements also differ.
Gutters (drainage pipes) can be made of stainless or galvanized steel, artificial materials (polypropylene, polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride), ordinary concrete, fiberglass-reinforced concrete (fiber-reinforced concrete) or polymer concrete containing organic binders and special fillers to improve the properties of the material.
The width of the gutters can vary according to the expected load. The standard width of gutters for private construction is 100-130 mm. Where the intensity of water collection is increased, gutters up to 200 mm wide can be used. The standard length of the gutter (one element) can be 500 mm or 1000 mm.
The diameter of the outlets for collected water must also be taken into account. As a rule, standard sewer pipes are used for drainage. Their diameter is 110 mm.
If the diameters of drainage pipes and outlets do not match, adapters must be used.
In cases where drainage is performed on a foundation limited in height, it is also important to consider the installation depth of the channel. Thus, for open terraces, exposed roofs, and balconies, shallow drains are used
All of the above parameters (selection of materials, components for the drainage system, load calculation, determination of standard sizes, length of drainage channels, etc.) are calculated in advance. For this purpose, a hydraulic project is being developed - documentation describing the future drainage system. As a rule, the number of drains and, accordingly, the throughput of the system exceeds the required minimum. This is due to the need to adapt the designed drainage system to the organization and design of the landscape on the site.
Drainage pumps
Submersible pumps with float
Relatively new equipment on the Russian market are drainage pumps. They are necessary for pumping liquids containing solid components. This is usually necessary when pumping from polluted reservoirs where sewage or rainwater has accumulated. .
On site, such pumps are necessary when pumping melt and rainwater flows to a higher level.
Most of these pumps allow you to pump water containing inclusions up to 5-10 mm in size. There are special types of pumps that allow pumping pulp with inclusions up to 35 mm.
To do this, special solid particle grinders are added to drainage pumps. Pumps also differ in the maximum height of liquid lift and in the maximum temperature. Usually it does not exceed 40°C.
Types of drainage systems
There are several types of systems that drain areas with high groundwater levels. Before installing any of them, it is worth understanding the installation methods more carefully.
Types of surface drainage systems
Surface drainage of areas with high groundwater levels in house and summer cottage areas is conventionally divided into two groups:
- Linear. It is constructed by digging trenches on the soil surface around the perimeter of the site and serves to remove moisture from rain and snow. It functions smoothly only on flat surfaces without sudden changes in relief. To do this, dig trenches up to 30 cm deep and fill the walls with fine gravel. The disadvantage of this system is that it looks quite unaesthetic and requires constant cleaning of leaves and small debris.
Elements of point and linear drainage Source makler.ua
- Spot. The simplest type of drainage is when catch basins are installed in places where water flows abundantly - under roof gutters, small ravines.
Installation of such systems does not require special knowledge or design calculations, and occurs “by eye.”
Deep drainage system
If the site is built on clay soil, with a sharp change in relief, or in an area with abundant groundwater, deep drainage is necessary. It is quite difficult to install. To develop a system design, you must contact a special bureau that provides geological soil exploration services. Its specialists will accurately determine the level at which abundant aquifers occur and will help to competently cope with this problem.
Drainage project development
All deep systems are built on the same principle. The site drainage project is developed in such a way that all secondary moisture collection pipes are connected to the central main. It, in turn, ends in the main receiving reservoir or is brought to the surface into a drainage ravine.
Classification of drainage pumps
There are various options for the manufacture and use of pumps. Depending on the purpose, the drainage pump device comes in the following types.
So:
- submersible,
- barrel,
- superficial,
- special for sewerage.
Submersible pumps are most in demand. All such pumps are equipped with special floats. The position of the float turns the pump on and off. Such pumps can pump out water in the presence of various impurities: silt, leaves and branches, paper and other small debris.
When pumping water from flooded basements or industrial wastewater with chips and other production waste, pumps are the most suitable. There are models with cutting knives for grinding impurities.
Barrel pumps are used when watering crops from any container on a personal plot. They have a mount that secures the pump to the wall of the barrel.
Surface pumps suck water out of any puddle using a special suction chamber.
Sewage pumps are needed when it is necessary to raise the level of wastewater from the domestic sewerage system, depending on the topography of the home.
Essential elements
The drainage system is a utility network that consists of pipes and wells. The pipes are connected to each other using special elements - couplings.
Pipes. The materials from which drainage pipes are made usually have filtering properties. Various types of plastic products are popular.
Wells. These structures are located on the surface and are placed at the lowest points of the slope of the territory on which the drainage is installed. This is done for efficient water drainage. In addition, the system is flushed through wells.
Pumps. If natural discharge of wastewater is not possible, the system is equipped with special pumps that transport and regulate the direction of movement of water through the pipes to the well. The range of pumps is quite large. They differ in their power ratings and hose flow rates.
Factors that determine the need to install drainage:
- Terrain. Drainage is mandatory if the site lies in a lowland or in watershed areas.
- Depth of groundwater location. Water that lies at a depth of 1.5 meters is already a sign that the area needs drainage.
- Soil density. Loamy, clayey, sandy and crushed stone soils have low water throughput rates. A site located on such soils should be equipped with a drainage system.
- Catchment area. It is worth paying attention to both the external and internal areas of the catchment area. If there is a river nearby, the areas adjacent to it may become swampy.
The main parts of the drainage system are the pipes through which water will flow.
Important! If the site is located on a slope, it is recommended to install open drainage. This will make it easier to intercept wastewater.
Plot
The site drainage system plan is made in the form of rows or a grid of drainage trenches every 5-10 meters.
Laying begins from the highest point of the site with a slight slope. You should not tilt towards buildings.
Below is a work plan for the construction of drainage on the site.
- digging trenches: width - from 0.4 m and depth 1-1.5 m. Slope no more than 3-4 degrees;
- filling with sand at the bottom 5 cm thick;
- laying a strip of geotextile, width 2 m;
- filling with crushed stone: thickness 20-40 mm, fractions 20-40 mm;
- laying pipes wrapped in geotextile, diameter 90-160 mm;
- filling with the same crushed stone 300-400 mm thick;
- covering the crushed stone filling with geotextiles with an overlap of 200-300 mm;
- on top of the textile – a layer of sand –50 mm;
- and finally - covering with a fertile layer.
Advice! High quality sand is not needed. Any sandy soil will do. If you don't expect a lot of water, you can save money and not lay a drainage pipe.
How to determine the need for a drainage system
The surest sign of increased soil moisture is the massive growth of plants, typical of swampy areas. These include weeping willow, sedge, and reed.
In addition to plants, evidence of the close occurrence of groundwater will be puddles that remain after rain or spring melting of snow. If they do not go away for a long time, then there is enough other moisture in the ground.
It doesn’t always rain, so it’s much easier to use a long-proven method of checking the soil moisture level. To do this, you need to dig a hole about half a meter deep at the highest point of the site. If water collects at the bottom within 24 hours, it means that the area needs drainage.
Active drainage
Active drainage involves the application of external force to ensure the outflow of wound fluid. The functioning of this type of drainage is based on creating a pressure difference between the wound and the outside. Currently, many models of active drainage are used, but the principle of their operation is the same. Negative pressure is created at the outer end of the drainage, and exudate is removed from the wound due to the suction effect. Active drainage is used if a sealed cavity is being drained (sutured wound, abscess cavity, chest cavity, joint cavity). This type of drainage cannot be used for interventions on the abdominal cavity, since the omentum or intestines can be sucked into the holes of the drainage tube. At best, it will stop functioning, but necrosis of the intestinal wall may develop.
Drainage is carried out as follows. One or two silicone and polyvinyl chloride tubes with holes in the walls are inserted into the drained cavity. They should not be carried out through the wound, but through a separate small incision. If necessary, several skin sutures can be applied for better sealing. The outer end of the drainage is connected to a container in which negative pressure is created. For this purpose, use a plastic accordion, special plastic cans or various types of suction (water jet, electric).
The simplest vacuum drainage is performed according to Redon. The essence of the method is as follows. The bottle heated to 100°C in water is sealed with a rubber stopper. As it cools, a vacuum of up to 75–100 mm is gradually created in the vessel. Hg Art. Connecting such a system to drainage ensures removal of up to 180 ml of exudate from it.
A very original system for vacuum drainage for pleural empyema was proposed by M. S. Subbotin. The vacuum at the end of the tube inserted into the pleural cavity is created by the movement of liquid in two jars according to the law of communicating vessels. The liquid from the top can is poured through a tube into one of the lower ones, while in the top can (closed hermetically) the pressure decreases. A decrease in pressure in the upper can leads to the suction of air from the second lower can, which is hermetically connected to a tube installed in the pleural cavity.
In the absence of special devices, you can use a simple hermetically sealed bottle. A vacuum is created in it by suctioning air using a Janet syringe.
This type of drainage is also called closed or vacuum. It can only be used when sealing a cavity. It is believed that active drainage is the most effective method. In addition to removing the contents, it helps to quickly reduce the wound cavity.
General information
Why is drainage needed?
A high level of humidity due to shallow groundwater or heavy rainfall on the site can cause many problems:
1.due to moisture, the soil under and around the building freezes unevenly. This is not a problem if the house is on stilts, but if the foundation is shallow, the higher the risk that it will be affected by frost heaving. When the soil under a building freezes, the foundation pushes upward, but under the building there is no such process. In such a situation, there is a possibility of damage to the foundation and walls of the house. The same can happen with droshkys lined with special tiles.
2. due to the high level of moisture in the room, fungus and mold may appear on the walls and in areas of ceilings. Mold has a detrimental effect on the health of people and children. Sometimes mold has an irreversible process that results in the building needing to be demolished.
3. if the soil has high humidity, then it is impossible to grow crops on the site. The roots of plants in water gradually rot.
4. if the soil is wet under outbuildings or garages, then things deteriorate and cars undergo premature corrosion.
In what cases is it necessary to make a drainage system?
All problems that high humidity can cause can be eliminated and prevented by drainage that removes moisture from the area. There are signs that indicate the need for a drainage system:
1.after the rains, puddles and mud remain on the site for a long time.
2. when plants in the garden die for no reason.
3. Mold forms in basements.
4.during drought, the soil on the site remains moist.
5. Of the weeds, those that love moisture grow in large numbers: nettle or cattail.
6. There are swamps or ponds near the site.
Attention! There are signs by which it can be determined that groundwater flows no lower than 1.5 meters, and this requires the organization of drainage systems on the site.
Dehumidification of hard artificial surfaces
Patios and walkways become impassable after every rain if they are not designed to drain water. When asphalting or concreting an area, a slight slope should be provided for water drainage. A slope of 1:40 will ensure a fairly rapid outflow of water to the edge bordering the soil (where it can be used by plants) or into a shallow drainage ditch leading to a catch basin or drainage well. The drainage ditch is constructed from halves of ceramic pipes embedded in cement, or from concrete, giving it a similar shape.
If desired, a hidden drain is installed in the patio or under the path. Halves of ceramic pipes are laid with a slight overlap of their ends under the center of the area, giving a slope to the surface towards the drain. A 1.5 cm gap left in the center will allow water to flow to the drain.
Organizing drainage using alternative methods
You can combat excess moisture in a site not only with the help of traditional drainage systems. So, one of the effective options is to use lawn gratings for grass. Such gratings are honeycomb-shaped panels. They are painted green. Typically, panels are made of high-density polyethylene. Such lawn gratings can withstand loads of up to 200 t/m2. During installation, the panels are laid on a sand and gravel base. The thickness of the base is determined by the load class for a particular zone.
The laid honeycombs are 90% overgrown with lawn grass. She mows regularly so that the area looks like a lawn. The use of lawn gratings allows you to provide high-quality drainage, as well as protect the soil surface from trampling, erosion, and damage from car tires. After rain, moisture goes into the soil through the honeycomb. An area drained in this way always remains dry and water does not stagnate on it.
Another interesting drainage option is offered by TerraWay, a German developer of the technology of the same name. TerraWay is a solid, environmentally friendly coating. It contains fractionated inert materials (granite, gravel, glass, quartz sand, etc.), as well as a two-component polymer binder. This coating has a porous structure that allows air and moisture to pass through. This provides drainage and gas exchange for plant root systems. At the same time, TerraWay is superior in wear resistance and strength to asphalt pavement.
It is assumed that this coating can be used for arranging paths, sports and children's playgrounds, parking lots, etc. Thanks to its characteristics, even after heavy rain, water will not linger on the surface.
TerraWay has a number of additional advantages.
- Ice does not form on the coating, as it does not retain moisture.
- The coating is elastic and has good adhesion to the sole of the shoe. This allows you to reduce fatigue in the leg joints and reduce the load on the foot.
- The coating can have almost any appearance. So, in its production you can use various fillers, as well as different polymer pigments. This allows you to change the texture of the material and create patterns and ornaments on its surface. Additionally, TerraWay can have internal lighting. The coating has the ability to transmit light. This can be exploited by placing fiber optic light sources underneath.
- High maintainability. Repairing damage is easy. To do this, it is enough to cut out the damaged area of the coating and refill it with the composition.
- Easy care. To care for the coating, you can use any tool and any equipment. The exception is a metal tool; it can damage the coating.
In order for the coating to provide high-quality drainage, it must be laid on a sand-crushed stone “cushion” using a technology similar to that of asphalt laying. The components that make up the coating are mixed in a mixer. After this, the mass is placed on the prepared site. Within 24 hours the coating hardens and can be used.