Drainage and storm sewerage: structure and types
When constructing or renovating residential buildings, builders and owners are interested in many questions.
Warmth and waterproofing, the strength of walls and foundations, reliable roofing and much more come to the fore. But many people are thinking about reconstructing gutters and storm sewers? Agree, it is not often that this issue becomes a solution to a problem of primary importance. Rain is not considered a big problem and many believe that creating a reliable, non-leaking roof is enough to solve this problem. Meanwhile, a faulty surface drainage system can cause damage to the thermal insulation of the facade and external cladding. Also, if there is no or damaged storm drain, the basement may be flooded and the integrity of the foundation may be compromised.
Important rules when installing a reliable storm drain
Regardless of the materials used for drainage and the quality of the roof, the basic requirements for storm drainage in an apartment building
the following:
- all installation points and connecting elements must be carefully sealed;
- the frequency of storm drain pipes in an apartment building
should be sufficient - no less than every 250 sq. m.; - risers must be equipped with openings for maintenance;
- the minimum distance of the funnel to the edge of the building must be at least 1 meter;
- risers inside the building must be protected with thermal insulation or panels;
- the location of funnels on the roof should be uniform;
- when forming the roof, you need to make a slope towards the drainage funnels so that water does not linger on the surface;
- After completing all stages of installation, it is necessary to check the functionality of the entire storm sewer system of a multi-storey building
.
The installation of storm drainage in a multi-storey building is a very important stage of its construction. An effective system for draining water from the roof not only ensures dry apartments, but also increases the durability of structures, floors, walls and foundations. In combination with a reliable drainage system, living in the house will be comfortable and safe - the design of the facade will not suffer from excessive moisture from water flows from the roof, and the walls will not become covered with cracks.
Drain and its technical structure
It is immediately worth noting that not every building equipped with a pitched roof is equipped with a drain.
For example, when building houses made of small timber with pitched roofs, in most cases they deliberately refuse to install a drain. However, in this case it is necessary that the roof protrudes a considerable distance from the facade. If the building is of small height and has a protruding roof, then slanting rain will not harm such a structure. However, you should plan the area near the house so that pedestrian paths and sidewalks do not pass under the roof without an organized drainage system. In most cases, the owners and developers of modern timber houses do not take risks and equip their roofs with a drainage system. A typical organization of such a system can be considered the installation of gutters on holders with a slight slope towards the funnel. Holders are usually installed at intervals of half a meter. The gap between the gutter and the roof is closed with a plank, one edge of which goes under the roof waterproofing, and the other into the gutter.
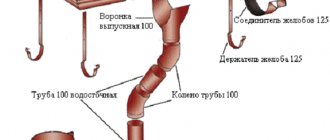
The drainage system consists of drainage gutters installed around the perimeter of the building, drainpipes, and connecting elements. The liquid, flowing down the roof slopes, enters the gutters, rolls down them, and enters the drainpipes through a funnel.
Gutters are made of plastic or metal and can have different cross-sectional shapes. The most common gutters are semicircular in shape. The color and shape of the gutters are usually chosen depending on the appearance of the building and should be in harmony with it. It is advisable that even at the construction stage the entire drainage system is designed and included in the general plan of the building. Their shape and the material from which they are made should also be indicated. The required number of pipes and the method of their fastening are calculated. The parameters are approximately as follows: for every ten meters of gutter, one drain pipe with a diameter of ten centimeters is required. Calculations are also made based on the area of the roof and the angle of inclination of the slope. When creating a drainage design, the design features of the building are also taken into account.
External storm drains in a multi-storey building
If the roof of the building has a pitched structure, then an external drainage system is installed. Their arrangement differs from the internal system.
Precipitation flows freely along the roof into gutters due to the slope. The devices prevent large volumes of precipitation from falling onto the ground near the building, damaging the walls and foundation.
The gutters transport liquid to the funnels, at the same time they represent the heads of the drains. Funnels are located at the corners of the building. If there is a lot of precipitation in the construction area, the devices are additionally installed along the walls in the middle.
Through the drainpipe, precipitation is transported to specially constructed storm water inlets located at the bottom of the drainpipe. It has the shape of a tray, buried in the ground and closed with a lattice.
The grille performs a protective function against leaves and branches getting into the pipes. A closed-type ditch is constructed for each tray; they are located along the perimeter of the building, one and a half to two meters away from the walls.
Attention! The material used to make trays can be concrete, cast iron or plastic. Plastic products are easy to install, light in weight, and highly wear-resistant, so they are widely used during the construction of stormwater systems.
Further, through the drainage pipes, the liquid enters the collectors of the city-wide storm sewer system.
Distribution of responsibilities for drainage repairs. The Housing Code states that the performance of common property in the area near the house falls within the scope of maintenance activities during the warm season. These responsibilities lie with HOAs and similar organizations. This company also monitors the work of storm drainage.
Taking into account the standards for the operation of the building from the technical side, according to the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation No. 170 dated September 27, 2003. The organization is assigned the following responsibilities: to clean the sewer system at least once every three months, and the storm drain twice a year in the spring and autumn.
Reference! The housing organization also undertakes to clean the non-pressure gravity networks, which include adjacent buildings. If violations are detected, the HOA must provide pressure systems to pump out the contents of the sewer pipes.
Work related to seasonal, emergency or ongoing activities is mandatory during the maintenance of houses, regardless of whether this is stipulated in contracts for the maintenance of buildings and territories, must be strictly carried out by these organizations.
The costs of cleaning drainage pipes and wastewater devices are borne by the residents; this item is indicated in the receipt as payment for the maintenance and repair of the home.
Standards used during design. Storm drainage is designed individually for each building. In order to correctly carry out all measurements and calculations, regulatory documents are used that set out the requirements for creating a design and installing the system.
Documents for the construction of storm drains are based on GOST 21.604 - 84.
When designing systems, the requirements according to GOST 3634 - 99, SanPiN 2.1.5.980.00, SNiP 2.04.03 - 85 are applied.
Relying on these requirements, they develop technical and economic justification for construction, its timing, and choose the method and method of regulation and control.
How is the drainage system installed?
The cheapest and well-known drainage system is made of galvanized steel. It has become widespread due to the fact that it is actively used by housing and communal services workers. The low cost and ease of replacing individual elements of such a system allow it to be widely used in mass construction, where workers with shovels and crowbars clean roofs in winter. In private sector and luxury housing, a special wire is passed along the edge of the roof, heating the edges of the roof, thanks to which other more expensive materials can be used to create a storm drain.
Storm drain
As mentioned above, water enters such a sewer system from the internal drains of residential buildings. The separation between storm and ordinary sewerage is necessary because with the water that washes away dirt from the streets, various reagents are supplied to neutralize which a conventional sewerage cleaning system is unable to do. When constructing streets and buildings, such sewerage must be included in the construction plan. Another thing is that usually housing and communal services and road workers during repairs often do not pay attention to it or deliberately spoil it. As a result, streets that are not equipped or have damaged storm drains turn into impassable swamps during rains. All parameters of a storm drain - its cross-section, materials and arrangement - are calculated by engineers and architects at the stage of creating a plan for a residential area.
Source
Classification of internal drainage systems
There are two systems of internal drainage for multi-storey buildings:
The gravity system is as simple as possible. It consists of a gutter running along the eaves of the roof, directing water into a vertical downpipe. Along with water, air enters the sewer system, which reduces the amount of water passing through the pipe. A clear example of this fact is a drainpipe; everyone can compare its diameter and the flow pouring out of it even in heavy rain.
The siphon system connects the water intake funnels on the flat roof of the house into a single horizontal network of pipes, which, using an L-shaped elbow, turns into a vertical drain. The design of the siphon system is more productive, more progressive. The design of such a system prevents air from being sucked into the stormwater pipelines, so internal drainage will require conduits of a smaller diameter than would be needed for the installation of a gravity-type stormwater system.
Installation of drainage in an apartment building
The design of internal drainage is more complex than external drainage and requires more detailed consideration.
In-house drainage requires individual design, since such structures are quite complex; miscalculations in this area of construction threaten flooding of the upper floors of the house, water overflowing over the edge of the roof, erosion of the foundation, and waterlogging of external walls, which can lead to a decrease in their strength.
SNiP regulate the number of storm sewer risers on the roof of a building - at least one for every 150–200 square meters of roof; a smaller number may not be able to cope with the discharge of water. Several risers on the roof of the building form a drainage system.
Water inlet funnels are made of either metal or plastic; pipelines for drainage risers can be made of the same materials. The lattice cover protects the funnel from debris.
The funnel is located in the center of small slopes, somewhat away from the outer wall. During the cold season, the junction of the roof and the wall receives the least amount of heat emanating from the heated interior of the building, so the water here can freeze. The device for attaching the funnel to the roof surface must prevent water from flowing into the joint area. The joint is sealed with special gaskets.
The riser pipes are equipped with revisions for access by utility personnel to clean them in case of blockage. Hatches are made in the walls of houses opposite the inspections - the plumber removes them and opens the inspection.
Technology for constructing an internal stormwater system
Proper installation of storm drainage in a multi-storey building
- a very important stage of construction, since it is much more difficult to correct errors during operation. It is recommended to place one drainpipe at least per 250 sq.m. roof area. A sparser arrangement of risers will lead to water retention and reduced system performance. To regularly clean pipes from debris and contaminants, it is necessary to provide inspection holes (inspections).
During the cold season, there is a possibility of ice blockages forming in the pipes, so they need to be well insulated so that you don’t have to replace the storm drain in an apartment building
. In the northern regions, it is impossible to do without installing an electric heating system for drainpipes.
The main stages of technology for installing storm drainage in an apartment building
:
- In order to correctly complete all the stages of creating a drainage system, a preliminary design of a storm drainage scheme for an apartment building
. Places for installing drainpipes and funnels are marked on the roof, taking into account future communications, features of walls and ceilings. At this stage, you need to think about the fact that when servicing the risers you will need easy access to the audits. - Holes are drilled in the walls for the outlet and fastening of drainpipes. Each type of material may require different fastening options, so the pipe manufacturer's recommendations must be followed.
- Drainage funnels are installed, carefully sealing the joints, connected to each other by a pipeline and, using a connecting elbow, an entrance to the drainage riser is made.
- The exhaust pipe is being installed. But first you need to think about where the water collected from the roofs will be discharged. A simplified option is possible when the drains are simply led at an angle beyond the blind area or into the surface drainage system.
- Hatches are installed in vertical drainpipes for regular inspection and cleaning.
- All connections and joints are carefully sealed with a product that is resistant to low temperatures.
- Install protective grilles on funnels and seals.
- After installing all elements of the storm drainage system in an apartment building,
the functionality of the system is checked.
Preventive maintenance and repair of storm drainage in an apartment building
- This is the responsibility of the utility service. Therefore, if drips appear on the walls of the upper floors, you should contact the housing and communal services service.
Siphon system and its features
The water intake funnels of the siphon system have a device that prevents water from swirling when it gets inside. Sometimes you can hear the water sucking in air.
Air entering the pipe system reduces the productivity of gravity drainage systems, forcing an increase in the number of risers and the diameter of the pipes, so the advantage of siphon systems over others is obvious.
When the water level in the vertical riser does drop, a vacuum is created in the pipeline, which sucks in the remaining water on the roof of the building - this property is the main feature of siphon systems. The role of a siphon is played by horizontal pipes laid on the roof in a special way.
To prevent the water in siphon systems from freezing, they are “dressed” in good thermal insulation, or even electric heating cables are laid nearby. The costs of installing heating and energy consumption are compensated in the future by the absence of worries about clearing ice from pipelines.
Additional rules when installing storm drains
Specialists carrying out installation work on installing gutters on the roof of buildings must take into account some rules:
- one storm drain riser serves no more than 250 m² of roof;
- all sewerage elements are sealed in the most thorough manner;
- fasteners should not “squeeze” the material of the main elements of the storm drain;
- the riser pipes must have inspections for their maintenance;
- The introduction of a storm sewer into operation should be carried out after its performance test.
Installation of sewerage systems and their maintenance are carried out only by certified specialists.
Design Features
Storm sewer consists of two sections:
- interior;
- outer.
Internal storm drainage is all elements located on the roof and vertical pipelines through which water moves to receiving tanks. The outer part is a system for transporting wastewater to a rain collector. The composition and design of the external sections are almost the same for all systems. The difference lies in the way water is collected and moved down from the roof.
Houses with pitched roofs
Buildings with sloping roof slopes are equipped with a system of receiving trays installed along the perimeter of the roof. Water flows into them, passes to the receiving funnels, goes down the drainpipes and is sent to the receiving tanks or to the main line. All systems of this type are gravity flow. This means that the installation of internal storm drainage must be carried out taking into account the slope of the trays. Repair and maintenance of such systems is simple, since there are no hidden elements. However, placing components at high altitudes makes work difficult and makes maintenance or replacement an extremely dangerous procedure. Open trays are often filled with small debris blown by the wind. Blockages quickly increase in size and become denser, blocking the flow of drains. If you do not periodically clean the gutters, moisture will overflow and fall on the walls and windows of the lower floors. This is the only drawback of such systems.
Flat roof houses
Internal storm drainage in a multi-storey building with a flat roof consists of one or more receiving funnels connected to a vertical pipeline. Another name is a siphon drain. It extends to the ground floor, exits the foundation and joins the main line. To organize efficient collection of water, a slope is made to the funnels. The diameter of the riser must provide sufficient throughput so that rainwater can be removed without delay.
Sometimes a more complex structure of internal siphon systems is found. Receiving funnels are connected to horizontal pipelines located under the floor slab. An L-shaped connecting element connected to the riser extends from the horizontal pipes. The principle of operation of the network does not change, the difference is only in design issues.
Repairing a storm drain in an apartment building is greatly simplified if it is assembled using a siphon type. All possible problems involve a clogged riser. Maintaining, repairing and replacing components with this arrangement of elements is much easier and safer.
The design of such systems is carried out based on the general configuration of the building. According to SNiP standards, there is one riser per entrance, or one vertical pipeline per 250 m2 of roofing. It is important to ensure high-quality sealing of all connections, otherwise leaks will occur that destroy the wall material or foundation. The sewer risers of high-rise buildings are common property, so concerns about the condition of these elements fall on the shoulders of management company employees.
You may also like:
Storm sewerage in a private house: design, installation, rules
Drainage and storm sewerage - types and features of systems
Sewerage in the bathhouse: a device, how to make it yourself