Working on a welding machine is a hazardous type of work. That is why, in order to carry them out, special conditions must be provided in the workshop that would contribute to a normal microclimate in the workplace. During welding work, the air masses in the room are saturated with carbon oxides and other chemical compounds harmful to the health of the worker. That is why the welding shop must be equipped with a proper ventilation system, which will ensure the flow of fresh air and the removal of waste materials.
Functions of the ventilation system of a welding shop
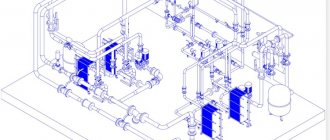
Welding shop with spot ventilation system
The main tasks of the welding shop ventilation system are:
- eliminating toxic impurities that enter the air during welding work;
- general air purification throughout the room;
- maintaining optimal levels of temperature and humidity in the room.
Important! In accordance with GOST 12.3.003-86, the welder’s workplace must be equipped with a local ventilation system. Also, general ventilation should be used in the workshop.
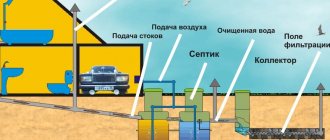
Air purification in the cellar
As a rule, a garage is used not only for parking a car, but also for storing food. Accordingly, this also provides additional moisture. But even if storage is not carried out, ventilation of the pit must be organized for comfortable work in it.
As experts note, natural ventilation is the best option in the cellar.
Provided there is good air exchange in the room, it is possible to use pipes with a diameter of 10 centimeters.
One of them is installed around ten centimeters from the floor, and the second on the opposite side, ten centimeters from the ceiling. The end of the top pipe is brought out.
It is also worth taking care of the protection of the hood.
Local ventilation of the welding station
The essence of the local ventilation system is to purify the air directly at the welder’s workplace, since at a distance of already 4 m the air masses in the workshop can meet the required sanitary standards. But directly near the welding machine, chemical combinations harmful to human health accumulate in the air masses, exceeding the norm by more than 10 times.
Types of local ventilation
Flexible air intakes
- Exhaust devices of lift-and-turn type. This ventilation system consists of an air inlet, which is fixed in any position using hinges, a hose with a diameter of 200 mm connecting the air inlet and a centralized exhaust system. This design allows you to eliminate up to 85% of substances harmful to health, since it can be placed in close proximity to the welding machine. Lift-and-swivel hoods contribute to complete air purification at a distance of up to 8 m from the installation site. The most popular lift-and-turn exhaust systems are the Lan and Sprut models.
- Local suction, which are installed at a height of 1.5 m from the workplace. Another option for installing suction units is to install them directly into welding tables. They are connected to the general ventilation of the workshop with special hoses.
To ensure proper air exchange, the welding shop is equipped with forced-air ventilation. The system must provide an influx of fresh air masses of more than 40 m3/hour.
Types of ventilation systems
Properly equipped ventilation in the welding shop reduces the concentration of harmful substances in the room atmosphere and minimizes harm to the environment. Depending on the number of workplaces and their location, the type and power of fans and the routing of air ducts are selected. Exhaust ventilation units can be located both on the roof of the workshop and near it. The air intake from the supply units should not be located in the area where the gaseous environment is emitted.
Local exhaust
Ventilation of welding stations is selected depending on the size of the parts being welded and the intensity of work. The amount and composition of gases formed will depend on this.
It is not recommended to install exhaust hoods above the welder’s position, since harmful substances will pass through his breathing zone.
In this case, it is better to use work tables with air suction through a grate located on its surface. With this type of local ventilation, the exhaust device must be equipped with a spark arresting filter.
The productivity of the workplace exhaust system can reach 5.5 thousand m³/hour. When welding or surfacing large products on tables that are not equipped with exhaust devices, removal of welding aerosols is carried out using local suction of mobile filter-ventilation units.
When performing some work, lifting and rotating hoods are used. A flexible receiving hose with a diameter of 200 mm is hinged on the console and is directed to the required area. The inlet pipe of this device can be located at a distance of 7–8 m from the welder’s position.
When using local exhaust devices, supply air should be supplied to the lower part of the room, and if not possible, to the upper part, with subsequent finishing to the welding station.
General exchange system
Such a system consists of a supply and exhaust fan and an air duct system with filters and adjustable air supply devices. General ventilation should provide the workshop with fresh air to reduce the content of harmful impurities. Its arrangement is mandatory if more than 200 g/hour of electrodes per 1 m³ of room volume is used during work. Otherwise, the influx of fresh air masses is ensured naturally. In winter, outside air must be supplied to the workshop with a temperature of at least +18 °C.
The design of the general ventilation system requires the presence of filters to clean the polluted environment before being released outside. The performance of ventilation units is selected in such a way as to ensure 10-fold air exchange.
The amount of exhaust air should be slightly larger than the supply air to prevent gas contamination of adjacent rooms.
The vertical speed of movement of air masses should be more than 0.1 m/s. This is sufficient to mix the environment and remove welding aerosols from areas outside the welding stations.
Regulatory mechanism for local ventilation
It is necessary to periodically clean fans and filters from accumulated dirt.
According to sanitary standards N 1009-73, a number of requirements are put forward for local ventilation devices:
- local suction must be installed at stationary and non-stationary welding stations;
- when manual welding, the workplace must be supplemented with rotary-lifting panels, the bottom of which should be no higher than 350 mm from the welding machine;
- when welding medium-sized products, it is necessary to install a fume hood, which is a type of local suction;
- the air speed when using manual welding and a device powered by carbon dioxide must be more than 0.5 m/s and 0.3 m/s when welding in inert gases;
- fume hoods must localize up to 90% of harmful substances from air masses, other types of local ventilation - up to 75%;
- 10-25% of harmful components in the air must be eliminated using a general ventilation system.
Release of pollutants from metal welding
Welding method and brand of welding material Pollutant emission, g/kg of welding material Other pollutants welding aerosol manganese compounds chromium fluoride hydrogen oxides nitrogen oxides carbon oxide name quantity Manual arc welding of steels with electrodes UONI-13/5518.60.97—0.93—fluorides 2.6 UONI-13/657.5 1, 41—1.17——fluorides 0.8ANO-46.00.69——————ANO-616.31.95——————ANO-1122.40.87——————EA- 606/1111,00,680,60,41,31,4——M33-III40———————TsT-157,90,550,351,61——nickel oxides0.39Manual arc welding of cast ironTsCh-413,80,43—1, 87—vanadium0.54Manual arc welding of copperSHCHZCh-114.70.47—1.65—copper4.42Tungsten under helium20—————tungsten0.08copper2.1СрМ-0.75 (wire) Manual welding of aluminum17.10.44—— —copper15.4ОЗА-138.1—————aluminum oxide20 aerosolWireEP-24512.40.54—0.36—iron oxides11.5PP-106, PP-108120.7——0.8—iron oxides0.7WireSV-08G2S9 ,70.50.02—14iron oxides7.48SV-Kh19N9F2SZ70.420.03——14iron oxides0.04SV-10Kh20N7ST80.450.03—————SV-16Kh16N25M61521——nickel oxides—EP-24512.40.61— ——3.2——SV-O8KhGN2MT6.5—0.03—0.811 titanium oxides0.4copper11WireMNZh-KG5-1-02-0.2180.3————nickel oxides0.8KMTs8.80.6————copper6WireD- 2010.90.09————aluminum oxides 7.6AMTS22.10.62——2.45——20AMG-6T500.25—0.33——8.5 Aluminum 10———0.9———Titanium 14.7 —————titanium oxides 5 Non-consumable electrodes 61—————aluminum oxides 28 OZA-2/ak, OZA-138.5—————— 20 Welding steel with fluxes OSB-450.090.03—0.20.006—other fluorides 0.36 FC-2 , FC-6, FC-70.090.01—0.050.005—silicon compounds 0.03 FC-11, FC-120.090.05—0.02———0.05AN-220.120.01—0.02————AN-26 , AN-30, AN-420,080.05—0.03————AN-60, AN-640,090.02——————AN-348A0.10.03—0.20.006—other fluorides 0.16ANK- 300.260.12—0.018——silicon compounds 0.05ZhS-4505.80.142—0.18—22.4——K-10.060.023—0.15—0.5——K-84.90.13—17.8— —K-111.30.089—0.140.6———When is general ventilation needed for a welding station?
In accordance with SNiP2-33-75, the ventilation system of the welding shop must be of the mechanical type, that is, equipped with special fans. The supply of fresh air should be carried out by air distributors installed at a distance of 6 m from the floor when supplying the flow downwards in a vertical position or at a distance of 4 m when supplying the flow in a horizontal position. You should also take into account the speed of air mass flow, which cannot be less than 0.1 m/s.
When installing ventilation with parallel flows, the most optimal conditions for performing work and purifying air are created, since exhaust air masses containing harmful gases and aerosols move in the same direction as the supplied air. The mass of the supplied flows must be less than the amount of polluted air removed. This principle can significantly increase the efficiency of the system.
How to make a hood in a garage
To install the structure yourself, you need to follow these steps:
- Step back 15-20 cm in height from the floor.
- Use a hammer drill to make a hole in the wall to bring in fresh air.
- Insert a piece of pipe and cover the area around it with plaster.
- Use a hammer drill to create a space in the ceiling, or step back from it 15-20 cm down the wall. Polluted air will escape into it.
- Insert the pipe into the prepared place in the roof. The longer it is, the more effective the air change will be. Cover its outer end with a cone-shaped dome to protect it from precipitation.
In a metal garage, you can make the simplest and cheapest option: in selected places, drill holes like a lattice with a drill, cover them with a mesh.
Installation of a structure for exhaust gas extraction indoors is a mandatory requirement of SNiP 02/21/99. To choose the right type, you should understand the work of each of them.
Garage ventilation system
Scheme of general ventilation of the welding shop
General ventilation includes exhaust fans.
The ventilation grille, the size of which is 23.5x43.5 mm with a hole diameter of 50 mm, provides fresh air at a speed of 4.5 m/s. Air masses, dissecting as they pass through the grille, rise vertically and cover the entire room. The speed of air movement in the workshop corresponds to 0.1 m/s, which makes it possible to eliminate all harmful components in the air. Air exchange in the room is ensured by fans installed under the floor, with a total capacity of 3400 m3/hour. Exhaust air is eliminated using fans installed on the roof with a total capacity of 6600 m3/hour. When the system operates for 20 minutes, all contaminated air masses are eliminated, and the concentration of harmful substances in the air is reduced to 2 mg/m3.
Requirements for ventilation in welding rooms
Harmful substances formed during welding have a temperature higher than the surrounding air and rise, gradually polluting the room. Being in such an environment has a detrimental effect on human health. To reduce the influence of harmful factors, a mechanical ventilation system is installed. In welding production it must meet the requirements:
- Creating and maintaining a microclimate in the room in accordance with the requirements of SP 1009-73 “Sanitary rules for welding, surfacing and cutting of metals.”
- Elimination of chemical components and emissions that go beyond the work area.
- Organization of constant air exchange in the welding shop by supplying fresh air to reduce the maximum permissible content of welding aerosols and gases.
The ventilation of the welding room must be autonomous and operate in an open cycle. Fresh air must be supplied to the welding zone, and its speed can be no more than 0.9 m/sec.
When manual arc welding of large-sized parts, the welding station must be equipped with rotary-lifting exhaust devices located no higher than 35 cm from the welding site. The air speed in this case should be within 0.5 m/sec.
The workshop ventilation system must operate in such a way that there are no stagnant zones in the room.
Local exhaust of the welding station can ensure the removal of 75% of welding aerosols. The remaining 25% is allocated by the general ventilation system.
Calculation of MPC (maximum permissible concentration) of harmful impurities and measurement of microclimate parameters are carried out in accordance with GOST 12.1.005–88 “General sanitary and hygienic requirements for air in the working area.”
Regulating mechanism of general ventilation
- If less than 0.2 g/h of welding materials is consumed per 1 m3 of room, the arrangement of general ventilation may not be carried out.
- The fresh flow rate cannot exceed 0.9 m/s.
- In the absence of a local ventilation system, mechanical ventilation should ensure the elimination of 2/3 of the air masses from below and 1/3 from above.
- If welding work is carried out inside a product (container, barrel), the air speed should be more than 0.7 m/s at temperatures not lower than 20 degrees.
Natural air exchange installation
Due to its ease of installation and low cost, such ventilation is suitable for many. It is also commonly used for cellars.
Installing ventilation in a garage necessarily begins with calculations.
According to SNiP, for every 10 square meters of area there should be 15 centimeters of air duct diameter.
For example, the size of a garage is 5 by 4 meters. The garage area will be twenty square meters. We calculate according to the formula: 20 * 1.5 = 30 centimeters.
As a result, we obtain a channel diameter of 30 centimeters. If you plan to install two hoods and two supply channels, this value should be halved.
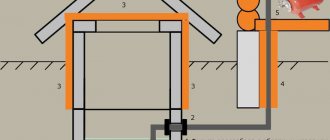
The figure shows the ventilation in the garage with your own hands, the diagram shows the location of the ventilation openings.
The next stage is preparing the opening for air intake. It is done using a hammer drill at a height of about ten centimeters from the floor. Proper ventilation of the garage will occur when the hood is installed in the opposite supply wall, and it is advisable that the hole be made diagonally.
Using a hammer drill we do the same thing, only under the ceiling. This is necessary because the ventilation pipe will be installed above the roof of the room to a height of approximately fifty centimeters.
Next is treating the voids between the wall and the pipe with sealant. For better bonding, you need to choose a sealant that allows you to connect different materials. At the very end of the installation, care must be taken to install protective devices. To prevent rodents and insects from entering your garage, install protective grilles. A small lid or dome will help protect against precipitation.
Thus, installation of ventilation will cost approximately 300 rubles. It is worth considering that natural air exchange is most effective when the outside temperature is less than 10-12 degrees Celsius.
Calculation of a ventilation system for a welding shop
Exhausts at the welding station
Calculation of the performance of the ventilation system for the welding shop should be carried out depending on the number of electrodes used per 1 working hour:
- manual welding method – for 1 kg of electrodes it is necessary to ensure a productivity of up to 4500 m3/hour;
- semi-automatic welding method - for 1 kg of electrodes it is necessary to ensure a productivity of up to 2 m3/hour.
Important! When working using the semi-automatic method, one worker can use more than 5 kg of electrodes, respectively, productivity increases by a multiple of the material used.
For the ventilation system to be effective, it is necessary to install powerful fans that are fixed outside the workshop. Ventilation ducts are installed using metal pipes. Ventilation grilles should be located near the welder’s workplace.
When installing an exhaust system, it is allowed to install special filters that allow the use of air recirculation in the workshop. There, the emission of harmful welding gases into the atmosphere is eliminated.
The welding shop ventilation system must provide fresh air to the shop and remove stale air. It is designed at the initial stage of construction.
DIY hood installation
In everyday life, welding work is most often carried out in the garage. Therefore, a garage system is slightly different from the ventilation system in a welding shop. It includes an umbrella with an exhaust fan, which is installed above the welding table. The exhaust vent is installed in the wall opposite the gate, and if this is not possible, it is brought out onto the roof. The air duct is made of corrugated pipe.
When installing a homemade hood, you should provide a supply duct in order to carry out welding with the garage door closed. The effectiveness of the system is tested experimentally. Low-power 220-volt motors are used as a stimulus. As practice has shown, a home-made hood allows you to ventilate a room to a level acceptable for work.