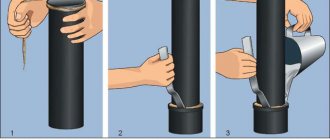
To create comfortable living conditions in a private house, a sewerage system is installed to ensure wastewater removal with further treatment and disposal.
Operating conditions of the sewer system
To correctly select the required sewage system, several main factors must be taken into account:
- the number of permanent residents in the house;
- average water consumption per day per resident;
- groundwater level depending on the season;
- the size of the plot and the area of land available for the construction of treatment facilities;
- amount of precipitation during the year;
- type of soil on the site.
Sewage installation options
The installation of a sewerage system in a country house involves the installation of pipelines through which wastewater is discharged to a storage tank located on the site.
Typically, designers recommend installing 2 types of sewage systems on a site:
- storm sewer system for a private home, ensuring the removal of rainfall, melt water and maintaining a given level of groundwater, preventing flooding of basements and cellars;
- a domestic sewer system for a private house, into which all wastewater generated as a result of the life activities of the residents of the house is collected.
It is possible to combine 2 types of sewage systems in one system with an increase in the volume of the storage tank depending on the number of residents living in the house.
Principles of sewerage installation for a private home
So, sewerage in a private house, as in an apartment, is a connection of sewer pipes with a vertical riser. Through these pipes, water from sinks, toilets and bathtubs enters horizontal pipes, through which it flows into a riser. Further along the riser, the liquid goes into the sewer or treatment plant.
If you are just planning to build a house, then you need to place the bathrooms and kitchen near the place where the sewage system is discharged from the house. If the house is multi-story, then the bathrooms should be located one below the other, for ease of installation of the system.
When planning a wastewater system, you also need to pay attention to additional factors that may affect future operation.
Therefore, when designing a sewerage system, it is necessary to take into account:
- landscape of the site - the water flow is directed downwards and the end point of its discharge should be at the bottom of the site;
- type of soil - to what depth it freezes and what is the height of groundwater. The depth of laying the pipe will depend on this.
Construction of sewerage systems
The general house sewerage system includes the following elements:
- Storage device for (with or without treatment system) wastewater.
- External (external) sewerage pipeline system.
- Internal sewer system.
The storage system can be designed as:
- A cesspool (without a bottom or with a bottom), in which wastewater is filtered by purifying the wastewater as it passes through the ground and processing it with the help of microflora living in the reservoir. Crushed stone or screenings are used to fill the bottom. Designed for wastewater flow rates up to 1 cubic meter. meters.
- A sealed tank - made of steel or plastic and having a specified volume that allows the collection of wastewater for a certain period. The plastic tank is installed in a pre-dug pit and does not require additional sealing and is not subject to corrosion.
- A septic tank in which wastewater is treated and after a certain period of time the waste is removed by pumping using a special vehicle equipped with a tank. In some areas, a two-chamber septic tank system is used, designed to serve a larger number of residents. The first well is used as a sump, and the second for filtering wastewater. A septic tank is a container divided into 2-3 chambers, in which stage-by-stage wastewater treatment is carried out. The septic tank “Purflo” (France) produces high-quality wastewater treatment and is designed for 2-10 people.
- Local treatment plants are systems capable of removing up to 98% of solids from wastewater, converting them into fertilizers. Such stations are designed to process wastewater in volumes from 1 to 10 cubic meters. meters per day, which meets the needs of consumers ranging from 4 to 50 people. An example is the Biosepter-Super-filter installation (Russia). The station has a durable body made of durable steel 5 mm thick, designed to operate for 30 years and consisting of several compartments for step-by-step wastewater treatment. At the initial stage, fat-containing components are separated, and the largest fractions are settled. In the second chamber, medium-sized fractions are separated, and the third chamber is filtered using special filters and microbiological purification.
To pump fecal water, in addition to the gravity method, a special pump Wilo TMW30 EM -30 (Germany) can be used, capable of pumping up to 72 l/min, providing a pressure of up to 30 m and operating from a 220 V network with a power of 700 W.
Features of internal water supply
Internal water supply systems refer to utilities that carry cold and heated water to residents or employees. In addition to pipelines, the system includes measurement equipment and other components. Such pipes deliver liquid: • to the fire hydrant; • to plumbing equipment; • to the process tap.
Requirements for the water supply system relate primarily to the quality of the delivered water and its characteristics. The main parameter of the transported liquid is temperature. The quality of water supplied for household needs can be determined by the following characteristics: • organoleptic qualities; • microbiological parameters; • degree of toxicity.
Rules for placing a septic tank when installing a sewer system
According to current standards, water consumption per person should be 200 liters of water per day. Then the installed storage device must have a volume that provides storage of 3 daily norms (600 liters per person) and is determined taking into account the number of residents living in the house.
Special requirements apply to the location of the storage device on the site, which must comply with:
- The drive should be mounted at the lowest point of the site.
- The distance from the drive must be at least:
- to the water supply source – 50 m;
- roadway – 5 m;
- reservoir (open) – 30 m;
- to a residential building – 5 m;
- to the neighboring area 2-4 m;
- the distance to fruit trees is from 3 to 4 m.
When is it prohibited to establish internal communications?
Sewage structures designed to drain wastewater cannot be installed in the following situations: • laying a sewer pipeline in residential premises is strictly prohibited; • installation of sewerage pipes is prohibited in the bedrooms of children's institutions and clinic wards; • it is forbidden to install sewer pipes in living rooms of sanatoriums and catering premises; • such pipelines should not be present in libraries and museums; • the ban also applies to ceilings in the kitchen and electrical rooms.
The entire list of places where it is prohibited to install internal sewerage can be examined in a specific chapter of SNiP. In addition, it is important to mention a number of restrictions and provisions that must be observed: • it is unacceptable to combine the ducts of the ventilation system and the exhaust of the sewer riser; • connection of hoods of sewer risers and chimneys is prohibited; • the design of the sewer system must have special revisions. • pipelines that were laid in a hidden way must be equipped with inspection hatches to ensure prompt access to existing communications.
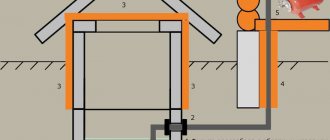
Sewage system diagram
Before the start of construction work, a layout diagram of all elements is drawn up, indicating all points associated with the water supply and wastewater drainage system. Such a scheme allows you to correctly install the sewerage system, taking into account all sanitary requirements and avoid installation errors.
When drawing up the layout of the sewer system, the following must be taken into account:
- all drain points planned for placement in the building with a floor breakdown;
- the location of the central riser (pipes with a diameter of 110 mm), and the outlets from the washbasin or toilet should not exceed 1 m;
- the placement of the sewerage network pipeline should be carried out according to a scheme with separation of the drainage from washbasins and toilets;
- all pipelines of the sewer network must have a slope with a pipe diameter of 50 mm - 3%, and with a diameter of 110 mm - 2% and ensure the free flow of wastewater into the storage tank;
- location of the drain pipe;
- placement of the passage of an external sewerage pipeline with the installation of inspection wells (with a distance of 10-15 m).
What standards regulate the location of objects on the site of a private house?
The main document according to which the construction of a house and the installation of communications is carried out is the project. It contains a work plan indicating all distances and dimensions. The distance from the house to the sewer drainage point is also indicated here. During design, we are guided by two standards:
- SNiP 2.04.01-85;
- SanPiN 2.2.1/2.1.1.1200-03 (or 2.1.5.980-00).
These documents detail all the requirements for sewerage and define the minimum permissible distances between objects and buildings. It must be taken into account that instead of SNiP, the updated version of SP 30.13330.2016 is used today. It is more in line with current realities, although there are no fundamental differences. Regardless of where and by whom the sewerage system is built, the rules and regulations must be strictly followed.
Some owners of private houses believe that the location of the sewer system is their own business. This is a wrong point of view. The rules and regulations specified in building and health directives must be followed by everyone without exception. If the system is being built on the site of a country house, the requirements are more relaxed. But, for a residential building, all existing requirements must be met.
It is noteworthy that the issue of the distance from the septic tank to the house is ambiguous. While the minimum value is clearly defined, the maximum value is not mentioned anywhere. Sanitary standards for sewerage for the private sector also do not mention a maximum. It is only noted that it is advisable to make the distance as large as possible. However, if the septic tank is too far away, blockages or defrosting of the pipes are inevitable. Under such conditions, the system will not be able to operate normally. Therefore, the location of the sewerage system on the site must meet not only sanitary, but also operational requirements.
Selection of pipe material for sewerage
Before laying the pipeline, it is necessary to select the pipe material for internal and external wiring.
The most commonly used materials for the manufacture of sewer pipes are:
- cast iron;
- polypropylene;
- polyvinyl chloride
Cast iron pipes used for installation of the sewer system are produced in 2 versions:
- with bell;
- without bell.
and are resistant to temperature changes, corrosion, alkalis and acids. They have low cost and durability during operation.
Plastic pipes have a number of positive characteristics compared to other materials:
- long service life;
- high level of strength and flexibility;
- high resistance to corrosion;
- light weight, which significantly reduces labor costs;
- high degree of internal surface treatment, which prevents the formation of deposits;
- ease of installation of structures.
Polypropylene pipes are produced in several brands:
- PN 10 (designed for temperatures up to 45 * C);
- PN 16 (designed for operating temperatures up to 60 * C);
- PN 20 (designed for operating temperatures up to +100 *C).
Certain brands of polypropylene pipes are resistant to high temperatures and are mainly used for laying internal piping. The pipe has a structure consisting of 2 layers, outer - polypropylene, inner - polyethylene.
Polyvinyl chloride pipes are highly resistant to mechanical influences from the external environment, resistant to temperature changes, and open fire. Pipes painted orange are used for laying external pipelines, and gray ones are used for internal ones.
External piping material
Various materials are used to make external pipelines. These may include:
- plastic _ There are different types - polyethylene, PVC, propylene pipes. The most common plastic sewer pipe is 110 mm, the technical characteristics of which ensure resistance to all loads. Plastic pipes have a lot of advantages - light weight, corrosion resistance, smooth surface. The disadvantages of plastic elements include temperature changes in size. The service life of such a system will be 50 years;
- asbestos cement . These are durable, lightweight products made from a mixture of cement and asbestos fibers. Not so long ago they were widely in demand, but with the advent of plastic parts of the system they ceased to be in demand. The reason for this is fragility, tendency to cracks;
- ceramics _ A material that has long been used for the construction of various systems. Ceramic sewer pipes for external installation are still used today. It is resistant to the appearance of deposits on the internal walls. The disadvantage is fragility and a large number of joints.
The length of one segment is small, so many connections have to be made;
- cast iron In Soviet times, cast iron pipelines made up any system. Then they did not make a difference between internal and external areas, which simplified the choice, but complicated the installation technology. For street lines, the minimum diameter is 110 mm, which is too much for the internal part of the system. In addition, the disadvantages were heavy weight and fragility. Installation required sealing each socket, which was time-consuming. This in total became the reason for the abandonment of cast iron systems.
Today, PVC pipes for external sewerage are confidently in the lead. They are inexpensive, quickly and reliably connected, and can be repaired or replaced. Industrial sewer lines sometimes use cast iron pipelines, which are more durable.
What do you need to know when laying internal sewerage?
The installation of the internal system is carried out in 2 stages:
- internal sewerage;
- ventilation.
The central riser can be laid by installing pipes without additional insulation using boxes or in special niches. The central riser must be provided with inspection hatches necessary for cleaning in case of clogging of the system. The most suitable place for placing and installing a riser are toilets.
At the points of connection or branching of pipelines, tees, bends, crosses, manifolds, as well as special fittings in the form of clamps, ties, gaskets, and seals are used. The bends have a pipe inclination angle from 15* to 90* and different diameters. The connection of pipes of the external and internal systems is carried out using adapters having an angle of 90-130 *, which allows to reduce the noise of the processes taking place. The joints between the pipes are sealed using special gaskets or liners treated with a waterproof sealant.
Drain points are equipped with water seals to prevent odors from entering the premises from the sewerage system.
A ventilation system in the house is necessary to remove gases generated in the sewer network and bring fresh air into the premises. To remove accumulated gases, a drain pipe is used, which is connected to the central riser of the sewer network.
The installation of a drain pipe must meet certain requirements:
- the outlet on the roof of the vent pipe (usually 110 mm) should not freeze during periods of sub-zero temperatures;
- the height of the vent pipe protruding above the roof covering must exceed the height of other outlets (stove, ventilation, fireplace);
- the drain pipe must be located at a distance of at least 4 m from balconies and windows;
- The connection between the drain pipe and the ventilation outlet is prohibited.
- The general layout of the sewer and ventilation system depends on the area of the house, the number of floors of the building and the number of drainage points.
Fan pipelines are equipped with special vacuum valves that prevent the formation of a rarefied environment when draining water and pumping wastewater from the storage tank, which helps reduce the noise level of the system.
Requirements for sewer pipes
Structurally, the sewerage system is an extensive network of pipelines running from plumbing fixtures to the treatment plant. When thinking about which pipes are best for sewerage, you need to remember that the sewerage network will be divided into two components that work together - an external and internal system.
In this case, the pipes for internal sewerage and pipes for external sewerage must be different, since they are operated under different conditions.
Requirements for pipes for internal sewerage
The interior of the system includes all the plumbing fixtures and the sewer pipes connecting them. Since the networks are located in the apartment, the sewerage pipes will be operated under gentle conditions.
In an apartment, sewer pipes can be laid hidden (in the walls, under the floor covering) or openly. In the latter case, the sewer pipes are secured to the wall.
Fasteners for sewer pipes are represented by clamps screwed to the wall. For sewer pipes laid indoors, the characteristics must be as follows:
- Be durable.
- Do not interact with the transported medium.
- Be resistant to thermal, chemical and biological influences.
- Have the smoothest possible inner surface.
- Provide the ability to connect various plumbing fixtures.
What pipe diameter should I choose? The diameter of sewer pipes is selected according to building codes. The sizes of sewer pipes differ depending on which device the pipe is planned to be connected to. Recommended diameter of the sewer pipe for drainage from:
- baths – 40 mm;
- shower cabin – 40 mm;
- washbasin – 40 mm;
- bidet – pipe 32 mm;
- toilet - pipe 110 millimeters. For installation of wall-hung toilets, a 90 mm pipe can be used.
The central riser in the apartment is made of a pipe measuring 110 mm, and branches from it can have a diameter of 75 mm. When building an internal sewer system for a private house, the diameter of the sewer pipe is selected according to the same standards.
Advice! If necessary, a smaller diameter pipe can be replaced with a larger pipe. So, if the recommended size is 40 mm, then it is better to choose a larger size; for example, a 50 mm pipe can be installed. But if the standards require the installation of a 110 mm sewer system, then it is undesirable to install a 90 mm pipe.
In addition to pipes, connecting parts are needed to assemble pipelines. What types of fittings are there? These are a variety of couplings, tees, bends, angles, and crosses. Thus, when assembling internal networks, pipe tees are often used.
Tees are used to connect an additional pipe to the main line. To assemble the sewerage system, oblique tees are used, since if you install tees with right angles, the risk of blockages will increase. Such a part as bends is used for assembling metal pipes. Spurs are threaded pipes; they are used where it is necessary to connect non-rotating parts.
Requirements for pipes for external sewerage
Special requirements are placed on materials for installation of the external part of the sewerage system. It is clear that underground sewerage pipes must be especially durable. Previously, pipes for sewerage into the ground were made only of cast iron or asbestos cement.
Nowadays plastic red sewer pipes are more often used. The red pipe is a model designed for assembling external networks. Red coloring is, of course, optional.
It’s just that the manufacturer makes it easier for customers to choose: the orange sewer pipe is intended for external networks, the gray one for internal ones. If a gray pipe, intended for internal networks, is chosen for installation in the ground, then the system will soon become unusable and sewer pipes will need to be repaired.
The red pipe is resistant to soil pressure and negative temperatures. For the installation of external systems, you need to select the appropriate fittings, so the tees for the sewer pipe must also be designed for use in external networks; they are also distinguished by their red color.
To install the external pipeline, large diameter pipes are used, most often a 160 mm or 150 mm sewer pipe is used. For large water flows, choose a 200 mm sewer pipe.
When building a collective drainage system for several houses, a 200 mm pipe may not cope with the load. Therefore, it is worth choosing a sewer pipe of 250 or even 300 mm.
External sewage system
Installation of external sewerage is carried out through a special sleeve with a cross-section of 150 mm, installed in the side wall when pouring the foundation of the house. To prevent the flow of wastewater stored in the storage tank, the external pipeline is equipped with a special check valve that also prevents rodents from entering the house through the pipes.
To lay the pipeline according to the plan, a trench is laid with a depth below the soil freezing level with the laying of a sand cushion 15 cm high, which helps maintain the integrity of the pipeline during soil shifts. In the case of a high groundwater level, pipes are laid to a shallower depth with preliminary insulation of the pipes. After all installation operations of the external pipeline, the system is pressed and leaks are subsequently eliminated.
To clean the external sewerage pipeline, inspection hatches are installed, which are placed according to the rules:
- the inspection hatch is installed at the connection of the internal and external pipeline systems;
- when connecting an external pipeline to a wastewater storage tank;
- when changing the direction of the pipeline line;
- in places where additional pipeline connections are inserted.
The entire external sewage system must have a slope of 2% in relation to the storage tank. When using a special pump for pumping wastewater, installation is carried out in a horizontal plane.
Primary requirements
There are some mandatory rules that must be followed when constructing internal communication networks. Let's try to evaluate the list of main requirements for such pipelines: • In the case of independent preparation of a drainage and water supply plan, it is necessary to combine such systems. This option is most effective and makes it possible to reduce operating costs. • The liquid supplied by the domestic domestic water supply must meet hygiene and sanitation standards. To achieve a certain quality standard, it is necessary for the water to undergo a number of special procedures, including clarification and purification. • Process water should not be used for drinking, but it also needs to be purified. The level of clarification of the liquid is determined according to its further use.
• In order for water to be supplied to consumers without harmful impurities, it is necessary to use communications made from environmentally friendly and non-toxic raw materials. It is important that the materials do not enter into a chemical reaction with H2O and do not release additional impurities into it.
The free water pressure in different situations should be as follows: • the free pressure of one-story buildings should be ten meters; • each new floor must provide an increase in pressure of at least four meters; • in cases of periods of lowest fluid consumption, the norm is to reduce the pressure on any subsequent floor after the first by one meter.
Step by step installation
Each developer must take into account how to properly install risers and horizontal branches when installing a sewer system in a private building. Internal work is carried out using a gray PVC socket pipe. No other material can compete with it. The wiring technology includes the following operations: • risers - from the basement along risers, if necessary, special compensators and revisions are used, the pipes have a diameter of eleven centimeters; • drain pipe - it is put on the riser, the pipeline is routed through the roof slightly above the ridge, it can be replaced with a vacuum-type valve on the top floor of the building; • horizontally located branches - sockets opposite the flow, pipelines for sinks with a diameter of five centimeters, for toilets - eleven centimeters; • siphons – installed together with any plumbing device in order to control the water seals located in them.
At the next stage, independent preparation of the sewage system on the territory is carried out. We are talking about an external drainage system: • installation of a septic tank - the level of occurrence is determined by the exit point of the internal sewerage system and the distance of the underground tank from the building, they must be connected by a straight line with a slope of four to seven degrees; • installation of pipelines – tan PVC-U pipelines are used for external systems, the sockets are located against the direction of flow; if necessary, inspection wells are installed in areas longer than four meters • or at bend points in the main line; • an infiltration system is created in the form of a filtration field or a well with a natural purifier, through which wastewater is discharged into the ground after treatment.
Water supply and sewerage
Plumbing, that is, the supply of water to a room (house, apartment, industrial facility) is a system that directly works to ensure the uninterrupted supply of water to buildings. To supply water to the water intake point, a variety of equipment is used, which must pump (well pumps), accumulate (reservoirs), purify (filtration system) and only after that supply water of the required quality to homes and facilities.
Sewage and its main task is to drain used water (wastewater) from the building outside, and then to treatment facilities, where it is completely purified.
Two systems, like no other, provide, on the one hand, the supply and, on the other, the removal of water, and if this cannot be called interaction, then their parallel, interconnected work ensures complete comfort of living in the house.
Sewerage
Sewage from the school building is removed through the central sewerage system of the locality. Washing latrines are installed inside the building. The number of toilets in them is established in accordance with the standards: in schools and vocational schools - one toilet and one urinal for 40 boys and one toilet for 30 girls; in dormitories of boarding schools - one toilet for 15 girls and one toilet and one urinal for 20 boys.
In the absence of water supply and sewerage in buildings no higher than two floors, restrooms with a ventilated cesspool can be installed. They are placed near the outer wall of the building. Sewage flows through a sewer pipe into a cesspool, the bottom and walls of which are made of waterproof material (brick, concrete, tarred wooden beams), and a “clay castle” 30-40 cm thick is placed around the cesspool. The cesspool is covered with a lid on top. An exhaust duct is located near the waste pipe, next to the chimney. The air in the channel, when heated, creates draft, so foul-smelling gases from the cesspool do not enter the restroom room.
Yard latrines with cesspools are less hygienic; they are installed in case of emergency. When placing latrines on a school site, it is necessary to comply with the sanitary rules for their design and operation. They must have watertight walls and roofs, self-closing doors and seats with lids. The ventilation holes are covered with a fine metal mesh to prevent flies from entering. The seats are made of hard and durable materials that do not deteriorate from frequent treatment with hot water and disinfectants.
Pit latrines are cleaned as they are filled to 2/3 of their capacity. All sewage through underground pipes (if there is a sewerage system) or in pneumatic sewage tankers (if there is no sewerage system) is delivered to the plowing or sewage disposal fields for neutralization.
After cleaning the cesspool, the surface of the earth around it is watered with a 20% solution of bleach (bleach “milk”).
To collect kitchen waste and garbage, use buckets with lids, from which they go into garbage receptacles or garbage pits. Solid waste from garbage receptacles must be removed in special vehicles - garbage trucks, at least every 2 - 3 days, in order to avoid rotting garbage and breeding flies in the warm season.