Home / Devices
Back
Reading time: 4 min
0
413
Plasma was first used for welding in the mid-twentieth century, with the creation of an industrial-type plasma generator - a plasmatron.
In the beginning, plasma welding was used only in narrow areas, in astronautics, for example. However, over time it has become common in other areas of production as well.
Technological progress developed, and private specialists began to use plasma welding. And now plasma welding devices are even more accessible and anyone can buy them.
This article contains basic information about what a plasma cutting machine is, how it works and its varieties.
- General information
- What does it consist of? Power supply
- Welding torch
- Cathode
- Cable package
- Microplasma apparatus
general information
Plasma is an ionized gas, also the fourth state of matter. Modern plasma welding machines are capable of producing temperatures from 5 to 10 thousand degrees Celsius. A device for plasma cutting and welding is often called a plasma torch. The plasma torch can form three types of arc: indirect, mixed or direct.
Before welding, the arc is “twisted” in a special way, since it is prone to decay. After “twisting”, a thin, stable arc is formed, since the gas is ionized very quickly. The end result is a very powerful arc, capable of generating energy at one point. It is at this point that the base metal melts.
A plasma arc can heat almost any metal, regardless of its thickness and composition. Heating to the melting point and even to the boiling point is possible. The only condition is that it is necessary to provide a sufficiently powerful arc.
Additionally, the welding zone is protected with another gas, inert. This can be nitrogen, argon or organic acetone vapor. The torch of the plasma torch is designed in such a way that it can supply shielding gas and plasma simultaneously. So the weld pool is protected while work is being carried out. The metal does not oxidize and the seams are of very high quality.
Types of plasma cutters
Plasma torches for plasma cutting of metals are produced in different modifications according to the type of cutting, arc ignition, and with different operating parameters.
Plasma cutters by cutting type
Based on the type of cutting, a distinction is made between manual machines and automatic CNC machines. It all depends on the work being performed and the maximum thickness of the metal being cut.
Plasma cutters for manual cutting
Plasmatrons for manual cutting are used in various industries - from small auto repair shops to industrial enterprises. The cutting process involves manually operating the cutter – i.e. The cutter independently regulates the cutting speed.
Photo 10. Manual plasma cutting
The manual cutting process does not provide as much precision and productivity as the automatic one. However, the devices are more compact, which makes them possible to transport. Inverter devices can even be carried manually, since their weight does not exceed 15-20 kg.
Plasma cutters for automatic cutting
Plasmatrons for automatic cutting differ in design - it depends on the type of equipment on which the device will be installed. The automatic cutting process is characterized by increased productivity; it is usually performed on a special table on which sheets of the metal to be cut are laid. There are also portable machines for cutting small workpieces. They are controlled by CNC (computer numerical control), which minimizes the human factor.
Photo 11. Automatic plasma cutting
Main advantages:
- high cutting speed;
- increased accuracy and quality of cut;
- automated adjustment of operating parameters (current strength, gas pressure, distance between the nozzle and the workpiece) taking into account the thickness and grade of the metal.
Plasma cutters by type of gas used
Plasmatrons work with different gases - inert, reducing, chemically active and mixtures thereof. They are selected depending on the grade of metal being processed:
- Compressed air – ferrous metals and copper up to 60 mm thick, aluminum up to 70 mm.
- Nitrogen – aluminum and copper up to 20 mm thick, low-carbon low-alloy steels up to 30 mm, with a high content of alloying elements up to 75 mm, brass up to 90 mm, titanium of unlimited thickness.
- Hydrogen nitric – copper, aluminum and their alloys up to 100 mm thick.
- A mixture based on nitrogen and argon - highly alloyed materials up to 50 mm thick.
- Argon and hydrogen – high-alloy steels, aluminum and copper alloys up to 100 mm thick.
Plasma cutters based on arc ignition type
Produced with direct and indirect action arc. A direct arc is excited as a result of the flow of electric current between the cathode (non-consumable electrode) and the anode, which is a metal workpiece. An indirect arc is ignited between the cathode and the nozzle, but such devices are used much less frequently.
Figure 12. Schemes of direct and indirect plasma torches
Plasma cutters by cooling type
Cooling of plasma torches can be of the following types:
- Water - mainly professional modifications are equipped that work continuously for a long time. The circulation of liquid in them is ensured by a special pump.
- Air – equipped with semi-professional and household models. The internal elements of the burners are cooled by the passage of compressed air or gas through the channels. Such devices have a lower duty cycle and require breaks during operation.
What does it consist of?
A plasma welding machine consists of several components: a power source, a special welding torch, a cathode and cable packages. Let's take a closer look at them.
Power supply
The previous generation plasma welding machine used a conventional transformer as a power source. Such a source itself was rather large and heavy, and therefore significantly increased the final dimensions and weight of the apparatus. As a result, old-style plasma devices were bulky and very heavy, which caused many problems.
Fortunately, progress did not stand still and over time, alternative power sources using transistors appeared. They began to be used in inverters, semi-automatic devices and, of course, plasma devices. Thanks to this breakthrough, it was possible to design compact and lightweight devices, which also became even more functional compared to their previous “brothers”.
The modern power supply, powered by IGBT transistors, ensures extremely stable arc burning and allows you to accurately and quickly adjust the welding current using a single handle. Professional plasma machines are equipped with additional functionality such as non-contact ignition of the arc or a pilot arc mode when welding at a low current value.
Welding torch
A welding torch is an essential component for plasma welding and cutting. Shielding gas is supplied through it, a plasma arc is formed through it, and a cathode is installed in it. There are many types of burners, all of them differ in their design and capabilities. In most cases, the torch is selected in accordance with the power of the welding machine.
Low-power and medium-power burners can be used manually. And burners for high-current devices are installed on a special robotic manipulator.
Cathode
The cathode is used to transmit current and can be made of various materials. In devices intended for household and semi-professional use, tungsten or copper cathodes doped with hafnium are used. They are the safest for the welder’s health. Professional-level plasma torches and plasma cutters can use beryllium or thorium cathodes. They can be dangerous for the welder because they emit harmful fumes. To reduce the negative impact, it is necessary to provide powerful ventilation of the workplace.
Cable package
The plasma welding machine must be connected to the torch. A special cable package is used for this. It consists of two hoses (for supplying shielding gas and for supplying working gas), two hoses for water supply, as well as current supply cables for the starting spark and for the control circuit. All of these components are housed in one large bundle-type hose, hence the name cable bundle. Despite the rich “filling”, this cable package bends perfectly and can be used without fear of breaking all the components inside.
How does a plasma device work?
Hand-held plasma devices are used for cutting all electrically conductive materials - structural metals, steels with various contents of alloying elements, copper, aluminum alloys, etc. They are most effective when working with materials of relatively small thickness (up to 40 mm), since the process is characterized by a high cutting speed and minimal release of thermal energy, which eliminates deformation of the cut workpieces.
Traditional plasma cutting is a separation fusion cutting process in which an arc is formed between a refractory electrode and the metal being cut and is compressed as it passes through a nozzle. The plasma-forming gas in the arc is partially dissociated and ionized, and therefore has electrical conductivity. Due to the increased density and temperature, the plasma expands in volume and moves at high speed towards the metal workpiece.
Figure 8. Plasma jet cutting principle
The process itself begins with ignition of a pilot arc between the cathode and the nozzle by applying high voltage to the plasma cutter for cutting metals. It promotes partial ionization, preparing the space between the plasmatron and the workpiece. When it comes into contact with the metal (anode), the power automatically increases and a cutting arc is formed.
The thermal energy of the arc and plasma gas causes melting and partial evaporation of the material being cut. Next, the molten metal is blown out of the cutting zone by a high-speed plasma flow. In this case, the energy required to melt the material is generated only by electricity.
Varieties
Plasma welding machines may vary in their characteristics and purpose. The main difference is the plasma arc current. Its meaning may vary significantly from device to device. Also, the differences lie in the design of the devices and welding torches. We have identified three conventional types of plasma devices and will further tell you about them in more detail.
Microplasma device
Microplasma devices are extremely functional, although they produce a maximum current of 25 Amps. Such devices are designed both for very precise and complex jewelry work and for welding thin metal. In addition, microplasma devices can be used for cutting parts up to 1 cm thick.
The microplasma apparatus is simple in its design and use. It operates on direct current. The burner nozzle diameter rarely exceeds 3 mm. Acetylene mixtures are used as the working gas. The cathode is copper, doped with hafnium.
Medium current device
The characteristics of a medium-current device are similar to a regular inexpensive inverter. It produces from 50 to 150 Amps. But its scope of application is not so wide. A medium-precision machine is often used for cutting metals. Air is often used as the working gas. But if desired, you can use any shielding gas.
Such devices are more complex in their design, and so are the burners. The cathode is tungsten. Some burners may be equipped with an additional water cooling system for the anode.
welding equipment
It is important not to confuse plasma welding machines with metal cutting equipment.
The former are also known as plasma-arc devices, the latter - air-plasma. The latter are not intended for welding metal workpieces! Among the well-known manufacturers are:
- ;
- "Multiplaz";
- "Plasarium".
Read more about the products of these companies and the products of a number of foreign companies in the following sections.
Gorynych
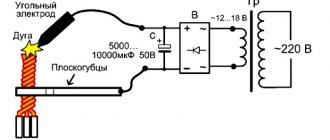
Devices under the Gorynych brand use water or its mixture with alcohol to form plasma, while water vapor performs a protective function. When processing products, a thin anti-corrosion film of oxides is formed over the seam.
To weld metal using Gorynych, gas cylinder equipment or transformers are not required, so a tangible advantage of the devices is their mobility. To activate the equipment, a household network with a voltage of 220 V or an independent current generator is required.
The Gorynych mobile plasma welding machine is designed for metal with a thickness of 0.5 to 8 mm. The temperature of the arc formed by water and plasma reaches 6000 degrees. The process safety requirements are very strict. For example, a well-thought-out ventilation system is not necessary, since the air is not only not poisoned by harmful gases, but is also partially saturated with oxygen.
The cost of installations depends on the power and current. Thus, the multifunctional plasma device “Gorynych” can have three modifications:
- 8 A (suitable for small household work, soldering; costs 29,000 rubles);
- 10 A (wide range of possibilities, including metal cutting; 30,000 rubles);
- 12 A (powerful unit for processing sheets more than 1 cm thick; 33,000 rubles).
Consumables for operating the equipment are inexpensive. For example, a welder will need a welding nozzle (about 200 rubles) and a cathode (200 rubles). The cutting nozzle costs the same.
Multiplaz
The operating principle of the installation is similar to the Gorynych MPK - plasma is formed using an aqueous-alcohol solution.
Another similarity is compactness (the power supply together with the plasma torch weighs just over 6 kg);
here - the absence of strict requirements for room ventilation. The difference from the previously named brand is in power and, therefore, cost. You can learn about the first from the labeling. The popular model “Multiplaz 3500” (3.5 kW) will cost 90 thousand rubles.
Plazarium
The equipment uses an inverter circuit that guarantees arc stability independently from voltage surges. There are sensors that monitor the process temperature and prevent equipment failure. User advantages - compactness, lightness of equipment, availability of consumables.
The modification "Plasarium SP 3", whose power is 2.6 kW, costs about 40 thousand rubles.
Models from foreign manufacturers
Among the popular plasma cutting machines are:
- Fubag (a German concern representing the PLASMA 25, 30, 40, 65 T, 100 models; they are practical, high-performance, but most models are suitable for cutting metal);
- BlueWeld and Telwin (Italy; the line includes devices with contactless start; there are single-phase and three-phase devices, including for manual operation);
- Aurora (China; inexpensive devices with a long cable; there is a non-contact start; some of the devices, in addition to plasma, perform semi-automatic and manual welding, which indicates versatility).
An example of a microplasma welding machine is the SBI PMI 50 TL (including the Basic model). The water-alcohol solution is replaced with an argon-helium or argon-hydrogen mixture. The device can be programmed for a specific operating mode and can be combined with robotic manipulators. Basic is a high-power device that has the functions of the basic model.
When choosing high-quality equipment for plasma welding, pay attention to the models of the above-mentioned companies. They are distinguished by ease of operation, environmental friendliness, and economical energy consumption. A wide range of capabilities makes plasma welding machines a leading position among analogues, and the moderate cost of the models makes the buyer’s choice easier.
Which plasma welding device do you think is the best? Share your opinion in the comments.
POWDER FEEDERS FOR PLASMA SPRAYING
In the case of spraying powder material, our installations use specialized powder feeders. These powder feeders can have one or two power flasks and allow you to regulate the volume of supplied material in automatic or manual modes. In order to ensure the accuracy of the installation, each powder feeder is equipped with a volumetric sensor for monitoring the volume of consumed material and has the following advantages:
|
PLASMATRONS FOR PLASMA SPRAYING
Plasmatron MEC 3 MB
The plasmatron allows the use of up to 4 assembled powder injectors, and can also be equipped with mounts for air nozzles for cooling the part. The delivery set includes a case for the plasma torch and tools for its maintenance. The plasmatron can be supplied in versions for manual or automatic deposition.
| Powder supply | Maximum power | Type of sprayed material | Water consumption | Plasma-forming gases |
| external | 40 kW | Powder | 16 l/min | Ar/H2, Ar/He, Ar/N2 |
Plasmatron MEC F4
Plasmatron F4 is used in plasma powder spraying installations to produce various heat-insulating, wear-resistant and other coatings. This is the most common plasmatron with one cathode and anode, as well as with an external supply of sprayed material. All plasmatron components are highly durable and reliable. The nozzles have tungsten inserts to reduce nozzle bore erosion and improve durability.
| Powder supply | Maximum power | Type of sprayed material | Water consumption | Plasma-forming gases |
| external | 45 kW | Powder | 10-14 l/min | Ar/H2, Ar/He, Ar/N2 |
Plasma torch MEC F4MB – XL
This plasma torch is developed on the basis of the F4 plasma torch and allows you to obtain greater output power of the plasma arc through the use of an improved water cooling system. The components of these plasma torches have a long service life.
| Powder supply | Maximum power | Type of sprayed material | Water consumption | Plasma-forming gases |
| external | 55 kW | Powder | 10-14 l/min | Ar/H2, Ar/He, Ar/N2 |
Plasmatron 9MB
The design features of the plasmatron allow for optimal heat removal through demineralized cooling water coming from a special cooled heat exchanger, which allows for high plasma arc power. Spraying is carried out with external supply of sprayed powder.
| Powder supply | Maximum power | Type of sprayed material | Water consumption | Plasma-forming gases |
| external | 80 kW | Powder | 14-17 l/min | Ar/H 2, Ar/He, Ar/N 2 |
Plasmatron MEC SG-100
The plasmatron has an improved internal supply of sprayed powder, which ensures heat transfer from the plasma arc to the sprayed powder. Combined with high power, this advantage makes the plasmatron extremely versatile and allows the deposition of a very wide range of materials.
| Powder supply | Maximum power | Type of sprayed material | Water consumption | Plasma-forming gases |
| internal | 80 kW | Powder | 10-14 l/min | Ar/H2, Ar/He, Ar/N2 |
Plasmatron MEC F-1
The plasmatron MEC MF-1 has found wide application for spraying the internal surfaces of products that have a complex structure with limited space. The plasmatron makes it possible to apply coatings on the internal surfaces of products with a diameter of 70 mm when operating at powers of up to 25 kW in continuous operation with an external supply of sprayed powder.
| Powder supply | Maximum power | Type of sprayed material | Water consumption | Plasma-forming gases |
| 45° or 90° | 25 kW | Powder | 10-14 l/min | Ar/H2, Ar/He, Ar/N2 |
The best manufacturers of plasma equipment
Plasma cutting is considered one of the most high-tech cutting technologies, so the equipment is in great demand. It is produced by both foreign and domestic manufacturers. The cost of imported machines is very high, so most firms and large enterprises give preference to Russian brands.
One of the leading domestic companies in the development and production of plasma cutting units is PURM LLC. It produces all types of equipment - from manual inverter and transformer devices to pipe cutters and fully automated machines with numerical control.
Video about using the settings:
Advantages of PURM brand machines:
- focus on harsh operating conditions;
- high precision and cleanliness of the cut;
- minimal energy consumption;
- simple maintenance and operation.
Metal laser cutting equipment
Metal cutting using a laser is an innovative technology in the field of metalworking, but it has confidently occupied a leading niche.
Equipment for laser cutting of metal provides the ability to quickly and efficiently cut workpieces of various sizes according to specified parameters. The part that comes out of this device practically does not need final processing. Types of laser cutting equipment
Based on the design properties, the following classification of equipment for laser cutting of metal is common:
Solid State Laser
(power reaches 6 kW) is structurally simpler, but therefore less powerful than gas. The main working body of a solid-state machine is a rod made of artificial ruby, yttrium aluminum garnet or special glass with the addition of neodymium. Thanks to the permanent light flux from the pump lamp passing through a system of mirrors and optical prisms, the laser beam is localized on the head of the rod. Wave radiation in solid-state machines can be both pulsed and continuous;
Gas laser design
(power no more than 20 kW) as a working fluid, it assumes a special gas-discharge chamber, which is filled with helium, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide. Continuous exposure to high-frequency electrical pulses ensures the directionality and monochrome of the beam. Gas laser cutters are capable of processing ultra-strong metal alloys. Slot-type installations operating on the basis of carbon dioxide are considered the most productive and easiest to maintain;
Gas dynamic machines
(power exceeds 100 kW) are structurally similar to gas appliances. However, in these devices there is a need to ensure heating of the gas to extremely high levels and its subsequent cooling, significantly increasing the cost of this installation.
The mechanism of any metal laser cutting equipment includes:
- radiation source with certain optical and energy parameters (consists of an active element, resonator, pumping system)
- a device for generating, converting and transmitting a beam/gas, responsible for precise transmission of the beam from the source to the surface of the workpiece (includes an optical system, a focusing mechanism, a focal surface stabilization complex);
- a coordination unit that controls the movement in space of the laser beam and the plane being processed;
- an automated control unit that regulates the technological process and monitors the parametric data of the equipment.
MASS FLOW PLASMA SPRAYING SYSTEM
The Mass Flow type plasma spraying system is the most modern high-tech plasma spraying system with a closed-loop control system, which provides data collection of the spraying process, their analysis for compliance with the specified ones and control, as well as storage of spraying recipes with the possibility of subsequent recall.
Features of the MASS FLOW spraying system
|
The control system automatically uses the programmed starting parameters for the selected plasmatron, controls ignition and spraying parameters. Programming of spraying parameters is carried out using a color touch panel with the ability to visualize parameters in graphical or digital form.
| The MASS VIEW plasma spray system is very reliable and easy to operate and is ideal for high temperature spray processes that require great flexibility and quality coatings. This system is a modern analogue of old Soviet installations for plasma spraying such as UPU 10 or UPU 3D. Unlike the UPU 10/UPU 3D installations, the MASS VIEW system has high-precision electronic flow meters, as well as a modern control system based on an industrial controller, which allows for higher quality coatings. The use of modern control systems makes the process of operating the system simple and reliable, without requiring highly qualified operator. |
Features of the MASS VIEW type spraying system
|