To view the video, you need a modern browser that supports HTML5 video.
Sheet metal rolling in Moscow (PZO) attracts customers primarily because it is democratic. But, despite the apparent simplicity of the process, it must be carried out according to drawings. The simplest option is when the customer transfers to the contractor technical documentation for rolling sheet steel or other rolled products. If there are no detailed drawings, a sketch of the future product can help out. If this is also missing, you can order metal rolling services “from scratch” - with the development of a project.
Sometimes in the process of metal processing it is necessary not to cut, but to deform it, giving it certain proportions. This problem is solved by special services - rolling. The operation is performed on machines equipped with rollers. These elements gave the technology its name.
How is rolling done?
Rolling technology depends on the type of product. Rolling sheet metal is considered the simplest. Working with it is divided into four stages. This:
- Installation of the workpiece into the gripping area of the machine;
- Equipment debugging (adjusting the distance between the rolls);
- Rolling itself is the passage of the sheet between the rollers;
- Removing the product, if necessary, rolling up one of the edges in order to achieve an equal radius of curvature.
The most difficult rolling, the prices for which are much higher, is work on rolled pipes. With it, a whole group of stresses is applied to the metal, which can lead to distortion at the structural level. Temperature treatment helps to avoid these negative changes.
Overview of rolling types
Since the different applications of rolling involve working with different types of material and for different purposes, the process itself also has many types.
Depending on the direction of sheet feeding during the processing process necessary to obtain a part of the desired configuration, three types of rolling are distinguished:
- transverse - long elements of open rolled pipe are processed by feeding the material in exactly this direction;
- longitudinal - process short elements and blanks of open pipes;
- screw - in this way, products that are not intended for further welding of the joint can be deformed.
To work with materials of different shapes and structures, different types of equipment are used. They differ in type of design, purpose and technical capabilities and include three main types:
- Manual machines are inexpensive, easy-to-maintain mobile equipment. Processing metal manually is possible only if its thickness does not exceed 2 mm, but this may also require significant physical effort.
- Electric machines are efficient installations, the main parameters of which depend on the power of the power motor. Reduced mobility is compensated by the ability to process materials with a thickness of 4-6 mm. Such machines are installed in the workshops of large enterprises, since significant energy costs are fully recouped only under the condition of mass production.
- Hydraulic machines are the most powerful and largest of the rolling mills, therefore they are used in the electrical, mechanical engineering and shipbuilding industries. Allows processing of materials up to 10 mm thick. Rolling on such machines is carried out using modern computer control.
For rolling - only go to a pro!
As we have seen, rolling a sheet along a radius and working with other workpieces require a professional approach.
After all, the denser the material and the more complex its shape, the longer and more intense efforts must be applied to it. But this must be done with great caution. When rolling metal, the cost of the service plays a decisive role, but if you are offered work too cheap, this is a reason to be wary. We will perform rolling for you in Moscow inexpensively and with a 100% quality guarantee.
Scope of application of sheet rolling
Rolling of sheet steel is a convenient and low-energy method for producing spatial products such as cones or open cylinders from flat initial blanks. Compared to other technologies for the production of products such as bodies of revolution (in particular, pressing or drawing), sheet metal rolling processes provide:
- Reduced operating costs for equipment and fixtures.
- Increasing the durability of tools and machines.
- Reduced changeover time.
- Possibility of effective use in small-scale and single-piece production.
- Simplification of routine and repair work.
- Equipment performance management.
- A sharp reduction in losses from marriage.
The introduction of metal rolling processes using sheets or strips as initial blanks is available not only to small industries, but even to repair shops, as well as home craftsmen. As will be shown below, the kinematic diagrams and design of rolling machines for processing sheet material are very simple, and in some cases their drive does not require external energy sources.
A fundamental feature of sheet metal rolling is that deformation does not occur simultaneously over the entire contact surface of the tool. Although this causes a slight decrease in equipment productivity, it actually helps to increase the durability of the working rolling rolls. The fact is that during rolling, the deforming force is not concentrated in a point or straight line (as, for example, during drawing), but is distributed evenly over the entire surface of contact of the rolls with the metal. Therefore, the specific effort of the process is very small, and the manufacture of tools does not require the use of expensive tool steels.
Any rolling machine costs significantly less than a hydraulic or mechanical press, and therefore pays for itself within six months of its active use. At the same time, durability also increases: the rolling force increases smoothly and gradually as more and more new sections of the workpiece enter the deformation zone. Therefore, the shock nature of the occurrence of working loads during rolling (even in a cold state) is not observed.
In the practice of operating rolling machines, there are never problems with tool wear, since the surface of the rolls is smooth. Accordingly, readjustment can only be reduced to replacing the rolls with equipment with a different diameter.
It is important that during the rolling process the operator can change the rate of metal deformation, which is not always possible during other sheet metal forming operations. This change reduces losses from marriage.
Thus, rolling is a cost-effective technology for pressure processing of sheet blanks made of highly plastic metals and alloys.
Features of the rolling process
Rolling is an affordable process for manufacturing all kinds of metal parts or pipe sections of the required format. Each tube flaring tool has its own specifics, but this process is also used for other purposes - processing a metal rod or thin sheet metal.
The name of the process comes from a primitive device - special rollers are quite simple in design and operation, but they provide a wide rounding radius for the workpieces. Industrial production involves the use of forging rollers (rolls) through which a piece of metal passes.
Correct use of the tool guarantees high-quality and uniform deformation along a given circle or at a certain angle. For example, you can get a blank of the correct cylindrical shape or a curl for a forged gate using rollers for a profile pipe with your own hands.
Rollers are selected according to the thickness of the metal product; rollers with a large radius are often required. Not only steel becomes ductile when processed with the above devices. Plastics, polymeric materials and some rods, sheets and metals are deformed in a similar way:
- aluminum;
- black metal;
- soft alloys;
- galvanization.
Rolling is also called rolling a pipe on a special machine in order to obtain a bent workpiece
Attention! Today, pipe bending and rolling is a common service, but you can master this process yourself if you have an easy-to-use device. Such skills are applicable in various folk fields and industrial production, in the manufacture of welded structures - stairs, gates, furniture.
The most common methods of forming metal products after rolling a profile pipe:
- stretching;
- bending;
- winding;
- flaring of holes.
The process involves securing the pipe into the lumen using expansion, and the diameter of the pipe must be smaller than the opening. To ensure reliable connection, rolling equipment is used. But this concept implies different processes:
- Rolling as a method of changing the width of the inlet hole, lumen or diameter of the pipe during heat treatment and welding.
- Rolling of pipe bends.
- Rolling as a method of reducing diameter.
- Rolling a section of seamless pipeline.
- Flaring the workpiece to change the diameter of the pipe (increase).
Attention! Without experience, pipe rolling is not an easy task, and with excessive force, the metal will lose its ductility and may crack, and other signs of destruction will appear.
This is interesting: Chrome plating - decorative coating of metal with chromium: technology, types
Making sheet-bending equipment yourself
To assemble a machine for sheet metal processing , you must have certain skills, consumables and tools.
The first thing you need is to draw it up yourself or find a drawing on the Internet. Next, you can begin preparing materials and assembling structural units, which include:
- roller frame;
- side racks;
- steel rollers (their diameter and number depend on the power of the device);
- a handle that sets the lower rollers in motion;
- drive unit (gear or chain), which ensures synchronous rotation of the lower rolls;
- spring type pressure unit.
The assembly of the rollers begins with the manufacture of the frame. It can be welded from thick steel blanks according to the dimensions indicated in the drawings. For the side racks, powerful channels made of low-carbon steel are suitable, which are attached to the frame by welding.
The elements of the drive unit are fixed on one of the racks, for which special holes are provided. After mounting the side posts, rollers are installed in the bearing units. They must be set in parallel and the remaining nodes must be finally fixed.
Rolling is widely in demand due to its undeniable advantages. Since this is a cold forming method , the material is not exposed to high temperatures during processing. This feature leaves the properties of the materials unchanged. The rolling operation makes it possible to obtain an accurate workpiece, a full-fledged part or a decorative element.
Purpose and methods
Processing of rolled pipes using the rolling method, as mentioned above, can be carried out in order to change the shape of the cross-sectional profile, as well as in order to change the initial parameters of the finished pipe - outer and inner diameters, wall thickness, shape of the final part. To change the cross-sectional shape, rolling is carried out through a system of rolls of special equipment, which, by exerting significant pressure on the pipe walls, form the required profile.
Rolling equipment uses various types of rolls to form a specific shape and size of the workpiece.
If the simplest devices are effective for expanding the end part of soft tubes for air conditioners, then for rolling tubular products made of steel alloys, the use of special tools is necessary. The latter, depending on the parameters and material of the rolled pipe that needs to be rolled, are divided into the following categories:
- T – for processing pipes with an internal diameter in the range of 5.6–12.5 mm (a feature of the tool in this series is that it can be used to roll to a limited depth);
- ST – for rolling welded products, the internal diameter of which is in the range of 6–11 mm (also has a limited rolling depth);
- P – for processing rolled pipes with a diameter of 1.2–4 cm (the maximum flaring value when using such a tool is 4.87 cm);
- RT - for working with pipes with a diameter of 0.55–1.15 cm (in this case, the internal diameter of the product can increase to 1.29 cm);
- CP - for rolling to a greater depth (the maximum flaring value with tools of this series is 3.23 cm);
- 5P – for processing thin-walled pipes made of stainless steel alloys.
Photos of some flaring tool models
There are several other series of rolling tools available on the modern market, but we have listed the most popular ones.
A specialized tool for pipe flaring is most often used when installing heat exchangers in which tube sheets are installed. The working body of such a device, which exerts a mechanical effect on the walls of the pipe, is subjected to special treatment, which makes it possible to endow it with high strength.
Sheet metal rolling
Workpieces of this type are easy to process. As a result of rolling, the sheets can be given any shape: cylinder, cone, pipe, trench. During operation, the workpiece is passed between special shafts, is uniformly deformed and takes the shape of a cylinder. In this form it is suitable for further processing on the machine.
For our work, we use special bending rollers with different types of drive. Our technologies allow us to produce even non-standard products of large diameters.
Rolling tools
Rolling of pipes and sheet blanks is not only different, but is also performed on different equipment. Most often, sheet bending or forging rollers are used - sheet metal is rolled between the rollers for uniform processing and obtaining a cylinder-shaped piece. It is impractical to undertake such a process manually - it requires a lot of time and experience, even if it is just rollers for a pipe bender. It is easier to deform products using a machine method, so it makes sense to contact a workshop if you do not have the skills or your own equipment, and alloy steel is difficult to work with.
Rolling of pipes from steel sheet blanks is carried out using special equipment, manual or automatic.
Rolling sheet metal between rollers produces a bend of a certain shape. Rollers and machine tools have a limit on the thickness and radius of the metal they conduct. An increase in the radius results in a decrease in the bending radius when forming a thin metal sheet on bending rollers.
Special machines are also used for flaring pipes and rolled steel. The universal tool is easy to use and allows you to mold products of the required shape. Rolling of sheet blanks is carried out through the circumference of the upper roller, but it can also make the opposite movement. After processing sheet steel with rollers, the length of the product increases slightly, and the cross-section becomes slightly smaller, due to thermal and mechanical treatment.
The most popular rolling tool:
- P series machine (products with a diameter of up to 40 mm);
- RT equipment (products with a diameter of up to 5.50-11.5 mm);
- T series equipment (products with a diameter in the range of 6-11mm);
- ST rollers (products with a diameter of 6-11mm);
- CP series equipment (parts of thick tube sheets);
- 5P series tool (thin-walled products).
Often, to change the bend of a pipe, a household pipe bender controlled by a handle is sufficient. In this case, the radial shape of the product is formed by means of a regulating roller during rolling.
Important! To prevent the pipe from flattening at the point of its bend, you need to pour sand into it before deforming it in order to preserve the natural shape of the walls as much as possible.
The three-roller pipe bender is also suitable for rolling metal products. Its purpose is to work with stainless steel products of rectangular and square shape. This tool bends such workpieces well into an arc. The pipe bender processes the product from both sides.
A three-roll pipe bender can easily process profile pipes - square or rectangular
Flaring of tubes with hand tools is carried out on aluminum and copper, since these are the softest metals. The limiting factor for industrial equipment is the power and wall thickness for which a particular device is designed.
Advice! You should not use thin-walled pipes for water supply in a private home. The result is simple flaring and joining, but it will not last long due to metal corrosion.
Tools and accessories for rolling
Special equipment is not always used for manual rolling. Often, for repair and household needs, pliers for rolling copper pipes are sufficient. Flaring is carried out using a tool with a conical element, which expands the end of the pipe to the required diameter. Despite this, experts call rolling only those processes that require structures with rollers.
The number and types of rolls may vary depending on the type of equipment. For manual installations, three rollers are most often used, since an increase in the number leads to a situation where physical strength is not enough to process metals. At the same time, the optimal number of rolls on an electric machine is 3 or 4. This determines the size and power of the motor.
To make certain operations easier, rollers may have specific technological characteristics. In particular, in order to work not only with sheet metal, but also with wire and rods, there must be working grooves on the surface of the rolls.
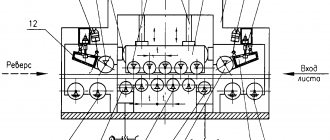
A rolling machine usually consists of:
- electric motor;
- gearbox or clinometer transmission;
- shaft with main roll;
- side posts with units made of rolling or sliding bearings;
- pairs of lower drive rolls;
- bed with a pair of support posts;
- protective casing;
- roller control systems.
These are the main components of the mechanism, the technological parameters of which can change along with the size of the gap between the rolls. Such regulation is carried out manually or automatically. For manual adjustment, a specific size wrench is sufficient. The rolling process does not involve the use of other devices or tools to adjust the equipment.
Technology
Like any other technological operation, rolling has its own GOSTs and OSTs that regulate and regulate the process and its parameters, for example: tightness control, calibration, tolerances on pipe wall thickness. Enterprises also have their own service stations for these purposes. Let us present a short list of these documents.
- GOST 13954-74 (reissued in January 1988 with Amendments No. 1, 2). Pipe ends flared for connecting pipelines along an outer cone. Design and dimensions.
- GOST R 55601-2013. Heat exchangers and air cooling units. Fastening pipes in tube sheets.
- GOST 28941.12-91 . Pipeline connections with pipe flaring. The ends of the pipes are flared.
- OST 26-02-1015-85. Industry standard. Fastening pipes in tube sheets. Ministry of Chemical and Petroleum Engineering.
- STO 002203680014-2009 . Fastening of pipes in tube sheets of shell-and-tube heat exchangers and air coolers.
It is worth noting that service stations are rarely publicly available and relate only to one enterprise. It is also worth considering the properties of the material from which the pipe is made, since the permissible forces during rolling depend on them.
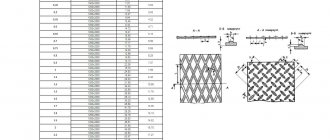
Equipment used
Rollers
| Specifications | Magnitude |
| The largest thickness of the sheet to be bent during radius bending | 50 mm |
| The smallest thickness of the sheet to be bent during radius bending | 1 mm |
| Minimum bending radius | 35 mm |
Flaring of pipes during installation of heat exchange equipment
Installation of pipes in heat exchange systems, performed using a rolling operation, is a fairly common procedure, so it is better to become familiar with it in more detail. The use of such technology and high-quality tools makes it possible to obtain reliable connections between pipes and the walls of the holes made in the pipe drum.
Scheme of pipe rolling with a roller tool: 1 – spindle with a working cone; 2 – cage with bearing; 3 – rollers; 4 – pipe; 5 – tube grid
So, you need to do the following.
- A piece of pipe is installed in a hole whose diameter is smaller than its outer diameter.
- The working body of the tool is inserted into the inner part of the pipe and its expansion begins. Its diameter begins to increase under the influence of plastic deformation, and the gap between its outer wall and the wall of the hole into which it is inserted disappears. After removing the gap, the walls of the hole in the pipe drum begin to deform, on which pressure is exerted by the expanding pipe. Thus, a tight and reliable connection is formed.
- When rolling with such a tool, you should be very careful and make sure that the walls of the pipe do not collapse under the influence of significant pressure. This can happen if its diameter increases beyond the technology limit. Such negative consequences can be avoided not only by strictly following technological recommendations, but also by choosing the right tool.
So, rolling means a fairly large list of technological operations, for the quality implementation of which it is necessary to correctly select the appropriate tools and equipment.