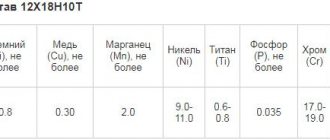
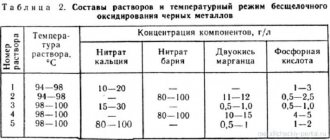
Stainless steel often requires surface treatment to achieve the desired aesthetic or performance properties. Treatment with shot blasting and sandblasting devices is limited due to the high probability of hardening. Modern production uses etching of stainless steel, after preliminary thermal or mechanical treatment. The complexity of this process, compared to conventional black, low-alloy steels, is explained by the presence of a chromium oxide film that acts as a protective barrier. It is this that forms hard scale that does not interact well with reagents. Technological influences may cause color changes on the surface. These include welding, soldering, and other operations involving high temperatures. Iridescent tarnish can be removed by etching. For different chemical compositions of stainless steel, individual pickling methods and compositions have been developed, taking into account the influence of the steel elements, to achieve maximum results.
The predominant
methods of etching stainless steels are alkaline and acid, which can be intensified by electrolysis or proceed without it.
Acid etching
The maximum effect of etching stainless steel with acids is achieved by sequential interaction of the stainless steel surface in baths with two types of acids - sulfuric and nitric. The sequence of stages is as follows
- Degreasing, removal of large snags, scale
- Pickling in a sulfuric acid bath (concentration 10-12%) or sulfuric acid bath (8% sulfuric acid, 4% hydrochloric acid). In this case, corrosion of scale and roughness on the surface occurs. The ideal temperature for the process is between 60 and 80 degrees Celsius. Monitoring this parameter is important for process control. The duration of treatment depends on the steel grade, the presence of a controlled ratio, and the concentration of acids. If the bath is depleted, pitting corrosion may occur. For example, steel with 18% Cr, 8% Ni requires 23 to 45 minutes of pickling in a sulfuric acid bath. Reducing the processing time by half can be achieved if this operation is carried out in a controlled atmosphere.
- Rinsing with plenty of running water
- Immersion of the workpiece in a bath filled with a solution of nitric acid and hydrofluoric acid (10 - 20, 1-2 weight percent, respectively). At a bath temperature of 60–70 degrees, the treatment time is 7–15 minutes.
- Repeated rinsing with large volumes of water
The presented method is basic and has many variations. Etching in one nitrate bath with an admixture of hydrofluoric acid increases the etching time to 30 minutes. Sodium fluoride can act as a substitute for hydrofluoric acid. Increasing the concentration of hydrofluoric acid to 10% allows the process to be carried out at low temperatures, avoiding preliminary immersion in sulfuric acid.
Reducing the etching time in sulfuric acid can be achieved by adding no more than 5% sodium chloride. This move gives the desired effect in 15 minutes, but at the same temperature, about 80 degrees Celsius.
Be careful: if it is necessary to carry out the procedure in a room with insufficient aspiration, replace the components of the second stage of etching. Acids produce harmful fumes when etching. A solution of ferrous sulfate (7%) and hydrofluoric acid (2%) is proposed as a replacement.
To correctly select the acid etching method, you need to know and take into account the state of the oxide film on the surface of stainless steel. Appearance can tell you about the composition of the film. The green color of the scale indicates a high content of chromium oxides. Accordingly, the action of acidic environments will be difficult and will require more time.
Mechanical methods and heat treatment after welding
Minimal processing is the removal of slag and scale by grinding the seam with a stainless steel brush. In some cases this is not enough and additional chemical treatment is necessary. Sanding with fine-grit sandpaper is very common.
Etching a stainless steel product using acid.
Mechanical methods include sand blasting, liquid abrasive and hydro-sandblasting. A prerequisite is a minimum iron content in the sand. After such cleaning, the surface is passivated.
Heat treatment of stainless steel is divided into several types: hardening (maximum temperature and rapid cooling), annealing (heating the metal and slow cooling), normalization (similar to annealing, the difference is that cooling occurs in fresh air and not in a furnace), tempering ( carried out after hardening).
The final result and quality of the product depend on proper heating of the workpiece. When exposed to heat, metal changes its structure and properties. When overheated, it acquires an undesirable coarse-grained structure. It is necessary to monitor the heating temperature very carefully. For example, a burnout is a defect that can no longer be corrected.
Chemical-thermal treatment of stainless steel - heat treatment with the application of various elements to the surface (chrome, aluminum, nitrogen, etc.)
Read also: What is the kinematic diagram of a machine
Etching with ready-made pastes
Modern industry offers a variety of stainless steel pickling pastes . Their main purpose is local processing of welds, the consequences of changes in the uniformity of surface coloring under the influence of temperature. The principle of working with such pastes is simple and can be used even in small workshops.
- Apply the paste in a thick layer up to 2 cm, using a brush
- Exposure 60-90 minutes
- Water jet rinsing
The use of pastes is advisable for processing welding seams of stainless steel grades. The treated seam is able to resist corrosion even in the damp conditions of a car wash.
Polishing stainless steel after welding
The next step in the complex of processing carried out in relation to the area of welding work is polishing the stainless steel after welding. It should be noted that not only individual areas of the product are subjected to such a process, but also the entire surface of the product as a whole, which guarantees a shiny final look.
Polishing provides an even greater level of cleaning of the surface being treated by obtaining a solid and smooth area, which subsequently results in the ability to withstand the external influence of aggressive liquids.
Initially, the area of the welds is exposed to a disk of vulcanite, the purpose of which is to give the weld the required shape and depth by forming the structure of the concave sample.
The next step is considered to be the application of a special paste intended for polishing. In most cases, GOI paste is used. The main objective of the polishing process is to achieve a mirror-like surface with the immediate absence of previously present matte spots.
Alkaline etching
Treating the surface of stainless steel with molten caustic soda is called alkaline etching. It should be noted that during this process the oxide film is destroyed, while the chemicals do not react with the metal. An increase in temperature promotes corrosion of the oxide film, improving the quality of the treated surface. Rapid cooling in liquid also helps to improve the treated surface.
It is almost impossible to achieve 100% results with this type of processing. Residual films from chromium oxides, nickel and iron oxides are possible on the metal. Among the recommendations for final finishing of such defects is a short-term treatment in a nitrate bath.
Polishing welds
In order for the product to acquire a finished appearance after welding, the welding seams must be processed with a grinding machine.
After welding, you need to bring the product into its proper, finished form, give it shine, luster and radiance. Thanks to the use of new technologies in polishing, the time required to carry out this work has been significantly reduced, and the quality has increased.
Polishing is the use of a special grinding machine. The mode you must choose is the one recommended by the manufacturer. The features of polished pipes are that they have an impeccable appearance, are wear-resistant and durable. Polishing can be manual, ultrasonic and machine. At home, regular sandpaper, grinding abrasives, and files may be suitable.
The first step is to get rid of the rough seam and make the surface smooth and uniform. To complete this task you will need a finishing wheel. It will easily remove rough seams and remove scale. Now the surface is prepared for further actions.
The second step is to remove the risks from the first treatment. The surface is brought to a state close to the final one. Sometimes you can stop at this stage. The surface already looks good.
The third step is final polishing. Bringing the metal to a mirror shine. At the same time, when polishing stainless steel, microscopic defects are removed from the surface, and when grinding, rough ones are removed.
Alkaline etching methods
The following methods are distinguished:
- Aging in soda. The sodium nitrate content should range from 20-40%, heated to a temperature of 460-500 degrees Celsius. Etching in such an environment lasts for 15 minutes. Some austenitic grades of stainless steel are prohibited from being heated above 450 degrees. This can lead to intergranular corrosion. This is followed by a rinsing step in a large amount of water, followed by a 5-minute immersion in a sulfuric acid bath and up to 10 minutes in a nitrate bath.
- Known in England since the first half of the 19th century, the etching method is combined with passing an electric current through the part being etched. At a current density of 11 A/m2, 15 seconds is sufficient. This reaction rate is associated with the electrolysis process. The release of sodium and hydrogen at the cathode contributes to the reduction of oxides. The reduced metal is deposited on the surface. This type of etching allows you to obtain degreased metal, characterized by purity and uniformity. This method uses soda. Variations are possible with the composition and addition of calcium chloride. This method is used for etching flat, rod blanks, and drawn products.
- Treatment with sodium hydrides is based on reduction by exposing the metal to sodium and hydrogen. The presence of sodium hydride is achieved by the interaction of hydrogen and sodium, which is in a molten state. A cylinder without a bottom plane is placed in molten caustic soda. The top plane has a hole. Sodium is poured into this hole, it reacts on the surface of the bath. A stream of hydrogen is passed through a spot of sodium on caustic soda. A hydride is formed and diffuses throughout the bath. Achieving the required concentration of 1-2% sodium hydride occurs within controlled threshold values. In the absence of an air separation product, dissociated ammonia is used. The parts are heated in such a bath to 400 degrees Celsius. Stainless steels show good pickling results with this technique and duration of 4-17 minutes. After etching, it is recommended to thoroughly rinse the parts. If necessary, carry out additional treatment in a nitrate bath. Given the high cost of this method, its obvious advantage is the fact that the metal does not interact with the etchant. Metal losses are minimal. Lower process temperatures reduce coolant costs and reduce operational safety.
Mechanical grinding
Stainless steel is characterized by the presence of a high level of corrosive properties, which determine its active use in environments where liquids are often used. Although products made from such material are in active contact with water and are subject to preliminary welding, their appearance does not change significantly over time. This feature can be traced as a result of the use of certain processing principles.
Among the main processing options, it is customary to highlight mechanical grinding of stainless steel after welding. During this process, the top layer of the oxide component that forms at the welding site and represents a weak point in the entire structure is eliminated. Distinct color transitions and existing irregularities in the weld joint are also eliminated.
This process is characterized by the following sequence:
- eliminating waves in the area of the metal seam by using a thick grinding wheel and grinder, as well as leveling out any bulges present;
- using petal circles for the functioning of the grinder; the main goal of such elements is more accurate work, along with longer process times and consumption of materials, which is especially important for large-scale work;
- the use of a specially designed equipment complex in the form of a grinding machine, the result of which is a one-color matte coating;
- mandatory use of a respirator to reduce the risk of abrasive dust and metal particles entering the respiratory tract that are in the air during work.
Read also: Gas hob design
Bath materials
Choosing the right material for making etching baths is a difficult task for chemists and materials scientists.
Recommended containers:
- ceramic coated
- glass covered brick
- wood, lead-coated concrete
- rubber derivatives
- Certain grades of stainless steel for acid baths.
The content of nitrogenous acid with impurities of hydrofluoric or hydrochloric acid allows the use of the same materials. The only exceptions are lead as a coating, ceramics with a high silicon content, due to their interaction. It is quite possible to use steel in alkali baths, monitoring the progress and intensity of electrolysis in close proximity to the material. Under certain conditions and acid content, its temperature, and nature, it is possible to use stainless steel grades for pickling tanks. Such, for example, as 8Х18Н8М or 10Х20Н25М4.
From the information provided in this review, we can conclude that the processing mode, the chemical composition of the bath, the need for additional mechanical processing, and the use of electrolysis should be determined based on specific initial conditions (steel grade, state of the oxide film, technological capabilities) and regulated in the context of the expected final result .
Grinding: practical recommendations
Classification of welds by position in space.
When doing this type of work, be sure to be well prepared. You should wear a mask to prevent dust from getting into your eyes. Products that have clearly noticeable defects: abrasions, scratches, etc. must be sanded. You will need sanding heads that have abrasive belts.
To obtain the desired result, the steel is polished in several passes. Remember that correctly selected materials and tools will allow you to reduce work time and improve its quality, this is a guarantee of excellent results.
Finished products are polished using abrasive sandpaper. This material has a paper or fabric base with a coating of a wide variety of grain sizes. Wet sanding is done using waterproof sandpaper. Coatings can be made of glass or silicon. Grinding is the final stage of the stainless steel processing process after welding. It evenly removes all the top layers.
Materials you will need:
- Bulgarian;
- grinding wheels with different grain sizes;
- wood glue;
- sandpaper;
- polishing paste.
To grind weld seams on stainless steel products, you will need a grinder.
The first step is to remove metal deposits from the weld. This can be done with a grinder. If the surface is sufficiently smooth and even, then you can immediately proceed to the second stage. Prepare a felt circle and apply wood glue to the surface of the workpiece using a regular spatula. Gently and carefully walk over the abrasive chips that can be obtained from sandpaper.
Then sand the surface three to four more times. In this case, the size of the abrasive should decrease. The stainless steel surface must be washed after each grinding.
It should be perfect, absolutely smooth and even, without roughness. Otherwise you will have to redo everything again. For the next step you will need a felt wheel and polishing paste. It is better to find a diamond one with a grit level that matches your metal. This is a final polish that removes visible marks. You will see how the surface transforms and becomes smoother.