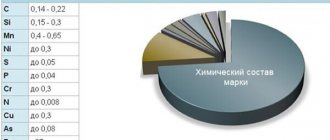
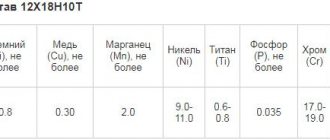
Chemical composition 12Х18Н10Т
| Chemical element | Silicon (Si), no more | Copper (Cu), no more | Manganese (Mn), no more | Nickel (Ni) | Titanium (Ti) | Phosphorus (P), no more | Chromium (Cr) | Sulfur (S), no more |
| % | 0.8 | 0.30 | 2.0 | 9.0-11.0 | 0.6-0.8 | 0.035 | 17.0-19.0 | 0.020 |
Effect of carbon content and alloying elements
It is the carbon content in steel, as well as the name and amount of alloying additives introduced into its composition, that are most interesting for analyzing the resulting properties of a particular grade.
Carbon comes first in importance, because steel is an alloy of iron and carbon . An increase in carbon content leads to an increase in strength with a simultaneous decrease in ductility. It also determines the ability of steel to be processed (cutting, weldability, forming).
Alloying elements are added in the required proportions depending on the need to obtain certain properties. Each element has its own characteristics. For example, chromium improves mechanical properties, nickel reduces the threshold of cold brittleness, tungsten and molybdenum help increase the heat resistance of a quick cutter, etc.
Mechanical properties of 12Х18Н10Т
| Section, mm | Section, mm | B, MPa | 0.2, MPa | 5, % | , % |
| Rods. Quenching 1020-1100 °C, air, oil or water. | 60 | 510 | 196 | 40 | 55 |
| The rods are ground and processed to a specified strength. | 590-830 | 20 | |||
| Hard-worked rods. | <5 | 930 | |||
| Stainless steel sheets, hot-rolled or cold-rolled. Quenching 1000-1080°C, water or air. | >4 | 530 | 236 | 38 | |
| Stainless steel sheets, hot-rolled or cold-rolled. Quenching 1050-1080°C, water or air. | <3,9 | 530 | 205 | 40 | |
| Stainless steel sheets, hot-rolled or cold-rolled, hard-worked | <3,9 | 880-1080 | 10 | ||
| Forgings. Quenching 1050-1100°C, water or air. | <1000 | 510 | 196 | 35 | 40 |
| Heat treated wire. | 1,0-6,0 | 540-880 | 20 | ||
| Seamless hot-deformed pipes without heat treatment. | 3,5-32 | 529 | 40 |
Table of Russian and foreign analogues of stainless steel AISI 304, 316, 430, 12x18n10t
APEX METAL offers customers a variety of types of stainless steel products made from the best grades of stainless steel that meet strict international standards and have excellent technological and performance characteristics.
High corrosion resistance of stainless steel is the main characteristic of products made from these materials for long-term operation in aggressive corrosive environments, over wide temperature ranges. The chemical composition of rolled products made of corrosion-resistant stainless steel AISI 304 of the austenitic class meets the requirements of the AISI standard - American Iron and Steell Institute (American Institute of Steel and Alloys). In accompanying documents, the designation of AISI stainless steel grades and its analogues is made in accordance with national or international standards:
| National standard | Stainless steel grade | |||
| AISI USA | steel AISI 304 | steel AISI 321 | steel AISI 316 | steel AISI 430 |
| RF standard | 08Х18Н10 | 12Х18Н10Т | 08Х17Н13М2 | 12Х17 |
| EN Europe | 1.4301 | 1.4541 | 1.4436 | 1.4016 |
| UNS USA | S30400 | S32100 | S31600 | S43000 |
| SIS Sweden | 2332/33 | 2337 | 2343 | 2320 |
| BS UK | 304S31 | 321S31 | 316S33 | 430S17 |
| JIS Japan | SUS304 | SUS321 | SUS316 | SUS430 |
| DIN Germany | X5CrNi18-10 | X10CrNiTi18-10 | X3CrNiMo18-3-4 | X6Cr17 |
Mechanical properties of 12Х18Н10Т at elevated temperatures
| ttest, °C | Quenching 1050-1100°C, air cooling | 700 | 650 | 600 | 550 | 500 | 20 |
| 0.2, MPa | 120-195 | 120-195 | 120-205 | 135-205 | 135-205 | 225-315 | |
| B, MPa | 265-360 | 270-390 | 340-410 | 380-450 | 390-440 | 550-650 | |
| 5, % | 20-38 | 27-37 | 28-38 | 31-41 | 30-42 | 46-74 | |
| , % | 40-70 | 52-73 | 51-74 | 61-68 | 60-70 | 66-80 | |
| KCU, J/m2 | 255-353 | 245-353 | 196-358 | 215-353 | 196-353 | 215-372 |
How do alloying elements change the structure of an alloy?
Naturally, each of the elements that is added to the composition has its own influence on the final characteristics of stainless steel 12x18n10t.
For example, nickel. The use of this element as an alloying element increases the g region. However, it is very important to note here that there must be a sufficient amount of it - from 8 to 12% in order to obtain the expansion effect. Another important fact is that the addition of this particular substance transforms the alloy into the austenitic class, and this is key. The transition to this class allows you to combine very high manufacturability of steel and a large number of different operational characteristics. Also, the addition of nickel increases corrosion resistance and allows the use of steel in places where there is constant contact with aggressive environments (acids).
Technological properties of 12Х18Н10Т
Forging temperature
The initial temperature during hot processing should be about +1200 °C, and upon completion it drops to +850 °C. If the cross-section of stainless steel sheets does not exceed 350 mm, then cooling is carried out in air.
Flock sensitivity
Not sensitive.
Machinability
In the hardened state at HB 169 and B = 610 MPa: Ku tv. spl. = 0.85, Ku b. Art. = 0.35.
Weldability
Stainless steel has excellent weldability, so welding can be carried out without any special restrictions. After welding, it is recommended to perform heat treatment.
Stainless steel
- General information about stainless steel
- Types and properties of stainless steel
- Chemical composition of stainless steel and compliance with standards
- Specifications of Austenitic Stainless Steel
- Electrochemical and crevice corrosion
- Practical use of fasteners on a ship
- Stainless steel in knife production
- Measuring the chemical composition of stainless steel with a hand-held device
Below is a table of physical properties of austenitic stainless steel. This data can be used to determine the loads on stainless steel fasteners.
Impact strength of stainless steel 12Х18Н10Т
| Delivery condition, heat treatment | Strip 8x40 mm as delivered | |
| Impact strength, KCU, J/cm2 | 20 | 286 |
| -40 | 303 | |
| -75 | 319 | |
Endurance limit
| -1, MPa | 279 |
| n | 1E+7 |
Use of steel
Alloy 12x18n10t, which can also be called stainless chrome-nickel steel, can be used in a wide variety of applications. For example, such a composition with varying degrees of strength is successfully used where it is necessary to combine high strength and elastic properties of metal parts operating in an aggressive environment.
Advantages and disadvantages
The 12Х18Н10Т grade of stainless steel is the only one of its kind, combining a large number of advantages, thanks to which it has become so widespread.
- Steel is smelted using the electroslag remelting method, which is one of the most inexpensive methods available today and has a high yield of usable metal. Through production allows the production of steel in large quantities (the volume of one melt is 60-160 tons), followed by rolling and heat treatment, which determines high productivity. For alloying, a small amount of available elements is used. All these factors ensure affordable prices for products and blanks made from the resulting steel.
- This ratio of chromium and nickel, with strict adherence to technological conditions, makes it possible to obtain steel with high resistance to intergranular corrosion.
- It has good welding ability for all types of manual and automatic welding.
- It is deformed in both hot and cold states (high degrees of deformation are allowed).
- Work in very aggressive acids and alkalis at temperatures up to 800° C.
- High wear resistance and strength.
Read also: How to check the ignition module with a tester
Among the disadvantages, it is worth noting the high requirements for maintaining temperature and time intervals during processing, which depend on the exact chemical composition. This is especially true for heating under high-temperature tempering to stabilize the structure.
Since heat treatment must be controlled, specialized equipment is required to carry out the operation, including for examination.
Assortment
The properties of 12Х18Н10Т steel are used to produce products operating in aggressive environments, at temperatures from -269 to 600° C. The main consumers are the oil and gas industry, where seamless pipes are used.
This steel is also used for structures produced by welding. These are all kinds of containers, parts of mechanisms (pumps, fittings) and equipment (heat exchange, capacitive).
Chemical and physical properties, composition
The mechanical properties of steel 12x18n10t depend on the chemical composition. For each product, depending on the cross-section and production method, heat treatment is carried out, which determines the final parameters.
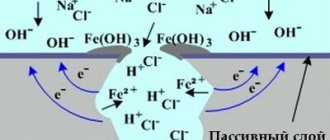
Chromium is the hardest metal and has the ability to form oxides in a volume not exceeding the chromium atom itself. They create a dense film on the surface, only 2-3 atoms thick, which prevents the penetration of oxygen. When the film is mechanically damaged, new oxides are immediately formed. At elevated temperatures, chromium carbides are formed at the grain boundaries. This leads to hardening and subsequent intergranular corrosion. To eliminate this process, steel is alloyed with nickel. It stabilizes austenite at room temperature: its inherent crystal lattice is capable of dissolving a large amount of carbon, which in this state does not form carbides. In addition, austenite has increased impact toughness, which determines its high ability to undergo plastic deformation in a cold state (steel can be deformed to a thickness of 1 mm).
For durability in aggressive environments, titanium is added, the properties of which are identical to chromium.
Technical properties
Steel has high manufacturability, i.e. the ability to be machined:
When processing, the exact chemical composition of the steel is taken into account, namely the ferrite content. Its concentration can reach 20% and affects the temperature range in which an irreparable defect can occur. Dependence of heating t on ferrite content:
- 20% - 1240-1250° C;
- 16-19% - up to 1255° C;
- Up to 16% - up to 1270° C.
Treatment of Me with pressure is carried out in the range of 1180-850° C. The cooling rate to room temperature is not limited. Hardening for martensite is carried out in the range of negative temperatures. High hardness is achieved after hardening and low-temperature tempering.
For welding, electrode wire of the Sv-08 grade containing chromium, nickel, niobium, and titanium is used. Flux - grade AN-26 or AN-18. As hand electrodes: EA-1F2 brands: GL-2, TsL-2B2, EA-606/11.
Heat treatment, modes, hardness
The most common technological treatment is HTMT. It is carried out by heating the steel to a temperature of 1180° C. Heating to recrystallization temperatures allows not only to relieve internal stresses, but also to obtain crushed grain. This structure has the lowest dislocation density and the absence of dendritic liquation.
At room temperature, the structure consists of austenite (ferrite composition is undesirable, but can reach 20%), with a decrease in temperature below 20 ° C, austenite begins to decompose. A change in parameters occurs during hardening, which is carried out in oil, air or water with a heating temperature of 1100-1050 ° C. For such steel, the relative elongation and yield strength decrease and the hardness increases.
Example of decoding markings
In Russian GOST, the name includes an abbreviation of alloying elements that impart the basic properties of the alloy. The steel grade 12Х18Н10Т can be deciphered as follows:
- Carbon - as an obligatory element, only its content is indicated in the labeling, which varies in the range from 1 to 1.2%;
- X - chromium - 17-19%;
- N - nickel - 9-11%;
- T - titanium - up to 0.8%.
The remaining elements are added according to the requirements of the standards, but are not indicated in the brand. This:
Allowed content of harmful impurities:
- P - phosphorus - up to 0.035%;
- S - sulfur - up to 0.02%.
What can be replaced (analogues)
Steel grade 12Х18Н10Т GOST 5632-72 requires the use of about 50 grades of stainless steel that have similar properties. But the closest analogues are:
There are no general EU standards for stainless steels and steel is produced in accordance with the requirements of the standards of each country. World classification of major manufacturers:
- USA - 321; 321H; S32100;
- Japan - SUS321;
- South Korea - STS 321;
- China - 0Cr18NiTi18-11;
- Sweden - 2337.