Peculiarities
Often, when cooking tin bronze, a phenomenon such as the formation of frozen drops is observed. This happens for the reason that fusible fractions float to the surface. Components such as lead and zinc are subject to waste. Their boiling point is lower than that of copper, so natural evaporation occurs.
The type of flame should be controlled. It must be strictly normal. An oxidizing flame burns out the tin, and a carburizing flame causes pores to appear. Acetylene consumption during gas welding should be 70-120 liters per hour per 1 mm of metal sheet thickness. The surface must be in the reduction flame zone, which is 7-10 mm. This is the only way to reduce the degree of tin burnout.
It is recommended to preheat cast bronze parts to a temperature of 450°C degrees. The filler material is BrOTs4-3 or BrOF6.5-0.15 wire. Difficulties in welding aluminum bronze are associated with the formation of an oxide film, which has a high melting point. It can only be dealt with with a special flux. The latter is a substance containing sodium fluoride, sodium chloride, barium chloride and potassium chloride. Silicon bronze, unlike other types of alloys, is weldable well due to the presence of elements such as silicon and manganese.
There are features characteristic of any alloy containing copper. The welder must be aware of these features, because he will certainly encounter certain difficulties. The presence of copper in an alloy determines its physical properties. The thermal conductivity of bronze, like brass, is quite high, as a result of which intensive heat transfer must be taken into account. Rapid crystallization is accompanied by the formation of cracks. Another factor influences here - a high coefficient of thermal expansion. When a metal crystallizes, it “contracts”, resulting in internal stresses.
Bronze is widely used by artists and sculptors in the manufacture of busts or monuments. It is used to make fittings and decorative elements. Welding work must provide not only a reliable connection, but also an aesthetic appearance. The presence of elements such as zinc, tin or lead in alloys largely determines the characteristics of welding work.
The burnout of the listed elements is due to a significant difference in boiling points. After the metal melts in the weld pool, atmospheric oxygen is absorbed. Alloying elements react with it. A film forms on the surface of the bath. At the same time, hydrogen enters the metal, and during crystallization, pores remain. They significantly reduce the quality of the weld.
Expert opinion
Bagrov Viktor Sergeevich
Welder of the highest 6th category. He is considered a master of his craft, knows the intricacies and nuances of the profession.
Welding technology must be strictly followed. Failure to comply with the parameters leads to the appearance of cracks and other defects.
Some problems can be solved by protecting the bath with inert gas. Argon is most often used. All of the above indicates that bronze welding is a rather complex process, so the welder must have certain knowledge and experience.
Preparing for work
Today, welding of bronze, like other alloys containing copper, is carried out in three ways: manual arc welding, argon arc welding and gas welding. Preparatory work is defined for each type of work and does not depend on the choice of welding method. The need to prepare metal surfaces is dictated by the requirements for the weld.
First of all, by mechanical processing it is necessary to form edges that will adjoin each other with the maximum area. Then, using sandpaper or any abrasive tool, you will have to polish the ends until a characteristic golden shine appears. This procedure must be performed in any case, since bronze is quickly covered with a layer of oxide, which can prevent the formation of a high-quality seam.
If it is not possible to carry out mechanical treatment, and the edges are in normal condition, then you can get rid of the oxide using a solution of nitric or hydrochloric acid.
Manual arc welding
Bronze welding is most often necessary when carrying out repair work, correcting defects or when surfacing. You can use preheating of the part to 350-450°C degrees, but it should be remembered that at high temperatures the strength of bronze decreases. Manual arc welding is carried out in the lower position. Metal or carbon electrodes are used as consumables.
- When using a metal electrode, a constant welding current of reverse polarity is set.
- Carbon electrodes require straight polarity.
Welding with alternating current is also possible, but for a stable arc the current strength must be significantly higher. If with direct current it is selected based on the calculation of 40 A per 1 mm (electrode diameter), then for alternating current the figure increases to 80 A. The seam is applied continuously, without transverse movements of the electrode.
After welding, cast bronze parts should be annealed at a temperature of 500°C degrees. The rolled product is forged without heating. Phosphor bronze can be arc welded, but it is recommended to use electrodes containing tin, phosphorus and copper. Tin bronze electrodes contain zinc, tin, lead, phosphorus, nickel, iron and copper. Aluminum bronze is welded with copper rods that contain aluminum, manganese and iron. Surfacing of bronze is carried out using bronze electrodes OSTS-5-3-20 or AZH-9-4.
Arc welding
Electric arc welding is carried out using inverter machines operating in MMA mode. For this purpose, special electrodes are used. The welding method depends on their type. A distinction is made between welding with brass or carbon electrodes. Welding with brass electrodes is carried out with direct current of direct polarity. The operation is characterized by a short arc at a current of 250 A; this parameter is given for electrodes with a diameter of 5 mm. With such indicators, the suture application speed reaches 30 cm per minute. After applying the seam, it is subjected to forging and heating to 600°C degrees.
Welding with carbon electrodes involves the use of graphite consumables (thickly coated electrodes). They consist of brass wire, which contains elements such as manganese, iron, aluminum and silicon. To produce the coating, mixtures of liquid glass with dry impurities are used. The most popular include manganese ore, ferromanganese, chalk chips, aluminum and graphite.
When using carbon electrodes, an additive coated with special fluxes is used. Such welding is carried out with the above parameters, however, they are already suitable for electrodes with a cross section of 10 mm. There are a number of mandatory conditions necessary to obtain a strong seam when conducting electric arc welding:
- Workpieces with a thickness of 6 mm or more should be locally heated before applying a seam.
- Thin sheets are welded in one pass. When several layers are applied to the workpiece, cracks will begin to appear in the seam area.
- The thickness limit for one pass is 3 mm.
- An asbestos lining is placed below or on the inside of the seam. It is needed to prevent metal leakage.
Argon-arc
This type of welding is fundamentally similar to manual arc welding. The only difference is that the process occurs in a protective gas environment. Argon is heavier than air, so it forms a protective zone through which atmospheric oxygen does not enter the weld pool. Argon arc welding can be carried out with non-consumable tungsten electrodes or consumable electrodes, the role of which is played by rods.
It is argon arc welding that is most often used when working with bronze and brass. This preference is especially given when the metal thickness exceeds 5 mm. Welding productivity is quite high, but the process itself requires the welder to have certain qualifications. An electric arc formed between the metal surface and the electrode partially melts the edges, after which a connection occurs to form a seam. As mentioned above, preliminary preparation of the edges is required.
There are a number of recommendations that allow you to obtain high-quality connections between parts made of copper alloys.
- It is advisable to form the seam in small sections.
- When the process is finalized, the voltage gradually decreases, and then the arc is moved to the side.
- To prevent evaporation of alloying elements, special additives containing silicon, aluminum or boron are used.
Welding bronze and brass is accompanied by the release of toxic substances, so it is carried out in compliance with all possible safety measures. Argon welding has a number of advantages over other types of joints.
- Obtaining an aesthetic seam.
- Economical process.
- There is no need to clean the part from slag.
- For bronze, argon welding is the most preferable.
- Argon welding can be used to fuse parts, restoring their previous shape (for example, when worn).
- It is possible to work with thin sheet metal.
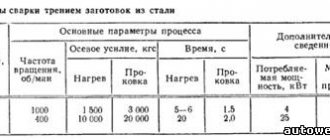
Bronze welding technology and modes.
Bronze welding
Gas welding of bronze is used in the repair of cast bronze products, surfacing friction surfaces of parts with a layer of antifriction bronze alloys, etc. The welding flame must be of a reducing nature, since with an oxidizing flame, burnout of tin, silicon, and aluminum from bronze increases. Rods or wires similar in composition to the metal being welded are used as filler material. For deoxidation, up to 0.4% silicon is introduced into the filler wire. To protect the metal from oxidation and remove oxides into slag, fluxes of the same compositions are used as when welding copper and brass.
Gas welding of bronze. Process technology and equipment used
Bronze is a metal alloy in which copper is the main element. Bronze can be obtained by alloying copper with tin. Such alloys are called tin bronze. Aluminum, silicon and other types of bronze are also common. In addition to the two main components, the structural composition of bronze may also include other chemical elements. This must be taken into account when organizing the gas welding process for processing bronze parts. Modern industry uses bronze mainly for the production of various fittings and shaped castings. Some types of bronze are used in the chemical and food industries.
The main method by which welding processing of bronze parts occurs is the argon arc welding method.
Welding technology for bronze processing
The first stage of gas welding work with bronze parts is preparatory. At this stage, mechanical cleaning of the welded surfaces is performed. In this case, high-quality removal of various scales, residues of molding sands and other foreign deposits is of particular importance. Cleaning is best done using a special metal brush. Progressive movements should be made until the surface becomes smooth and shiny.
After cleaning, the edges are cut to form a V-shaped profile. The profile should be located at an angle of 70-90 degrees. This stage must be carried out in a room with forced ventilation. To avoid inhaling tin bronze fumes that are harmful to the human body, the parts being processed must be securely fastened directly under the ventilation device. It is worth considering the fact that bronze has a high degree of fluidity in the molten state. In order to avoid spreading of the metal, it is necessary to lay special linings, which consist of materials such as asbestos or graphite, before the processing process in the area of the future seam.
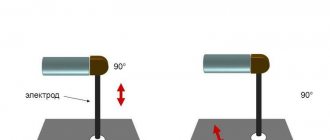
Before welding begins, fluxes must be applied to the edges of the parts being welded. It is worth remembering that the same fluxes are used for welding bronze as for welding copper. Then the part is preheated using a gas burner to a temperature of 250-300 degrees. After this, the actual welding process begins. To do this, the gas burner mouthpiece is positioned at an angle of 90 degrees relative to the weld pool, and the edges of the parts being welded and the filler material are gradually melted. It is recommended to use welding wire containing phosphorus as a filler material when welding bronze.
When laying a welding seam, the gas burner flame should be located at a distance of ten millimeters from the surface to be welded. This is necessary so that tin evaporation does not begin in the weld pool area.
Experienced welders recommend periodically stirring the molten metal, filler material and flux used in the weld pool while laying the weld. This can be done using a welding rod. This will allow you to remove all formed oxides in time and make the welding seam smooth and durable.
After completion of the welding process, the processed bronze part is subjected to heat treatment. It is gradually cooled using construction sand or asbestos for this purpose. After this, the welding seam is cleaned of carbon deposits, oxides, slags and flux residues. It is best to wash the weld seam on bronze products using a two percent sulfuric acid solution. In some cases, the use of nitric acid of appropriate concentration is allowed.
Technical gases required for bronze welding.
In order to weld bronze, it is necessary to use technical argon gas, which has protective properties. Welding in argon allows you to completely eliminate oxidation of the surface of the weld. This makes the resulting product durable and of high quality. Argon can be supplied to the production site either in cylinders for small volumes of welding work, or through a special gas pipeline. This is necessary in cases where bronze welding is put on an industrial basis.
It is recommended to use acetylene as the basis for the flammable mixture, but most often a fairly high quality of bronze welding is achieved using propane and butane mixtures. You will also need technical oxygen.
Equipment for welding work with bronze.
Bronze can only be welded using the argon arc method. In order to organize the welding process using the argon arc method, it is necessary to use special equipment. In particular, you will need a special installation for argon arc welding. At the moment, there are several samples of such equipment on the market; in our opinion, the best technical and production indicators are distinguished by such installations as: argon arc welding installation UDGU-251-02, argon arc welding installation UDGU-351-02, argon arc welding installation UDGU-501-02 , installation of argon arc welding VD-306D with BUSP TIG, installation of argon arc welding VD-506D and some others.
To produce high-quality welding of bronze parts, it is also necessary to use special torches for argon arc welding. Among those currently in use, the following samples have the largest number of positive reviews: argon arc welding torch GDS-500 (500 A AC/DC).
Gas
Gas welding of copper alloys is used primarily in order to minimize the waste of alloying elements. The welding flame is adjusted so that three zones are clearly distinguished. The metal surface should be on the border of the second and third zones. Working with silicon bronze requires an oxidizing flame. It is obtained by burning a mixture of oxygen and acetylene, if the ratio of the first gas to the second is 1.2. Bronze containing aluminum causes many problems during welding, since a film of aluminum oxide is formed, thickening the contents of the weld pool.
In the absence of preliminary and subsequent heat treatment of the seam, the quality and strength of the joint obtained using gas welding is 85% of the strength of the base metal. A good result can only be obtained after forging the seam. Gas welding requires a lot of experience from the master. At low burner speeds, pores may form in the metal. It is necessary to correctly select the burner power, gas composition, based on the type of bronze and the thickness of the workpiece.
Welding brass semi-automatically at home
Brass has long been known to people as a durable and stainless alloy. Tools and household utensils, parts of mechanisms and weapons were made from it, and even coins were minted. Welding brass is the main method of creating permanent joints from this metal. It is performed using gas welding, manual electric welding and in a protective argon atmosphere. If you have the appropriate equipment, brass can be welded at home. To do this, you need to thoroughly prepare the surface and follow the instructions.
- Main difficulty
- Preparing parts
- Selection of filler material
- Fluxes for gas
- Technique
- Features in an argon environment
- Advantages of argon arc
- Electric arc
- Gas
- Welding quality of brass of various brands
- Conclusion