Having your own well at your dacha is not that uncommon, but if you have just bought a plot of land, it is unlikely to have a source of drinking water. When setting up a dacha, you need to not only take care of building a house, but also start building a well. In the future, it will not only provide you with drinking water, but will also help organize watering of the garden.
In today's article we will look at how to choose a place for a well so that it is always filled with water and does not dry out even in severe drought. In addition, we will tell you what rules should be followed during construction and how to properly install wells in your dacha.
- Glass jars
Choosing placement and determining depth
When building a well, you need to determine its expected depth and number of rings. If the site is new and construction has not yet begun, the search for water should begin by examining the sources used by the neighbors.
How to find the right location for a well
To find it, you need to know the following information:
- The depth of wells and wells in neighboring areas;
- Volumes of water loss;
- Terms of use;
- Features of operation.
If there are no neighbors, the task becomes more complicated. Then it is recommended to use one of the methods for determining the water source. The most popular of them:
- Dowsing;
- Hydrogeological indications;
- Local manifestations of water.
None of them will give a 100% guarantee of data accuracy. However, you should know that it can be carried out at a certain distance from water supplies in neighboring areas. Otherwise, the water from them may simply go into newly formed wells. In addition, this method is quite expensive and is more suitable for undeveloped areas.
Find out how to make a well house with your own hands.
See photos of crafts made from tires for the playground.
Video of fish breeding in a home pond: .
Criteria for choosing a site on the site
Careful selection of location is a prerequisite for creating a reliable and high-quality source of water supply. This approach will eliminate the risk of receiving water that does not meet sanitary standards. When choosing a location, they are guided by the following criteria:
- Convenient location on the site;
- Distance between wells and objects of use;
- Distance from sources of pollution.
Answers to popular questions
Is it legal to place a well in a basement?
Regulations do not prohibit drilling in the basement. But such wells cause a lot of inconvenience. They can only be drilled before the house is built. Repairing and eliminating sources poses serious difficulties. A drilling machine is needed for plugging, but it will not be able to return to its original point.
Why can't you drill a source next to the fence?
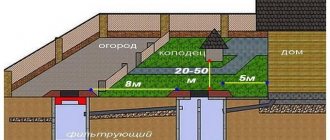
The distance from the well to the fence must be at least 3 meters. This rule was introduced to protect neighboring areas from sudden flooding. Even if you are drilling a common source, you should not place it too close to the fence. In addition, the operation of special equipment at the border may cause dissatisfaction among residents of the neighboring area.
What you need to know about the distance of the well to the foundation
The problem of the location of a well on a site is especially relevant for owners of small plots. The structure should be as convenient as possible. To do this, it is positioned so that it is possible to easily organize the supply of water to buildings on the site, such as a house or a bathhouse, as well as to a vegetable garden. Usually, the highest place on the site is chosen for the well; it should not be allowed that the cesspools of neighbors are located higher in the terrain.
Find out what a pumping station for a well is here.
In addition, the impact of the mine on the neighboring building should be taken into account. For a well, choose a place closer to the house. This is due to the peculiarities of organizing water supply: supplying water to a house over long distances is an expensive pleasure. Wells can even be built inside a house. Usually, they first build a shaft for the well, and then dig a pit for the foundation. In this case, the type of soil and topographic conditions of the site should be taken into account.
It’s another matter when the house is already ready, but the well is only in the plans. Houses on shallow foundations may suffer from the proximity of well shafts. You should not install wells in close proximity to such buildings. Shallow strip foundations on clay are especially dangerous in this regard. Here it is worth considering the depth of the well. Shallow mines are more troublesome for buildings. Water can wash away the foundation.
You may also be interested in information about decorative covers for wells.
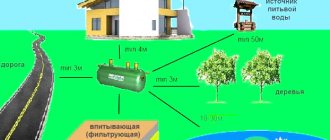
Wells can be located at a distance of at least 3 m from the foundations of buildings. This norm is prescribed in SNiP 30-02-97.
The minimum distance to buildings for keeping animals is 4 m, other buildings – 1 m, trees – 4 m, bushes – 1 m.
Application of various items
“Old-fashioned” methods help to find water for a well using various objects and devices. Such techniques have also been developed over centuries and sometimes turn out to be very effective. The following recommendations should be noted:
- Using cans. Glass jars of the same capacity should be placed on the ground with their necks down early in the morning. This procedure should be extended to the entire dacha area. Exactly one day later, all banks are checked. The appearance of condensation on the walls indicates the proximity of groundwater, and its amount increases as they approach the surface.
- Use of salt and bricks. We need to wait for dry weather to last for 2-3 days. A mixture of finely crushed red brick and table salt is prepared, which is poured into an unglazed clay pot. Everything is weighed with good accuracy, and then the mixture is placed in a gauze bag and buried in the soil to about 50 cm. After 24 hours, the bag is removed, the mixture is placed in the same pot and weighed again. If the mass increase is significant, then the proximity of an aquifer can be expected.
- Application of silica gel. The procedure is carried out similarly to the method described above. In this case, silica gel is a modern substitute for folk remedies.
What should be the distance between wells
The installation of local water supply on the site must be carried out according to the project. If it clearly states how many and what structures will be required for the system, then many questions will disappear by themselves. The documentation must also indicate the exact distances from well to well.
The technology for drilling water wells is described here.
Owners of country houses often build a water supply system with their own hands, without drawing up a project. Therefore, we need instructions that will tell you how to calculate the location of the wells.
When creating a home water supply, one well is not enough; additional tanks are needed. They are necessary for maintaining the network, as well as eliminating emergency situations.
The number of shafts and tanks depends on:
- Distances of the well to the foundation of the house;
- The presence of other buildings, pipelines and other structures on the site;
- The complexity of the terrain, taking into account changes in height.
Installation of water supply with a well near the house
The best and simplest option is one inspection well. It is suitable for areas where the drinking well is located as close as possible to the house. It is located at the entrance of the pipeline into the building.
This material will tell you how to choose a pump for a well.
Calculations are made taking into account the fact that external pipe routing is carried out 20 cm from the wall. If the diameter of the well is 1 meter, then the distance from its axis to the wall will be at least 70 cm.
Installation of a water supply system with a well remote from the house
The situation becomes more complicated when the source of drinking water is significantly distant from the house. In this case, it will be necessary to construct several inspection tanks. The maximum distance between water supply wells is 15 m. For sewer inspection structures, this norm is no different.
Check out this article for the dimensions of concrete rings for wells.
If it is necessary to change the direction of the pipeline, construct a rotary well . The connection of all nodes must be as precise as possible. Blockages occur in these places more often than others.
In areas with height differences, it is necessary to change the depth of the pipes. For this purpose, a differential structure is built. The entire water supply system is laid at an angle to the well.
The distances from this structure to other components of the water supply system are regulated solely by the terrain features of the site. To optimize maintenance costs and save money on the device, both auxiliary structures can be combined with inspection wells.
How to find water in an area, where to dig a well and how deep should you dig?
Summer cottages, where active gardening and gardening activities are carried out, simply cannot do without a well. And even in year-round households with a centralized water supply, as a rule, they still dig a well for watering the site and other household needs. Actually, it’s not difficult to build it, the main thing is to understand where to dig so as not to violate sanitary standards and get water in the right quantity and quality
Everything is according to the law
Layout of aquifers
Having made a fundamental decision to build a well, first of all it is necessary to familiarize yourself with the provisions of Article 19 of the Law of the Russian Federation “On Subsoil” dated February 21, 1992 No. 2395-1, as well as with the latest edition of the Federal Law “On Gardening and Vegetable Farming by Citizens” for own needs and on introducing amendments to certain legislative acts of the Russian Federation" dated July 29, 2017 No. 217-FZ. In particular, it says that wells for drawing water from the artesian horizon (located at a depth of over 50 m) are subject to mandatory licensing, but 5-meter wells can be dug without any permits.
This means that only the so-called perched water and the upper free-flow groundwater flow are “freely accessible”. Verkhodka are localized water lenses located close to the surface of the earth, in which precipitation, melt and flood water collect, carrying pollutants from the soil (domestic wastewater, fertilizers, etc.). It is permissible to use such water only for technical purposes. Gravity groundwater, replenished by the same atmospheric moisture, steam condensation and infiltration from reservoirs, can also be heavily polluted. In addition, they are subject to significant seasonal fluctuations in level and cannot serve as a stable source of water. To extract clean water - in a constant volume and suitable for drinking, you need to get to the interstratal aquifer, which lies at a depth of at least 8-10 m. There are a number of restrictions on water intake from it, and therefore, the construction of a well will have to be coordinated with local water management authorities.
Water samples from the well must be submitted for analysis. Moreover, it may happen that groundwater raised from a shallow depth, according to its chemical and microbiological indicators, turns out to be absolutely safe and suitable for drinking, but extracted from a deep aquifer - not
Another must-read document is SanPiN 2.1.4.1175-02 “Hygienic requirements for the quality of water from non-centralized water supply. Sanitary protection of sources." Among other things, it indicates how the well should be constructed and equipped, how to properly locate and operate it. Based on the requirements for the distance of water intake from roads, sewerage structures and other sources of microbial or chemical water pollution, the necessary sanitary zone should be conditionally designated on the site and within its boundaries begin to search for a place for a well. Note:
according to the Decree of the Chief State Sanitary Doctor of the Russian Federation dated November 25, 2002 No. 40 (clause 2.5),
“if it is impossible to comply with standard distances, the location of water intake structures in each specific case is agreed with the center of state sanitary and epidemiological supervision.”
Far and near, high and low
To begin with, it makes sense to contact the territorial geological service, where you will be given the results of engineering and hydrogeological surveys, if any have been carried out in the area. Of course, you will not receive any accurate information about a single dacha plot, but you will still clarify the overall picture (direction of flow and chemical composition of groundwater, structure and thickness of layers, boundaries of aquifers, etc.).
Be sure to talk with the owners of nearby plots about the depth, flow rate and quality of water in the wells, find out how their filling changes depending on the season. If your neighbors have already built a building or are doing preparatory work, ask what groundwater level measurements have shown. Of course, groundwater level is a variable value even over a relatively small area, but such information will still be useful to you.
Pay attention to where the dog lies down on a hot day in the absence of shade.
Another tip is to take a closer look to see if there is dense fog in any part of the area early in the morning; aren’t thick clouds of mosquitoes and midges hovering there at sunset; Do moisture-loving woody and herbaceous plants (willow, alder, birch, viburnum, elderberry, sorrel, red clover, coltsfoot, marigold, spurge, etc.) feel good on your land? Observe where in the sun - in the absence of shade - the dog prefers to lie down. (The advice to pay attention to where the horse likes to paw on the site should perhaps be omitted as irrelevant for the average summer resident.) However, all these signs, in fact, only indicate a relatively close occurrence of groundwater to the surface and depend on many climatic and other factors .
By the way, it also depends on the dog’s breed: the behavior of, say, a northern husky should be taken into account, but, sorry, not a Yorkshire or a Chihuahua. Ants and voles can also serve as a natural “indicator” of water level: their abundance in the area indicates a low groundwater level (about 2 m or more).
When doing “natural history” in order to find water, if possible, it is better to focus not on the planted cultivated plant varieties, but on those that originally grew on the site or in the immediate area
Map of aquifer depths for wells (Moscow region).
The depths of drilling for limestone are indicated at the top, and for sand at the bottom. If the height of the groundwater level can be judged by indirect signs, then the depth of the interstratal horizons cannot be determined in this way.
The only things that will help here are the terrain (if the site is in a lowland, most likely an aquifer is very close) and the presence of springs nearby. A definite guide in this matter will be a depth map for wells, compiled for each region and exactly available from drilling companies operating in your area.
A natural reservoir located near the site can provide a useful hint. You need to arm yourself with an aneroid barometer,
take readings from it at the water's edge and at the place where you plan to install the well. The difference between the obtained values will indicate the depth of the vein (0.1 mm on the barometer scale = 1 m height difference).
There is also a “Pulse” device,
which records electromagnetic vibrations created by the pressure flow of groundwater.
We ground the electrodes and look at the voltmeter readings: the higher the water horizon approaches the surface, the greater the voltage the device will show. In addition, there are professional vertical electrical sounding devices that
measure resistance in layers of mineral rocks: it will be lower where the soil is saturated with moisture. A specialist should analyze the results of such a study.
Aneroid barometer BAMM
Aneroid Barometer Salisbury Antiques
In particularly difficult cases, you can resort to the services of companies engaged in hydrogeological exploration. In their arsenal there is a “Hydroscope” device, which allows using nuclear spectroscopy (nuclear magnetic resonance) to examine aquifers located at a depth of up to 120 m
Today, online trading platforms offer a wide variety of devices from China designed to detect water underground. There are multi-channel smart detectors, digital depth meters, underground locators, sensors, sensors, etc. at prices ranging from $20 to $5–7 thousand. The attitude of specialists towards this kind of equipment is very skeptical. If any of the readers have practical examples of its use - successful or unsuccessful, write to us in the comments at the end of the article.
Where should I dig?
There are several methods of finding a specific point where you need to dig a well.
1.
Throughout the search area,
glass jars of equal volume are dug in, bottom up,
deepening them by about 5 cm. A day later, before sunrise, the jars are removed and the amount of condensate in them is compared. It is believed that where there is more of it, that’s where you should dig.
2.
The method is addressed to owners of a certain number of
unglazed ceramic pots.
Hygroscopic material (for example, ordinary salt) is poured into containers, weighed, wrapped in non-woven fabric and dug to a depth of half a meter in the places where the well is supposed to be located. A day later, the containers are removed and returned to the scales. The conclusion is this: under the heaviest pot, which means that it has absorbed the most moisture, there is an aquifer.
3.
The method of detecting an underground source of water using
pieces of aluminum wire (frames)
or
a forked willow rod
has been known since time immemorial and still has many adherents. The point is that in dry weather (it shouldn’t have rained for three days at this point), you need to walk around the area at certain hours, in the direction from north to south and from east to west, holding these simple dowsing devices in front of you. In the place where they “feel” the water, the frames will intersect at one point (or deviate in one direction), and the rod will begin to “peck” the tip into the ground. It is clear that this method cannot provide a 100% guarantee. And even if we assume that its error is, say, only 5% (instead of a full-flowing source, there is a high probability of hitting, for example, a small water lens, or even a piece of metal or an electrical cable), in reality this will result in wasted labor and financial costs. losses.
The use today of the frame technique or so-called dowsing, as well as jars with pots, resembles the situation when a person lost in the forest, having a compass in his pocket, decides to navigate solely by the moss on the tree trunks. When applied to wells, such “principle” is expensive in the literal sense of the word. However, in any case, such methods should not be discounted: firstly, nothing prevents you from using them in addition to modern evidence-based methods of finding water, and secondly, they may simply turn out to be the only ones available.
Drilling the soil for water
4. The most productive way to find a place for a well with sufficient water flow is drilling the soil.
The work can be done independently by making test holes at the designated points of the site using a hand drill Ø 30 cm or a special probe (bailer) on the collar, or you can contact a local company engaged in exploration drilling, as well as the construction of wells for sand and limestone on a turnkey basis "
In the first case, you will have to evaluate the characteristics of the soil and the achieved watercourse yourself, but in the second, professionals will do everything for you, and with a guaranteed result. An engineer will first come to the site to help you choose the right place for water intake (based on a map of aquifers and taking into account the features of the landscape) and draw up an estimate for the upcoming work. Depending on the possibility of access and the size of the site for equipment, a standard (URB 2A2 based on ZIL 131, URB 210 based on KAMAZ) or small-sized (MGBU crawler-mounted) drilling rig is used. Specialists will examine the geological section, prepare a design for a water intake structure and select the necessary structural materials. Having completed the excavation and installed the well casing, it is pumped with a compressor to wash out the cuttings and reach production capacity. The price of drilling is mainly influenced by the depth and type of well, work technology and the structure of soil layers.
The cost of the service starts from approximately 1800–2000 rubles/linear. m.
Small-sized drilling equipment requires a small working area, practically does not harm the landscape of the site, but increases the labor intensity of drilling, and therefore costs more for the customer
5. The spectral seismic profiling (SSP) technique shows high efficiency in determining the exact coordinates of the water intake.
Its essence lies in scanning the area with special equipment, which makes it possible to clearly identify local zones of tectonic disturbance - it is through them that clean deep water rises close to the surface of the earth. In this case, no heavy equipment is used, and preliminary data is announced to the customer at the end of the first day of research. Over the next two to three days, the diagrams are processed, BSC profiles are applied to the plan, and documentation is drawn up. As a result, you receive a diagram of the site with a marked point of maximum water inflow, SSP sections, as well as a specialist’s opinion on the features of underground sources, indicating the recommended well depth (the error is ±10%). As the performing companies assure, the effectiveness of geophysical surveys using the SSP method reaches 92%, and the cost of this service is comparable to 3-4 meters of drilling.
Sewer
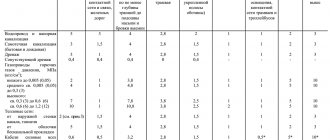
In order for the water supply to fulfill its function, it is necessary to maintain distances from sources of pollution to the well with drinking water and between the elements of the sewerage system of the site. These standards are prescribed in SNiP 2.04.03-85. In this case, structures are taken into account not only on one’s own site, but also on neighboring ones.
Layout of the septic tank in accordance with established standards.
Distance between sewer and septic tank
Water structures need to be built as far as possible from landfills, industrial facilities, septic tanks, sewers and other sources of pollution. The minimum distance from the source of drinking water to wells with drains and cesspools is 50 m, buildings for livestock farms is 30 m. The distance from the septic tank to residential premises is 7 m.
The main rule here is that the further the water is from the source of pollution, the less negative impact it has.