Forging chisel PICARD. Photo ForgingPRO
A chisel (a cleaver with a handle) is one of the oldest tools for processing cold or hot metal . Scientific and technological progress has made very minor improvements to this tool, offering high-strength materials for use and formalizing the sharpening angles of the blade. However, the appearance and methods of working with a chisel have not changed for many centuries. This article provides complete information about blacksmith tools for chopping metal, types, the possibility of making it yourself or purchasing a factory-made cleaver.
Bench chisels
The blade and head of a bench chisel are hardened and tempered . The length is usually 10-20 cm, and the width of the blade is 5-5.2 mm. The sharpening angle of the blade depends on the metal for which this chisel will be used - the harder or more brittle the metal, the more obtuse the sharpening angle should be. Standard sharpening angles for cutting various metals are as follows:
- hard steel, bronze, cast iron – 70 degrees;
- medium hard steel – 60 degrees;
- copper, brass – 45 degrees;
- zinc, aluminum alloys – 35 degrees.
The tool is also widely used for more specialized tasks, such as cutting grooves and narrow grooves. This instrument is called a crossmeisel .
How to use a chisel
Despite the fact that the modern market is full of various power tools, in some cases it is impossible to do without the use of a conventional chisel.
And here the question arises, how to properly use this simple tool.
Basic Rules
The work pattern depends on the type of chisel.
When working with it, you need to be extremely careful so that the task is completed efficiently and you do not get injured.
- Check that the hammer is securely seated on the handle.
- Before starting work, put on glasses and gloves.
- The tool must be dry.
- When working with sheet metal, consider the type of metal and its thickness.
It is better to cut thick sheets in several approaches.
• If you need to cut off part of the wire, do not do it in one fell swoop.
First, make a small cut, then break off the rod; it will remain in your hand and not fly away in an unknown direction.
Modern models are equipped with “fungi”.
This is a special head that performs a protective function, so its presence increases work safety, minimizing the risk of injury.
But in some situations this does not help, so you need to work with the tool very carefully.
Blacksmith chisels
The main design difference between a blacksmith's chisel and a mechanic's chisel is the hole in its middle part for mounting on a wooden handle. The cutting part of a forging chisel is called a knife, its length is from 30 to 50 mm. The length of the entire tool for cutting cold metal is 16-19 cm, for cutting hot metal – 18-24 cm.
Cold cutting forge chisel
Kinds
Varieties:
- Metalworking. With its help, metal cutting is often carried out. Due to the sharp working part, the tool can be used for marking sheet metal, unscrewing bolts, and removing rivet heads. The tip is slightly wider than the rod.
- Ditcher. Designed for cutting out shaped grooves. Groovers are divided into separate groups depending on the shape of the cutting part, which can be semicircular, wavy, U-shaped, or oval.
- Kuznechny. These chisels can have different shapes. The main design feature is the presence of a groove in the tail, which is needed to secure the tool in a metal or wooden handle. Using a forge chisel, holes are punched into heated metal parts and notches are left.
- Pike. The working part is practically no different from metalworking chisels. The main difference is the shape of the shank. It tapers and does not have a hammer. The tool can be mounted in a hammer drill. The working part can be wide, narrow or point.
- Boaster. Designed for stone processing. Outwardly similar to a spatula. A wide rubber bumper is attached to the tail section. It protects your hand from being hit by a hammer or sledgehammer.
What types are there: intrinsically safe with a wooden handle and others, photo
There are several types of blacksmith chisels:
- Non-sparking tools are designed for use in potentially explosive areas. The head of such chisels is made of bronze alloys, which ensures antimagnetic properties and a high level of corrosion resistance, and the handle is made of wood.
Blacksmith chisel. Photo ForgingPRO
- Chisels with a thin blade are designed for chopping hot metal, while those with a thicker blade are designed for separating cold workpieces.
- The shape of the working part can be straight or round.
Chisel rating
When making chisels, manufacturers pay attention not only to performance characteristics, but also to shape, size, and appearance.
Choosing a good tool from a wide range is quite difficult. Below is a rating of the best chisels (according to experts and buyers).
- FIT 46755. Tool steel hand chisel with a hex shank that is virtually impossible to bend.
Rubber handle reduces vibration. The buttplate is equipped with a mushroom guard to prevent shock to the hand.
- TOPEX 03A149 is used for making large recesses.
A strong grip and comfortable use are provided by four wavy ribs on the handle.
The hexagonal rod with stiffening ribs does not deform under loads.
- Stanley FatMax 25x305 mm is used for processing various metals; it fits securely in the hand and does not slip thanks to the shaped rubberized handle with an increased diameter.
The tool is equipped with a durable, bend-resistant hexagonal rod and a protective “fungus”.
The width of the working part is 25mm.
- SDS MAX MATRIX 70343 is a model for a rotary hammer with which you can lay communications.
The tool is resistant to deformation and corrosion, easy to use, and has a long service life.
- MATRIX. The oxidized chisel is protected from corrosion.
The model is made of carbon steel 50 CrMo, the tool is successfully used for cutting various materials.
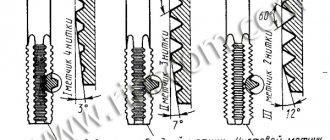
Sharpening chisels, angle
Sharpening is performed on a special sharpening machine. The chisel is placed on the tool rest and, pressing slightly, slowly moved along the entire width of the rotating abrasive wheel, alternately sharpening one or the other edge. In this case, the blade should be often immersed in cold water to prevent overheating of the metal, during which it loses the necessary hardness.
After sharpening is completed on the grinding wheel, the burrs are removed from the chisel, and then the cutting edge is threaded on the abrasive wheel.
Hot forging chisel with a sharpening angle of 70-80 degrees
The sharpening angle of the chisel knife for hot cutting is no more than 50 degrees, and for cold cutting - at least 60 degrees.
Important! The wooden handle on which the forging chisels are mounted is not wedged (to avoid kickback and breakage).
Finally, the correct sharpening angles of the blade are checked with a special template . As such a template, a metal block is used, in which grooves are cut. The angles in these grooves have the required values, therefore, by inserting a sharpened chisel blade into this groove, you can visually determine the correct sharpening.
Requirements
The main requirement for a blacksmith chisel is its serviceability . Safety of using the tool includes several characteristics that the chisel and its individual parts must have:
- The strikers must have a smooth surface , without chips, cracks, burrs, or deformation.
- The handle, necessarily made of hardwood or synthetic materials, must have an oval shape with a thickening towards the free end and a smooth surface, without cracks. Metal handles are also used, which also do not fit tightly, and rope handles.
- The length of the chisel should not be less than 150 mm.
- When working with a chisel, individual parts of the metal may fly off to the sides, so it is necessary to wear safety glasses.
Types of chisels and their purpose
Product classification is carried out according to a variety of criteria. The functionality and scope of application depend on the type. Hand tools are very common, as they are much cheaper. The main classification is as follows:
- Metalworking is considered the most common type; it is used exclusively for processing unhardened material, since the cutting edge can quickly become dull. It is worth considering that all manufacturers must produce metalworking chisels in accordance with GOST, since only in this case the required properties can be ensured.
- There is a separate category for an instrument that resembles a pike. It is often used as an attachment when working with concrete, as well as brick and some other durable materials.
- The Kreutzmeisel is not only sharpened, but also produced in a narrowed form. Such a groove chisel allows you to obtain the required recess.
- The blacksmith chisel has also become quite widespread. It is characterized by the presence of a handle, due to which it can be used for cold and hot cutting.
- A round metalworking chisel is also common and is used to work with various materials. The surface of this version is slightly rounded, thereby expanding the scope of application.
Such tools are usually quite sufficient to perform basic work with metal. Some drawings indicate which design option should be used to obtain the required surface.
Malfunctions
Among the most common breakdowns of a forging chisel are:
- break;
- dullness;
- the appearance of notches;
- deformation, curvature of the striker;
- cold hardening on the striker, which is fraught with chips and flying fragments.
Chisel striker broken
Malfunctions arise in the event of incorrect cutting, during prolonged use of the tool, or in the presence of manufacturing defects. Periodically (at least once a quarter) it is necessary to inspect the chisel for any damage to the striker or handle. Faulty tools that have defects must be removed from service.
Tools for hot metal forging
Blacksmith hammer-smoother. Photo ForgingPRO
Each master creates a set of necessary equipment independently, depending on the level of skills and assigned tasks. The blacksmith's kit includes a different list of tools: basic and auxiliary:
- hammer, sledgehammer and anvil;
- pliers (tongs);
- nail shop;
- manual and lining forks;
- vice.
Using the listed tools, various operations for processing metal workpieces are performed: chopping, bending, giving the desired shape through deformation.
Hand tools for artistic forging have a simple design, so they are easy to make with your own hands.
Device and characteristics
The chisel is a metal rod, sharpened on both sides, with a flat butt.
Depending on the design features, devices are divided into two types: manual and for power tools.
The rod can have an oval, rectangular, circular cross-section or polyhedron shape.
Main characteristics:
- type of instrument;
- appointment;
- shank type;
- length and width of the working part;
- diameter;
- material of manufacture;
- design;
- weight.
For comfortable operation, the models are equipped with special “fungi”.
This is a rubber pad that absorbs recoil and ensures an accurate hit with a hammer.
Material
One of the most important criteria that you should pay attention to when choosing is the material of manufacture.
Models designed for processing different types of metals are made of carbon tool steel, and for stone processing - from structural steel.
Dimensions and weight
A flat chisel is most often used in this work.
There are more than 20 species.
The models differ from each other in various parameters.
Total width – 5-25 mm.
Total length – 100-200 mm.
The length of the working part is 25-60 mm.
There are models used for processing soft, medium, and hard metals.
The weight of the device depends on the size.
Light hand-held ones weigh on average 210-380 g, heavy ones, intended for use with different types of power tools - 590-750 g.
Where to buy or order, manufacturers (manufacturers) and suppliers
Not all craftsmen have the necessary skills to make their own chisels. In such cases, it is recommended that you familiarize yourself with the list of manufacturers and suppliers of this tool, which are collected in a separate section. Companies offer a wide range of tools: pliers, hammers, nails, etc.
Sections: Tools
Tags: Forging - basics
Previous article: Mini forge - how to organize a workplace Next article: Decorating forging