It is not always possible to produce solid structures, and the use of massive workpieces is impractical due to the generation of a large amount of waste. In this case, fusion welding is used. The method is suitable for processing any materials that change their state when heated. In some cases, thermite welding is used.
Fusion welding is used in cases where it is not always possible to produce solid structures.
The essence of the process
The principle of operation is to use a powerful energy source that transfers heat to the weld pool. Molten wire is fed into the working area, which when cooled forms a weld. By moving the torch, the treated area is increased, and filler material is added at the same time. As the melt cools, it crystallizes, forming a strong compound. The process of exciting an electric arc occurs in 3 stages:
- the electrode touches the workpiece, a short circuit occurs, heating the tip;
- the rod is retracted to the required distance, which is determined experimentally;
- maintain stable arc burning.
Some devices are equipped with a contactless ignition function. For this purpose, a special device is used - an oscillator.
Areas of application
The method is widely used in construction. It is used for reliable connection of metal elements: sheets, profile and standard pipes. However, the scope of application is not limited to construction. The technology is widespread in automobile and aircraft manufacturing, and other branches of science and technology.
Aircraft manufacturing is one of the industries where fusion welding is used.
Classification of the main types of fusion welding
Depending on the method of heat transfer, methods are divided into gas and electric. The latter technology, in turn, has several varieties.
We recommend reading: How to cook with an autogenous oven yourself
Plasma
A shortened arc is used for heating. The carrier of energy is an electrical discharge. The metal heats up due to the action of the ionizing gas. To start the process, an increase in temperature to +5500 °C is required. The operating principle of the method is based on the melting of the material by a plasma flow generated by a plasma torch. The arc is surrounded by gas, which quickly ionizes. Charged particles form a directed flow. The method is used for welding workpieces from:
- tungsten;
- molybdenum;
- nickel alloys;
- stainless steels.
Plasma welding can be used to join and cut metal sheets up to 1 cm thick.
Plasma welding.
Gas
Welding with smooth heating is used for fastening copper, aluminum, cast iron, and steel workpieces. The distance between the parts to be joined is filled with filler material, which melts along with the edges of the structural elements. The joint is heated with a burner, the flame in which is formed when a mixture of oxygen and another gas is ignited:
- hydrogen;
- propane;
- butane;
- acetylene;
- gasoline or kerosene vapors.
Gas welding.
Gas welding does not use electrical energy, so work can be performed in any conditions. The disadvantage is the inability to fasten thick parts.
Dugovaya
The metal is heated by an arc that occurs when current passes through the parts and the electrode. A weld pool is formed from the molten edges of the workpieces and filler material. After the liquid metal cools, a weld is formed. Arc welding methods are classified according to the following characteristics:
- type of electrode (non-consumable, consumable);
- type of current (direct, alternating, with direct or reverse polarity);
- level of mechanization (automatic, manual, semi-automatic);
- type of arc (direct or indirect);
- method of protecting the working area (fluxes, use of coated electrodes or inert gas).
The filler material must be made of the same metal as the workpiece. If it is impossible to determine the steel grade, transition electrodes are purchased. They are also used for welding parts made of dissimilar steels. Carbon, tungsten or graphite rods are used as non-consumable electrodes.
We recommend reading How explosion welding is carried out
Arc welding.
Laser
The edges are heated under the influence of the beam. Laser welding is considered the most precise method of forming complex structures.
To reduce the cost of work in industrial conditions, the laser beam is divided into several parts that heat many joints. In home workshops, compact installations are used that form seams with surface or deep melting.
Laser welding is suitable for working with precious and non-ferrous metals, stainless steel, titanium. The advantages of the method include:
- no heating of areas adjacent to the seam, minimizing the likelihood of deformation;
- ability to work in hard-to-reach places;
- switching the device to cutting mode without using additional modules;
- possibility of working without gaseous medium and flux.
Laser welding.
Disadvantages include low efficiency and high cost of equipment.
Electroslag
To melt the metal, the energy released when current passes through a layer of liquid slag is used. The workpieces are installed vertically, with a short distance.
The wire is fed into the gap through nozzles connected to a power source.
The weld pool is supported by sliders. They move as the seam is formed. Electroslag welding is used to connect dimensional elements made of nickel, copper and titanium alloys. The advantage is the formation of a seam of any thickness in 1 pass.
Electroslag welding.
Induction
The workpiece is heated under the influence of electromagnetic induction. For this purpose, high-frequency currents are used that penetrate the metal. The seam is formed in a few seconds. The heating duration does not depend on the thickness of the workpieces or the thermal conductivity of the material. This welding is most often used to connect elements of steel pipelines.
Induction welding.
Electron beam welding
The source of high temperature is a focused beam produced by a special gun. The process is carried out in a vacuum chamber. Melting is promoted by intense bombardment of the metal by electrons moving at high speed. The kinetic energy of particles upon impact is converted into thermal energy. The metal melts and a seam is formed. The method is widespread in instrument making, aviation, and the space industry.
Electron beam welding.
Thermo-mechanical welding class
These are combined types of metal welding performed using elevated temperatures and mechanical forces. As a rule, the method is used to connect small-sized parts that cannot be joined using conventional classical methods.
The working process is carried out using sponge electrodes, in which two parts of the product are simultaneously attached. The main types of thermomechanical class welding are forge, contact and diffusion.
Forging equipment
Performed using hand tools. The metal first heats up, then parts are overlapped from one bottom to another and blows are applied from above with a hammer.
To achieve the highest quality joints, it is first necessary to thoroughly clean the workpieces from deposits and oxidation formed on the surface.
This method is not suitable for all metals. Low performance is considered a significant disadvantage. Therefore, blacksmithing is actively being replaced by other more modern and technological types of welding.
contact welding
The welding process is performed as follows. Heating of the surface is achieved due to the contact of the needle surface with the product. The metal is prepared by mechanical sedimentation or compression. Then an electric current is supplied through a tool with the required diameter.
Thanks to the chemical action of metal atoms, even the smallest elements can be welded with maximum reliability and strength.
Types of metal welding using contact technology are divided into butt, roller and spot welding. Such methods are actively used in mechanical engineering and other industrial areas.
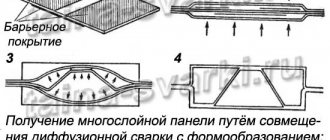
Diffusion method
Used for materials with poor contact properties. The method is based on the process of diffusion of atoms at an increased level of vacuum. The top layer of the welded surface is heated to a temperature similar to melting. Through enhanced mechanical action, contact and joining are carried out, while 20 MPa should be the minimum compression power.
The docking process takes place in a special chamber. The parts placed in it are exposed to electric current for a long time.
Fusion welding technologies
The process of joining parts when using any method includes the following steps:
- Preparation of elements. The edges are cleaned of grease and corrosion, and the edges are cut off taking into account the thickness.
- Installing parts in the desired position and fixing them.
- Ignition of the arc (using some methods). In other cases, parts are heated in a different way.
- Seam formation. After cooling, the connection is cleaned of slag.
Recommended reading Plasma welding technology
Mechanical class
The classification of welding methods includes another type - mechanical joining of materials, performed by physical impact on them. In this case there is no need to apply the melting point. Heating occurs when mechanical energy transforms into kinetic energy and when the melting point is reached, the products are connected with strong seams.
Mechanical welding classes involve the use of several effective technologies.
Friction method
In most cases, friction welding is used for rod structures and small diameter pipes. The process is automated and takes place in special installations in which workpieces are fixed into a spindle. The machine moves the moving part to the stationary one, as a result the elements heat up and melting occurs.
The technique allows you to weld metals consisting of different alloys, quickly performs the necessary tasks and is economical.
Cold welding
Mechanical cold welding is in demand when it is necessary to join pipes, wires or tires. The workpieces are connected due to the deformation of plastic materials under pressure from 1 to 3 GPa. In this case, the temperature can even be minus.
The surfaces to be welded must be thoroughly cleaned of dirt and rust. Since docking occurs at the interatomic level, the surfaces of the elements must be flawlessly processed and perfectly smooth.
Explosion welding
The connection of parts in this way occurs through plastic synchronous deformation. The moving part of the product is applied in parallel to a securely fastened target. Next, a maximally controlled explosion is performed.
The technique is suitable for joining dissimilar metals. Mixtures of ammonite, granulotol and hexogen are used as explosives.
Ultrasound technique
When listing the types of metal welding included in the mechanical group, attention should also be paid to ultrasonic technology. In this case, energy sources are used that produce ultrasonic vibrations at the output.
The method is relevant for creating point and suture joints under mechanical influence. Due to dry friction, the oxide films are destroyed, then welding is carried out in the process of pure friction.
An important advantage here is that there is no need to pre-clean surfaces, which saves time. The disadvantages include the high cost of the equipment, as well as the scanty range of thicknesses of the materials being connected.
Standards and requirements
The fusion welding process is regulated by the following documents:
- GOST 11969-79 (basic terms and designations);
- GOST R ISO 5817-2009 (requirements for seam quality);
- GOST R 55143-2012 (welding parameters);
- GOST 30242-97 (description and methods for eliminating defects).
The requirements for seams depend on the purpose of the structure. However, the joints must have hardness and strength values close to those of solid elements.
Features of choosing the appropriate type and technique of welding
The classification of welding types is so broad that quite often specialists (especially beginners) wonder what types of welding exist with which even a non-professional could weld and obtain joints of impeccable quality.
If it is not difficult to list all types of welding, then it is impossible to definitively answer which one is the best. The fact is that each type of welding differs in the technique of execution and the equipment used. It is also necessary to consider what advantages and disadvantages specific types of welding have and their use has clear limitations.
Argon welding
The essence of the technique is the use of non-consumable electrodes. The advantages are:
- ideal fixation of thin elements;
- the ability to control the depth of metal heating;
- much less splashes from sparks when compared to other types of welding that exist and are actively used;
- an even, uniform, externally beautiful seam, which is especially important in cases where great importance is given to the aesthetic characteristics of the finished product.
Flaws:
- during manual welding, productivity is very low;
- automatic connection is contraindicated for joints with different directions or too short;
- expensive equipment.
Argon welding is used in the manufacture of metal structures from aluminum, copper, titanium, stainless and alloy steel, and non-ferrous metal alloys.
Arc welding
A fairly common classification of welding, which has a number of positive features:
- the ability to connect parts in any spatial positions;
- versatility of use in places with limited access;
- the working process is available on AC and DC;
- low cost.
As a continuation of the advantages, there are also disadvantages:
- the seams are not of the desired quality, they have lack of penetration and tubercles;
- very low efficiency due to the high amount of waste;
- not suitable for joining thin workpieces;
- low performance indicators.
Arc technology is used for the manufacture of stairs, canopies, fences, pipe joining, and installation of main pipelines. The seam does not have high aesthetic properties, but if you choose what types of welding exist to create products from thick metal, then arc is considered one of the best methods.
Gas flame technology
Comparing modern types of welding, which are suitable for welding assemblies and connections made from pipes, as well as for installing pipelines of medium and small diameters, here it is worth giving preference to the gas method.
Obvious advantages:
- complete independence from power supply;
- ease of transportation of equipment from one place to another;
- absence of overheating and metal burns;
- the ability to create internal seams in small diameter pipes.
But the technique also has some disadvantages. These are increased demands on the professionalism of the welder, a fairly large heating area, and low productivity coefficients.
Semi-automatic welding
The technology is similar to arc technology, but here the electrode is supplied automatically. Among the advantages it should be noted:
- ease and safety of the work process;
- efficiency;
- excellent accuracy and good performance;
- evenness of seams;
- ability to connect parts from 2 to 30 mm thick.
Negative points of the semi-automatic method:
- the inability to adjust the joint during the work process, since it cannot be seen;
- if the current is more than 200A, then the molten metal splashes heavily and it is necessary to remove all scale;
- The semi-automatic device can only be used indoors.
As for application, this technique is suitable for creating and installing metal fences, stairs, gates, garages and other structures.
To choose the most suitable method for joining elements for specific purposes, you need to know what types of welding there are, draw an analogy for each of them, and only after careful analysis give preference to a specific technology.
Quality Control Methods
When working with structures that do not belong to the critical category, they are limited to visual inspection. The seam is cleaned of slag and oxide deposits, and the fasteners are removed. The connection must be uniform, fine-scaled, and have the same width along its entire length. There should be no through holes, sagging or foreign inclusions. To check critical structures, use:
- radiation method;
- ultrasonic flaw detection;
- magnetic control;
- capillary method.