Chemical composition aisi 304 316
Changes in the composition of 316 consist of additions to the composition of molybdenum, a decrease in carbon and an increase in the amount of nickel. In all other respects, the chemical composition of both metals is identical.
AISI 316/304:
- Chrome - 16.0-18.0%/18.0-20.0%
- Nickel - 10.0-14.0/8-10.5%
- Carbon – up to 0.03/up to 0.08%
- Molybdenum – 2.0-3.0%/absent.
For a complete list of their chemical compositions and properties, see table.
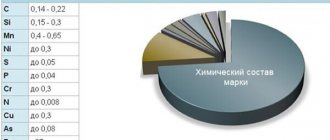
| Stamps | C | Mn | P | S | Si | Cr | Ni | Mo | Ti |
| AISI 304 | <0,08 | <2,0 | <0,045 | <0,03 | <1,0 | 18,0-20,0 | 8,0-10,5 | — | — |
| AISI 316 | <0,03 | <2,0 | <0,045 | <0,03 | <1,0 | 16,0-18,0 | 10,0-14,0 | 2,0-3,0 | <0,5 |
Martensitic stainless steels 410, 420, 431 and 440
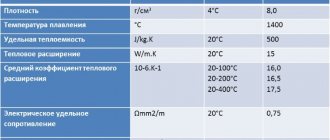
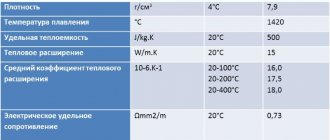
| Type | Compound | Density ρ, kg/m3 | Elastic modulus E, GPa | Coefficient of linear thermal expansion α, 1/K | Thermal conductivity coefficient λ, W/m • K | Hardness HRC (HRB) | Hardness | Note |
| 410 | <0.15% C, 11.5-13.0% Cr, <1.0% Mn | 7750 | 200 | 9,9 | 24,9 | — | 225…388 | Basic martensitic steel. Moderate corrosion resistance in fresh water, food environments, low-concentration acids and alkalis. |
| 420 | <0.15% C, 12.0-14.0% Cr, <1.0% Mn | 7750 | 200 | 10,2 | 20,2 | — | 277…385 | A close analogue of 20X13. Moderate corrosion resistance in fresh water, food environments, low-concentration acids and alkalis. |
| 431 | <0.20% C, 15-17% Cr, 1.25-2.50% Ni, <1.00% Mn | 7750 | 200 | 10,3 | 24,9 | — | 262…444 | Anti-corrosion qualities are slightly lower than those of type 304 steel. |
| 440A | 0.65…0.75% C, 16-18% Cr, 0.75% Mo, <1.00% Mn | 7650 | 200 | 10,1 | 24,2 | 55 | — | Moderate corrosion resistance in fresh water, food environments, low-concentration acids and alkalis. |
| 440B | 0.75…0.95% C, 16-18% Cr, 0.75% Mo, <1.00% Mn | 7650 | 200 | 10,1 | 24,2 | 57 | — | Analogue 95Х18. Corrosion resistance equal to 304 steel. |
| 440C | 0.95…1.20% C, 16-18% Cr, 0.75% Mo, <1.00% Mn | 7650 | 200 | 10,1 | 24,2 | 59 | — | Corrosion resistance equal to 304 steel. |
The information was prepared based on materials from the sites:
https://www.azom.com/ https://www.bssa.org.uk/ https://www.suppliersonline.com/.
Properties of 304-316 steel
And yet, despite seemingly insignificant changes in the chemical composition of the alloy, the properties of 316 differ significantly from 304 in some respects.
Thanks to alloying with molybdenum, alloy 316 acquires the ability to resist corrosion damage such as crevice and pitting. Especially with direct contact of structures made of this alloy in such aggressive environments as acidic vapors, chlorine compounds, sea water (cold). It is well known that pitting corrosion, which selectively affects hard-to-reach places, is especially dangerous for structures. Therefore, for structures that are operated in such conditions, the question does not even arise - aisi 304 aisi 316 which is better, it is so obvious. The same applies to structures and products whose operation takes place in contact with vapors of many acids - formic, phosphoric, acetic, boric, oxalic, sulfuric or lactic.
When comparing AISI 304 to 316 steel, it is clear that AISI 316 alloy has significantly high performance properties and technological characteristics, including strength indicators. Moreover, what is especially important when operating structures made of 316, these properties are maintained throughout the entire service life and do not change even at temperatures tending to zero ˚C.
Steel 316 has greater strength than 304, as well as much greater creep resistance at higher operating temperatures. This difference between 316 and 304 is due to the addition of molybdenum.
Due to the high level of resistance to corrosive formations and non-susceptibility to oxidation, aisi 316 is characterized by physical properties that are practically no different from the properties of aisi 304 (a slight increase in density has little effect on performance properties).
Which stainless steel to choose AISI 316 or AISI 304
The choice of stainless steel depends on your goals and objectives. If the formability of steel is important in your production, then you should choose AISI 304 . If the metal structure will be constantly exposed to water or aggressive chemical elements, then AISI 316 .
The specialists of the Metallobaza No. 2 company will help you select and buy stainless steel , taking into account the characteristics of the alloy, operating conditions and your requirements.
M2 company is a specialized supplier of stainless steel products in Russia. The trade and warehouse complex has branches in St. Petersburg, Moscow, Yekaterinburg and other cities. have stainless steel AISI 304, 316 and other grades in our warehouses To get specialist advice and place an order for stainless steel, please contact the branches of the M2 company.
Areas of use of alloys - difference between aisi 304 and 316
Considering the peculiar properties of aisi 316, steel 304 and 316 have differences in application. Although under normal operating conditions they are completely interchangeable.
Due to its resistance to the formation of all types of corrosion in sea water, first of all, alloy 316 is indispensable in shipbuilding and the transport field - containers, units and installations on ships, elements of marine instruments. It is also widely used in the petrochemical industry, oil refining, mining, chemical and mining industries. It is advantageous to make tanks and containers from this alloy for storing and transporting aggressive liquids, since they are the most durable.
In all areas in which both steels are used, there is no need to decide whether aisi 304 or aisi 316 is better, since in all other performance indicators they are similar.
- Pipelines
- Metal constructions
- Elements of technology
- Units and parts in mechanical engineering
Stainless steel in the pool grades 316 and 304
Stainless steel 304 and 316, what is the difference?
The parts for the pool use high-quality chromium-nickel steel AISI 316 and universal steel AISI 304.
The pool nozzle is made of 316 and the side ladder is made of 304.
Stainless steel AISI 304 steel. AISI* 304 steel is an austenitic steel with a low carbon content. AISI 304 stainless steel is acid-resistant and can withstand short-term temperature rises of up to 900 degrees Celsius. It is used for the use of embedded parts in swimming pools, as well as chimneys and ventilation systems.
Stainless steel steel AISI 316 (316L, 316Ti). AISI 316 is a steel grade that is an AISI 304 grade improved by adding 2.5% molybdenum. Thanks to molybdenum, this grade of steel is especially resistant to corrosion, high temperatures and aggressive environments. It is used both in household items and in aggressive water-chemical environments in swimming pools, in pools with sea salt water. 304 steel contains: 18% chromium and 8% nickel. 316 steel contains: 16% chromium, 10% nickel and 2% molybdenum. Molybdenum in 316 is added to help resist corrosion from chlorides (like seawater, de-icing salts or water treatment chemicals).
304 steel is the most common stainless alloy and is used in swimming pool components. It has a low cost compared to other steels. Type 304 stainless steel is resistant to oxidation and corrosion, but it is advisable not to use it in salty marine environments with chloride-containing environments, as stainless steel is quite sensitive to pitting and crevice corrosion.
316 steel contains 16 to 18% chromium, 10 to 14% nickel, and 2 to 3% molybdenum. This type of steel has a greater degree of corrosion resistance compared to others. Can be used in pools with sea water, as well as with salt solutions. Thanks to the molybdenum in its composition, it is more resistant to chemical attack than 304 steel. The 316 steel type is quite durable, easy to process, and easy to weld. 316 steel for applications where a high level of resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion in chloride-containing environments is required. Such stainless steel is of course more expensive, but in the long run you will save significantly on equipment.
*AISI - The American Iron and Steel Institute - standards developed by the institute to designate alloy and stainless steels.
The appearance of rust (corrosion) on stainless steel parts in the pool. Possible reasons.
Low pH on the acidic side. One of the reasons for the appearance of rust is the pH value falling below 7.0 in the acidic direction. If pool equipment is neglected or not maintained, the dosing station may over-inject pH-minus into the water. Moreover, the smaller the volume of the pool, the greater the acid overdose. You will feel this on yourself through irritation of mucous membranes, eyes, open wounds and cracks in the skin. Chlorine in excess. Stainless steel in the pool can withstand excess chlorine up to 3 mg/l, i.e. shock chlorination conditions. But not more. Excess hypochlorous acid is just as harmful to stainless surfaces in water as is excessively low pH.
Stray currents. Corrosion of metal parts in the pool can be affected by strong electromagnetic fields, as well as stray currents. Stray currents are generated along the location of an electrified DC railway, DC power lines, and also near cathodic protection installations. The influence of stray currents can extend up to 30 km from their source. The solution may be to ground all metal parts of the pool equipment without exception.
Mechanical defects. In addition to chemical exposure, the cause of corrosion can be a manufacturing defect in the embedded part itself. If these are stairs, then cutting with a grinder without sanding the cut will definitely lead to rust. Welding seams and all places of mechanical impact in production are etched with acid. The same processing is carried out when welding stainless steel sheets, when an entire metal bowl is made, welding seams and scratches are carefully ground.
Pitting corrosion.
The formation of rust is influenced by: - hardness - salts of carbonates, sulfates, chlorides. Chlorides accelerate oxidation in the presence of copper, iron and carbonate ions; — presence of iron ions; — impurities of heavy metals (copper, mercury); — saturation of water with oxygen;
The speed of the corrosion process is affected by: - an increase in water temperature; - Still water.
How to remove rust from stainless steel in a swimming pool?
If rust appears, a solution of nitric acid (concentration 10-15%) will help. Rinse the treatment area generously with water. In severe cases, surface grinding and chemical treatment with special detergents - passivation - are used. These substances include nitric and hydrochloric acids. Nitric acid promotes the formation of a protective film of chromium, which prevents further corrosion. Then rinse and dry. It is possible to use 8% citric acid, which can be heated. Regular passivation, once every 2 months, will preserve the stainless steel from oxidation.
To clean ordinary non-corrosive contaminants on steel, non-forming pastes containing nitric or phosphoric acid are used. It would be good to use synthetic brushes, soft fabrics, napkins, and soft sponges. It is unacceptable to use cleaning products that contain hydrochloric acid, pH, chlorides, soda, abrasive materials, especially those containing metal, or metal brushes. Chlorine is the main enemy of stainless steel.
Stainless steel characteristics
Does your company produce various stainless steel tools? Then you need specialized material. These can be carbon hot-rolled and cold-rolled steels, as well as their alloyed analogs with the addition of chromium, manganese, vanadium, molybdenum and tungsten. Depending on the alloying material, it is possible to achieve heat resistance at temperatures up to 700 - 800 o C, as well as wear resistance.
Each brand has its own characteristics. For example, AISI 304 has special characteristics. It is capable of withstanding short-term temperature increases of up to 800 - 900 o C, which is inaccessible to many analogues. It also does not react with liquid media, including food products (milk, sour cream, honey, etc.). This allows it to be effectively used in the food industry, medicine, and pharmacology. There is a thin oxide film on the surface of the material.
Definition and chemical composition
There are specific requirements for containers and equipment that come into contact with food. Sanitation, storage, transportation, and preparation of products are carried out under conditions that negatively affect the properties of materials. Food grade stainless steel has a special composition, which determines its scope of application.
Chromium and alloying additives that increase the corrosion resistance of metals are present in stainless steel. Its surface is formed with the participation of chromium oxides, forming an insoluble self-healing layer that is resistant to aggressive and chemical influences.
The elements that increase anti-corrosion properties include copper, cobalt, sulfur, manganese, nickel, phosphorus, niobium, molybdenum, titanium. Their presence directly affects the cost of products.
As part of a moonshine still
Stainless steel is an ideal material for a moonshine still. It has many advantages over silicone, copper, brass, due to its inertness to temperature and alcohol vapors, excellent thermal conductivity and long service life.
Advantages of stainless steel for moonshine brewing:
- wear resistance;
- light weight;
- flexibility to twist, the ability to make turns of any diameter;
- safety, stability of chemical characteristics;
- no risk of depressurization.
But before purchasing all the components, you need to decide on the grade of food-grade stainless steel for the moonshine still, taking into account the characteristics of some types that cannot withstand exposure to aggressive liquids or cannot be bent.
The most common brands in moonshine are:
- AISI 304 (08Х18Н10) - contains chromium and nickel, which increase its cost, has high anti-corrosion properties, which together increases the performance properties of the devices;
- AISI 430 (12X17) - easily susceptible to mechanical stress; due to the chromium content, products are flexible and ductile, although this does not reduce chemical inertness;
- AISI 201 (12X15G9ND) is an economical brand with nitrogen and manganese in its composition, not inferior to more expensive options.