The best gas burner manufacturers
Gas burners are fire hazardous devices; you should choose models made by well-known manufacturers of household and industrial gas equipment. Despite the different specifics of production, compact models of burners are present in the catalog of each of them:
- Indesit
- Primus
- Bosch;
- Kovea;
- Ariston;
- Fire Maple;
Having decided on a specific burner model and familiarized yourself with the characteristics, it is necessary to compare them with the conditions in which operation will be carried out. It’s easier to do this taking into account user reviews that are presented on thematic forums and on social networks on the Internet.
Peculiarities
Modifications of the first type include the design of supplying air and gas separately. Additionally, the process involves elements responsible for the process of mixture formation. During operation, a filler of gas and air is supplied to the furnace in the form of a turbulent flow with different fields of fuel and oxidizer concentrations in the cross section. After the composition enters the high temperature compartment, it ignites.
Part of the working flow, where the gas and air capacity is presented in stoichiometric proportions, burns out kinetically. In areas of incomplete formation, this procedure occurs in a diffuse mode. The combination of fuel components in the firebox is carried out using a special device that is responsible for the movement of individual particles and the criteria for the flow exiting the mixer.
The following are the characteristics of the turbulent type gas burner:
- The mixing of gas and air is carried out by diffusion.
- Since the combination of composition components is an inhibiting part of the overall process, intensification of operating conditions is required. It is achieved by reducing the supplied flow by tightening the guide vanes or by introducing the mixture in small doses.
- Scope of application of the burners in question: heating of domestic and industrial boilers.
- The device has a wide control range, which allows you to increase its productivity.
- It is possible to burn a significant amount of gas with relatively small dimensions.
- Simplicity of design with the combined use of coal dust or fuel oil.
- Power indicator – from 60 kW to 60 MW.
Types of gas burners
Modern burners currently on sale are divided into several conventional categories depending on the principle of operation, type of fuel and functional purpose.
Classic atmospheric gas burners
Devices based on the principle of burning natural gas - the most common and cheapest type of fuel. The combustion process occurs due to the supply of fuel through a regulator to a special burner, the appearance of which resembles a classic gas stove. The power source is both liquefied gas, sold at gas stations in five-liter cylinders, and miniature disposable aerosol cans of gas, which can be purchased at travel equipment stores. Advanced models are equipped with a special gearbox that allows operation from a stationary gas network.
Advantages
- Compact dimensions;
- Consumables are extremely cheap and are sold everywhere;
- Give an even flame in any conditions;
- Affordable cost;
- High functionality;
Flaws
- Some models are quite bulky;
- Fire hazard, require careful handling;
Gas burners equipped with pressurization
Devices whose principle is similar to those described above, but the method of supplying the oxidizer to the combustion site differs radically. These models require the presence of a special fan that forces air to the source, making the flame stable and powerful. The amount of supplied air is regulated, and with it the power and intensity of combustion changes.
Advantages
- Steady flame;
- High efficiency;
- Suitable for performing various operations - both domestic and industrial;
- Ability to work even in adverse conditions;
Flaws
- Noisy;
- Complexity of design;
- Tangible dimensions and weight;
- More expensive than atmospheric analogues;
Injector burners
Devices that provide a powerful and uniform flame, allowing for serious technological operations, including cutting metal. The principle of their operation is to form a mixture by supplying compressed air under pressure through a special injector, which significantly increases the efficiency of such a device. The source of compressed air is almost always oxygen cylinders or a compressor, which increases the dimensions of the device and makes it stationary.
Advantages
- Stable and powerful flame in any operating conditions;
- Simple design, unpretentious to maintenance and care;
- Allows you to perform a huge number of technological operations;
Flaws
- Requires a source of compressed air nearby;
- Expensive;
- Heavy and bulky;
Burners with piezo ignition
Almost always compact and miniature devices used for domestic purposes. The source of such devices is a compact collet gas cartridge, which provides compact dimensions and allows you to take it with you on a hike. A piezoelectric element is used to ignite the fire, which significantly improves the capabilities of the device and guarantees ignition even in wet conditions and strong winds.
Advantages
- Compact dimensions;
- Low cost;
- Ideal for tourist purposes;
- Reliable and simple design;
- Possibility of ignition even in harsh conditions;
- Light weight;
Flaws
- One collet cylinder is not enough for a long time;
- The piezoelectric element tends to fail;
Gas burners and their classification by type of operation
Fan burners.
Fan burners (they are also called forced-air burners) primarily have the following property. Air enters them thanks to the built-in fan. Moreover, in the burner itself it is mixed with some kind of fuel. As a rule, the resulting mixture is pumped into the firebox. Fan burners, for example, can run on gas or liquid fuel (diesel, waste oil). When operating on gas, fan burners are least dependent on the pressure at which the gas will be supplied. Even if the pressure drops by 50%, the boiler will heat the coolant.
Fan burners are much more expensive than gas burners, but are less dependent on gas pressure in the network. Even if it drops by 50%, the boiler will still heat the coolant, with a loss of power. At the same time, fan burners are quite noisy (up to 60 dB). It is not so much the fan that makes noise as the torch coming out of the burner nozzle under pressure. To protect against noise, boiler manufacturers offer a number of measures, including a muffler, which is installed at the junction of the chimney and the boiler.
Fan burners in most cases are not part of the boiler. They are supplied separately and attached (“hung”) to the boiler.
Diffusion burners and intermediate burners.
In diffusion burners, the air necessary for fuel combustion is primarily supplied from the surrounding space. Towards the combustion front due to diffusion.
Diffusion gas burners are characterized by a more uniform temperature along the length of the torch. However, these gas burners require an increased excess air ratio (compared to injection ones). They create lower thermal stresses in the combustion volume and worse conditions for post-burning of gas in the tail part of the torch. First of all, this can lead to incomplete combustion of gas.
Diffusion gas burners are used in industrial furnaces and boilers, where uniform temperature along the length of the torch is certainly required. In some processes, diffusion gas burners are indispensable. For example, in glass melting, open-hearth and other furnaces, when the combustion air is heated to temperatures exceeding the ignition temperature of the combustible gas with air. Diffusion gas burners are also successfully used in some hot water boilers.
In powerful combustion chambers, gas is quite successfully burned primarily using diffusion burners with low gas and air resistance. These latter do not require pre-mixing of gas and air. Allows high velocities of gas and air exit into the furnace. As a result, when using such burners, fire-resistant tunnels with a significant total cross-section are no longer required. Requiring high-calorie gas, high-quality refractory and relatively frequent repairs. Finally, diffusion burners are easily designed as mixed gas and oil burners. Allowing efficient combustion of both gaseous and liquid fuels (and, if necessary, also pulverized solid fuels).
Application
Therefore, in powerful boiler units that burn either natural gas or blast furnace gas and coal dust, diffusion or mixed type burners are usually used. In diffusion burners, gas and air are supplied to the firebox separately and the mixing of gas and air occurs in the combustion chamber itself. In this case, the air usually has time to warm up before mixing with the gas. To a temperature sufficient for intense combustion. In this case, the combustion process occurs very quickly and the combustion front, i.e., the diffusion combustion zone separating the areas of the mixture of fuel with the oxidizer (air) and the mixture of combustion products with excess air, is a very thin layer. In intermediate type burners, mixing is primarily carried out partially in the burner itself. From it, a stream of air enters the firebox, penetrated by separate jets of a mixture rich in gas.
Diffusion burners, for example, operate on low and medium pressure gas.
The so-called boilers have become widespread. hearth gas burners , which are a type of diffusion gas burners that are placed inside the firebox, in its lower part. A hearth gas burner consists of one or more gas distribution pipes in which holes are drilled. A pipe with holes is installed on a grate or firebox in a slotted channel. Lined with refractory bricks. The required amount of air enters through the fire-resistant slot channel. With this device, the combustion of streams of gas emerging from the holes in the pipe begins in the fire-resistant channel and ends in the combustion volume. Hearth burners create little resistance to the passage of gas, so they can operate without forced blast.
An observation window is usually used to monitor the combustion and ignition process of a gas burner. Hearth burners can operate at low and medium gas pressure and are used in sectional boilers, TVG, KV-G, DKVR boilers.
Oil burners.
The use of fuel oil, that is, the heavy fraction remaining after oil is processed, is by no means rare in industry. Mainly, fuel oil burners, both autonomous and industrial, are used to convert fuel oil into thermal energy, and this is done by combustion. For the most part, oil burners use a mechanical fuel atomization system, using either steam or compressed air. Some of the modifications of oil burners are primarily equipped with low-pressure nozzles, this is aimed at effectively reducing fuel consumption. In addition, this type of fuel oil burner device wears out more slowly than its analogues, and this, in turn, reduces both the cost of the process and maintenance costs.
Oil burners produced nowadays are equipped with such equipment as electrical panels, a control system, and a fuel supply motor-pump group. A fuel oil burner equipped with this type of equipment will automatically clean the nozzle as soon as it can be said to be finished, which also leads to a reduction in the need for equipment maintenance.
As a result, oil burners use a fuel heating system. This is done so that the fuel oil is constantly maintained in a viscous state. Fuel atomization usually occurs using compressed air or steam under a pressure of 8 bar. There are also modifications in which the gas burner is ignited by a pilot gas burner.
Oil burners are rightfully considered economical and practical. In view of these properties, fuel oil burners are used everywhere and widely, both as the main source of thermal energy and as a backup option if there are suddenly interruptions in the supply of other fuel. The industrial fuel oil burner has found its application for industrial purposes and in urban heating plants, providing centralized heating of residential buildings. In conclusion, we can say that there is a wide range of fuel oil burner devices for the consumer to choose from. When purchasing such equipment, you can choose by power, modification, and other parameters - the market allows this. And, of course, oil burners are distinguished by their reliability and high quality.
Gas-oil and dust-gas burners.
For a quick transition from one type of fuel to another (especially in the winter months), as well as for the joint combustion of different types of fuel, combined burners are used: gas-fuel oil and dust-gas. Combination burners are also used when it is necessary to create a luminous flame or when it is impossible to achieve the required temperature in the firebox using gas.
The gas-oil burner consists of a gas burner, an air burner. and liquid parts, respectively providing the supply of the amount of gas, air and fuel oil required for combustion.
In a dust-gas burner for burning natural gas in large electric boilers. stations, gas enters through peripheral openings and is directed to the center, mixing along the way with a swirling air flow. The burner is equipped with a telescopic a device with a screw drive that allows you to remove a pipe inside, through which an air-dust mixture is fed into the firebox when boilers operate on gas fuel. Telescopic the device prevents dust from entering the cracks between the mobile and stationary parts of the pipe.
Example of gas-oil burners:
gas-oil burners PGMG-10; thirty; 40 ,
gas-oil burners RGMG
Injection burners
In injection burners, as a rule, combustion air is sucked in (injected) due to the energy of the gas stream and their mutual mixing occurs inside the burner body. Sometimes in injection gas burners the suction of the required amount of combustible gas, the pressure of which is close to atmospheric, is carried out as a result of the energy of the air stream. In full-mix burners (all the air necessary for combustion is mixed with the gas), operating on medium-pressure gas, a short flame is formed, and combustion is completed in a minimum combustion volume.
Partial mixing injection gas burners receive only part (40-60%) of the air required for combustion (the so-called primary air), which is mixed with the gas. The remaining amount of air (so-called secondary air), for example, comes to the flame from the atmosphere due to the injection action of gas-air jets and rarefaction in the furnaces. Unlike medium-pressure injection gas burners, low-pressure burners primarily produce a homogeneous gas-air mixture with a gas content greater than the upper ignition limit; These gas burners are stable in operation and have a wide range of heat loads.
Injection burners are distinguished: by pressure - low and medium pressure; by type of torch - multi-flare (with a distribution manifold) and single-flare; also the number of nozzles - single-nozzle and multi-nozzle; according to the location of the nozzles - with a central and peripheral location. The volumetric ratios of gas and air sucked in by the injection burner are determined by the injection coefficient and the excess air coefficient. The higher the calorific value of a gas, the more air is required for its combustion. All the more, for the same excess air coefficient, the injection coefficient should be. The more air must be sucked in by 1 m3 of gas.
Pressure interval
In the gas pressure range from 2000 to 9000 kgf/m2, the injection capacity of the burner remains almost unchanged. When the gas pressure in front of the burner and vacuum in the furnace change.
At pressures below 2000 and especially below 1000 kgf/m2, the excess air coefficient increases. To ensure a normal combustion process, the consistency of the gas fuel composition is of great importance. A change in density leads to a change in the injection ability of the burner, and a change in the heat of combustion requires, first of all, a corresponding change in the amount of air supplied for combustion. With slight fluctuations in the specified characteristics of gas fuel (Wobbe number), the required excess air coefficient can be maintained by changing the pressure in front of the burner and the degree of opening of the air control damper.
Advantages of injection burners: use of gas energy to suck in air; good mixing of gas and injected air and maintaining, within certain ranges, the calculated ratio of their quantities when the thermal power of the burner changes. The main disadvantages of burners with one gas nozzle are their considerable length, especially at high thermal powers: the need for strict alignment of the nozzle axis with the burner axis; high noise level, and low-pressure burners - a significant length of the torch and the dependence of the supply of secondary air on the vacuum in the furnace.
Example of injection burners: Kazantsev gas injection burners
Burners are usually placed in two or more rows on one or two opposite sides of the firebox. The number of burners is chosen to be significant in order to be able to regulate the load by turning off part of the burners, since nozzles with an unregulated outlet cross-section usually used in stationary boilers do not work well at reduced loads. Air velocities in the narrow cross-section of the embrasures that the burners have are about 20-35 m/sec. The minimum depth of the firebox with front-mounted burners must be at least 3 m for small burners and 4 m for large ones.
Classification of burners by type of regulation.
Single stage burners
They operate only in one power range and operate in a mode that is difficult for the boiler. When single-stage burners operate, frequent switching on and off of the burner occurs, which is controlled by the automatic control of the boiler unit.
Two stage burners
They have two power levels. The first stage typically provides 40% of the power, and the second 100%. The transition from the first stage to the second occurs depending on the controlled boiler parameter (coolant temperature or steam pressure), the on/off modes depend on the boiler automation.
Smooth two-stage burners
Allows for a smooth transition from the first stage to the second. This type of burner generally occupies an intermediate position between two-stage and modulating burners.
An example of the three types of burners described above is the Max Gas from Ecoflam.
Modulating burners
heat the boiler continuously, increasing or decreasing power as necessary. The range of combustion mode changes is from 10 to 100% of the rated power.
Modulating burners are divided into three types according to the operating principle of modulating devices:
– burners with a mechanical modulation system;
with pneumatic modulation system;
and burners with electronic modulation.
Unlike burners with mechanical and pneumatic modulation, burners with electronic modulation allow for the highest possible control accuracy, since mechanical errors in the operation of burner devices are eliminated.
Modulating burners have a number of advantages over stepped burners. The mechanism for smooth power control allows you to reduce the cycle of turning on and off boilers to a minimum, which significantly reduces mechanical stress on the walls and components of the boiler, and therefore prolongs its “life”. Fuel savings are at least 5%, and with proper tuning you can achieve 15% or more. And finally, installing modulating burners does not require replacing expensive boilers if they are functioning properly, while increasing the efficiency of the boiler.
An example of burners with power modulation is Max Gas Blu from Ecoflam.
On the other hand, modulating burners are more expensive than stepped models.
Burning fuel oil
Fuel oil reserves amount to hundreds of millions of tons, so it is very important to achieve efficient and safe use of this fuel. Taking into account modern environmental requirements, a number of Swiss companies are working on the creation of heating systems with oil burners that produce a blue flame, like gas fuel. In conventional fuel oil burners, which produce a yellow flame, the processes of mixing fuel oil with air, evaporation and combustion occur simultaneously.
In the burners of the new system, fuel oil first evaporates and mixes with air, and only then the resulting gas mixture ignites. This results in less soot and carbon monoxide being produced. In addition, the design of such burners provides for the recovery of exhaust gases, as a result of which the flame temperature decreases and less nitrogen oxides are released. For better mixing of air and exhaust gases with fuel oil, burners with rotating heads are used
Gas burner selection parameters
Once the type of device and its functional features, as well as the operating conditions, have been determined, it is necessary to carefully study its characteristics and compare it with the closest analogues. It is necessary to pay attention to the following technical points.
Battery type
All of the above burner models operate on liquefied gas - propane or butane, which, in turn, can be supplied in completely different containers.
The most compact and portable burners, used for domestic and tourist purposes, use compact collet gas cartridges as a battery. Some devices have a separate compartment for such a can, others are fixed on top of it.
Classic tourist burners with one or two burners operate from five-liter gas cylinders connected through a special reducer. Such devices are widely used for both cooking and heating;
! Preference should be given to models that allow the use of several power sources with equal efficiency, and also have the ability to connect to a stationary gas pipeline.
Gas used to power the burner
- Isobutane mixture is the most common and versatile type of fuel. Provides clean combustion without large amounts of emissions and high heat transfer;
- Propane is a gas that is prone to clean combustion and does not tend to emit harmful substances during the combustion process. It is less common on sale than isobutane mixture;
- Butane is similar in properties to propane, but its combustion process is less clean, and it is also quite unstable in the cold season.
How to choose the power of a gas burner
The power of a gas burner is a parameter that reflects its operating efficiency and efficiency. It is impossible to achieve one hundred percent effect from gas combustion, however, many modern models have an efficiency rate of 80-90%. Power is traditionally measured in kilowatts and indicated in the technical specifications. In field conditions, the power of the burner is calculated quite simply - one kilowatt of energy is enough to cook one liter of food. For example, for a company of four people it is necessary to prepare about 2-2.5 liters of food, and therefore the most suitable burner will be capable of producing a power of 2.5-3 kilowatts. The same principle is used to determine the power of a gas burner used for other needs - heating a tent, water heating.
Ignition type
- Inexpensive gas burners in this regard are deprived of all conveniences - the valve opens the gas supply to the nozzles, and ignition is carried out using matches or a lighter. This principle is both reliable and not - there are no mechanical elements that can fail, but matches tend to get damp, and a lighter tends to fail at the most inopportune moment;
- Piezo ignition is used in advanced devices. It is a compact piezoelectric element that produces a spark and ignites the gas-air mixture when the button is pressed. It should be remembered that such ignition requires careful handling and periodic maintenance, and also that it may not work at altitudes above 4 kilometers. Even if your burner is equipped with piezo ignition, matches will never be superfluous;
Types of burners
Gas burners are distinguished according to several parameters:
- heat of combustion of gas;
- gas pressure;
- design features;
- purpose;
- air supply;
- gas combustion method, etc.
It is most advisable to consider methods of supplying air for combustion, which depend on the designs of the burners.
There are gas burners in which the combustion air is taken directly from the atmosphere. Burners of this type have little sensitivity to gas pressure fluctuations. The disadvantage is the need for large combustion chambers. Injection burners use air to ignite a fire within a structure.
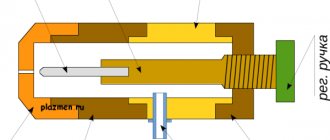
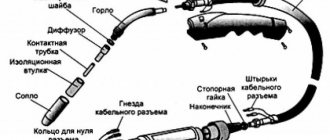
Injection burner
These burners come with full or partial mixing, and consist of four main elements:
- mixer (for mixing air and gas);
- gas nozzle (for supplying gas to the burner);
- nozzle (ejection of combustion mixture);
- air regulator (primary).
Among the variety of gas burners, there are also forced air burners that use fans for these purposes. Combination burners are distinguished by the ability to burn air by using several types of fuel. Oil-gas and dust-gas burners are also widely used.
Choosing a gas burner for a hike
A camping gas burner is designed to solve a variety of tasks related to cooking and heating a tent. Preferred are standard atmospheric burners or tourist stoves, the power of which is 3-4 kW, and the power source is an isobutane mixture. The ignition mechanism does not play a significant role, and therefore there is no point in overpaying for models with piezo ignition.
Choosing a torch for soldering
Soldering or cutting cannot be done using ordinary gas torches. For this purpose, powerful and productive devices are needed, equipped with an air blower or an injector. By adjusting the composition of the supplied mixture, you can achieve the flame of the required strength and perform the necessary work related to soldering metals or other materials. Professional torches used for soldering are expensive, and therefore they are needed by a narrow circle of specialists. The power of such devices is 10-15 kW.
In the following articles, our experts tell you how to choose a travel backpack and the secrets of choosing a thermos.