Flotation is a purification method.
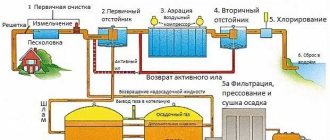
Effluent undergoing treatment passes through a settling tank, in which large fragments sink to the bottom because they weigh more than water. Non-sinking large particles remain in the water; flotation is a cleaning method that helps to isolate complex contaminants of this type. The method is one step at the stage of the sewage purification process.
What is the essence of the flotation method? The wastewater undergoes flotation to remove impurities that are lighter than the water composition. In English, the word flotation means “floating on the surface”, similar to the Russian word fleet. The purpose of the method is to raise particles whose density is close to water to the surface, and they do not sink.
Cleaning of drains
This method is successfully used to treat wastewater containing fibers, petroleum products, oils and fats, as well as other substances that are poorly soluble in water. Previously, wastewater is converted into a suspension and emulsion using special substances.
The flotation process is based on the ability of gas bubbles to attach to particles, helping them float to the surface of the liquid.
Flotation based on physical laws.
Flotation occurs due to compliance with physical and chemical laws. It is based on the property of substances to be wetted. The peculiarity of the particles in this process affects their behavior when they are in the boundary state between liquid and gas.
The following types of particles are distinguished:
1.hydrophilic type has good wettability.
2.hydrophobic type does not wet out
If the substance is hydrophobic, it is amenable to flotation and is isolated by this method.
Efficiency of the method.
Certain conditions and factors contribute to increasing the effectiveness of the method.
The most important factors are considered to be:
1.level of hydrophobicity of substances. If this property is high, the substances will quickly join the air bubbles, forming large sludge complexes. Some particles include substances of two compositions, hydrophobic and hydrophilic types. Reagents are added to waste water to increase hydrophobicity and speed up the flotation process.
2.level of strength and size of foam bubbles. During flotation, the bubbles must reach a size at which they can easily rise to the surface.
Attention! Bubbles with a very large size float up faster, not having time to attach pollutants in sufficient quantities. The bubbles must be durable in order to be less likely to collapse as part of the flotation complex.
3.The foaming process must be uniform and continuous. Efficiency is determined by the uniform distribution of bubbles in the water and their frequency.
These factors are increased by adding special reagents to the sewage.
General principles of the method
The simplest act of flotation is the attachment of insoluble particles (for example, mineral, oil or any other) to air bubbles. The success of purification depends on the speed at which a bond is formed between the particle and the bubbles, on the strength of this bond and on the duration of existence of this complex. Which in turn is determined by the nature of the particles, their tendency to be wetted by water and the characteristics of their interaction with reagents. Thus, flotation is a process that depends on many factors.
An elementary act can be carried out using one of the following mechanisms:
- bubbles form immediately in suspended particles;
- suspension particles attach to the gas bubble upon collision with it;
- a small bubble forms on the surface of the particle, which combines with another upon collision and increases in volume.
The complex that is formed during the flotation process can float in a practically stationary environment only if the lifting force of the gas bubble is greater than the weight of the particle. This will lead to the formation of a foam layer on the surface of the water being purified.
In addition, the surface areas of bubbles and particles at the point of contact must be in a certain ratio. The adhesion forces increase in proportion to the size of the particles in the square, since the perimeter of their connection is limited by the size of the largest of their faces. And the tearing force directly depends on the mass of the contaminating particle (i.e., its linear dimensions in a cube). Thus, when a certain particle size is reached, the detachment forces exceed the adhesion forces. This means that for successful wastewater treatment by flotation, not only the nature of the connection between the suspension and bubbles is important, but also their size.
Kinds
The main active force in flotation purification is microscopic air cavities , which are obtained by direct separation from water or by crushing the gas component throughout the entire thickness of the liquid.
The method of obtaining air-saturated wastewater and crushing bubbles determines the classification of flotation methods.
With the release of air from the solution
Purification technology by releasing bubbles from a contaminated aquatic environment involves the use of pressure or vacuum.
Nadornaya
During pressure flotation cleaning, an air stream is pumped into the solution pumped into the saturator. After which the mass enters the flotation chamber, the pressure in which is equal to atmospheric pressure.
Reference . A sharp pressure drop creates a hydraulic load on the wastewater, as a result of which “boiling” occurs in the thickness of the water layer with the release of a large number of bubbles.
The resulting air capsules fix impurity particles on their surface;
aggregated complexes rise to the top layer, forming flotation foam. The number of microscopic air cavities can be adjusted by the pressure intensity , which allows the method to be used for a large amount of contaminants at a concentration reaching 5 g/l.
For more information about the pressure method of flotation wastewater treatment, watch the video:
Airlift
To remove waste from wastewater supplied to the chemical industry, an airlift modification of the method is often used. Cleaning occurs due to differences in heights at which the tanks are located , which significantly reduces energy costs for flotation.
The wastewater tank is located at a height of up to 30 m. The dirty flow enters the aerator, located much lower. Air is pumped into it, and then the mass is lifted through airlift pipes into the flotation chamber.
The rise of the air flow stimulates the formation first of air bubbles and then of aggregated complexes. All the dirt floats up in the upper layer, and relatively purified water remains below, which is subjected to further processing to bring it back to normal.
Vacuum
With this cleaning method, the aqueous solution is aerated to saturate it with air, then the undissolved air part is removed in a special compartment. In the flotation chamber, the resulting solution enters a zone of low pressure, the values of which are less than atmospheric values.
This results in abundant bubbles in a calm environment. The adhesion of impurities to the surface occurs firmly and remains reliably until the aggregate floats to the surface completely.
Each of the presented methods makes it possible to successfully purify industrial wastewater with not very large dispersed particles of impurities.
With the solution saturated with air
For certain types of wastewater contamination, the solution is additionally saturated with air using one of several possible algorithms.
Impeller
Saturation through small special turbines - impellers allows you to obtain small bubbles that can adsorb molecules of fats and petroleum products.
The rotation of the blades oriented upward creates a vortex movement in the water mass, leading to the formation of a large number of small bubbles of equally small size.
The impeller rotates at a strictly specified speed , ensuring the formation of a large number of small bubbles.
Important! Exceeding the speed of rotation of the blades can interfere with the formation of aggregates with polluting particles, and is therefore unacceptable.
The method allows you to remove insoluble particles from wastewater when their concentration in solution reaches 3 g/l, as well as components of oil fractions and fat molecules.
Non-pressure and pneumatic
Without pressure, the solution can be saturated with air by rotating the impeller connected to the pump. In a non-pressure method, relatively large air bubbles are formed, which fix on themselves :
- fibers;
- wool particles;
- fat capsules.
The resulting units rise upward in a complete state, cleaning the wastewater.
When using pneumatic air injection, pipes with nozzles are placed at the bottom of the flotation tanks. Pneumatic installations with nozzles on the bottom are used if the environment contains aggressive substances whose contact with rotating working parts must not be allowed.
Bubbler
Porous structures with equally small cells are sometimes used as sources for saturating wastewater with air bubbles, through which an air flow is passed at a given speed.
The pore diameter does not exceed 20 microns, which makes it possible to supply microscopic portions of air.
The advantage of the method is the intensive saturation of wastewater, the disadvantage is that small cells are often clogged with mud impurities . If the volume of wastewater is not very large, bubbling is carried out in a chamber with porous caps. Aggregated dirt forms foam in the top layer, which flows outside the tank through a special channel.
Electrolytic
Electrolysis of wastewater demonstrates greater efficiency, during which hydrogen is released at the cathode and gaseous oxygen at the anode electrode. The intensity of electrolysis can be controlled by the composition and shape of the electrodes.
The gases released, especially when anodes made of aluminum or iron alloys dissolve, further increase the rate of aggregation of impurities, contribute to the disinfection of water, and simplify its subsequent purification.
Chemical and biological nature
The use of mechanical methods for the formation of aggregates and their floating to the surface does not always lead to the complete release of dispersed particles. of an oxidizing or carbonate nature are used as an additional source of gas bubbles
Chlorine-containing oxidizers carry out disinfection and release molecules into space
- active chlorine,
- oxygen.
Carbonate additives initiate the formation of carbon dioxide. The resulting gas bubbles adsorb impurities and carry them into the surface foam layer.
During flotation treatment of wastewater with a large content of organic waste, most often of domestic origin, loose foam is formed. To compact it, biological technology is used, which consists of heating the mixture and leaving it for several days.
Due to the presence of microorganisms, biomass actively ferments under such conditions, releasing gases that
- penetrate into the foam
- compact it,
- additionally remove impurities from the solution.
Methods for saturating water with bubbles
There are many techniques that ensure the appearance of gas bubbles in wastewater. The main methods used in flotation are:
- Compression (or pressure) method, based on increasing the solubility of air in water with increasing pressure.
- A mechanical method based on intensive mixing of liquid with air.
- Passing wastewater through porous materials, causing it to disperse.
- An electrical method based on the process of electrolysis of water, accompanied by the appearance of gas bubbles.
- A chemical method that causes the formation of bubbles during chemical reactions of certain reagents with wastewater components.
- Vacuum method, characterized by a decrease in pressure.
Types of technology
Various methods differ from each other primarily in the saturation of the liquid with gases. It is common to talk about:
- release of air from the solution;
- dispersion when using mechanical action;
- the use of porous materials to supply air flow;
- chemical technology;
- biological flotation;
- use of electricity.
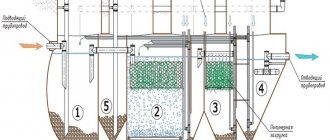
Installations that carry out the flotation of surfactants and other impurities in liquids can be two-chamber or single-chamber. If there is only one chamber, then the liquid in it is filled with gases and polluting components are released from it. If there are two chambers, in one there is contact with the air flow, and in the other the mixture can settle, during which the sludge floats up and the liquid becomes clarified.
Pressure flotation
It is most effective for extracting fine and colloidal suspensions of low concentration. The purified water is saturated with air under pressure up to 7 MPa in a special reactor - a saturator. After the water leaves it, the pressure drops sharply to normal (atmospheric), which provokes an intensive process of release of air bubbles.
In order to significantly increase the efficiency of water purification, flotation is combined with coagulation and flocculation. Both of these techniques increase the size of undissolved particles. Coagulants are both inorganic compounds, usually salts of ferric iron or aluminum, and some organic substances. Flocculants are special polymers whose molecules in an aqueous environment form a charged network that can attract polluting particles, which leads to the appearance of flocculent aggregates.
Areas of use
- Enrichment of minerals (non-ferrous metal ores, rare and trace elements, coal, native sulfur);
- Separation of complex ore minerals;
- Salt separation;
- Wastewater treatment, in particular for the separation of droplets of oils and petroleum products.
- Yeast production (concentration method)
Around the world, thanks to flotation, deposits of finely disseminated ores are brought into industrial production and the comprehensive use of minerals is ensured. Factories produce up to five types of concentrates. In some cases, flotation tailings are not waste, but are used as building materials, fertilizers for agriculture, and for other purposes. Flotation is the leading process in the beneficiation of non-ferrous metal ores. The use of recycled water is being introduced, which reduces pollution of water bodies.
Installations and technological schemes
Installations that carry out pressure flotation can be located not only indoors, but also outdoors. So, the former are suitable for small volumes if the water flow is no more than 20 m3/h, while the latter have much higher productivity. Often a combined arrangement of structures is arranged, when large objects, for example, a saturator and a flotation chamber, are located in the open air, and pumps are indoors.
If installations are located in conditions where the air temperature may drop to negative values, it is necessary to provide a foam heating system. A classic installation for compression flotation consists of the following equipment:
- Pump for supplying liquids.
- A compressor for supplying air (or any gas) to the water treatment system.
- A saturator (another name is a pressure tank), in which air is dissolved in wastewater.
- Flotation chambers, if the process includes a stage of coarsening of suspended particles.
- A reagent device, including devices for dosing and mixing reagents with the liquid to be purified.
- Cleaning process control system.
Technological schemes providing for wastewater treatment by flotation with increasing pressure can be:
- Direct-flow, when the full volume of the liquid being purified passes through the saturator.
- Recirculation, when only 20 - 50% of the clarified liquid passes through the saturator.
- Partially direct-flow, when about 30-70% of untreated water enters the saturator, and the rest is supplied directly to the flotation chamber.
When choosing one of these schemes, the physicochemical properties of the wastewater being treated, requirements for the degree of purification, local conditions and economic indicators are taken into account.
Technology and precision
Flotation makes it possible to identify bacteria that are resistant to acids, as well as to conduct an immunological analysis. The simplest and easiest to implement method is gravity flotation, also known as standing flotation. It requires relatively little time to implement.
An alternative option is to use medical centrifuges. This method is more sensitive, its results are approximately eight times more accurate. If the patient's organic secretions contain a small percentage of helminths, the gravity method may show their absence, but this result will be false. To be sure of the accuracy of the results, centrifuges should be used.
Electroflotation
This method began to be used in the second half of the 20th century. Then it was discovered that electrolysis gases are much more effective than inert gases or air in increasing the intensity of flotation. This makes it possible to isolate water-insoluble petroleum products, lubricating oils, and poorly soluble compounds of heavy and non-ferrous metals, which form stable emulsions in wastewater. But in addition to electrolysis gases, the removal of some impurities is influenced by an artificially created electric field in which charged particles move towards oppositely charged electrodes.
A significant disadvantage of electroflotation is low productivity, high cost of electrodes, their wear and contamination, as well as explosion hazard.
Pros and cons of the cleaning method.
The flotation method is considered popular. The method is used for industrial wastewater and in urban treatment systems.
Flotation has its positive characteristics:
1.low price method.
2.No complex special equipment is required.
3. Some particles are subject to flotation faster than they would settle to the bottom.
4.Even petroleum products can be extracted from water using this method.
5. The sludge that is formed contains almost no water, so its loss is small.
The method has not only advantages, but also disadvantages.
The disadvantages include:
1. not all dirt particles can be removed by flotation, but only those that are hydrophobic.
2.additional costs for reagents that have to be used in some situations.
3. any type of dirt has its own removal characteristics; there is no single method for extracting suspensions of different types.
Ore beneficiation
The flotation process is successfully used in the primary processing of all kinds of ores, making it possible to separate a valuable fraction with a high content of metal or its compounds. It is based on differences in the surface properties of the separated minerals.
Ore flotation is a three-phase process:
- the solid phase is a crushed mineral;
- the liquid phase is the pulp;
- the gas phase is formed by air bubbles passed through the pulp.
Flotation can be foam, film or oil, depending on the form of the product formed on the surface of the liquid phase.
It is important!
In modern industry, various ores are highly valued; not all of them are hydrophobic, which means that the described technology will not work for their extraction. Then chemical compounds - reagents - are used. These are components due to which the target particles either acquire hydrophobic properties or lose them.
The following reagents are available:
- foam formers;
- regulators that increase hydrophilicity;
- gatherers;
- activators that create conditions in which collectors are attached to the surface;
- depressants that prevent an increase in the hydrophobicity of substances (used to make the process more selective).
Reagents used
To increase the efficiency of purification, chemical collectors are used:
- coagulants - reagents that promote the formation of flakes and are iron and aluminum salts;
- flocculants (polyacrylamide compounds) – substances that create larger and more stable flakes (flocs);
- acid and alkaline reagents that allow you to adjust pH. They are added to water to ensure normal operating conditions for the two previous types of reagents.
To stabilize foam formation, pine oil, phenols, and cresol are also used. They help protect air bubbles from destruction, making them elastic. This helps remove more contaminants from the sewer.
The use of chemical reagents to improve the process requires precise dosage selection, which can only be achieved experimentally.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of flotation devices has both advantages and disadvantages. The advantages include:
- ease of machine maintenance;
- low cost of most methods;
- high quality and speed of wastewater treatment.
Using the technique, you can remove most of the fine impurities, but not all. Disadvantages also include the need for additional use of reagents to increase the degree of hydrophobicity of mud particles. When using an electric flotator, it is necessary to fine-tune the device to create bubbles of the required diameter.
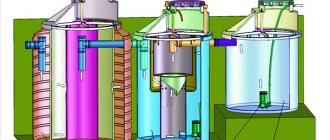
Design and purpose of flotators
Industrial flotation device
Liquid purification is carried out using flotation block units. The main components of the devices are:
- a container with a pump that mixes oxygen with liquid and reagents;
- flotation tank with a valve to eliminate excess air;
- degasser to remove residual oxygen.
Flotation blocks are not used as independent purification tools. They are used in combination in treatment plants of industrial enterprises and car washes, since they require preparation - mechanical treatment of sewage.