Elements of pumping units
The borehole pumping unit has an SSN drive, which allows the object to be moved directly under the influence of sucker rods. Among its main operating elements, according to GOST 2002, well sucker rod pumps stand out:
- one-piece fixed-type cylinder with extensions;
- movable pump plunger;
- valves, including suction and discharge valves;
- locks.
Each of the CH extensions is screwed onto the cylinder from all sides. They must push the plunger out of it while the pumping structure is operating. Industrial well rigs operate without residual deposits inside the stationary cylinder. As a result, the plunger does not jam, so the repair of rod pumps can be carried out without any problems. Insert pumps used in domestic industry are equipped with the following types of components:
- Castle support.
- Cylinder.
- With a plunger.
The borehole pump installation is under tension, so high-alloy steels are required to manufacture parts for various types of well pumps or sucker rod pumps. The duration and reliability of the useful use of pumping equipment depends on these materials. The tightness of their fit is ensured by the high precision of the production of parts for pumps. This also applies to threaded connections. All elements of the installation are completely interchangeable. Among the main elements of its design, there is a ground part, consisting of the following links, which are:
- Column.
- Chain with tension screw.
- Counterweight with stop.
- Suspensions (cable rope, wellhead rod).
- Rope block assembly.
- Tooth coupling.
- Asterisks driven and leading.
- Rope slip limiter.
- Fencing and compartment door.
- Belt drive casing.
The design of the pumping unit with an electric motor and control station provides several platforms:
- driven sprocket maintenance;
- gearbox;
- rope blocks;
- front rotary.
The equipment has a complex, which is a ground segment of the installation, which is called a pumping machine. The elements of this design remained unchanged for many years. The installation with a differential converting mechanism and gearbox is equipped with a V-belt drive that allows you to drive the pumping machine.
Russian enterprises produced exclusively the chain drive for sucker rod pumps. The devices that replaced the manual pump have been still in the process of improvement since 2002.
This is interesting: Deep well pumps: operating principle, types, selection rules
Operating principle of SRP
- Operating principle of SRP
- Types of sucker rod pumps
- Advantages and disadvantages of pipe and insert pumps
- Operating principle and marking of a rod pumping unit
- Sources:
SRP pumps are designed for pumping liquids from wells with a temperature of no more than 130 degrees, water cut of no more than 99% by volume, viscosity of up to 0.3 Pa*s, mechanical impurity content of up to 350 mg/l, and free gas at the intake of no more than 25%.
The sucker rod pump consists of a solid fixed cylinder, a movable plunger, suction and discharge valves, a lock (for plug-in pumps), connecting and installation parts.
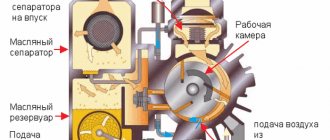
A plunger pump consisting of a cylindrical body 1 (cylinder), inside of which there is a hollow piston 2 (plunger), is lowered into the well on a string of lifting pipes. A discharge valve 3 is installed in the upper part of the plunger. A suction valve 4 is installed in the lower part of the stationary cylinder. The plunger is suspended on a column of pumping rods 5, which transmit to it reciprocating motion from a special mechanism (pumping machine) installed on the surface.
As the plunger moves upward, liquid from the well enters through the suction (receiving) valve into the pump cylinder, since a pressure is created under the plunger much less than in the well. As the plunger moves downwards, the suction valve closes under the action of liquid pressure under the plunger and the volume of liquid from the cylinder through the hollow channel of the plunger and the open discharge valve, the opening of which occurs from the pressure of the liquid under the plunger and the hollow channel of the plunger, enters the lifting pipes.
During continuous operation of the pump, the liquid fills the volume of the lifting pipes and is then directed to the surface.
The most widely used types of pumps are: inserted and non-inserted (pipe).
Rod pumps are used to supply fluid from deep wells. Most often, a sucker rod pump is used in oil production.
A check valve is installed in the piston of the rod pump, allowing fluid to flow in one direction.
The closing element of the presented valve is a ball.
As the piston moves downward, the ball moves up and the valve opens, allowing fluid to pass through the piston.
When the piston moves upward, the ball is pressed against the seat, and the valve closes under the pressure of the liquid column.
Design features and principle of operation
The main design elements of a sucker rod pump, which is placed in a well on a special column consisting of lifting pipes, are:
- a cylindrical body, in the inner part of which a hollow piston (displacer), called a plunger, is installed;
- a discharge valve installed in the upper part of the displacer;
- a ball-type suction valve, which is located in the lower part of a fixed cylindrical body;
- pumping rods connected to a special mechanism (pumping unit) and a plunger and imparting to the latter a reciprocating movement (the pumping unit itself, which drives the downhole rod pump (SRP), is mounted outside the well - on the surface of the earth).
The device of a sucker rod pump
The operating principle of deep-well sucker rod pumps is quite simple.
- When the plunger moves upward, a vacuum of pressure is created in the lower part of the pump chamber, which facilitates the suction of the pumped liquid medium through the inlet valve.
- When the plunger begins to move downwards, the suction valve closes under the influence of the pressure of the pumped liquid medium, and it begins to flow into the lifting pipes through the hollow channel of the piston and the discharge valve.
- During the non-stop operation of a deep-rod pump, the liquid medium it pumps begins to fill the internal volume of the lifting pipes and is ultimately directed to the surface.
Operating principle of SRP
Terms of use of ShSN
Manufactured types of downhole sucker rod pumps lift liquid. The state standard provides for the division of tubing columns according to the fastening method into 2 types:
- Plug-in (NSV).
- Non-insertable (NSN).
A pipe pump or pump, having a VC (suction valve) seat, is equipped with a cylinder, which is lowered into the well on the tubing. The plunger, which contains valves, must be lowered into the well before the suction, and then enters the cylinder. This is done through rods. To ensure the connection of the installation plungers with the balls of suction-type valves, special rods are used.
The disadvantage of the NSN is not only the complexity of the assembly process, but also the long time it takes to lift the device to the surface. Eliminating structural faults is difficult. Insert pumps are assembled on the surface, and then they are lowered underground on rods inside the tubing columns to a certain depth of the well.
A pipe well pump requires that when lifting the pump cylinder of the installation from underground, it must be removed entirely. This condition is considered the main distinguishing feature of NSN from NSV. Insert pumps increase the speed of hoisting operations by 2-2.5 times, which facilitates the work of workers carrying out well repairs.
An insert pump has a lower flow rate than a non-insert pump. This is due to the presence of pipes of a given diameter. The descent of the NSV is carried out on rods, and the strengthening or compaction of the element, if there are landings, is carried out on the locking support of the cylinder. It should descend onto the tubing.
The lifting of the pump from the oil well using the NSV should be carried out simultaneously with the removal of the rod string at a significant depth of descent. Operation of the NSV is carried out if the well has a low flow rate. The movement of the NSN plunger is vertical, since the descent and ascent are carried out through the rods.
ADAPTATION TO CHANGING FISHING CONDITIONS
The design of the UVNP is distinguished by a number of features that ensure the adaptation of our equipment to changing fishing conditions. This is, in particular, a wide range of control of the installation’s performance within a narrow range of rotation speed.
The equipment operating as part of the “smart well” must provide the required range of change in the installation’s flow. This installation allows you to do this. The high volumetric efficiency of a screw pump remains practically unchanged when regulating productivity or changing pressure, so we do not need to take into account the adjustment characteristics, which also simplifies the process of regulating and selecting the necessary parameters.
Another feature is ensuring maximum well production through minimal immersion under the dynamic fluid level and creating a constant depression on the formation.
And, finally, the efficiency of changing operating parameters due to the low inertia of the rod string at low rotation speeds. This indicator is important because if we are talking about regulation, then we must understand that technically this problem can be solved by fairly simple means without additional negative consequences.
The rotary nature of the rods, rather than the reciprocating nature of the rods, is also more preferable when changing the nature of the movement, since in this case many of the problems that are typical for the reciprocating movement are eliminated.
Option for equipping a “smart” well with UVNP
Types of sucker rod pumps
There are two main types of sucker rod pumps:
- plug-in
- pipe (non-insert)
Pipe Rod Pump
The pump plunger moves in a sleeve that is attached to the pipe string. The sleeve is installed in the well along with the pipes; in addition, it can only be removed together with the pipes.
There is a check valve 1 in the plunger. Another valve 2 is attached to the bottom of the sleeve.
When the plunger moves downwards, valve 1 opens, passing liquid from the well into the cavity above the plunger, valve 2 is closed at this moment.
When the plunger moves up, valve 1 closes, the plunger displaces liquid up the well. Valve 2 is open at this moment, fluid from the formation fills the cavity in the well.
Insert Rod Pump
The plunger and sleeve of the plug-in rod pump are placed in the already installed pipe string.
When the plunger moves downwards, valve 1 opens, allowing liquid to pass through, valve 2 is closed.
When the plunger moves up, valve 1 closes, allowing the liquid to flow back, the liquid rises up the well. Valve 2 is open at this moment, liquid from the formation flows under the plunger.
Types of wellhead equipment
A wellhead rod, which is a special rod, is necessary to connect the rod column to the rope suspension. It has a polished surface and is produced without heads with the type of thread provided by the standard. To protect the polished rod from corrosion, painting, galvanizing, and inhibition are carried out. The functions performed by the PS wellhead equipment are as follows:
- ensuring sealing of the annulus;
- well production withdrawal;
- tubing suspension.
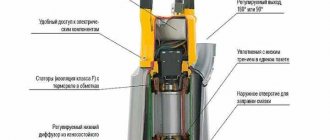
The pumping unit is equipped with wellhead equipment, including:
- Wellhead seal. Provides sealing of the outlet of the wellhead rod due to the stuffing box head.
- Tee. It is screwed into the tubing coupling; it is necessary for the removal of well products.
- Cross. Allows you to hang the tubing string on a cone in order to correctly position it relative to the well axis.
- Shut-off valves and check valves.
A ball joint is provided for self-installation of the stuffing box head. This is ensured in case of misalignment of the stuffing box rod and tubing, whose axes do not coincide. This is important to prevent wear of the sealing packing and to make it easier to change the special packing. The presence of a cross allows the instruments to be lowered into the annulus through a wellhead pipe with a valve.
This is interesting: Repair of centrifugal pumps - maintenance, adjustment, types of malfunctions
Complete set of pumping machine
Among the components of the pumping machine the following stand out:
- Frame.
- A stand in the form of a truncated 4-sided pyramid;
- Balancer equipped with a rotating head.
- Traverse with connecting rods.
- Gearbox.
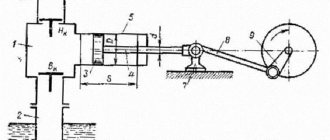
The SK package includes a set of pulleys that allow you to change the number of swings by discrete regulation. Changing and tensioning engine belts occurs quite quickly using a rotating frame-slide. The pumping machine is installed on a frame mounted on a reinforced concrete foundation. To fix the pump balancer, a pulley is used, which is called a brake drum. The head ensures the passage of the pumping unit during the process of repairing a well underground.
The movement of the balancer head in an arc involves its connection with the rods and the wellhead rod due to a flexible rope suspension that regulates the fit of the pump plunger into the CH cylinder. The amplitude of movement of the head of the balancer is adjusted by changing the area of the articulation of the crank with the connecting rod relative to the axis of rotation. Moving weights onto the balancer balances the action of the pumping machine. The process is considered as a balancing, rotary or combined rod balancing.
OPERATING PRINCIPLE AND ADVANTAGES OF SCP LINEAR DRIVE
However, despite the shortcomings of the SC, the use of ultrasonic pumping remains a very promising method of well operation, since it has a high potential for reducing costs per unit of extracted formation fluid.
Therefore, technologies aimed at increasing the efficiency of pulverizer pumping units are of particular interest to oil industry workers. One of the technologies that has recently appeared on the market is the linear drive (LP) of a sucker-rod deep-well pump of the LRP brand. This is a rack and pinion drive, with the help of which the reciprocating movement of the deep pump rod in the well is ensured by transmitting rotational motion from a reversible asynchronous motor through a gearbox and gear transmissions to a rack to which the polished rod is attached (Fig. 1). With each power stroke, the post is lubricated by immersion in a completely enclosed oil bath. And thanks to this kinematic rack and pinion transmission, the movement of the rod can be adjusted over a wide range of specified parameters. The drive is installed on the christmas tree faceplate directly at the well. No additional supporting structures or foundation are required.
During the operation of the LP, electricity is consumed only during the upward stroke of the rod and sucker rods, and during the downward stroke, electricity, on the contrary, is generated and used to brake the system. The LP control station is designed to automatically regulate the operating modes of the pumping unit in the optimal range of liquid inflow. In the case of LRP, the drive and motor control functions are implemented using a controller and software from the system developer (UNICO) based on the developed mathematical model of the well. This allows the system to control production parameters in real time and automatically adjust to optimal production modes without operator intervention.
Rice. 2. Unicon linear drive system at a well in the Krasnoyarsk field
Main varieties
According to their design, sucker rod pumps can be:
- plug-in;
- non-insertable.
Lowering of plug-in sucker-rod deep-well pumps into a well, as well as their removal from it, is carried out in assembled form. In order to perform such an operation, the plunger is placed inside the cylinder, and the entire structure on the sucker rods is lowered into the shaft.
Types of SRP pumps by method of attachment to the column
Plug-in SRPs are also divided into two types of devices:
- plug-in pumps with a top lock (HB1);
- pumps, the lock of which is located in their lower part (HB2).
Insertion devices are used primarily for servicing deep wells, which are also characterized by a small flow rate of the liquid medium pumped out of them. The use of such SRP pumps, to remove which it is enough to lift the rods to which the entire pump structure is connected, greatly simplifies well repairs if the need arises.
Scheme of operation of the installation with a sucker rod pump
In order to place a non-insert-type sucker rod pump into a well, more complex steps must be performed. A cylinder is first placed into the well, for which tubing is used, and only then, using rods, a plunger with valves is lowered into the already installed cylinder. Removing a deep-rod pump of this type is also carried out in two stages: first of all, the plunger with valves is removed from the pump cylinder, and then the cylinder with tubing is lifted from the well.
Non-insertable devices are also divided into several categories:
- pumping units without a catcher (LV);
- non-insert deep-well pumps with a gripping rod (НН1);
- non-insert pumps with catcher (НН2).
Deep-well sucker rod pumps are produced in various sizes and designs, including special orders for operation in special conditions
Among the types of non-insert equipment listed above, the most popular are devices equipped with a catcher (HH2). The high popularity of the latter is explained by the fact that the mechanism for emptying them is characterized by a simple design and, accordingly, greater reliability in operation.
The choice of equipment of a particular model is made depending on the specific operating conditions, as well as on the characteristics of the liquid medium that is planned to be pumped out with its help.
Downhole rod pump, version NN2B
Advantages and disadvantages of chain drive
Model PC-80x6.1 in our country is produced by Izhneftemash JSC. Domestic equipment was created based on the development of the American company Weatherford called Rotaflex. The drive structure is equipped with a frame, which is placed on a separate base. During the equipment assembly process, the following parts are installed on the frame:
- electric motor;
- gearbox;
- belt drive;
- driving and driven sprockets;
- carriages with counterweight;
- rod columns
To connect the elements, flexible links of a continuous type are used. In the oil industry, not only balancer drives, which are considered traditional, are widely used, but also non-balancer drives, i.e. chain drives. The advantages of a chain drive for a downhole sucker rod pump can be as follows:
- The dimensions of unbalanced drives and their weight depend less on the stroke length than the parameters of these elements of a balancing-type pumping machine.
- The speed of movement of the chain drive rods is 1.6-1.7 times less in part of the stroke than the column lifting speed parameter per cycle for balancing-type pumping machines.
- Equipment productivity increases, and energy costs for lifting well product are reduced.
- The power utilization factor (PUF) increases because the electric motor load on the rod pump drive is uniform.
The load of various types placed on the rods is reduced under conditions of quiet pumping of well fluid over a long stroke. The listed advantages make it possible to harmonize the following types of indicators characterizing the operation of the equipment:
- pumping out a composition with a high degree of viscosity;
- the number of accidents that occurred with the rods;
- wear of pipes, including rods;
- well pump filling factor;
- the service life of the wellhead seal and its performance.
Despite all the reliability of the device, the balance drive has the following disadvantages:
- Short life of the gearbox.
- Destruction of parts included in the transforming mechanism.
- Complicated rearrangement of connecting rod pins.
- High level of labor intensity in the movement of goods when achieving their equilibrium.
- Mass imbalance.
- The importance of arranging a foundation for installation, which has a high cost.
Modifications of Russian-made pumps differ in connection parameters.
Non-insertable pump with a short cylinder and a long plunger NNBKU
| In connection with the increasing requirements of oil producing enterprises for equipment for oil production, caused by the complicated conditions of its operation, the Perm Oil Engineering Company (PKNM) proposed a new design of a downhole rod pump (SSP) - a downhole rod pump with a short cylinder, a long plunger, with non-removable enlarged suction valve and knock-down pin. For different pump flows, models NNBKU-44 and NNBKU-57 were developed, made in accordance with the technical specifications TU 3665-007-26602587-2013. In contrast to serial pumps, the new design of the downhole rod pump developed and put into production has a number of advantages:
Currently, the pumps are operated in Tatarstan, Bashkortostan, Kazakhstan and Sakhalin. The new PKNM equipment made it possible to increase the operating time by 1.5–2 times compared to the basic one. (PKNM has a patent for a utility model.)p |
How to read labels
In order to determine which category a deep-well sucker rod pump belongs to, as well as to find out what characteristics such a device has, it is enough to decipher its markings. This marking, which is not very difficult to decipher, looks like this:
XXX X – XX – XX – XX – X
The letters and numbers present in such markings consistently indicate the following parameters:
- type of sucker rod pump, which, as mentioned above, can belong to one of the following categories: HB1, HB2, NN, HH1, HH2;
- type of design of the cylinder and design features of the device as a whole;
- nominal diameter of the plunger, measured in mm (modern models of sucker-rod deep-well pumps according to this parameter can belong to devices of the following categories: 29, 32, 38, 44, 57, 70, 95 and 102 mm);
- the maximum stroke that the plunger can make (in order to find out how far in mm the plunger moves, the value in the marking must be divided by one hundred);
- head in m of water Art., which is capable of providing the presented deep-well pump (this value in the marking must also be divided by one hundred);
- landing group (according to the degree of increase in the distance between the plunger and the inner walls of the cylinder, the devices in question can correspond to one of the following landing groups: 0, 1, 2, 3).
Groups of pump landings depending on the size of the gap between the cylinder and the plunger
Structural elements
The performance and efficiency of using deep-well sucker-rod pumps are determined by the following elements present in their design:
- cylinders, which can be solid or composite;
- plungers (ordinary or sandblasting type);
- ball-type valve assemblies, the closing elements of which are the seat and the ball;
- anchor shoes used to secure plug-in type sucker rod pumps in tubing pipes (when installing such elements, it is necessary to ensure that the suction cavity of the pump is sealed from the discharge cavity).
Of course, a mandatory element of the design of a sucker-rod pump is a rod - a round rod made of steel with upset ends. The main purpose of the rods, which can have different diameters (12, 16, 18, 22 and 25 mm), is to impart reciprocating movement to the plunger.
Sucker rod and coupling
Since the rods experience serious loads during the operation of a deep-well pump, high-quality steels are used for their production, and after production they are subjected to normal annealing and high-frequency hardening.
Rod pumping devices, depending on the design features of the plunger and cylinder, as well as the location of their anchor shoe, can fall into one of 15 categories.
The photo shows a ball-type suction valve housed in a cylindrical body