Many of us have to deal with the need to replace water pipes. You can solve this issue yourself or with the help of a professional technician. When replacing a pipeline, it is important to understand what diameter of pipes for the water supply is optimal from a technical point of view. There is a wide variety of pipes on the market today, which vary in material quality, size and diameter. Our article will tell you what diameter products are suitable in this or that case.
Pipe dimensional characteristics
Modern water supply is a rather complex structure, the important element of which is pipes. The most popular are metal-plastic, steel and copper pipes. The main physical characteristics that determine the size of water supply pipes are:
- Inner diameter is a single characteristic for units and pipes of a water supply system. The internal diameter must be the same for both the pipes being connected and the fittings connecting them.
- Nominal diameter is a nominal value, measured in millimeters, used when installing water pipes.
- Wall thickness.
- Pipe length.
It is important to choose the correct diameter of plastic pipes for the water supply, otherwise you may encounter constant noise and problems in the water supply. This is due to flow turbulization, a process that occurs as a result of the use of small diameter pipes.
Purpose and characteristics of plastic pipes
To designate polypropylene pipe products in the international format, two letters are used - PP. This material is produced by the chemical industry; thermoplastic polymers are used to make it.
The specified pipe products are produced according to a certain standard, which regulates the sizes of plastic pipes and their characteristics.
As an example, here are some data and their corresponding standards:
- The density of the material according to GOST 15139 is 0.9 g/cm3.
- The melting point, determined by GOST 21553, reaches 1490C.
- The elongation of the material upon reaching the yield strength in accordance with GOST 11262 is about 50%.
- Tensile strength is regulated by GOST 11262, and can have a value of 34-35 N/mm2.
- The linear expansion coefficient according to GOST 15173 is 0.15 mm/m0C.
Relationship between characteristics
How does the length of the water pipe affect the diameter of the pipes?
The average flow speed in a standard water supply is 0.02 km/s. This indicator affects the selection of pipe diameter. How to calculate the diameter of a water pipe taking into account the length of this communication:
- If the length of the system is less than 30 meters, you should pay attention to pipes with a diameter of 25mm.
- If the length of the system is more than 30 meters, the use of pipes with a diameter of 32 mm is considered relevant.
- If the length of the system is less than 10 meters, pipes with a diameter of 20 mm are perfect.
The standard length of domestic water supply pipes is 4 meters. But in practice, pipes up to 14-15 meters long can be used.
When choosing long products, special attention should be paid to the quality of fittings, couplings and other connections. They will ensure reliable and durable operation of the water supply system.
Why does the diameter of the pipes determine the throughput of the water supply system?
The diameter of the pipe determines an important characteristic - the throughput of the water supply system. For example, pipes with a diameter of 25 mm can move up to 30 liters of water within a minute. For a 32 mm pipe, this figure increases to 50 liters.
It should be borne in mind that an ordinary faucet in the kitchen or bathroom can flow no more than 5 liters of water. Thus, the choice of pipe diameter directly depends on the consumption of water resources.
The more points of water consumption, the larger the diameter of the pipes should be. Pipes for hot and cold water supply can be selected of the same diameter, but the wall thickness of pipes for hot water should be an order of magnitude higher.
When deciding what diameter of water supply pipe you need, pay close attention to the following parameters:
- The length of the water pipe.
- Number of proposed joints.
- Number of turns.
- Water pressure in the system.
Complex technical calculations used by professionals make it possible to calculate the complex influence of these factors on the plumbing system. However, their use is hardly advisable for premises in an apartment building.
Scroll
First, let's look at the list of materials.
- Polyvinyl chloride is used for the manufacture of pressure and non-pressure sewerage . Water pipes made from this polymer are not widely used due to the combination of fragility and low (no more than 60C) operating temperature.
- Polyethylene is used primarily for laying pressure cold water supply pipelines . Temperature restrictions for this polymer are even stricter than for PVC: polyethylene begins to soften already at 45 - 50 degrees.
Note! Large-diameter plastic pipes used as sewer collectors are predominantly polyethylene.
- Polypropylene, on the contrary, is very heat resistant . The operating temperature range up to +95C allows it to be used for heating and hot water supply. In addition to pressure pipelines, plastic is used to construct sewerage systems.
- Cross-linked polyethylene is also used for these purposes: the formation of cross-links between polymer molecules radically changes its physical properties . The price of the material, of course, is noticeably higher than that of ordinary polyethylene.
Pipe made of cross-linked polyethylene and fittings for it.
Standard solutions
As a general rule, pipes with a diameter of 10 or 15 mm are selected for water supply, while the diameter of the pipes for the riser should be 25 mm. When purchasing pipes of the specified diameter, be prepared for the fact that these products do not have pinpoint accuracy. That is, a 10 mm pipe can actually have a diameter of 10-12 mm.
Complex plumbing work requires the use of pipes of increased diameter. They are optimal for operating a system with numerous joints, turns and permanent changes in water pressure.
To summarize: when choosing, pay attention to the following points:
- The more complex the design of the water supply system, the larger the diameter of the pipes.
- Hot water pipes require pipes with reinforced walls.
- The higher the water consumption rate, the larger the diameter of the pipes.
It is impossible to install a modern plumbing system without understanding the size of the pipes. The cross-section of such pipe products is of utmost importance.
Dimensions
Plastic sewer pipe elements are produced in accordance with GOST 51613-2000. The dimensions of PVC pipes are determined by such indicators as length, outer diameter, inner diameter of the socket, bore diameter, wall thickness. The outer diameter assumes the nominal size of the product. The throughput depends on the bore diameter.
The wall thickness determines the strength of the pipeline and what load the pipe structure can withstand.
They are classified according to strength class:
- lightweight SN2 structures with a wall thickness of less than 2.3 mm can withstand loads of up to 630 Pa;
- medium-heavy SN4 with walls from 2.5 to 12.3 mm depending on the diameter, cope with pressure from 600 to 800 Pa;
- heavy SN8 pipes with wall thicknesses from 3.2 to 15.3 mm, varying in diameter, withstand pressures from 800 to 1000 Pa.
The sewer pipeline, capable of withstanding pressure up to 1.6 MPa, is made of unplasticized PVC with a wall thickness of 0.5 to 1.9 cm. It is used for laying to great depths, under highways, in pressure sewer systems.
Sewer pipes are divided depending on the installation location. There are external and internal drainage systems. For the installation of internal sewerage, gray pipes are used. Standard diameter sizes are 32, 40, 50, 75, 110 and 160 mm. The wall thickness is not designed for high loads, varies from 1 to 3.2 mm. The length can be 0.3, 0.5, 1, 1.5, 2 and 3 meters.
Pipes for external drainage are orange. Depending on the amount of wastewater, diameters of 110, 125, 160, 200, 250, 300, 400 and 500 mm are produced. The wall size starts from 3 mm, the length varies from 1.2 to 3 m. For the arrangement of urban sewer systems, a diameter of 200 mm is used.
Depending on the pressure to which the walls of the pipeline are exposed, pressure and non-pressure sewer systems are distinguished. For internal gravity sewerage, pipes with a wall thickness of 1.8 to 3 mm are used. For street pipelines with free-flow drainage, products are produced with a wall size from 3.2 mm with a diameter of 11 cm to 1.2 cm with an outer diameter of 50 cm.
A pressure sewer system with pumping equipment requires increased strength characteristics. Plastic pressure pipes are made from unplasticized PVC with a greater thickness. The table shows possible wall parameters depending on the pressure tested from 800 Pa to 1.6 MPa.
Source
Characteristics of water pipes
When installing water supply networks, it is important to know the basic characteristics of pipe products. Materials of manufacture and diameters of water pipes are of great importance.
Material of manufacture
To decide which material is best to choose pipes from, you need to know the specifics of their use. Pipes for water supply are made from polypropylene and metal (steel, cast iron, copper).
The outer and inner diameters of plastic pipes for water supply differ from the same parameters of metal pipes. This is very important to take into account when making calculations.
This difference is an indicator of the thickness and strength of the pipe walls. And this directly affects the period of operation.
The advantages of steel pipes are strength and reliability. Their disadvantages include susceptibility to corrosion, heavy weight, and the formation of plaque on the walls.
Steel pipes of different diameters
The plastic analogue has more advantages, thanks to which it is more often chosen:
- light weight;
- does not corrode;
- simple and convenient installation;
- plastic;
- relatively inexpensive.
Polypropylene pipe (PN25) for water supply
However, there is a drawback here too. When the temperature changes, it undergoes linear expansion. A metal-plastic pipeline solves this problem. In addition, it is durable and reliable.
Therefore, it is very important to know all the above characteristics.
Water pipe length
The average flow speed is 0.02 km/s. Taking into account this indicator and the length of the water supply lines, you can select the diameter of the pipes:
- with a length of less than 10 m – 20 mm;
- for a length less than 30 m – 25 mm;
- for a length greater than 30 m – 32 mm.
For a riser, the diameter must be at least 20-25 mm. For a water pipe – 10-15 mm.
Diameter as the main parameter of the plumbing system
The main characteristic of water pipes is their size, which is their diameter.
Measured as an external and internal indicator. It is necessary to know the wall thickness, since this parameter is used to calculate the internal size.
It is important to remember that the correct choice of diameter will determine the throughput of the water supply and the quality of the supply of drinking water to the population.
When choosing the diameters of water pipes during the construction and repair of communication systems in a private house or high-rise, be sure to take into account the difference between the external and internal dimensions. If it is chosen incorrectly, plumbing fixtures may fail.
Diameter tables
When installing a pipeline made of dissimilar materials, some features should be taken into account.
For example, on products made of steel and cast iron, the outer diameter and wall thickness of the water pipe are indicated in mm.
If you need to connect pipes made of steel and plastic, special fittings are used. They are equipped with metal threads on one edge.
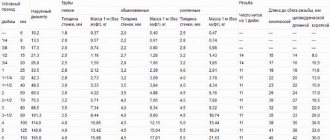
- Diameter table for steel water pipes
Steel pipe diameters GOST 854362989
- Size Chart for Copper Materials
Typical sizes of copper and steel pipes in inches and mm
A special feature of the marking of copper products is the indication of the external size in inches. Therefore, you need to know that 1" (inch) = 25.4 mm.
- Table of diameters of plastic pipes for water supply
Pipe diameters (PN10, PN16) for cold and hot water supply
On plastic pipes there is a designation of the outer size in inches and millimeters. It depends on the manufacturer.
Diameters inside and outside. Correspondence
The material becomes the basis for pipelines, which differ from analogues in their simple installation and ability to resist corrosion processes. Electrical energy does not flow through polypropylene. It rarely leaks and has an attractive appearance.
Pipeline systems for water supply made of polypropylene are used not only in domestic buildings, but also in agriculture, industry, external pipelines for water supply, sewerage, and water supply.
There is the following classification for polypropylene pipes:
- PPs . A special variety in which the internal environment moves while maintaining a temperature of 95 degrees
- PPR . The most common variety. The basis is a random copolymer. Conducts cold and hot water. Suitable for underfloor heating, conventional radiators.
- PPB . Block copolymer product. Relevant for systems that carry cold water, air, and heated floors. Polypropylene pipes have their own internal diameter.
- PPH. The base is homopolypropylene. The strength characteristics have been improved; it is used in ventilation shafts, cold water supply, and in various industries.
Polypropylene products can be reinforced or unreinforced. Fiberglass and aluminum foil are most often used as reinforcement. The foil is placed in the middle of the wall, or near the outer surface.
How to calculate the diameter of a water pipe
Select the diameter using ready-made tables; they contain average data.
It is important to take into account that if the pipeline is long, there are many turns and joints on it. In this case, choose a larger diameter.
You can also use special formulas that will help you calculate the diameter of the water pipe as accurately as possible.
If you cannot calculate it yourself, you can contact specialists in this field. They will help you do it right.
Accurate selection of diameter is a procedure that requires attention and a serious approach.
The external dimensions of cylindrical pipe products are one of the main parameters indicated in the marking. The internal diameters of water pipes are determined by subtracting the wall thickness multiplied by two. The exception is materials made of steel and cast iron, which are marked by nominal size. This circumstance should be taken into account when installing systems made of different materials.
| Diameters of steel water pipes | ||
| Thread size (mm) | Internal section (mm) | Designation |
| 20.4 — 20.7 | 12.7 | 1/2″» |
| 22.4 — 22.7 | 15.9 | 5/8″» |
| 25.9 — 26.2 | 19.0 | 3/4″» |
| 29.9 — 30.0 | 22.2 | 7/8″» |
| 32.7 — 33.0 | 25.4 | 1″» |
| 45.8 — 46.2 | 38.1 | 1/5″» |
| 57.9 — 58.3 | 50.8 | 2″» |
The marking indicates the outer size and wall thickness. For example, with a diameter of 76x3 - a product with an outer section of 76 mm, a wall of 3 mm and an internal section of 70 mm. To connect steel materials to plastic, fittings are used, on one end of which there is a thread for steel, on the other there is a smooth coupling for soldering plastic. To select a connecting element, you need to focus on the thread size of the steel material.
Copper pipe products are marked by outer size, but in inches, which can also create difficulties during installation. In this case, it should be taken into account that in the marking 1″ is equal to 25.4 mm, that is, the numbers correspond to metric standards.
Standard diameters of plastic pipes
The dimensions of polyethylene pipe products are determined by GOST 18599-2001. The range is quite large - from 20 to 1200 mm. The most common: 63, 80 and 100 mm. for water supply PE 63 is a product that has short-term strength, but is not resistant to cracking and even destruction. Does not withstand pressure more than 6.3 MPa. At the moment it is almost not used due to its short service life.
PE 80 water supply pipe products are highly resistant to internal pressure. Made from low pressure polyethylene. Designed for transporting water with temperatures from 0 to 40°C. They are used to install water pipelines and sewage systems. They are supplied to the retail chain in black, with a longitudinal blue stripe, with a diameter of 16 to 110 mm. There are 9 types of these products, differing in operating pressure (from 0.32 MPa to 2.00 MPa).
Water pipe PE 100 is a pressure pipe, manufactured by extrusion and intended for installation of external water supply and pressure sewerage systems with temperatures from 0 to 40°C. They are supplied to the retail chain in coils and in lengths. The product is black with a diameter from 16 to 110 mm.
The marking of polyethylene materials contains the word “pipe”, grade of polyethylene, nominal diameter, wall thickness, “drinking” or “technical”, GOST designation.
Cross-linked polyethylene is designated as PEX-a, PEX-b, PEX-c, PEX-d.
Labeling of polypropylene products
The marking usually contains certification information, trademark or name of the manufacturer, name of the conformity standard (for example, 2458 ISO 4200/DIN), material designation, outer size and wall thickness, pressure rating (PN).
The outer size can be indicated in both the metric system and inches. It all depends on the manufacturer.
The table shows that the size designations do not correspond to the traditional metric system.
The diameter in the marking is indicated in the same way as on polypropylene. The material name can be PVC (PVC), CPVC (CPVC) or UPVC (plasticized PVC).
Marking of metal-plastic products
The marking of metal-plastic must contain the designation of the type of plastic, outer size, nominal pressure (PN), transported medium, batch number, year and date of manufacture and 13 digits containing information about the number of the shift, conveyor line, machine, etc.
If steel and a plastic water pipe are used to install the water pipeline, the diameters can be determined from the corresponding table. To connect sections of different materials, there are fittings that take into account all these features.
One way or another, we all had to deal with installing a plumbing system or replacing water pipes. If a person is not a professional in this field, it will be somewhat difficult for him to navigate the extensive offerings on the market, especially if he has to set up the system from scratch.
But regardless of whether you hire a professional or do the work with pipes yourself, it will be very useful to understand what the diameters of water pipes can be, as well as the difference between the diameters of steel and plastic water pipes.
Areas of use
Now let's get back to a more practical area. What sizes should you use when building water supply, heating or sewage systems with your own hands?
Water supply, heating
- A 16 mm plastic pipe is used to connect one to three plumbing fixtures (faucets, shower cabins, toilet cisterns, etc.). It can also be used for installation in underfloor heating (cross-linked polyethylene is usually used for this purpose) or for manifold heating distribution.
- 20 mm is enough to distribute water supply throughout a cottage with 4-6 plumbing fixtures and to operate a heating system with forced circulation, serving a house with an area of up to 100 m2.
- 25 mm are used as heating and water supply risers in houses with no more than 5 storeys.
- A diameter of 32 mm is typical for risers in high-rise buildings and for bottling water supply and heating in a small number of apartments.
- 40 mm – bottling in an apartment building or in a cottage with a gravity (gravity) heating system.
Sewerage
Gravity waste systems are characterized by the following size distribution:
- A 50 mm plastic pipe is used to connect 2 – 3 washbasins, sinks, shower cabins, etc. In short, any plumbing fixtures, with the exception of toilets.
The sewerage installation for the bathtub, washbasin and washing machine is made with a 50 mm pipe.
Important: to connect a simultaneously used bathtub and shower cabin, a plastic pipe of 75 mm or higher is used. What is the instruction related to? With the fact that when draining a full bath, the 50 mm sewer will be filled; We will not talk about normal drainage from the shower stall.
- A 90 mm plastic pipe is used relatively rarely, mainly for connecting installations of wall-hung toilets. But the 110-mm one, on the contrary, is extremely in demand: this diameter is used for connecting a toilet, laying sewer risers and beds (horizontal branches connecting risers).
- 150 – 600 mm are used as an outlet to a well and for transporting wastewater between wells.
- A diameter of 600 mm or more is typical for collectors that combine wastewater from an entire city district.
The photo shows the laying of a polyethylene sewer collector.
General information about the diameters of water pipes
Water pipes made from different materials differ somewhat in size, in particular in the classification of measurement measures.
What determines the dimensions of water pipes:
- internal diameter
is the main conditional characteristic of both connecting nodes and water pipes; - Dу, diameter of the conditional transition
- this is the name of the nominal value of the internal diameter calculated in millimeters, its rounded value; - Dn – nominal diameter
; - outside diameter
; - wall thickness
etc.
In those days, when progress was carried out somewhere nearby, bypassing the countries of the post-Soviet space, the diameters of water pipes simply did not raise any unnecessary questions for the reason that there were no other diameters.
Diameters of pipes for water supply from various materials
Today's market may offer a slightly more diverse selection. For this reason, an amateur has a hard time trying to navigate and choose among plastic, metal-plastic and other diameters that meet his needs.
The choice is especially difficult when it is necessary to join pipes made of different materials when making repairs.
When installing water fittings, changing “inch” water pipes made of steel to pipes made of plastic, it is necessary to take into account that the names and designations for inches do not correspond to real metric sizes.
Systems for calculating the diameters of pipes made of various materials
When joining water pipes made of steel with pipes made of plastic, you can use standard transition elements - they are made taking into account the size of water pipes made of each material.
It may be somewhat more difficult if copper and aluminum pipes need to be replaced, since they are produced according to metric standards. In this case, the actual metric size of both the outer and inner diameters should be taken into account.
The size designations for water supply pipes are somewhat different from the generally accepted ones, and given that plumbers are quite inventive people, it is not surprising that they found an excellent way out of the situation. A special convenient thread system for the outer diameter was developed.
It can be described something like this. A half-inch pipe is produced with a diameter of less than 21 mm, the same diameter as the external thread. But when designating it, it is indicated in accordance with the internal diameter and the word “pipe” is added. In the documentation it looks like this: 1/2” pipes.
Diameters of steel water pipes
The internal diameter of pipes with different threads will be as follows:
- 1/2 inch pipe – 12.7 mm;
- 3/4 inch pipe - 19.0 mm;
- 7/8 inch pipe - 22.2 mm;
- inch pipe – 25.4 mm;
- 1.5 inch pipe – 38.1 mm;
- 2 inch pipe - 50.8 mm.
Pipe thread diameters:
- pipe 1/2 inch - 20.4 - 20.7 mm;
- pipe 3/4 inch - 25.9 - 26.2 mm;
- pipe 7/8 inch - 29.9 - 30.0 mm;
- inch pipe - 32.7 - 33.0 mm;
- 1.5 inch pipe - 45.8 - 46.2 mm;
- 2 inch pipe - 57.9 - 58.3 mm.
After familiarizing yourself with the sizes of water pipes, it is much easier to navigate the choice. To ensure that as few problems as possible arise when joining steel and plastic pipes, you can study special tables that show the dimensions of water pipes made of different materials.
How does pipe diameter affect throughput?
The diameter of the water supply pipe in a private house or apartment building determines the throughput of the system. For example, a pipeline network with a diameter of 25 mm is able to pass 30 liters per minute, and a 32 mm pipe - 50 liters. However, it is worth taking into account the throughput of the mixer, which does not exceed 5 l/min.
Steel water pipe dimensions GOST
The calculation of the diameter of the pipe for water supply is also influenced by the number of water consumption points - the more there are, the larger the diameter of the pipeline should be. In addition, how to choose the diameter of a pipe for a water supply system is also influenced by such factors as:
- temperature of the transported medium (pipes for hot water must be thick-walled);
- number of turns and joints in the system;
- operating pressure (water pressure).
Note: If you plan to create a system with a large number of joints, many turns, pressure drops, then you will need to choose pipes of increased diameter. Dimensions increase as water consumption increases.
If you expect to join steel and polymer water pipes, then standard adapter fittings are useful - they are chosen so that the diameter of the elements corresponds to both sizes. This can be difficult if you are expected to work with aluminum and copper products, since they are manufactured to metric standards. So you should carefully check the metric dimensions of the outer and inner diameters and relate them to the inch ones.
The table in the photo below clearly demonstrates how the diameter of water pipes correlates.
Read about which pipes to choose for water supply in an apartment in our separate article. We consider the pros and cons of different options.
If you choose polypropylene pipes, you will also need to select a soldering iron for their installation. Information about this is in our material.
All about polyvinyl chloride pipes for external sewerage here https://okanalizacii.ru/truby/vidy/truby-kanalizacionnye-naruzhnye-pvh.html
Selecting the diameter of the water pipe
It is advisable to choose the diameter for the pipes in accordance with the water pressure in the system, the number of joints and turns, and the length of the water pipeline.
Of course, there are special calculation formulas that take into account the reduction in water pressure, which will depend on the number of joints, turns, as well as the length of the pipeline with the corresponding coefficients.
However, the practical use of such formulas for intra-apartment wiring is quite rare.
Usually they simply choose pipes for water supply - the diameter of which is:
- 15 millimeters (1/2 inch)
- 10 millimeters (3/8 inch).
When installing a riser, select pipes whose internal diameter is equal to:
- 25 millimeters (one inch);
- 20 millimeters (3/4 inch).
The diameter of the pipes is still a rather delicate issue. Given that the internal diameter of a half-inch plastic pipe ranges from 11 to 13 mm, and a one-inch one - from 21 to 23 (depending on the manufacturer), only plumber with extensive experience.
In case of complex wiring, multiple joints, turns and the need to lay pipes over a significant distance, when the pressure in the system for some reason is lower than the standard pressure, you should consider the possibility of installing pipes with a larger diameter.
Of course, it hardly makes sense to do the wiring in such a way that the diameter of the water pipes chosen for this purpose is larger than that of the riser. The larger the diameter chosen, the correspondingly better the pressure will be, but the situation is unlikely to be so serious that a highly accurate calculation of pipe diameters will be required.
Plastic pipes for heating
Drawing up a correct design for a heating system made of plastic pipes requires special attention to selecting the correct diameter, which determines the throughput and volume of transported coolant and the predicted level of heat loss. The throughput capacity alone determines how extended and branched the heating system can become, and how many heating radiators can be installed.
Good to know! Products with a diameter of 200 mm or more are usually placed at large facilities where a significant number of people are constantly present.
Small diameter pipes are used for heating, this saves energy
When installing a heating system with forced circulation of coolant, it is recommended to reduce the cross-section of the pipes to the minimum possible value, which allows:
- save on heating the coolant;
- reduce its movement speed to optimal - 0.3-0.7 m/s;
- simplify installation;
- achieve overall savings.
Calculations of the required pipe diameter are based on the condition that for comfortable heating of a square meter of a small room in a house with ceilings no higher than three meters, 0.24 kW is required. This involves installing a heating radiator on each window. Using an online calculator for a two-pipe heating system, we see that you will need products with an internal cross-section of 8 or 10 mm.
In large rooms and high ceilings, the use of too small a diameter when laying pipes will have a detrimental effect on both the efficiency of the system and the level of noise emanating from it.
The following external diameter values (in mm) are recommended for heating systems:
- for a warm water floor – 16-18;
- for hot water supply pipes – 20 (for risers – 25);
- for small buildings – 20-32.
Plastic pipes can also be used for ventilation; their size depends on the type of room, its purpose and other factors.
Calculation of capacity for water pipes
Definition of throughput
Before you familiarize yourself with the rules by which the throughput of water pipes is calculated, it is necessary to study what the throughput is in general, and why it is necessary to find out this indicator.
Throughput is a metric characteristic, thanks to which it is possible to calculate and show the ratio of the maximum volume (in this case, liquid) passing through a pipe cross-section per unit of a certain period of time.
In addition to the usual ones, pipes made of metal-plastic or polymers have recently begun to be used in large quantities. It was then that the attitude towards the capacity of water supply pipes changed.
Unlike steel pipes, polymer pipes do not overgrow inside and are not subject to corrosion in the most inappropriate places, that is, the channels in such pipes are not in danger of becoming clogged inside with natural multi-layer deposits, and their throughput remains normal for a long time. With a steel pipe, the throughput capacity changes downward over time.
Sewer plastic pipes: diameters, prices
Every owner wants everything in his household to work, nothing to break, and to be easy to maintain and install. And sewerage is no exception. It needs to require as little attention as possible - it’s very inconvenient if it gets clogged, but it’s no less unpleasant to clean it. If you want to have a trouble-free drainage system, pay attention to plastic sewer pipes. They are gradually replacing cast iron ones, and all because they cost less, are easier to install, have a wide range - different diameters and lengths, almost no deposits form on their smooth walls, and even have a service life of about 50 years. This whole bouquet of properties determines their popularity.
Plastic sewer pipes are made from various polymers and their compositions
Types of plastic sewer pipes
Products made from different types of polymers are sold under the general name “plastic”:
- polyethylene (PE): high pressure (HDPE) - for internal sewerage distribution;
- low pressure (LDPE) - can be laid outside, in trenches (they have greater strength);
And a number of other thermoplastics and their combinations, but they are rare - people prefer to use already known materials.
The material of plastic sewer pipes is selected depending on the application. For example, polypropylene is more suitable for installing sewerage inside a house or apartment. It has a higher operating temperature range - it normally tolerates environments up to 70°C, and for a short time - up to 95°C. If you have various household appliances that discharge waste hot water into the sewer, this will not be superfluous. PVC pipes, which have lower prices, are more appropriate when laying external sewers - here the drains are usually already mixed, so the temperatures are lower and PVC can withstand them without harm (working up to +40°C, short-term increase to 60°C).
An example of an in-house sewerage system made from plastic pipes
Sewer pipes can also be smooth or corrugated. Moreover, not only siphon bends can be corrugated. There are profiled pipes for sewerage with an internal smooth wall and an external ribbed one. They have greater strength - they can better withstand compressive loads (they have increased ring rigidity) and can be buried to great depths. Available in diameters from 110 mm to 1200 mm.
Dimensions and diameters
Sewage plastic pipes, unlike water and gas pipes, are produced in the form of lengths of 50 cm, 100 cm, 200 cm, etc. - up to 600 cm. The maximum length is 12 meters, but some manufacturers can make longer sections upon request. When laying long routes, this is convenient - there are fewer connections, fewer possible places for problems to arise (leaks or blockages).
Another important characteristics of plastic pipes are diameter and wall thickness. In the markings they usually go side by side: the numbers are 160 * 4.2. What it means: the outer diameter of the pipe is 160 mm, the wall thickness is 4.2 mm. It’s worth remembering here that manufacturers indicate the outer diameter of plastic pipes, and many calculations and planning require knowing the inner one. It is easy to calculate: subtract twice the wall thickness from the outer wall: 160 mm - 4.2 mm * 2 = 151.6 mm. Calculations and tables usually show a rounded result—in this case, 150 mm.
Parameters of sewer plastic pipes
In general, the industry produces plastic pipes for sewerage with a diameter of 25 mm. The maximum cross-section depends on the type of pipe (smooth or corrugated) and the material from which it is made. For example, smooth PVC sewer pipes can have a diameter of up to 630 mm, and profiled two-layer pipes can have a diameter of up to 1200 mm. But these dimensions are of no use to homeowners or apartment dwellers. In private housing construction, diameters up to 100-110 mm are mainly used, rarely up to 160 mm. Sometimes, for a large cottage with a large number of plumbing fixtures, a pipe of 200-250 mm in diameter may be needed.
How to choose a diameter for connecting plumbing fixtures
According to the rules, a calculation must be made; it is fully spelled out in SNiP 2.04.01085. This is a complex matter, a lot of data is required, so few people really think as it should. Over the years, accumulated practice has made it possible to derive the average diameters of polyethylene sewer pipes for each of the plumbing fixtures. You can safely use these developments - all calculations usually come down to these dimensions.
As you can see, plastic pipes for sewerage with a diameter of 30-40 mm are mainly used. Only the toilet requires a much larger size - 100-110 mm. This is due to the peculiarity of its functioning - it is necessary to remove a large amount of water in a short period of time. At the same time, there must be room for air in the pipe, otherwise it will break the water seals on other plumbing fixtures and “aromas” from the sewer will enter the room.
When installing, you need to remember a few more rules:
- The system should not make 90° turns. If there is such a need, the rotation is made up of two 45° angles. Sharp turns are problematic places where blockages often form, and the cable for drain cleaning does not pass through such corners.
Correct turn
The main thing is not to forget anything
You also need to remember about insulating or heating the sewer outlet in a private house. The vertical section that runs from the outlet to the entrance to the trench must be well insulated. Additionally, heating cables for pipes are often used. In the case of sewers, they are usually laid outside and then covered with thermal insulation material.