Free-flow pipes made of low-pressure PE are most often used to protect cables when they are installed underground, laying sewers, and organizing drainage. In other words, they can be used in areas where there is no pressure of liquids or gases inside the pipe. Gravity pipes are considered technical and cannot be used to supply drinking water or organize a gas pipeline. What determines the scope of application of free-flow pipes?
First of all, the characteristics are affected by the diameters of the HDPE pipe : the throughput and maximum volume of laid cables, as well as flexibility, depend on this. Large diameter HDPE pipes (110 mm and 160 mm) are used to drain sewerage and lay cables under the road. A small diameter is used if you need to lay wires at home or in the ground.
Common outer diameters of HDPE pipes.
Factory marking of pipes is carried out according to the outer diameter, which is what you need to focus on. The outer diameter of HDPE pipes produced by our plant varies from 20 mm to 160 mm, and the choice of wall thickness depends on the needs of the client. If the exact size is unknown, you can focus on common diameters:
- Small diameter pipes (from 20 mm to 63 mm) are used for laying electrical cables in houses and for laying in the ground;
- Pipe diameter from 50 mm to 75 mm is suitable for draining wastewater from a bathtub, washing machine, sink and other plumbing fixtures. If we talk about cable insulation, these diameters are used to protect lamp posts and lay wires along the road;
- One of the most common is a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm - it is used for sewerage and drainage of toilet drains. This diameter has earned no less popularity when installing electrical and fiber optic highways;
- Pipes with a diameter of 160 mm are recommended for use in houses of five floors and above (for sewerage). In addition, such a pipe is used for laying cables in the ground, including under roads.
But it is worth considering that these are external indicators. In addition to different diameters, HDPE pipes have different wall thicknesses, which determine whether technical pipes belong to one of six types:
- Light and medium-light;
- Medium and light medium;
- Medium-heavy and heavy.
The thicker the walls, the heavier the pipe. The thickness of the pipe walls is responsible for the strength and flexibility of the pipes. Thus, a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm can have walls as thick as 4.2 mm or 10 mm. The thicker the walls, the higher the strength, while the internal diameter of the pipe and flexibility are smaller.
Other sizes
One of the main characteristics for pressure pipelines is the ratio of the nominal outer diameter to the thickness - SDR. It is this indicator that determines the maximum permissible operating pressure (MOP, MPa) in the pipeline, which the pipe can withstand without compromising its integrity. That is: the lower the SDR, the higher the MOP can be. The relationship between these values is different for different diameters of polyethylene pipes and is calculated using a formula adjusted for the temperature regime of the environment.
GOST also defines the concept of “nominal wall thickness”, which in a product cannot be lower than the S strength indicator approved for each series for long-term (up to 50 years) operation of the system.
According to the standard, HDPE pipes with a diameter of more than 180 mm are produced only in separate products, up to 25 m long. Products of smaller diameter can be supplied in coils.
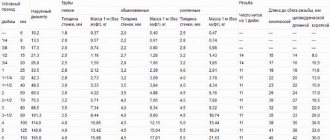
| SDR 26 | SDR 21 | SDR 17 | SDR 13.6 | SDR 11 | ||||||
| PE 80 | PN 5 | PN 6.3 | PN 8 | PN 10 | ||||||
| PE 100 | PN 6.3 | PN 8 | PN 10 | PN 12.5 | PN 16 | |||||
| Outer diameter, mm | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1 m, kg | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1 m, kg | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1 m, kg | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1 m, kg | Wall thickness, mm | Weight 1 m, kg |
| 20 | 2,0 | 0,116 | ||||||||
| 25 | 2,0 | 0,148 | 2,3 | 0,169 | ||||||
| 32 | 2,0 | 0,193 | 2,4 | 0,229 | 3,0 | 0,277 | ||||
| 40 | 2,0 | 0,244 | 2,4 | 0,292 | 3,0 | 0,353 | 3,7 | 0,427 | ||
| 50 | 2,0 | 0,308 | 2,4 | 0,369 | 3,0 | 0,449 | 3,7 | 0,545 | 4,6 | 0,663 |
| 63 | 2,5 | 0,488 | 3,0 | 0,573 | 3,8 | 0,715 | 4,7 | 0,869 | 5,8 | 1,05 |
| 75 | 2,9 | 0,668 | 3,6 | 0,821 | 4,5 | 1,01 | 5,6 | 1,23 | 6,8 | 1,46 |
| 90 | 3,5 | 0,969 | 4,3 | 1,180 | 5,4 | 1,45 | 6,7 | 1,76 | 8,2 | 2,12 |
| 110 | 4,2 | 1,420 | 5,3 | 1,770 | 6,6 | 2,16 | 8,1 | 2,61 | 10,0 | 3,14 |
| 125 | 4,8 | 1,830 | 6,0 | 2,260 | 7,4 | 2,75 | 9,2 | 3,37 | 11,4 | 4,08 |
| 140 | 5,4 | 2,310 | 6,7 | 2,830 | 8,3 | 3,46 | 10,3 | 4,22 | 12,7 | 5,08 |
| 160 | 6,2 | 3,030 | 7,7 | 3,710 | 9,5 | 4,51 | 11,8 | 5,50 | 14,6 | 6,67 |
| 180 | 6,9 | 3,780 | 8,6 | 4,660 | 10,7 | 5,71 | 13,3 | 6,98 | 16,4 | 8,43 |
| 200 | 7,7 | 4,680 | 9,6 | 5,770 | 11,9 | 7,04 | 14,7 | 8,56 | 18,2 | 10,4 |
| 225 | 8,6 | 5,880 | 10,8 | 7,290 | 13,4 | 8,94 | 16,6 | 10,9 | 20,5 | 13,2 |
| 250 | 9,6 | 7,290 | 11,9 | 8,920 | 14,8 | 11,0 | 18,4 | 13,4 | 22,7 | 16,2 |
| 280 | 10,7 | 9,090 | 13,4 | 11,300 | 16,6 | 13,8 | 20,6 | 16,8 | 25,4 | 20,3 |
| 315 | 12,1 | 11,600 | 15,0 | 14,200 | 18,7 | 17,4 | 23,2 | 21,3 | 28,6 | 25,7 |
| 355 | 13,6 | 14,600 | 16,9 | 18,000 | 21,1 | 22,2 | 26,1 | 27,0 | 32,2 | 32,6 |
| 400 | 15,3 | 18,600 | 19,1 | 22,900 | 23,7 | 28,0 | 29,4 | 34,2 | 36,3 | 41,4 |
| 450 | 17,2 | 23,500 | 21,5 | 29,000 | 26,7 | 35,5 | 33,1 | 43,3 | 40,9 | 52,4 |
| 500 | 19,1 | 29,000 | 23,9 | 35,800 | 29,7 | 43,9 | 36,8 | 53,5 | 45,4 | 64,7 |
| 560 | 21,4 | 36,300 | 26,7 | 44,800 | 33,2 | 55,0 | 41,2 | 67,1 | 50,8 | 81,0 |
| 630 | 24,1 | 46,000 | 30,0 | 56,500 | 37,4 | 69,6 | 46,3 | 84,8 | 57,2 | 103,00 |
| 710 | 27,2 | 58,500 | 33,9 | 72,100 | 42,1 | 88,4 | 52,2 | 108,00 | 64,5 | 131,00 |
| 800 | 30,6 | 74,100 | 38,1 | 91,400 | 47,4 | 112,0 | 58,8 | 137,0 | 72,6 | 166,00 |
| 900 | 34,4 | 93,800 | 42,9 | 116,000 | 53,3 | 142,0 | 66,1 | 173,00 | ||
| 1000 | 38,2 | 116,000 | 47,7 | 143,000 | 59,3 | 175,0 | 73,5 | 214,00 | ||
| 1200 | 45,9 | 167,000 | 57,2 | 206,000 | 71,1 | 252,0 | ||||
What does the internal diameter of HDPE pipes affect?
First of all, the internal diameter of HDPE pipes affects the throughput. In other words, the larger it is, the greater the volume of liquid that can pass through the pipe at a time. So, despite the fact that the bathtub holds 100-250 liters of water, due to the small drain hole, you can use pipes with an internal diameter of about 32 - 50 mm.
But the toilet has a wide drain hole into which a large amount of water enters. Therefore, it is advisable to connect pipes with an internal diameter of up to 11 cm to it. An internal diameter of pipes greater than 11 cm is justified for organizing the removal of sewage from the building.
It is worth paying attention to the fact that in any case there are air masses in the pipes, which, if the pipe diameter is insufficient, can cause a number of inconveniences. This includes improper movement of wastewater and a constant unpleasant odor.
If HDPE pipes are used for laying cables, the internal diameter is calculated based on the number and thickness of the cables that will be placed in it.
Features of low pressure polyethylene pipes
One of the popular polymers used to produce components for pipelines for various purposes is low-density polyethylene. Pipes from it are molded under fairly mild conditions, allowing to create a strong structure without destroying polyethylene molecules (temperature 150 degrees and pressure up to 2 MPa).
Products obtained using this technology have the following features:
- biological and chemical inertness - polyethylene is not a comfortable environment for the growth of bacteria and fungi, does not react with transported substances, the external environment and other materials used for laying the pipeline;
- absence of seams - HDPE pipes are molded immediately in the form of tubes, so they do not have weak points that are susceptible to gusts;
- the strength of the material in compression, tension and bending allows us to produce long pipes, using which you can stretch a network of any geometric shape with a minimum number of nodes;
- density and elasticity of the walls - the HDPE pipeline can withstand temperature and pressure fluctuations in the working and external environments;
- tightness - the walls of the pipes do not allow particles of transported substances to pass through and prevent the gas exchange of the working environment with the outside air;
- light weight, simplifying transportation and installation - even a coil of the longest pipe can be easily carried in your hands;
- sound absorption - the soft walls of polyethylene pipes dampen vibration of the working environment and do not make noise;
- smoothness – the pipes have low hydrodynamic resistance;
- instability to ultraviolet radiation, extreme temperatures and intense loads - street parts of utility networks made of HDPE pipes must be laid deep underground or protected with a casing;
- fire hazard - polyethylene is highly flammable and begins to release toxins that are life-threatening.
Note! Despite the strength and elasticity, sharp corners cannot be made from polymer pipes. Firstly, this worsens the performance of the pipeline, as its throughput is reduced and nodes appear that are susceptible to clogging. Secondly, in places of strong bending, creases and stretching of the walls are formed, which are easily damaged during operation, forming leaks.
Taking into account all the listed features, HDPE products are used for the installation of pipelines for various purposes:
- water supply,
- drainage,
- gas supply,
- protection of electrical cables and communication lines,
- watering.
We recommend that you read: How to properly hide water pipes in the bathroom?
Table of HDPE pipe diameters.
The internal and external diameters of HDPE pipes are presented in a wide range from 10 mm to 400 mm. In addition to standard diameters, there are many pipes with non-standard sizes. The table below shows the main diameters of pipes produced at our plant.
| Diameter | Coil length, cut (m.) |
| 20 | 100, 200 |
| 25 | 100, 200 |
| 32 | 100, 200 |
| 40 | 100, 200 |
| 50 | 100, 200 |
| 63 | 100, 200 |
| 75 | 100 |
| 90 | 12 |
| 110 | 12 |
| 125 | 12 |
| 160 | 12 |
Let's understand the terminology
Our country has a metric number system. And we measure everything in meters, centimeters and millimeters. Traditionally, the diameter of steel pipes is measured in millimeters. But the pipe has two diameters - internal and external, and is also characterized by wall thickness. So what diameter are we talking about when we talk about the size of steel pipes? Depends on the standard to which they are made. In some cases this means the outer diameter, in others the inner diameter. That's how difficult it is.
Diameters of steel pipes: which one to use
Nominal and nominal diameter
Pipes are used at different pressures. For a higher one, greater strength is required and this is achieved due to the wall thickness. In this case, the outer diameter of the pipe is left fixed. Otherwise, it will not be possible to connect the segments, and difficulties will arise with threads, fittings, etc. So the outer diameter is only an external parameter. Therefore, such a concept as conditional passage was introduced. In general, this is an outdated name and according to modern standards they say “nominal diameter”.
The nominal diameter of the pipe (nominal diameter) is a calculated value that is calculated during design. This value approximately corresponds to the internal diameter of the pipe in millimeters. Approximately, because the walls, with the same outer size, are of different thickness. This means that the clearance is changing. To somehow harmonize all this, a nominal diameter was introduced. This is a specific list of quantities defined by GOST 28338-89. They are shown in the table. Actual dimensions are rounded to the nearest nominal.
A number of standard nominal values of the nominal diameter of gas and water pipes and fittings for them
The designation of this value is DN, sometimes the Russian version is called Dn. After these letters there is a number without metric signs: DN30 or DN150. This is read as a nominal pipe diameter of 30 or 150, or a nominal diameter of 30 and 150. There are no units of measurement, since this is a conventional value.
Once again: all existing elements of water supply and gas pipeline systems are marked in accordance with the list of standard values - nominal diameters Dn. The actual size of the internal cross-section of a pipe or fitting may be larger or smaller. It is rounded to the nearest standard value.
In fact, the nominal diameter of a pipe or nominal size is a value that reflects the throughput. It is approximately equal to the inner diameter. After all, when you assemble a system, you use elements from different materials, with different wall thicknesses. Therefore, it is more reasonable to focus not on the diameters of the internal part, but on the nominal diameter. This will make it possible to ensure the same throughput of all elements of the system.
Production of HDPE pipes of any diameter.
In addition to common sizes, pipes can be not only standard. Our company’s own production allows us to produce HDPE pipes of any diameter - both external and internal, with thick or thin walls. In addition, pipes can be of any shape - round, square and even triangular. It all depends on the needs, the scope of application and the exact characteristics specified in the project.
It is worth considering that when installing such pipes using fittings, finding the required sizes of fasteners can be problematic. Therefore, pipes of non-standard shape are often connected by welding. However, recently, fittings have become available, including for the installation of pipes with non-standard diameters, which makes the installation of electrical and drain communications even easier. And in many cases it is possible to order a batch of fittings with individual parameters.
Steel pipe diameters: inches, millimeters, compliance
Until you are faced with choosing a pipe, it seems that there is nothing complicated about it. There is a size, and you need to select the material according to it. That’s how it is, but you can measure it both inside and outside. So which measurement is correct? Oddly enough, both. There are standards according to which pipes are marked by outer size, and others that indicate the inner size. And the diameters of steel pipes are only available in a certain set. So, with the same outer diameter, we can have a pipe with different capacities and operating at different pressures.
HDPE pipes of large diameters in sections.
HDPE pipes with a diameter of 20-75 mm can be produced both in coils and in sections, but pipes with a diameter of 90 mm or more are produced only in sections. This is due to the fact that wall thickness and flexibility depend on the diameter. Accordingly, the thicker the wall, the more difficult it is to roll such a pipe into a coil. At the same time, the weight also changes significantly - so, if a meter of pipe with a diameter of 75 mm weighs about a kilogram, then a 110 mm pipe will weigh a little less than two.
HDPE pipes of large diameters are produced in lengths up to 12 meters, but shorter lengths are possible.
How to deal with import designations
There are not only products from domestic manufacturers on the market. There are pipes marked according to the American system. Let's start with the fact that they distinguish between two types of pipes: pipes and tubes. Both words translate as pipe, but they are intended for different systems and the requirements for them are different.
Pipes type
Type of Pipes - electric welded and seamless. They are designed for transporting liquids and gases. So this is exactly the type that can be used in our heating and water supply systems. The main characteristic of pipes type pipes is the internal diameter. There are two strength standards in this group, which determines wall thickness and operating pressure.
- Schedule 40 or standard. The designation may include st (as in the figure below). These are products with standard wall thickness.
- Schedule 80 or extra heavy. The designation is EX. This is a material for use in high pressure pipelines.
Difference in internal diameters of Pipes of different strength categories: standard and heavy
As you understand, with the same external size, the clearance will be different. Let's take a two-inch pipe as an example. It is designated as NPS=2″ internal diameter in different designs differs:
- standard (standard) schedule 40 - 2.067 inches (which is approximately equal to 5.25 cm);
- extra heavy schedule 80 - 1.939 inches (approximately 4.925 cm).
These categories standardize wall thickness and maximum operating pressure. The outer diameter remains constant, but the actual inner diameter changes with the wall thickness. That is, NPS=2″ describes the inside diameter, which will be about two inches, but will vary depending on the wall thickness. Here the situation is similar to our standards: there is a certain list of values to which actual parameters are rounded when labeling. Once again: if we are talking about a two-inch Pipe type pipe (the marking says NPS), you need to understand that we are talking about the internal diameter, but it will not be exactly two inches. It will be either a little more or a little less. Same with other sizes in inches.
Type Tubes
The word Tubes refers to pipes that are marked by outer diameter. The internal one will depend on the wall thickness. Therefore, this standard also contains the concept gauge, which can be translated as gauge. It just indicates the wall thickness.
HDPE pipes of small diameter in coils.
Pipes of small diameter (from 20 mm to 75 mm) are much more convenient to store in coils or on reels. Due to their small diameter and wall thickness, they are quite flexible and are produced in sections only upon request. The standard length of the bay is 100 meters and 200 meters. In addition, pipes are sometimes produced in coils up to 1000 meters long. For a small diameter pipe, the sections can be of different lengths.
Correspondence table for pipe diameters in inches and millimeters
Let's say right away that pipes are measured not in ordinary inches, but in pipe inches. If a regular inch is 25.4 mm, then a pipe inch according to GOST is 33.249 mm . And pipes with such an outer diameter (or close to it) are usually called inch. But the internal diameter can vary greatly: the wall thickness of an inch pipe can be 2.5 mm, or it can be 8 mm. The correspondence of the nominal diameter in inches and millimeters is given in the table. Note! These are not outer/external size values. This corresponds to the nominal diameters of our standard and the DIN standard.
Correspondence table for nominal bore or nominal diameter of pipes in inches and millimeters
If you look at the correspondence table, you can see that when calculating the nominal diameter, the usual inch is used. We use pipe when it is necessary to convert the symbol into outer diameter. But even knowing the size of the pipe inch will not help to obtain the exact value of the outer diameter. It gives an approximate correspondence by which you can navigate. The exact details are shown in the table below.
Steel pipe diameters in inches, outside size in millimeters and nominal equivalent in our metric system
So, let's summarize. How to convert pipe dimensions in inches to centimeters and vice versa? If you convert Du into inches, you must divide by the usual inch and round the resulting number to the nearest standard. The diameters of steel pipes of common sizes are summarized in tables. If there is no table, the outer diameter can be calculated approximately using the “pipe inch”. We multiply the pipe size in inches by 33.249, we get a number close to the table value. Why not accurate? Because we are trying to convert the nominal (read - conditional) diameter into a real value - the external size. Therefore, the result is only close to the table.
Wholesale and retail sale of HDPE pipes of various diameters.
Depending on the quantity of products ordered, there is a system of wholesale discounts. We also engage in retail sales of HDPE pipes of all diameters.
The production of technical pipes from HDPE takes place in the Moscow region, which allows us to significantly reduce the cost and, as a result, the final price for the buyer. At the same time, delivery is possible both to Moscow and throughout the Russian Federation.
Selling HDPE pipes directly from the manufacturer means fast production, prompt deliveries without delays and very affordable prices!