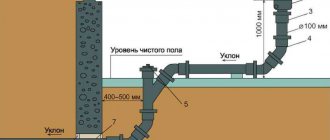
The most typical opinion is the idea that the greater the angle of inclination, the better. But this is a completely wrong approach, and in this way you can provoke the appearance of blockages. Experts say that for a pipe with a diameter of 110 mm, the corresponding slope during installation should be no less and no more than 2 cm per meter.
This figure is not pulled out of thin air. Under such conditions, any wastewater is able to maintain an ideal speed as it moves through the sewer pipes. Thus, along the way, they carry along all the fairly large elements, which, with a large slope, invariably remain in the pipe.
At the same time, if you make the slope smaller, or don’t do it at all, then the soda will stagnate in the pipe, leading to blockages and the appearance of unpleasant odors.
Official standards
There are official standards for the required slope of pipes, prescribed in SNiP 2.04.01-85, paragraph 18.2. This paragraph contains information regarding the arrangement of the sewer system inside the house and to wells, which are located no more than 12 meters from the house. According to these data, the slope of sewer pipes does not exceed 2 cm per linear meter if the pipe diameter reaches 100 mm, and 3 cm per meter with a diameter of about 50 mm. However, in small areas the angle of inclination does not matter, therefore, in the area of a kitchen, for example, or a bathtub from one structure to another, it is quite possible to do without inclination in principle.
For the street network of sewer systems, the standards indicate the required 2 cm of slope, which is standard. However, for a domestic or industrial sewer network within a block or production area, a slope of 1.5 cm is acceptable. Reducing this parameter is possible depending on the minimum speed of movement of wastewater that is permissible in the selected area. They are usually used for wider pipes because it makes sense there.
Rules for draining sewerage from a private house
To avoid damage to the communication line, the depth of the main sewer pipe at the exit from a private house must be at least 0.5 m from the blind area.
It is also necessary to take into account other requirements of SNIPs and SanPiNs:
- The distance from the sewer under the floor of the house to the storage tank is 5–10 m.
- It is not allowed to construct a cesspool at a distance of less than two meters from the neighboring plot and 30 meters from a well or borehole (for sandy soil, at least 50 meters).
- The slope is created so that the decrease for each meter of the pipeline is approximately 3 cm.
- The depth of the sewer line is below the freezing point of the ground. If this cannot be done, the pipe sections will have to be insulated or equipped with electrical heating.
The rules also take into account the installation of an inspection well with a hatch, which must be located at a distance of at least three meters from the building.
For gravity flow of sewage, the storage tank is located lower than the level of the building, or pumping equipment is installed.
Installation of a sewer line under the foundation of a house must be carried out according to certain rules. The pipes are assembled by inserting them into each other. Special rubber gaskets are installed in the sockets, the joints are thoroughly cleaned of dirt and coated with liquid soap or special lubricants.
How to arrange a route on a slope
The most important point in arranging sewer systems is the issue of laying a route in areas that have a natural slope. After all, on a flat area there is no problem making a slope at the desired angle, but on the slopes there are a number of difficulties! If you lay a pipe simply parallel to a piece of land that has a slope, then it is impossible to maintain the required correct slope, and this leads to the formation of blockages in the pipe section.
In this case, it is necessary to carefully consider a detailed plan for the arrangement of the sewer network in order to comply with the slope required by the regulations. Sometimes this requires very serious excavation work, since structures have to be buried to a more impressive depth. This is the only way in some cases it is possible to maintain the correct angle of inclination so that various kinds of problems do not arise as a result.
At what depth is the sewer pipe laid near the house?
Standardized standards indicate that the pipe leaving the room must be positioned so that it rises above the average freezing depth by approximately 30 cm.
The depth of the trenches should exceed 70 cm. For the middle zone, the minimum depth of the sewerage should reach 50 cm. This is quite enough if there is no area nearby that needs to be cleared of snow and there is no roadway.
It is very important to comply with the last requirements described above. The fact is that the pressure of the machines can lead to pipeline breakdown, and if there is a large accumulation of snow, the pipe will simply freeze.
To create gravity flow of sewage drains, you need to know exactly what slope needs to be created for the sewer pipe, especially in a private building.
In principle, you can ask your neighbors. They know well what trench depth is needed. They have already laid such pipes and tested the system. Therefore, their data will be the most optimal, especially for winter.
If you have any doubts or difficulties when carrying out such plumbing work, you should contact a professional. Such companies employ highly qualified specialists with extensive experience and appropriate tools. If you do not have the skills for such work, then independent operations can lead to damage to the material and additional financial costs.
How to make the right slope
It is possible to lay a pipe without violating the requirements of SNiP using a building level with a length of 1 meter. By placing the level above the pipe so that one end rests against the pipe, and the other has a gap of 2 cm with the pipe (if we are talking about a pipe with a diameter of 110 cm), you can quite accurately meet all the necessary requirements.
Under the pressure of the gravity of the soil, the pipe may well change position, and in order to prevent this from happening, you need to thoroughly sprinkle the pipe with sand and compact it (to do this, just pour water on the sand around the pipe). This ultimately avoids the risk that the pipe will change its angle of inclination when the soil moves. It is important to remember that soil settlement in a dug trench is inevitable, which means there will definitely be movement!
Selection of pipes for the device
Previously, when laying sewers, only metal pipes were used: cast iron or steel. Indeed, these materials are like no other suitable for laying in the ground. They are strong, durable, low cost, and easy to install.
However, along with advantages, metal structures also have significant disadvantages. The disadvantage of steel lines is the possibility of corrosion, and cast iron pipes are heavy.
In terms of strength and durability, cast iron pipes have no equal; this material can lie in the ground for decades without losing its qualities, but due to their heaviness, laying a water pipeline becomes much more difficult
A certain difficulty is present in sealing the joints of a cast iron pipe, as well as its internal surface, which, due to the characteristics of the material, will never be perfectly smooth. The latter characteristic affects the speed and quality of movement of waste inside it; over time, blockages can form in the pipe.
Asbestos-cement pipes can be used for sewer installation. They have a smooth surface, which eliminates the possibility of blockages, are simply connected using special couplings, and their weight is significantly less than that of metal structures.
But they also have a significant disadvantage - they are very fragile, which complicates their transportation and installation. Ceramic pipes have the same fragility.
Reinforced concrete structures have many advantages: they have exceptional strength, water resistance, and frost resistance. It is possible to make large-diameter pipes from reinforced concrete, which is impossible to do from other materials.
But laying such pipes is a big problem - due to their heavy weight, it is necessary to use special equipment, which is not always advisable in an individual household.
Today, when installing private sewer systems, polymer pipes are most often used, which, despite their strength, are lightweight, which allows them to be installed by one person. They are very simple and easy to connect, resulting in excellent tightness.
Orange polymer pipes are used for the installation of external sewerage. They have increased strength compared to gray pipes intended for internal piping, and also have the ability to withstand heavy loads
There are three types of polymer pipes - polypropylene, PVC or HDPE (low-density polyethylene). PVC structures, in addition to the above advantages, are also resistant to UV radiation and have slight changes in parameters due to temperature changes.
However, the PVC sewer pipeline does not withstand very low and very high temperatures, and can also be deformed under mechanical loads.
During its operation, the sewer system is subject to dynamic loads, which are best withstood by corrugated pipes. Even if it freezes, the integrity of the line will not be compromised, but deformation of its walls may occur.
The diameter of the pipes is selected based on the amount of plumbing equipment installed in the house. So, for a country cottage with two toilets, pipes with a cross-section of 110 mm will be sufficient.
If the house building has three or more bathrooms, it is necessary to use a pipeline with a diameter of 160 mm.
Image gallery
Photo from
Polymer pipes in the installation of an external branch
Polypropylene products in sewerage organization
Cold welding pipe connection
Range of fittings for plastic pipelines
What types of pipes should be used for laying in the ground?
When laying sewer pipes in the ground, it is worth knowing that the same pipes that were originally intended to create a network indoors are not suitable here. Heavy layers of soil are gradually capable of causing serious deformation to the walls of the pipes, flattening them, which can even lead to complete blocking of the route. One of the most unpleasant consequences will be that you will have to completely redo all the work, which is especially inappropriate in already landscaped areas near the house, when excavation work is simply no longer possible or undesirable. In addition, the situation threatens to become critical, and work will be required as urgently as possible, since it will be impossible to use the sewer system in order to avoid other problems.
For external work, pipes with a wall thickness of at least 3.2 mm are used so that they can withstand the appropriate load. They are usually red in color, but sometimes they are gray or deep black. It is these pipes that should be laid in underground structures so that they can withstand the weight of the earth poured on top of the pipes.
What is needed for wiring
Each private house has a unique design, and therefore it is impossible to use a general wiring system without taking into account the specifics of the object, as this can lead to disastrous consequences. Before you begin installing a sewer system in a private house, you need to pay attention to the recommendations of specialists who will not only draw up a wiring project, but also explain how it should be done. This is necessary in order to avoid making mistakes.
Elements of the sewerage system.
The main elements of the sewer system are as follows:
- a plot of land through which contaminated water flows from the central drain into a septic tank or pit;
- wiring inside the house, which is used to collect water from all household plumbing fixtures;
- Other devices.
A separate system for drainage and collection of rainwater is connected to the sewer system, and if necessary, then a sewage pump - then the wastewater is pumped out forcibly.
How to find the right pipes
An elementary test will help you choose the right type of pipe. If you squeeze the pipe with your fingers, the cheapest thin pipes begin to move, and their cut takes on an oval shape quite easily. A good pipe suitable for external excavation work is almost impossible to squeeze with a man’s hand, and this is the easiest way to determine on the spot the required type of pipe for external sewerage installation.
In some cases, special corrugated double-layer pipes are used for sewerage, which are laid under roads or in other areas with significant loads. This is required in cases where the sewer system is laid under the roadway or parking area, and these pipes are also relevant for organizing village routes.
Prices for materials and installation
Prices for materials for sewerage systems depend on their material of manufacture and linear dimensions . Tentatively they will be as follows:
- PPR pipe for internal sewerage with a diameter of 110 mm, length 1 m – 830 rubles;
- the same with a diameter of 50 mm - 720 rubles;
- revision 50 mm – 150 rubles;
- plug 50 mm – 10 rubles;
- toilet connection unit 110×87 – 200 rubles;
- PVC pipe for external sewerage 5 m long – 1200 rubles;
- 300 l septic tank (Ekoprom Rostok Mini) – 37,000 rubles.
The total cost of the system will depend on the number and distance of plumbing fixtures, as well as the distance to the septic tank.
If you plan to hire third-party workers to install the sewer system, then the prices will be approximately as follows:
- installation of internal sewerage – 175-620 rubles. for 1 p.m.;
- plumbing connection – from 200 rubles;
- installation of an external highway 100 mm – 200-350 rubles. for 1 m.p.
When performing the work on your own, the cost of installation will only be wasted time.
Carrying out road cleaning
In a situation where autonomous sewer systems are located at a distance of more than 15 meters from the house, then, according to SNiP, the equipment of various inspection wells or cleanings is required. Such special inspection wells should be installed every 15 meters of the pipe, or even every 10 meters if we are talking about straight, level sections.
Special inspection wells for an entire network of sewer pipes with a diameter of 100 mm or more are usually installed in sections of the pipeline where there are turns in the circuit or changes in slopes, as well as connections of branches or pipes of different diameters. This will increase the level of reliability of the entire system, as well as simplify monitoring the operation of the system and the use of sewerage.
Why do we need sewerage?
Today there is no need to talk about the need and importance of sewerage. A person needs to perform natural needs, maintain hygiene, cook food, wash, clean, etc. For this purpose special devices have been invented that make all hygiene and household procedures simpler and more convenient.
The ability to equip a modern bathroom, bathtub or shower, solve problems with laundry, cooking and other household concerns - all this ultimately confirms the need for a sewer system that facilitates the functioning or makes these benefits of civilization possible in principle.
Sewerage can be created with your own hands , you only need a diagram and funds to purchase the necessary materials and devices.
The sewerage system is a diagram of the arrangement of plumbing fixtures, pipes and external components responsible for the accumulation, disposal and removal of wastewater.
An autonomous sewer system is created based on several conditions:
- number of people;
- volumes of waste;
- plot size.
How to install a sewer system in a private house - this issue can be solved by simply calculating the needs.
- If the housing is only periodically visited by residents, then the simplest and most inexpensive .
- If we are talking about the permanent residence of a family of several people, then the sewage system must meet their needs and provide them even with some reserve power (in case of guests, for example).
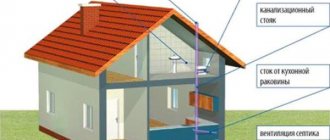
The sewerage scheme for a private one-story house is divided into two parts:
- Internal is a diagram that determines how to correctly position sewer pipes - from the toilet, bathroom, kitchen or other sanitary rooms, if any.
- External , which combines the external components of an autonomous system for accumulating and recycling wastewater.
The design is not created by eye, a diagram is needed, the depth of pipe laying , the volume of the tank, etc. To obtain the necessary data, you need to follow a certain sequence of actions.
Analysis of existing communications
The very first and most important step is to examine nearby communications.
If you find a local sewer network to which it is technically possible to connect, then this is a great success, since all work will be limited to connecting the house drain pipe to this system.
The only difficulty will be various kinds of formalities and obtaining various permits, but this is an administrative matter.
The costs of this work will be minimal compared to any others.
If there is no sewer network nearby (and most often this is the case), then you will have to completely create your own system.
Tank Type Determination
The sewage system in a house is, first of all, a container into which wastewater is discharged. Whatever scheme you choose, it certainly contains a reservoir, a sump of a certain volume.
The type of tank is determined by the volume of wastewater and the capabilities of the owner. The simpler the system, the more primitive and cheaper the tank, but cheapness in this case is a relative concept. The fact is that the simplest and cheapest option - a cesspool - will require frequent calls to sewerage equipment for cleaning, which costs money. The most expensive and complex version of the system rarely needs to be cleaned, but such a system is not available to everyone, and it is only needed when there are large volumes of wastewater. Essentially, deciding how to install a sewer system in a private home means choosing the type of tank.
Selecting a container installation point
The location of the reservoir is regulated by sanitary requirements and is at least 10 m from housing and 20 m from a well (well). At the same time, it is recommended to find the lowest point of the relief in order to reduce the volume of excavation work.
In practice, it is very rarely possible to combine this, only if the plot of land is very large, and there is no difference where to dig a recess for the tank.
Most often, no attention is paid to the relief; a point is selected that satisfies sanitary standards.
Pre-planning
All information received is compared, approximate (if possible, accurate) calculations are made, and the amount of costs for arranging the system is determined.
Practice shows that these calculations must be increased by at least a third.
This increased amount is the approximate cost that it will cost to build a sewer system in the house . It is necessary to decide how much she will be able to do, and whether these expenses will be excessive for the wallet. If not, then you can begin practical actions.
Design options
The system can be implemented in different versions. The most common (in increasing order of complexity):
- Cesspool .
This is the simplest option - wastewater is discharged into a container, where it is stored until it is filled to a certain limit.
Then a sewage disposal truck and the cesspool is cleaned. Depending on the size of the container and the volume of wastewater, this has to be done once or twice a year. The system is very simple, but the need for frequent cleaning combined with an odor that is not eliminated by any lids is not the best advertisement. - Sealed tank. In fact, this is a more successful version of a cesspool. The same tank, but equipped with a thinner neck with a hermetically sealed hatch for periodic cleaning. This design prevents odor, but does not prevent the need for cleaning.
- Single chamber septic tank. The most primitive treatment system used for volumes not exceeding 1000 l/day. It consists of a sealed container to which supply and drainage pipes are connected. The feeder is a common sewer pipe leading out of the house. Sewage flows through it. Drainage is designed to discharge clarified wastewater into the soil. The principle of operation is to settle the wastewater, when the more solid fraction settles to the bottom, and the more liquid, as the septic tank fills, rises to the level of the drainage pipe, through which it is discharged into the bulk drainage layer (well) created in the soil around the septic tank. Passing through it, the wastewater is additionally filtered and absorbed by the soil.
- Two-chamber septic tank. The first chamber is a receiver where wastewater from the house flows. This is where settling and primary clarification of wastewater occurs. The volume of the receiver is 3/4 of the total volume. When a certain level is reached, partially clarified wastewater enters the second chamber. Here approximately the same process occurs, but adjusted for the absence of the heavy fraction. As the wastewater settles and the level increases, it is discharged.
- Septic tank with biofilter. A biofilter is a highly effective wastewater treatment device capable of removing 90% of contaminants. The wastewater removed from the biofilter can be discharged into water bodies without threatening their condition . It consists of a chamber filled with expanded clay or granules, where mechanical filtration of wastewater occurs, as well as a container for bio-treatment using special bacteria.
There are two types of biofilters:
- Anaerobic. The cleaning chamber is sealed.
- Aerobic. An aerator with forced air supply is used.
Both types provide for wastewater treatment using special bacteria - anaerobic and, accordingly, aerobic. They are the ones who participate in the decomposition of residual organic matter - sludge remaining after two-stage cleaning inside the septic tank. After such treatment, the sludge is almost completely destroyed, decomposing into CO2, water and nitrogen. The remaining sludge (a little, but remains) settles at the bottom, gradually accumulates and begins to slow down the operation of the biofilter, which indicates the need for cleaning.
Internal system diagram
Drawing up the diagram begins from the farthest plumbing fixture in the attic or top floor . All horizontal lines must be reduced to one riser. To save money and consumables, bathrooms on different tiers are placed along the same vertical line.
The sewage system in the house consists of:
- Water seals that prevent odors from entering the room;
- Drains from all plumbing;
- Pipes leading wastewater into the external sewer system;
- Elbows and tees connecting pipes into a single system;
- Clamps in walls that support pipes and give them direction and angle.
- Central riser.
It is important that there is no transition in the house from a larger sewer diameter to a smaller one.
Therefore, in the diagram, the toilet should be located as close as possible to the riser. The exact drawing of the internal system depends on the number of floors of the building, the presence of a basement, the amount of plumbing used and the number of users. The depth of the septic tank and connection to additional equipment (pumping station or household pumps separately for each device) also matter.
The diagram should display all elements to scale , so that in the event of a planned repair or emergency, you can quickly understand the wiring and find a breakdown.
Method for calculating the depth of a pipe connected to a storage tank
The size of the pipe outlet in the room increases by the length of the external line, multiplied by a coefficient, the value of which is selected according to the diameter of the pipe:
- D 50 mm – 0.03;
- D 110 mm – 0.02;
- D 160 mm – 0.008;
- D 200 mm – 0.007;
The calculation is carried out according to the formula:
h2=h1+l*k+g,
h2 – depth of the point from where the exit and connection to the storage tank is made;
h1 – the value of the exit from the room. Take 1.4 m;
l – distance from the foundation to the storage well. Usually 10 meters.
k is the slope coefficient of the sewer pipe, always equal to 0.02;
g – natural slope of the surface. Usually does not exceed 0.3 m.
h2=1.4+10*0.02+0.3=1.9 m.
According to the calculation data, a sewer trench is created.