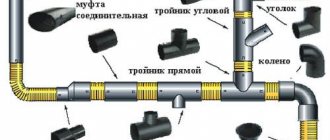
Types of plumbing fittings
Let's start with the typology of shaped parts with the material used for their manufacture. The material of the fittings does not have to match the material of the water supply pipes. For example, to branch cross-linked polyethylene pipes, plastic tees are used.
According to the material, shaped products can be:
- Steel;
- Cast iron;
- Plastic (plastic);
- Bronze (bronze alloys);
- Brass (brass alloys);
- Combined.
According to the type of fastening, fittings can be:
- Welded: attached to water pipes by hot or cold welding;
- Threaded: attached to water pipes with threads;
- Flanged: installation of water supply from pipes of medium and large diameters on bots with nuts.
Knees
a-steeply curved; b-welded sector
Steeply curved elbows are made using hot drawing or stamping methods. The bending radius of such elbows is from one to one and a half outer diameters of the pipe. Their high strength is due to the absence of wall thinning in the convex part. Due to their small dimensions, a compact arrangement of pipelines is achieved when used. It is possible to use stamped-welded elbows made of pipes or sheets using stamping and welding. Bent seamless bends are made from pipes on pipe bending machines. When bending, the walls become thinner; in addition, such elbows have straight sections at the ends. They are recommended for use in the absence of steeply curved knees. Sector bends are made from sectors of seamless or welded pipes welded together. The angle of an individual sector should not exceed 30°. Such elbows have a small radius, from one to two outer diameters of the pipe. In terms of strength, they are inferior to steeply curved and bent elbows; they are used in the absence of such elbows of the required diameter.
Basic plumbing fittings
The main (basic) shaped parts are:
- 90º angles: products for turning the water supply route at right angles;
- Tees: Provide a branch of the water supply line from the main route.
- Crosses: Provide division of the water supply system into two mutually perpendicular directions;
- Elbow: Provides a smooth turn of the water supply route.
- Transitions: Provide narrowing or expansion of the water supply system. Allows you to join pipes of different diameters.
Read: What are the types of water meters in water supply systems?
Legislative framework of the Russian Federation
valid Editorial from 01.01.1970
detailed information
| Name of document | “STATE ELEMENTAL ESTIMATED STANDARDS FOR CONSTRUCTION WORK. COLLECTION No. 22. WATER PIPELINE - EXTERNAL NETWORKS. GESN-2001-22" (approved by the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation on January 1, 2002) |
| Document type | norms |
| Receiving authority | Gosstroy of the Russian Federation |
| Document Number | GESN-2001-22 |
| Acceptance date | 01.01.1970 |
| Revision date | 01.01.1970 |
| Date of registration with the Ministry of Justice | 01.01.1970 |
| Status | valid |
| Publication |
|
| Navigator | Notes |
“STATE ELEMENTAL ESTIMATED STANDARDS FOR CONSTRUCTION WORK. COLLECTION No. 22. WATER PIPELINE - EXTERNAL NETWORKS. GESN-2001-22" (approved by the State Construction Committee of the Russian Federation on January 1, 2002)
Table 22-03-001 Installation of fittings
Scope of work:
01. Lowering and installing fittings onto the finished base.
02. Connection to the pipeline by welding, rolling up flanges or sealing sockets.
03. Welding of flanges to fittings (standards 5-7) and counter flanges to the pipeline.
Meter: 1 t fittings
Installation of cast iron fittings with diameter:
| 22-03-001-1 | 50-100 mm |
| 22-03-001-2 | 125-200 mm |
| 22-03-001-3 | 250-400 mm |
| 22-03-001-4 | 500-1000 mm |
Installation of welded steel fittings with diameter:
| 22-03-001-5 | 100-250 mm |
| 22-03-001-6 | 300-800 mm |
| 22-03-001-7 | 900-1600 mm |
| Resource code | Name of cost elements | Unit measured | 22-03-001-1 | 22-03-001-2 | 22-03-001-3 | 22-03-001-4 |
| 1 | Labor costs of construction workers | person-hour | 47,00 | 37,74 | 34,30 | 22,98 |
| 1.1 | Average job level | 3 | 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 2 | Driver labor costs | person-hour | 1,05 | 2,88 | 2,53 | 3,54 |
| 3 MACHINES AND MECHANISMS | ||||||
| 400001 | Flatbed vehicles with a carrying capacity of up to 5 tons | mach.-h | 1,05 | 0,85 | 0,75 | 1,05 |
| 150701 | Pipe-laying cranes for pipes with a diameter (loading capacity) up to 400 mm (6.3 t) | mach.-h | — | 1,75 | 1,53 | — |
| 021141 | Truck-mounted cranes when working on other types of construction (except main pipelines) 10 t | mach.-h | — | 0,28 | 0,25 | 0,35 |
| 150703 | Pipe-laying cranes for pipes with a diameter (loading capacity) of 800-1000 mm (35 t) | mach.-h | — | — | — | 2,14 |
| 4 MATERIALS | ||||||
| 103-0746 | Shaped cast iron connecting parts for cast iron pressure pipes outer diameter 50-100 mm | T | 1 | — | — | — |
| 103-0747 | Shaped cast iron connecting parts for cast iron pressure pipes outer diameter 125-200 mm | T | — | 1 | — | — |
| 103-0748 | Shaped cast iron connecting parts for cast iron pressure pipes outer diameter 250-400 mm | T | — | — | 1 | — |
| 103-0749 | Shaped cast iron connecting parts for cast iron pressure pipes outer diameter 500-1000 mm | T | — | — | — | 1 |
| 402-9086 | Asbestos cement mortar | m3 | 0,014 | 0,012 | 0,0081 | 0,0042 |
| 101-0311 | Heeled | T | 0,02327 | 0,01849 | 0,01415 | 0,00905 |
| Resource code | Name of cost elements | Unit measured | 22-03-001-5 | 22-03-001-6 | 22-03-001-7 |
| 1 | Labor costs of construction workers | person-hour | 353,80 | 154,10 | 93,72 |
| 1.1 | Average job level | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| 2 | Driver labor costs | person-hour | 105,35 | 83,26 | 55,02 |
| 3 MACHINES AND MECHANISMS | |||||
| 150202 | Two-station welding units for manual welding on a tractor 79 kW (108 hp) | mach.-h | 103,16 | 65,11 | 42,24 |
| 400001 | Flatbed vehicles with a carrying capacity of up to 5 tons | mach.-h | 2,19 | 2,02 | 1,13 |
| 150702 | Pipe-laying cranes for pipes with a diameter (loading capacity) up to 700 mm (12.5 t) | mach.-h | — | 16,13 | — |
| 150705 | Pipe-laying cranes for pipes with a diameter (loading capacity) of 1400 mm (63-90 t) | mach.-h | — | — | 11,65 |
| 4 MATERIALS | |||||
| 300-9506 | Steel flanges | set | P | P | P |
| 103-1009 | Shaped steel welded parts diameter up to 800 mm | T | 1 | 1 | — |
| 103-1010 | Shaped steel welded parts diameter over 800 mm | T | — | — | 1 |
| 101-1529 | Electrodes with a diameter of 6 mm E42 | T | 0,09 | 0,06 | 0,035 |
Connecting elements
The photo shows bushings and couplings designed to connect parts of the pipeline. The sleeve is put on in order to reduce the internal diameter. Such a need is not uncommon. The coupling allows you to connect pipes.
The danger of using couplings is that they form joints through which there can be leaks, so experts try to minimize the number of couplings. However, it is impossible to completely eliminate such shaped pipes. The need for them is especially great when there are obstacles along the straight sections.
Pipeline components
Pipeline fittings are auxiliary parts that complete the water supply system. They provide reliable pipe connections, bends and branches, as well as many other functions.
From this we can conclude that the fittings are designed to assemble the entire pipeline system together and give it the necessary angles of rotation and outlets for each individual user. Even if your pipeline is a straight pipe, you cannot do without connecting elements at its ends.
Scope of application of fittings
Shaped parts are used in the following cases:
- if you need to connect steel pipes with a diameter of 260 mm with an ethinol coating that has anti-corrosion properties;
- if it is necessary to join thin-walled steel pipes with a spiral-type seam with a diameter of 260 mm and a zinc double-sided coating;
- if you need to connect steel pipes whose wall thickness ranges from 160 to 1250 mm;
- if it is necessary to join electric-welded steel pipes D 160-430 mm;
- if you need to connect thin-walled steel pipes with varnish ethinol coating. The diameter of the pipes ranges from 220 to 450 mm;
- if it is necessary to connect asbestos-cement pipes D 140-550 mm;
- if you need to combine polyethylene pieces D150-350 mm;
- if you need to join cast iron sections D 140-450 mm.
Cross
Another type of connecting parts used when connecting cast iron pipes is a cross. In shape, it is two hollow cylinders with internal threads connected to each other.
If the task is to connect 4 pipes of the same diameter, then to solve it, use a straight cast-iron cross, which allows you to start a new branch of the pipeline without interrupting the previous one. To disconnect from the main line, a special valve is installed on this branch.
The process of connecting pipes using a cross is the same as when using a tee:
- At the end of the first pipe, a short thread of 7 turns is cut. After wrapping the thread with a sealant, the pipe is screwed onto the crosspiece;
- In the same way, two pipes with external threads wrapped with a sealant are screwed onto the other two sides of the cross.
- Then a long thread is cut on the last pipe. First, a lock nut is screwed onto the pipe, and then the pipe with the lock nut is screwed onto the threads of the cross.
Appearance of the crosspiece and installation diagram: 1 – crosspiece; 2 – lock nut; 3 – pipe with long thread; 4 – pipe with short thread.
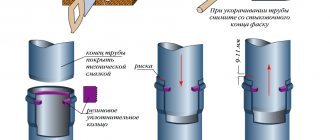
Shaped parts
During installation, it is necessary to achieve maximum tightness, so experts recommend using special sealing elements with a built-in spacer. In this way, the connected elements remain motionless. During the inspection, the spacer and sockets are washed and cleaned. It is important to remember that during installation it is necessary to apply a lubricating coating to the smooth end of the shaped pipe. It can be either silicone or a special paste.
With the help of lubricant, the parts fit into each other more easily during installation. In this case, there is a decrease in friction during operation, so gluing of elements is eliminated, and stress in parts is minimized. Lubrication is also necessary to ensure that rubber seals retain their properties longer, and only the outer part is lubricated.
Pipeline fittings or fittings - what are they and what are they?
Installation of technical pipelines is a complex technical task, the solution of which takes into account a lot of data. There may be an obstacle in the way of installation, an additional component may be mixed into the transported medium according to the technology conditions, or the design may plan to separate the fluid flow. All this cannot be solved only with the help of a straight, homogeneous workpiece.
A whole family of parts of various configurations is located on the pipeline. The name of these necessary materials is fittings
.
They are connecting elements
.
Installed in places of turns, transitions to another diameter, places of frequent assembly and disassembly and branches
.
There are a huge number of varieties, types, types of connecting materials. Their size and weight can be enormous, and some are smaller than a matchbox.
About fittings
The photo shows what the fitting is. When installing a sewer main, shaped pipes connect the branches. In this case, elbow 900 is used. The production also provides elbow 450. With its help, the horizontal and vertical sections are branched. If it is necessary to make a turn in the horizontal plane, then, as a rule, two 450 elbows are needed.
Sewer fittings
If there is little space, then GOST allows the installation of an adapter 450 and an elbow 450. When making a small turn, it is not prohibited to use a shaped pipe 22 and 50. If it is necessary to make an insertion, then a triple fitting is used, called a Y-shaped or T-shaped (depending on the features design execution).