The problem of sewage treatment has always been one of the main challenges that humanity has faced in organizing civilized places of residence. Already in ancient Rome there were public toilets in which water was drained through pipelines into special settling tanks, where household wastewater was purified from human waste products. At all times, people have tried to apply modern methods of purifying MUNICIPAL wastewater and to use the latest achievements of science and technology. Since the times of ancient Rome, much has changed in solving this large and important task, but the basic principles of cleaning have remained the same.
Stages of wastewater treatment
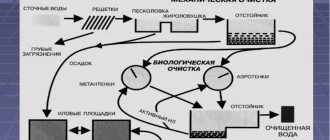
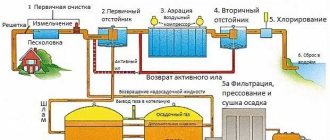
All processes of the sewage treatment plant system can be divided into the following stages:
- mechanical cleaning;
- averaging (primary settling tank);
- anaerobic stage;
- aerobic stage;
- nitrification stage;
- secondary settling;
- tertiary treatment stage;
- disinfection stage.
Mechanical cleaning
Wastewater flows through a common gravity collector into a receiving chamber in which stations are installed to retain coarse impurities larger than 6 mm in size. Coarse solid waste (garbage, paper, etc.) from a lattice container is manually unloaded into plastic bags, which are then transported by special transport from the territory of the domestic wastewater treatment plant. This procedure can be carried out using the following equipment:
- mechanical gratings;
- drum sieves;
- sand traps (sand traps);
- grease traps.
Also, if there is a large amount of petroleum products and fat-containing impurities in the local sewage system, a flotator can be installed, which will serve as an additional pre-treatment stage.
Averaging
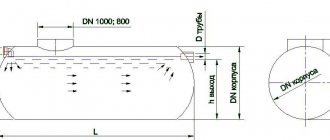
Wastewater cleared of debris enters the homogenizer, which is designed to average the wastewater in terms of composition and flow rate. The homogenizer is equipped with mixers (see catalog) and systems for supplying wastewater to biological treatment. A mixing system using a pump prevents sedimentation of suspended particles and ensures averaging of wastewater by composition. The intensity is changed using a slider.
Anaerobic stage
With the help of PNP feed pumps, wastewater from the homogenizer is uniformly supplied at an average hourly flow rate to the denitrifier, which is equipped with a modern hydraulic system for homogenization, consisting of a PND submersible pump, a pressure manifold and drop pipelines with nozzles at the end. At this stage, nitrates are removed. Excess sludge from the denitrifier is periodically pumped out using a pumping station into a sludge storage tank.
Aerobic stage
In the first stage aeration tank, a highly loaded biological treatment process is carried out, in which, thanks to microorganisms and oxygen, the majority of existing organic substances are oxidized. Aeration, as well as mixing of the sludge substance in the aeration tank, is carried out using tubular fine-bubble aerators of the “Polypore” type; the intensity is adjusted using valves.
Denitrification and nitrification stage
From the aeration tank, through a gap in the lower part of the partition, wastewater flows independently into the nitrifier, where the second stage of biological treatment is implemented with the nitrification procedure (the transition of ammonium nitrogen into nitrates). To intensify and stabilize the process, an inert loading of the “Framework” type is used, on which microflora is fixed in the form of a biofilm. The process of aeration, washing of the load and mixing in the nitrifier occurs due to the work of tubular aerators. The intensity of the aeration unit is regulated by valves.
Secondary settling
After the nitrifier, the sludge mixture enters the secondary settling tank, where sludge sedimentation occurs. The flow rate of the recycle sludge mixture is regulated depending on the concentration of pollutants in the source sewer water. Abundant sludge from secondary settling tanks is periodically, based on the measurement results, pumped out using airlifts into a sludge storage tank.
Post-treatment stage
As a rule, having gone through these previous stages, wastewater does not have the necessary degree of purification that meets the requirements for discharge into fishery waters, so additional purification is required. This is done using microfilters that contain various absorbent elements, for example, active carbon. The clarified sewage runoff from the surface of the secondary settling tank passes through perforated pipes into a collection tray, from where it enters the above-filter space of the filter with a floating load through a weir. At the same time, constant aeration of the load is carried out using an aerator. From the above-filter space, wastewater is directed to the adsorber, where a carbon filter is used. This adsorber ensures effective removal of high and low molecular weight organic substances from water.
Disinfection stage
The purified water flows by gravity into the clean water compartment. Compressed air is supplied to the tank through the aerator by a turbo blower to saturate the water with oxygen. From the reservoir, purified water enters the bactericidal installation for ultraviolet disinfection of the treatment unit and then through the meter-flow meter RS1 to outlet. This equipment is used to destroy bacteria by ultraviolet irradiation, as well as ultrasound. The advantage of this system is the presence of an amalgam ultraviolet lamp, which has significant characteristics that affect the bactericidal properties.
Sludge dewatering
Excess sludge formed during the treatment of domestic wastewater is collected in a sludge tank and, as it accumulates, using a submersible pump, PNI is sent to dewatering bags and disposed of by transport to places approved by local environmental authorities. It is also possible to use the sludge for commercial purposes. In Europe, for example, sludge is used to produce synthetic fuels, biosoils and as a raw material in cement factories. Such recycling methods help preserve the environment. At this stage, complete wastewater treatment is completed.
Biological wastewater treatment from organic pollutants
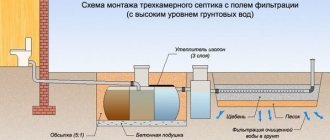
The huge amount of organic substances contained in wastewater provides a favorable breeding ground for the proliferation of microorganisms (bacteria) that have the ability to absorb these substances. This method of treating domestic and industrial wastewater is based on this property of bacteria. During the respiration process of bacteria, all organic matter is oxidized and decomposed into relatively harmless components. Thanks to this, the water does not rot, becomes transparent, and the level of bacterial contamination is reduced. Mineralization of organic substances is carried out by two types of bacteria: aerobic and anaerobic. The respiration process of aerobic bacteria occurs with the participation of free oxygen dissolved in water, while anaerobic bacteria do without it. Mineralization without air access (anaerobic) is carried out in reinforced concrete containers (two-tier settling tanks, septic tanks, digesters). The process involves fermenting organic compounds with the help of bacteria, which produce methane. The main disadvantage of this type of cleaning is the release of methane and, consequently, the formation of unpleasant odors, which is not very safe from a sanitation point of view.
Efficacy of B.ECT
When choosing one or another component of equipment for sewage treatment plants, you should pay attention to the incoming waste. Analysis of incoming wastewater will help determine equipment configuration. Therefore, it is very important to assemble an optimal module that will be as efficient as possible at the lowest cost. To accurately calculate the cost of domestic wastewater treatment plants, you need to fill out questionnaires that will help our engineers choose the right work plan and the equipment itself. Here, the salvo discharge indicators will be taken into account (maximum total, suspended solids content, BOD, ammonium, etc.
Advantages over fiberglass
B.EST is a fully prefabricated container-block station. The containers can be made from both stainless steel and ST3 steel with the latest generation anti-corrosion coating. Thus, the advantages of these settings include:
- Optimal price-durability ratio compared to fiberglass products (FRP);
- Large regulatory and legislative framework for design;
- Simple and reliable operation and design.
Features of B.EST series stations
- Highly efficient cleaning up to standards for discharge into fishery reservoirs;
- compactness;
- complete set of electrical power technological equipment, shut-off and control valves, instrumentation, automation system and others;
- the presence of a homogenizer makes it possible to ensure a uniform supply of sewerage and water supply runoff in terms of both quantitative and qualitative indicators, and also allows one to abandon the construction of a receiving tank, which significantly reduces the cost of sewage treatment facilities and the area they occupy;
- the presence of a two-stage post-treatment unit, which guarantees high efficiency of wastewater treatment before discharge into a reservoir of fishery value.
- UV disinfection device, which ensures complete disinfection of treated wastewater;
- absence of external odors;
- high stability at peak loads;
- low power consumption;
- minimal amount of sediment formed;
- reliable equipment that does not require repairs.
Advantages of autonomous sewage systems TM Rainpark
- Durability of the housing structure without the need for additional reinforcement;
- Tightness of housings and resistance to corrosion;
- Maintainability of the case;
- Supply of equipment in full factory readiness for installation on site;
- Service life – more than 50 years;
- Professional consultations on the selection and installation of equipment by company specialists;
- Simplicity and ease of maintenance;
- Warranty period – 1 year.
TM Rainpark products are certified in accordance with the standards of the Russian Federation and the EU.
The Standardpark company is a manufacturer, provides professional technical solutions and supplies equipment for organizing autonomous sewerage and solving problems of wastewater treatment or accumulation at an affordable price. We offer our clients modern and efficient technologies and equipment that are produced using the latest scientific advances.
For advice or any other questions about products, please contact the managers of the office closest to you!
Cost and conditions
Price
To determine the cost of block-modular installations, you need to understand the need for certain cleaning technologies. Local sewage treatment facilities are a mandatory requirement for enterprises and other organizations that have contaminated wastewater that does not comply with legal and sanitary standards. We are manufacturers of biological treatment systems, our staff includes professional engineers, project managers, electricians, etc. Buying wastewater treatment plants from us means getting design services, competent advice and recommendations on the optimal configuration of the system, as well as the ability to order installation, commissioning and maintenance.
The minimum price for an installation with a capacity of 6 m³/day is 1,822,500 rubles, which is called B.EST-6U. It is designed for 30 people. The calculation of treatment facilities is based on the number of intended users.
Deadlines
The delivery time for products varies depending on the complexity of the project being carried out and its stages. Any installation requires labor-intensive work, which takes 30 working days.
Delivery
Ours) delivers in any accessible and fast way. It is also worth considering the delivery time, as it varies depending on the region of the object. We have a lot of completed projects behind us, which you can familiarize yourself with by clicking on the link.
Features of drains
To begin with, it is worth understanding the composition and characteristics of domestic sewage wastewater.
This is the name of the water that was used in households. needs or in production. In addition, wastewater includes atmospheric waters that are collected from the surface of the earth. For the correct selection of household cleaning technology. and industrial wastewater, you need to know the nature of the pollution. Thus, there are three types of wastewater pollution:
- Mineral pollutants. This includes all inorganic impurities, for example, soil particles, salts of various origins, as well as various inorganic chemical elements and compounds. Such pollutants can be present both in domestic wastewater and in wastewater received from industrial enterprises.
- Organic pollutants are present in large quantities in households. drains. This includes complex elements of animal and plant origin. Also included in this group of pollutants are various chemical and polymeric organic compounds. As for household sewage wastewater, 80-90 percent of it consists of impurities of organic origin. As part of the household In wastewater, such pollutants are present in the form of fecal matter, food debris, and peelings from vegetables and fruits.
- Biological pollutants are various microorganisms that live in wastewater and feed on the elements contained in the effluent. So, bacteria, fungi, viruses live in large quantities in sewage, there are helminth eggs and other protozoa.
Important to know: the concentration of biological pollutants depends on their presence in the environment, as well as on the composition of the wastewater. Thus, in unfavorable conditions of industrial wastewater, the concentration of microorganisms may be minimal, but in households. wastewater contains the necessary nutrient medium, so there can be many times more biological pollutants.
Design of treatment systems
Treatment facilities for industrial wastewater are designed taking into account the following factors:
- groundwater level,
- design, geometry, location of the supply manifold,
- completeness of the system (type and number of blocks determined in advance based on biochemical analysis of wastewater or its predicted composition),
- location of compressor units,
- availability of free access for vehicles that will remove waste trapped by grates, as well as for sewage disposal equipment,
- possible placement of the purified liquid outlet,
- the need to use additional equipment (determined by the presence of specific impurities and other individual characteristics of the object).
Important: Surface wastewater treatment facilities should be designed only by companies or organizations with an SRO certificate.
Types of treatment facilities
In order to understand what blocks a treatment complex may consist of, you should know the main types of wastewater treatment facilities.
These include:
- mechanical structures,
- biorefinery installations,
- oxygen saturation units that enrich already purified liquid,
- adsorption filters,
- ion exchange blocks,
- electrochemical installations,
- physical and chemical cleaning equipment,
- disinfection installations.
Effluent treatment equipment also includes structures and tanks for storage and storage, as well as for processing filtered sludge.
City wastewater treatment plants