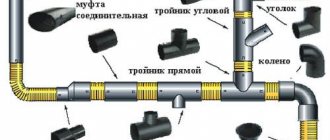
To protect wastewater from freezing, there is a heating cable for sewer pipes. Heating of sewerage is necessary in situations where pipes have to be located in unheated rooms, basements, and basement levels of buildings.
Sometimes it is not possible to lay the system at the required depth, which makes the pipeline susceptible to the risk of freezing drains and the formation of an ice plug. In such cases, it is necessary to insulate the pipes. The best option is a heating cable for sewer pipes, which allows you to solve the problem effectively and reliably. Let's take a closer look at this issue.
Types of wires
There are several types of cable used for pipeline heating, which have different technical characteristics and installation methods, which allows the use of one or another type depending on the technical specifications.
The operating principle of a heating cord is quite simple: an electric current heats the pipe to above-zero temperatures, preventing the passing liquid from freezing. The cable used for heating can be:
- Shielded, having a metal braid, used as additional protection against mechanical damage.
- Unshielded, double insulated.
- Zonal. Spot heating of certain areas.
- Self-regulating. A pair of copper conductors and a working matrix between them.
- Resistive, single or double wire.
Installation of the heating wire can be done both outside and inside the system; the latter option is economical in terms of electricity, but more expensive when performing installation work.
The most effective use of external heating is in combination with the use of thermal insulation materials, which reduce heat losses. Sewage systems made of metal and plastic of almost any diameter can be effectively heated.
Self-regulating heating cable for heating sewer pipes
The distinctive ability of a self-regulating cable is the ability to cut it into sections of any length, thus, sections can be manufactured (coupled) directly at the installation site.
Self-regulating cable SAMREG 16-2
- Power: 16 W
- Purpose: pipeline
- Screen: no screen
- Type: self-regulating
- Type: low temperature
- Application: without explosion protection
Price src=”https://ProUteplenie.com/images/uploads/images/products/srl_kabel_122739-image_product_card.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”401″ height=”300″[/img]
Self-regulating cable SRL 16-2
- Power: 16 W
- Purpose: pipeline
- Type: self-regulating
- Type: low temperature
- Application: without explosion protection
- Max. temperature (operating): 65 °C
Wholesale price
Self-regulating cable SAMREG 24-2
- Power: 24 W
- Purpose: pipeline
- Screen: no screen
- Type: self-regulating
- Type: low temperature
- Application: without explosion protection
Price src=”https://ProUteplenie.com/images/uploads/images/products/srl_kabel_122739-image_product_card.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”401″ height=”300″[/img]
Self-regulating cable SRL 24-2
- Power: 24 W
- Purpose: pipeline
- Type: self-regulating
- Type: low temperature
- Application: without explosion protection
- Max. temperature (operating): 65 °C
Wholesale price
Self-regulating cable SAMREG 30-2
- Power: 30W
- Purpose: pipeline
- Screen: no screen
- Type: self-regulating
- Type: low temperature
- Application: without explosion protection
Price src=”https://ProUteplenie.com/images/uploads/images/products/srl_kabel_122739-image_product_card.jpg” class=”aligncenter” width=”401″ height=”300″[/img]
Self-regulating cable SRL 30-2
- Power: 30W
- Purpose: pipeline
- Type: self-regulating
- Type: low temperature
- Application: without explosion protection
- Max. temperature (operating): 65 °C
Wholesale price
Also, the heating system for a household pipeline based on a self-heating tape does not require complex controls. Sections up to 20 m long can be connected directly to the network without the use of controllers and automatic devices. The self-regulating cable is not subject to overheating even when installed overlapping.
The maximum length of one section of a heating cable depends on its linear power, as well as inrush currents.
More detailsMaximum length of the heating cable in a sectionMore detailsService life of the heating cable. Protection from UF raysRead more Heating cable in a pipe. Heating inside the pipeline
Calculation and selection of cord
It is very important to correctly calculate the power of the heating cord, especially for plastic products, otherwise overheating will lead to deformation, leakage and damage to the network. When calculating, factors such as:
- Diameter of the sewer system.
- The material from which the pipeline is made.
- Network laying depth.
- Technical characteristics of insulating material.
Taking into account the totality of information, the heat loss of one linear meter of the network is calculated using the formula:
- Qtp – heat losses of the pipeline (W).
- Λ – thermal insulation coefficient.
- Ltp – pipe length.
- Tbh – liquid temperature in the network.
- Thap – minimum ambient temperature.
- D – outer diameter of the pipe together with thermal insulation (m).
- 1.3 – increasing thermal conductivity safety factor.
External system design
It is most in demand, as it takes much less time compared to installation inside the pipeline.
The technology for laying the cord is quite simple, which allows you to do the necessary installation work yourself. For external heating, a self-regulating cable is mainly used, consisting of several conductors and a matrix in a polymer sheath, which, at the slightest temperature fluctuations, change the resistance in the electrical circuit.
As the temperature drops, the resistance decreases, which automatically increases the passage of electricity, resulting in increased heat transfer to the pipeline.
Depending on changing temperature conditions, heat output in different sections of the network will be produced as needed with optimal use of electricity.
Internal system design
The heating wire is located directly inside the pipeline, and this method is usually used on an existing network. This eliminates the need for excavation work to install frost protection.
Please note that the cable for internal heating should be used in small areas with a minimum number of turns. Kinks and loops will cause blockages and clog the drain.
It is almost impossible to control the location of the cable in the pipeline, since the liquid is heated directly.
IMPORTANT: It must be located in the lower zone of the pipeline.
Advantages and disadvantages of internal and external heating systems
A positive quality of internal heating is that it can be easily installed in existing pipelines without opening the soil and using thermal insulation. Heating the directly passing drain liquid does not require much electricity consumption.
Negative points include:
- Reducing the internal cross-section of the pipe.
- Possibility of congestion.
- A labor-intensive installation process on long sections with transitions and bends.
- The need to install an inlet tee.
Please note! The cord is well protected from mechanical damage, but is susceptible to aggressive chemical attack by wastewater.
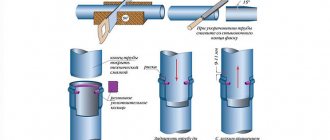
The external heating cable for sewerage is attached directly to the outer wall of the pipe using plastic clamps or adhesive tape, which greatly facilitates installation work.
To lay or not
To understand whether there is a need to use a heating wire, you should proceed from several parameters:
- depth of placement of water supply and sewerage pipes. In situations where pipes are placed above the freezing level of the soil, it is highly desirable to install the cable along its entire length. It should be borne in mind that for different areas of our country, the depth of soil freezing may have different values. So in Kaliningrad this level corresponds to 70 cm, and for Chelyabinsk – 190.
- region of residence. This characteristic can also influence the decision of whether a heating wire is needed. In regions with a frostier climate, emergencies occur more often, from which we can conclude that water supply systems should be protected with the help of such a device. If the pipes are placed to a considerable depth, then you can limit yourself to only insulating certain sections of the pipe. The most susceptible fragments in the water supply and sewerage system are those that are located closest to the surface of the earth. Usually these are plots laid next to the house.
Installation of an external heating cord, recommendations
When installing the wire, two methods are used: linear arrangement along the pipe or tangential wrapping.
Adhesive tape or synthetic cable bandage is used as fastening. The distance between the fastening points should not exceed 200 millimeters.
Often, to increase the efficiency of heat transfer, the pipe is initially wrapped in aluminum foil (this can significantly increase the heating area), to which the heating cable is directly attached. This method is recommended for installation on plastic products, which have low thermal conductivity compared to metal ones.
When laying the heating element, you should avoid creating kinks and make turns at an acute angle to avoid accidental damage to the electrically conductive wires and damage to the insulating layer. The final stage will be the installation of thermal insulation material.
Resistive heating cable for sewer heating
For domestic use, ready-made sets of resistive heating cables (or constant power cables) are also convenient. The main advantage is the price, which is much lower than that of a self-regulating cable.
The difference between a resistive cable is that it lacks the ability to self-regulate temperature. This function is performed by a thermostat located in the section end coupling. For reliability, it is recommended to use a two-core resistive cable - one of the two wires is heating, the other is supplying. The advantage of a two-core resistive cable is that there is no need to return the cable.
Installation of a heating cord inside a pipeline
First of all, you should decide where the element will be inserted; the best option is the point inside the building at the outlet of the pipeline. This must be taken into account when laying a sewer system in a new building if you plan to install an internal cable for heating the network.
It will be a little more difficult to deal with an existing sewer system, when access to the intended entry point is often severely limited or impossible. In this case, it is possible to move the access point to the pipe exit from the building, for which you can provide access by digging a hole near the wall and partially dismantle the line to install a tee.
The pipes should be cleaned, rinsed thoroughly from the inside and dried. The most difficult thing is laying the cable inside, especially if the pipeline has turns and connecting elements. It is recommended to lay the wire before installing the coupling, carefully pushing it through so as not to damage the insulating layer. If for some reason it is not possible to install the cable, you must first stretch a thin steel wire to the entrance well or septic tank. Then attach the end of the cord to the wire with adhesive tape and pull it along the main line.
After laying the cable, install a tee and connect it to the wire supplying electricity.
Independent connection to the power grid
Quite often, a malfunction occurs precisely at the connecting junction, which leads to de-energization of the sewer cable. Correct installation is carried out in the following order:
- A large heat-shrinkable tube is placed on the end of the heating cord.
- The outer insulating layer is stripped from the end at a distance of 50 mm, the braid is cut 10 mm from the edge of the insulation.
- The heating cores are separated and the internal insulation of about 6 mm is removed.
- Next, on the cord, as well as on each core, a small-diameter tube and a medium-diameter tube.
- It is necessary to place the twisted braid in a metal tube and crimp it to make a tight connection with the braid.
- The end of the power supply wire is cleared of 80 mm of outer insulation.
- The cores are separated: the ground wire remains as is, and the phase and neutral wires are cut to a length of 35 mm.
- The ends of the wires are freed from secondary insulation by 6 mm.
- The stripped ends of the supply and heating cables are sequentially inserted into heat-shrinkable couplings and connected by heating with a hair dryer or open fire.
- Additionally, each joint must be wrapped with insulating tape.
- The ground wire is inserted into a metal sleeve crimped onto the braid and is also clamped.
- A medium-sized heat-shrinkable tube is moved onto the resulting joint, and after thermite treatment - a large one, followed by heating.
Such a connection completely prevents moisture from entering the connecting joint, so there will be no short circuit in the wiring.
Principle of operation
Heat is generated due to the fact that the wire that is the basis of the cable has a certain electrical resistance.
When current passes through metal, heat is generated. This principle is used in the manufacture of incandescent lamps and heaters. To ensure that energy is not wasted, the cores are insulated with dielectric materials with the maximum degree of thermal conductivity and flexibility. The heating cable is made from flexible metal with medium resistance. The heat generated is enough to prevent ice from forming and not melt the insulation.