Advantages and disadvantages of water supply to a private house from a well
The quality and operational characteristics of borehole water intakes vary over a wide range. They largely depend on both local characteristics and the type of structure. Thus, shallow wells have a lower flow rate compared to wells, springs, and open sources. In addition, they are prone to silting. The water from artesian water intakes is sometimes overly saturated with minerals, requiring complex purification. Due to excessive mineralization, it may not only be unsuitable for consumption, but even for watering a country garden, unlike water from a shallow well.
However, often artesian water intakes are famous for their quality both in terms of biochemical indicators and debit. Their capacity is practically not subject to seasonal fluctuations, and the exploited horizons are highly protected from technogenic pollution.
The main disadvantages of artesian wells are the high cost of their construction, which requires a special permit. This procedure is slow and troublesome. And if the lack of a license for shallow drilling sites is overlooked, an artesian drilling site cannot do without permission.
An important advantage of many wells is that their construction, compared to mine wells, takes a matter of days. And with the exception of artesian ones, their cost is significantly lower.
Well in a water supply scheme: types, features of design and operation
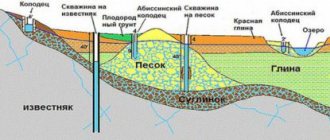
Regarding the nature of the water intake horizon (aquifer), three types of wells are distinguished:
- To the high water . Water is supplied from a well to a house sometimes from a depth of a few meters.
- On the sand . The source of recharge is groundwater seeping from the surface through layers of sand and sandy loam. The depth reaches 20-50 m.
- On limestone or artesian . They are fed from interstratal waters located at depths of more than 50 m. Often the aquifer is layers of ancient Cretaceous deposits - limestones.
Wells of the first type are most susceptible to the influence of the environmental situation and seasonal fluctuations in the water level. Thus, a well “for high water” may become empty in August or be “deteriorated” by a spring flood, autumn rains, or waste discharge from a nearby enterprise. Even in ecologically favorable areas, the water from them is safe to use for drinking only after purification and boiling.
The second type of well – for sand – is characterized by optimal consumer qualities. They are characterized by productivity that is already sufficient to meet the needs of a country house. Much less susceptible to external influences than perched waters. Sometimes the quality of water is not inferior even to artesian springs.
The third type of water intake is for limestone; apart from its high cost and possible excessive mineralization of water, it is the best. With a stable flow rate of 1.5 m3/hour, artesian water resources are practically not subject to external influences.
Features of selecting equipment for different types of wells
The heart of the autonomous water supply scheme is, of course, the pump. Depending on the type of water intake structure and the layout of the water supply system, submersible or surface pumps are used.
Submersible
The scheme for supplying water from a well to a house using a submersible pump provides for its placement with complete or partial immersion in the aquifer. From such a submerged position, the pumping unit is capable of supplying water to a height of 40 m or more. The height of the liquid supply is called pressure. To roughly estimate what pressure is needed for a water supply scheme, it is necessary to add to the depth of the unit’s placement the height above ground level to which it must pump water.
Deep pumps designed for wells and boreholes differ in appearance. The latter look like long narrow cylinders made of stainless or chrome steel. After all, if the diameter of a well pump is not standardized, then for a well pump it should not interfere with the free descent/ascent of the unit in the casing pipe. For this purpose, an installation gap of at least a centimeter is recommended. For example, for sand wells using casing pipes Ø 100 mm, three-inch units are used, and for artesian wells with casing pipes from Ø 120 mm, four-inch units or more are used.
Superficial
An undoubted advantage of surface pumps is ease of maintenance. Unlike deep ones, they are mounted on the surface of the earth, and only their suction pipe is immersed in the aquifer.
Surface units with a normal suction mode are capable of pumping water from a depth of a maximum of 8-9 m, and those equipped with a remote ejector - from a depth comparable to submersible pumps. However, such equipment is bulky and exhibits lower consumption characteristics.
A prerequisite for the operation of external pumps is pre-filling with water upon first start-up. Once the system is filled, the check valve prevents it from leaking. Therefore, there is no need to refill the system after stops.
Rubber or plastic reinforced hoses are used to supply water. For powerful systems with significant flow rates - plastic or steel pipes.
Water supply standards
As always, we will start by getting acquainted with the regulatory documentation. Water supply standards (including cold water) are established by the set of rules SP 30.13330.2012.
Here are the key requirements of this document:
- Water pressure on plumbing fixtures should not exceed 4.5 kgf/cm2;
However: if a building is being erected in a microdistrict with an existing multi-storey building and is powered from a common water supply with the surrounding houses, the pressure can be increased to 6 atmospheres.
- The minimum water pressure must ensure the functionality of household and sanitary appliances;
Help: most washing machines, dishwashers and water heaters operate at a pressure of 0.3 atmospheres or higher.
- The composition and quality of water must comply with SanPiN 2.1.4.1074-01 standards;
- The pipes used for installing water supply systems must last at least half a century;
- During operation of the water supply system, its hydraulic resistance must remain unchanged.
It’s curious: this clause of the joint venture actually prohibits the use of non-galvanized steel pipes, which are used to install most of the water pipes in Soviet-built buildings. However, most of these buildings, along with standard water supply systems, continue to be used at the present time.
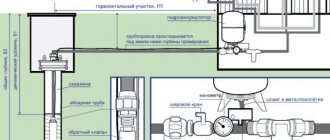
Scheme of water supply for a private house from a well with a deep pump
For a capital system designed to operate all year round (Fig. 1), only a deep-well pump with a hose is not enough. Required:
- A device that allows you to lower/retrieve a pump from a well. In this regard, a temporary scheme for connecting water supply from a well in the country with a small “Stream” as a submersible pump is content with a strong rope. However, for heavy equipment you will already need a steel cable with a block and a winch.
- Transition unit between the hose and the main pipe. This small pipe on one side has a fitting where the hose is put on, on the other - a fastening corresponding to the type of main pipe: fitting, coupling, union nut, etc.
- Yard highway. Typically, pipes made of polypropylene or low-density polyethylene are used for the external installation of private houses and summer cottages.
- Node for entering the main line into the house. Adapter from the main pipe to the in-house wiring.
To accommodate the equipment, the well head is equipped with a pit or caisson. A caisson is a sealed structure that prevents precipitation and debris from entering the well. To prevent freezing of the pipeline, the caisson must be deepened. If for some reason this is not possible, it is insulated and provided with electricity. heating.
The main pipeline is introduced into the building through the wall of the pit and the foundation of the house. The passage section is decorated with a steel or plastic sleeve with sealing of its external and internal gaps.
If the well is located nearby (up to 10 m), the pit can be installed directly in the building or a basement can be used instead. With this option, the main hose is laid through a channel (canister) made of steel or plastic pipe. For its reliable connection to the well casing, an overhead clamp is used.
The deep pump is activated manually or automatically. When operating a hydraulic accumulator, the start/stop of the water-lifting unit occurs according to the commands of the pressure switch, and when operating the storage tank, according to the commands of the float level sensor.
Problems and solutions
Alas, often the cold water supply to buildings does not function as well as home owners would like. Fortunately, some problems are easy to solve on your own.
Weak pressure
Problem number one is insufficient water pressure.
Lack of pressure is most often observed on the upper floors
Possible reasons:
- Mixer aerator clogged. In this case, you observe equally weak pressure of cold and hot water at one water intake point;
The mixer aerator adds volume to the stream with minimal water consumption
- Clogged cold water line. It can be caused by large debris stuck at a pipeline bend or in front of fittings (including in the mixer body), or by the accumulation of deposits on the walls of a steel pipe;
- Clogged mechanical filter at the inlet;
- The valve or tap on the inlet or riser is not fully open;
- Deposits in the riser or bottling;
Rust and lime on the walls of a steel cold water pipeline
- Low pressure in the main water supply.
Hint: in the last two scenarios, the management company or higher organizations should deal with the problem of low pressure. The function of residents is reduced only to submitting an application to the maintenance service.
The problematic bottling area must be cleaned or replaced
Solutions:
- Unscrew the aerator and rinse it under running water. If the aerator is equipped with several stainless mesh, remove most of them, leaving one or two;
Cleaning the faucet aerator
- Try plugging the faucet spout with your finger and opening the cold and hot water taps at the same time. As a rule, the pressure of the hot water supply is higher, and the reverse flow of water often eliminates the blockage of the supply line;
- Turn off the tap on the supply line, open the mixer and try to clear the blockage in the supply line with a cable or elastic steel wire;
- If the water is blocked, open the filter and clean its mesh from sand and other debris;
The photo shows a filter disassembled for cleaning.
- Open the taps on the inlet and riser all the way.
Valve leak
Another typical problem is a screw valve or ball valve leaking along the stem. It usually occurs after it closes.
In most cases, to stop the valve from leaking, it is enough to open it all the way with a little force. At the same time, the thread of the rod presses the stuffing box.
Open the valve completely and the flow will stop.
If this does not help, you need to fill the oil seal.
Here are step-by-step instructions for performing this generally simple job:
- Close the valve;
- Remove the lamb from it;
- Unscrew the gland nut with an open-end, adjustable or pipe wrench;
- Pry the seal with a screwdriver and remove it from the valve stem;
- Place several turns of a graphite or oil seal around the rod, sealing each turn with a screwdriver;
- Reassemble the valve in reverse order and open it, checking the stem for leaks.
Screw valve packing
Ball valve stems are usually sealed with a fluoroplastic or Teflon washer. To stop the leak, just tighten the oil seal nut 1-2 turns.
Ball valve stem leaking
Fistula of the riser or eyeliner
Through fistulas occur, as a rule, on welds (transverse or longitudinal - all water and gas pipes are made by welding a flat piece).
Fistula in a steel pipe
To eliminate a leak, the easiest way is to use a bandage made of an aluminum clamp and a piece of rubber (for example, a gasket for a faucet).
Aluminum clamp will help eliminate leaks
- The section of the pipe near the fistula is cleaned with a file or knife to remove rust and paint;
- A clamp corresponding to its diameter is put on the pipe;
- A rubber gasket is inserted under it;
- The clamp is tightened, pressing the gasket to the leak.
Installed bandage
By the way: instead of a clamp, you can use annealed steel or copper wire. In this case, the bandage is tightened with pliers.
Scheme of water supply from a well with a surface pump
The scheme, where water is supplied to a private house from a well by an external pump (Fig. 2), is suitable for shallow depths, when installed on high water or sand.
This option is somewhat more practical than a system with a deep-well pump - no equipment is required to lift the unit, and maintenance is simplified.
The pump or pumping station is located next to the well in a pit - a caisson. Placing equipment in the house is undesirable due to the noise it produces.
Water is supplied to the house, as with the option with a deep-well pump, through the yard main. The pumping system is controlled automatically, but if necessary, this can be done manually.
The building water supply system includes:
- Sanitary fixtures
- Pipelines and pipeline fittings
- Drinking water purification plants (household filters)
- Pumping installations for domestic and fire-fighting water supply
- Shut-off valves
- Water meters
- Water heating installations - boilers
- Spare and control tanks
Installation of a caisson and laying a main line to the house
The pit (caisson) is constructed after the completion of drilling operations. Construction begins by cutting out a hole around the top of the casing.
Further steps are dictated by the type of caisson design. For example, ready-made plastic containers are placed on sand preparation, secured with special anchors, and then backfilled. If the material of the caisson walls is ceramic brick or well rings, then a concrete bottom is first made. Then they carry out masonry or install concrete elements, waterproofing, and complete everything by backfilling the soil.
To cover the pits, slabs with a hole for the entrance hatch are used. Lightweight concrete insulation is laid on top of it. They form a slope and install waterproofing. It is also necessary to take care of the ventilation of the pit.
In order not to spoil the appearance of the site, you can pour fertile soil on top of the floor slab and lay out a lawn or place decorative elements of landscape design.
The construction of the caisson is carried out simultaneously with the laying of the yard main for supplying water to the cottage. A trench is dug for it, where a pipe is laid with a slope towards the well or house. The direction of the slope dictates the location of the emergency drain.
You can connect the supply pipe to the irrigation system to the common main inside the house or directly in the caisson. To do this, use an additional outlet with a valve. Since irrigation is carried out only for a few months, there is no need to deepen the irrigation line. However, it is imperative to provide fittings for emptying it in the winter.
The building sewage system includes:
- Sanitary fixtures
- Pipelines and pipeline fittings
- Installations for additional wastewater treatment (grease trap, sand separator, gypsum sedimentation tank)
- Transfer pumping units (if it is impossible to discharge wastewater in gravity mode)
- Internal drains that drain atmospheric water from the roof of buildings
Water supply and sewerage systems of buildings, like vessels in the body, carry water necessary for life and healthy functioning, used for cooking, washing and washing, production, taking waste and contaminated water back.
Pipelines laid from sanitary fixtures are sloping towards the sewer riser. If drainage of wastewater in gravity mode is impossible (the sewer riser is far away, the level of the street sewer is higher than the level of the sanitary fixture), in this case, household sewage pumps are provided. They are compact, aesthetically pleasing and do not spoil the appearance of the bathroom. Important! Sewerage from a washbasin, bathtub or bidet is carried out with pipelines with a diameter of 50 mm. Wastewater from the toilet is discharged through a 100 mm pipeline. The recommended slope of a pipeline with a diameter of 50 mm is 3%, for 100 mm - 2%. Forbidden! Failure to maintain the slope will cause sediment to build up in the pipes with frequent blockages. It is not advisable to pour construction waste and solid household waste into the sewerage system; pipes may become clogged with cementation of the pipe space, which can only be removed by completely replacing the pipes. Laying sewer risers and pipelines in living rooms, bedrooms, treatment rooms, and classrooms is not allowed.
Recommendations for the internal wiring diagram from the well water supply
The diagram for connecting a well to the water supply in a house does not differ from wiring with other types of autonomous sources (wells, open reservoirs, etc.)
It is advisable to install a hydraulic accumulator and a water reserve tank. These devices increase the comfort of using water supply, make work more stable, and reduce equipment wear.
To increase the pressure in the water supply, a small booster pump with a pressure sensor is additionally installed at the outlet of the reserve tank. It increases comfort and allows you to use equipment with an operating pressure of 4 bar (showers, Jacuzzis, washing machines, etc.).
The booster pump makes it possible to place the storage tank anywhere, even in the basement. However, it is better to place it as high as possible - on the second floor or attic. In this case, when the power is turned off. energy, it will be possible to use water, albeit with little pressure.
For pipe wiring, polypropylene pipes with soldered joints are optimal. They are characterized by a good price-reliability ratio. If there is a water heater for the DHW circuit, they are used with fiberglass reinforcement or a metal screen.
You can see some of the details and subtleties of the water supply system from a well in the video:
How to choose a device
When choosing devices, be sure to pay attention to shut-off valves. Gate valves, taps, valves, shutters and other parts must be of high quality. Use systems that are highly resistant to corrosion.
Pay attention to control and safety fittings. Safety valves protect the system when operating under high operating pressure conditions.
Reducers are also used to reduce the pressure in the system. Air vent valves are used to remove excess oxygen that dissolves in the water.
Choose devices equipped with monitoring devices that indicate water leakage. These can be pressure gauges, counters, sensors. Individual pumps and complex pumping stations with automated control of water supply.
Filtration equipment helps purify water from various impurities; water must meet sanitary and hygienic standards. The devices include coal, sand, membrane and others.
Be sure to take into account the expected water consumption; it is calculated based on the number of plumbing points and the number of residents. This influences the choice of equipment.