When organizing an autonomous water supply in a private home, wells are most often used. But the quality of drinking liquid in such sources often does not meet standard requirements, so homeowners resort to different cleaning methods. Among them is water deferrization.
Purifying well water from iron will make it safe to drink and increase the life of your plumbing fixtures.
Natural forms of iron
Often, aquifers contain different forms of iron. They influence the chemical composition of drinking liquid and determine its properties.
In surface waters
Iron can be found here in organic complexes (humates). They form colloidal suspensions.
In borehole waters
With private water intake from wells installed within a cottage or dacha, several types of iron can be detected in drinking liquid. Among them:
Types of iron in water.
- 2-valent. It is a free 2-valent substance that is completely soluble in water and therefore cannot be visually determined. Impurities can be detected only by the characteristic smell and taste of water. During the settling process, iron reacts with oxygen and forms 3-valent iron oxide.
- 3-valent. Formed as a result of oxidation of the previous form. An increased concentration of this compound makes the liquid reddish and provokes the accumulation of plaque on household appliances or dishes.
- Colloidal. This form is present in water in the form of small suspended particles, the size of which does not exceed 0.1 microns. The substance does not settle and cannot be removed using conventional carbon filters.
- Bacterial. This type of iron appears due to the presence of bacterial colonies in the liquid that convert the 2-valent form into the 3-valent one. Microorganisms generate a dense film of rainbow light on the surface of the water layer and make the water viscous and unsuitable for drinking.
Iron in water: main sources
According to experts, the content of this chemical element in the earth’s crust exceeds 5%. Fe is found mainly in the form of various oxides. Moreover, in the surface layers of sedimentary rocks there is predominantly oxide iron (Fe2O3), of which more than two-thirds of the various hematites consist. Thus, water in open reservoirs and aquifers is constantly in contact with compounds of this metal and is saturated with them.
In addition to natural sources of iron, water contains a large number of impurities that are technogenic (artificial) in nature:
- Steel pipes for water supply systems.
- Industrial discharges from metallurgy, metalworking, chemical and petrochemical industries, as well as sewage.
- Excessive use of mineral fertilizers, some of which dissolve and enter the deep layers of the soil.
All of the listed causes of water contamination with iron are usually called secondary. In some cases, and especially in old and heavily worn water pipelines, impurities from these sources make up the overwhelming majority. In such cases, filtration stations of municipal enterprises produce purified drinking liquid, and it reaches the consumer heavily contaminated with oxides of the metal in contact with it. You need to purify water with iron yourself or using special devices.
Harm from iron in well water
An increased concentration of iron provokes a number of negative consequences:
Iron in water harms pipelines.
- Reduces the taste and beneficial properties of water. It gets a ferrous taste and an unpleasant odor. Regular drinking of water with a high concentration of iron impairs the functionality of the liver and kidneys. Traces of pigmentation appear on the skin, tooth enamel turns yellow, and hair becomes brittle. In addition, iron negatively affects the cardiovascular system, causing general weakness and rapid fatigue.
- Makes washing more difficult and degrades its quality. During processing, white laundry becomes yellowish.
- It puts a strain on the pipelines through which water is transported, water heaters and household appliances that consume liquid from the well. Over time, sludge appears on the surfaces of the pipes, impairing the movement of the substance.
- Provokes the appearance of plaque on the surfaces of dishwashers and washing machines, irons and coffee makers.
- Forms a yellow coating on plumbing fixtures. This worsens the appearance of equipment, bathtubs, sinks and sinks.
Methods for determining the amount of iron in aqueous solutions
Underground and open water sources are highly polluted. The current Russian sanitary standards introduce the concept of total iron content, which is present in water in four forms:
- Divalent - found in the form of soluble compounds and can oxidize upon contact with air.
- Trivalent - present in the form of insoluble salts and hydroxides.
- Colloidal is finely dispersed particles of pure metal or its compounds that do not settle under the influence of gravity.
- Bacterial - has the appearance of translucent mucus or fibers, which are the waste product of a special type of bacteria.
To remove iron from water yourself, laboratory analysis is required to accurately determine the Fe content, but this is not always possible.
How to determine iron in water at home? A high concentration of a harmful chemical element can be determined without special equipment by the following signs:
- Unpleasant ferrous taste of water and food cooked in it.
- Untidy red stains on earthenware plumbing fixtures and other surfaces.
- The appearance of a gelatinous brown precipitate, which takes on an extremely unpleasant odor when exposed to air.
- Rusty deposits on the bottom of the kettle and the appearance of a brown sediment when the liquid is heated.
- After washing in such water, white fabrics acquire an uneven yellowish tint.
The listed methods do not work with relatively small excesses of the MPC. Thus, 0.4 mg of iron per liter of water practically does not change its organoleptic qualities. The metallic taste becomes pronounced at least when the maximum permissible value is exceeded several times.
How to determine excess iron in water
Excessive concentration of iron in drinking liquid can be determined by the following signs:
- Metallic taste.
- Characteristic shade (from brown to red, depending on iron concentration).
- A brown precipitate that appears without boiling the liquid.
- Turbidity and lack of transparency in the composition.
- Formation of stains on linen and clothes after washing.
The increased iron content in water gives it a brownish color.
The listed troubles appear when there is a critical excess of iron. Minor deviations from the permissible norm are almost unnoticeable. But frequent and constant drinking of such water can negatively affect your health. When irrigating indoor flowers or garden crops, their oppression and death cannot be ruled out. If the faucet leaks, a rust coating with many harmful microorganisms will be found.
The limit for iron content in water for home use reaches 0.5-0.20 mg/l. In public institutions, cafes, restaurants, hospitals and educational institutions, sanitary standards provide for an acceptable level of 0.3 mg/l.
In what cases is it required?
In order to verify the presence of iron impurities, the water must first be carefully examined immediately after pumping, then some time after settling .
- The presence of iron oxides and hydroxides is detected by the presence of red-brown impurities in the solution. If such water is allowed to stand, after a short time a brown sediment will appear at the bottom.
- Divalent iron ions have no color and are not visible in solution. After a short stay in air, they oxidize, causing the liquid to become red in color. Gradually, a brown sediment forms at the bottom.
- Iron in the trivalent state immediately imparts color to the liquid. If such ions are present in a solution, it has a reddish color.
- Sometimes water from wells contains iron-organic compounds, the presence of which is indicated by a red film with rainbow highlights on the surface.
it is impossible and impossible
to use water with iron impurities .
In heating appliances it quickly forms sediment and flakes.
When washing, red stains remain on the laundry, and when washing dishes, brown stains remain.
Problems begin to be felt when the concentration of iron compounds exceeds 0.5 mg/l .
Reference. The change in taste and color becomes very noticeable at 1 mg of iron per liter of water.
If the mass of iron impurities reaches 3 mg per liter, then mixers and taps soon fail. In any of these situations, special cleaning is required - deferrization.
Reagent-free water deferrization
When using this method, the key consumable element is electrical energy, which powers the operation of the treatment plant. At the same time, for complex water purification with the removal of insoluble impurities, it is necessary to use special catalysts - substances that stimulate oxidation and promote more efficient treatment of the working environment.
Modern units are characterized by environmental safety and the ability to preserve the beneficial composition of water. In addition, they do not require complex maintenance and are quite easy to operate.
Advocacy
The method is characterized by minimal financial costs for electricity and treatment plants, because involves settling the liquid in a large container. To increase the effectiveness of the procedure, it is necessary to expand the area of contact of the water mass with air. This is done by using large-volume tanks.
The system will be more effective if you organize not a direct supply of liquid, but its spraying in the form of fog.
Compressor aeration
The operating principle of a primitive aeration plant with compressor equipment is quite simple. A pipe with holes is lowered into the tank with the medium being processed, through which air is supplied. Interacting with the flow, the liquid is saturated with oxygen, and soluble types of iron acquire a 3-valent form, precipitating. The water treated by this method is poured into another container and then pumped to additional purification facilities.
Operating principle of a compressor aeration unit.
A typical aeration station layout includes the following components:
- A compressor responsible for pumping air into the tank.
- An aeration column that saturates the aquatic environment with oxygen.
- A column with a mechanical purification filter, where additional oxidation and separation of sparingly soluble impurities are performed.
- Automation, which is responsible for pumping sludge from the column into the sewer pit.
Electrolysis
Water treatment technology according to this principle involves the decomposition of iron impurities as a result of the action of electricity on oxidizing substances: hydrogen, oxygen, hydroxide OH ion, ozone, chlorine. The activated components interact with 2-valent iron, converting it into a 3-valent form.
Electrolysis is widely used in industrial settings and is practically never found in domestic use. This is due to the increased consumption of electrical energy (0.2 kW m3) and the need to include additional chlorine-containing particles in the aquatic environment.
Scheme of using electrolysis for water purification.
Ejector aeration
The technique makes it possible to purify the aqueous layer at an iron concentration of up to 2 mg/l. The main components of the system are a deferrization column and an air intake mechanism.
The station operates on the following principle: a working medium and air under pressure are supplied to a mixer with an ejector located outside, or to an automatic unit on a column. A working ejector disperses the flow, connecting it with air. As a result of this effect, finely dispersed water suspensions are saturated with oxygen.
The next cycle involves pumping water with insoluble impurities to a deferrization column.
Ozonation
Such systems make it possible to effectively remove iron impurities in water using ozone, which oxidizes the chemical element more effectively than the 2-valent form.
Existing types of equipment differ in their internal structure. At the same time, their main components are an ozonator, which generates ozone, and mixing tanks, where it starts a chemical reaction.
The treated medium is further purified in a carbon filter, and the sludge is sent to wastewater.
The ozonation process is the purification of water using oxidizing agents.
The advantage of the installation is high-quality disinfection and fight against bacteria. In addition, it clarifies the liquid and improves its taste.
The negative aspects include the high cost and explosiveness of the equipment. To avoid risks, it is important to follow strict rules and measures during operation. Do-it-yourself repair and maintenance of the system is impossible. This will require the involvement of experts.
How to make an iron remover for a summer house or country house with your own hands?
Purification of water coming from a well in the local area has its own specifics. It is difficult for the owner to purchase and maintain expensive equipment. This is often unsafe.
Therefore, homemade installations are popular among many users.
To make them you need the following:
- Storage tank;
- Additional pump;
- Several filters.
The volume of the tank must correspond to the daily needs of the family.
For effective cleaning, two filters are often sufficient:
- The first is with sieves for mechanical separation of impurities;
- The second is with any sorbents (for example, activated carbon or charcoal).
If your budget allows, you can buy a ready-made cartridge with filler for standard cleaning.
The operating principle of the installation is simple :
- The water flow from the well is supplied under pressure into a storage tank.
- At the same time, it is automatically mixed with air, aeration occurs, which stimulates oxidation.
- After settling, the water above the sediment is drained through the bottom tap.
- Then, from the receiver, an additional pump supplies the flow to filters installed in series.
Important. As a result, the output is water that does not contain iron and other harmful components.
The operating principle of the installation is shown in the video:
Reagent deferrization
The method is based on the use of special reagents. Automation is responsible for the correct execution of all stages.
Catalytic method
The technology involves the use of a method of accelerated conversion of iron using catalytic reagents. As a result of such processing, the chemical element acquires an insoluble form. By default, the reaction is carried out in a factory deferrization column, into which a special backfill is immersed. When using the technique, catalytic oxidizers (glauconite, zeolite, dolomite) are used.
Ion exchange resins
Systems based on ion exchange resins use the following principle: cation exchangers (with a negative charge) are balanced in neutral water on the surface of the resin granules in contact with positive charges.
Scheme of ion exchange water purification.
In most cases, ion exchange resins are used to soften liquids, i.e. to clean it from calcium and magnesium ions.
Both softening reagents and complex formulations based on universal resins are available for sale, which provide both softening and deferrization of liquids.
Chemical oxidizers
Even the average consumer is familiar with chemical reagents that have oxidizing properties. They are widely used in everyday life (potassium permanganate, bleaches, etc.). Such substances are enriched with active oxygen, which provokes the formation of an insoluble precipitate of 2-valent iron.
Treatment of the aquatic environment with the help of chemical reagents does not require special efforts. However, the technology has not become particularly widespread in everyday life due to the following negative aspects:
- The need to maintain precise dosage. Hypochlorite and manganese are unsafe for the body if the permissible limit is exceeded. But choosing the optimal dosage at home is problematic.
- Financial costs associated with the rapid consumption of oxidizing agents. Unlike ion exchange resins, which can be used for 5 years, manganese and hypochlorite are quickly consumed.
- Difficulty in automating the process. To operate the station, you need to provide a special dosing pump with automation. Such equipment is found only in industrial installations.
- The need to implement a manual or automated system for draining wastewater into the sewer system. This is accompanied by additional investments and does not justify the everyday use of the technology.
A special reagent for purifying water from iron.
Signs of the presence of iron compounds
There is no doubt that drinking iron-rich water is not safe for your health. However, in addition to harm to the body, rusty water also brings trouble to plumbing: pumps, taps and other parts work much less, and snow-white bathtubs and sinks soon acquire an indelible yellow coating. So how can you tell if there is iron in your water supply?
Untreated water can be harmful to health and technology
In order to determine the content of this element in water, you need to pay attention to several signs:
- As already mentioned earlier, ferrous iron dissolves in water, and therefore it is impossible to see it in a stream of water. However, if you take tap water into a container and let it stand for some time, an unpleasant brown sediment will be clearly visible at the bottom.
The simplest and most reliable way to detect divalent iron is to let the liquid settle
- Ferric iron makes itself known in the form of unpleasant-smelling, dark yellow water. If such water is left in a container, it will become lighter in color and the iron it contains will precipitate. This phenomenon is most common in city apartments in centralized water supply systems.
- The presence of bacterial iron compounds in water can be seen by a thin oily film on the surface.
The film, shimmering with rainbow colors, indicates the content of organic iron
Thus, the presence of iron in water is indicated by a yellow or brown color, sediment, an unpleasant sharp metallic odor, as well as an iridescent film.
Below are various options for purifying water from iron from a well in a country house to drinking water.
Types differ according to many criteria, including installation complexity and cost.
Other methods of water deferrization
At home, iron can be removed from drinking water by boiling, freezing or settling. As an inexpensive alternative to industrial methods, you can consider assembling a homemade filter with filler.
When boiled, ferrous iron reacts with dissolved oxygen to form an insoluble form.
In the case of freezing, the principle of temperature difference is used at which clean and contaminated aquatic environments acquire a solid state.
Traditional methods of deferrization
Folk, or old-fashioned, purification methods are used in cases where obtaining clean water is required from time to time and the purchase of expensive equipment is impractical.
Advocacy
This is a simple, least expensive method of deferrization.
To implement the home method, you will need a reservoir equal to the daily fluid consumption. Use a container made of neutral materials - food-grade plastic, stainless metal.
The manufacturing process is simple; cheap components are used in the design.
To prevent freezing in winter, the container is placed in a room with a positive temperature.
A shut-off valve is installed at the inlet to prevent overflow. The oxidation process is accelerated by a compressor. Water is supplied to the container through a food hose with a spray nozzle at the end of the tube.
There are two holes at the bottom of the tank:
- The first, at the bottom level, will be used to drain dirty water with flakes.
- The second hole is made at a level of 20-30 cm above the bottom, through which the clarified liquid is taken.
Important! Clean water is taken no earlier than 10-15 minutes after the last air supply. Otherwise, mixed dregs will enter the house. To improve cleaning, magnets are installed that attract iron residues.
Advantages of the method:
- Simplicity and the ability to independently manufacture a sump.
- A water reserve is created in case of a power outage.
- Hydrogen sulfide present in artesian wells is removed from it.
Flaws:
- Incomplete removal of iron.
- Labor-intensive maintenance. It is necessary to regularly drain the sediment and periodically wash the walls of the container from sediment. The frequency depends on the degree of water contamination.
- It is necessary to monitor the liquid level in the reservoir.
Aeration
This method and the principle of its effect on water were described above. The method can be used at home. For this purpose, a special installation is made. The operating principle can be understood from the figure.
Boiling, freezing
The methods are used to obtain a small amount of clean water.
Iron precipitates after 10 minutes of boiling.
Freezing allows you to combat salt impurities. The water is placed in the freezer. Pure water molecules freeze first; salts turn into ice at lower temperatures. After freezing half the volume of liquid, the remainder is drained. Thawed ice is pure water without impurities.
Purifying water from iron requires a careful and responsible approach. Self-purification is a method applicable to obtaining small volumes of liquid for one-time use. The best option would be to contact specialized organizations to purchase and properly install a filter system. This will allow you to avoid mistakes when choosing equipment, installing it, and will allow you to obtain a guarantee.
Features of the use of installations for water deferrization
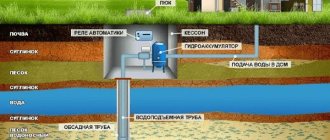
The design of a treatment plant for a well is carried out through a complex chemical analysis of water. The consumer should receive information about the concentration of impurities of hydrogen sulfide, manganese, potassium and iron ions.
Based on the research results, specialists assemble a water treatment system. When the content of a chemical element is high, installations with aeration are used. If the liquid is enriched with hardness salts, complex backfills with resins are required. If there is a large amount of contamination, a multi-level installation will be required.
Water settling
This method is the most accessible and easy to implement. It consists of including an additional reservoir in the water supply system of a country house or cottage, the capacity of which is selected according to the daily water requirement. The advantages of this method are that it is cheap and can be used when the electricity is turned off. The following facts oppose the use of the settling method:
- complete removal of iron does not occur,
- a periodic, rather labor-intensive procedure for shutting down the tank to clean it is necessary,
- Water consumption must be constantly monitored.
Which method of removing iron from water should I choose?
In each specific case, it is necessary to take into account all the factors that may affect the quality of water purification from iron. To simplify the system selection process, it is recommended to be guided by factors such as:
- Cleaning speed.
Each method has its own period of complete cleaning cycle.
- Performance level.
Determined based on the volume of water intake in one cycle. The use of large filters increases productivity, but also increases the costs associated with maintaining such systems.
- Filter medium.
In addition to the speed and force of water supply, it is necessary to take into account external conditions that can affect water quality and human health.
- Scope of application.
For example, for domestic purposes it is not necessary to have a fine filter, but to purify drinking water from iron it is absolutely necessary.
Do not forget that the quality of water in a well may change over time. This is influenced by the time of year, frequency and volume of precipitation, and soil composition.
To obtain the maximum effect when purifying water from iron, several methods are used at once, using their competent combination.
Read material on the topic: Softening kit for home
Filters using strong oxidizing agents
To purify water from iron for a private home, the easiest way is to use filters. There are units on sale with different operating principles.
Catalytic iron removers
One of the most common methods of water treatment both for industrial scale and for small objects (private houses, dachas, cottage villages).
Installations can have a capacity from 0.5 to 30 m³/h. There are also more powerful industrial cleaners.
The filter is made of fiberglass or stainless steel. A bulk filter layer-catalyst is used inside.
The most common brands of catalysts:
- BIRM.
- MTM.
- Green Sand.
- AMDX.
- Quantum.
- Pyrolox.
The average cost of a household model is from 8000-8500 rubles. The catalyst layer needs to be periodically replaced. The average cost of 1 bag (BIRM brand) is about 3,500 rubles.
Reverse osmosis filters
Reverse osmosis filters are complex water purification units of compact size, which are often installed under sinks in both houses and apartments. In reverse osmosis devices, water is purified in several stages, sequentially passing through 3 containers:
- Container with activated carbon and polypropylene: purifies water from solid particles up to 0.5 microns in size.
- Container with coal: filters organic and chemical impurities (metals, petroleum products), up to 1 micron in size.
- Container with a membrane, cells 0.0001 microns in size.
After passing through all 3 containers, the flow is divided into 2 separate ones: purified water and a concentrated solution of filtered impurities. Clean water is supplied further into the water supply of the house, impurities are drained into the sewer.
The most common household filters of this type are:
- Atoll.
- Aquaphor.
- New water.
- Osmo barrier.
- Geyser Prestige.
The average cost of household models (enough for a house with a family of 3-5 people) is 7500-8000 rubles.
Filters using ion exchange resins
Ion exchange filters are arranged in the form of 2 containers made of plastic or steel. Each of them has free space (top) and a part filled with reagents (bottom).
The advantages of such filters include:
- high degree of purification;
- quiet operation;
- rare replacement of the filter filler (may be required once every 7-10 years).
The disadvantage is the relatively high cost: the cheapest filters will cost 17-22 thousand rubles. Also a disadvantage is low productivity: household models can filter on average up to 0.5 m³/h.
Electromagnetic filters
In such devices, filtration takes place in several stages:
- The flow is treated with ultrasound (to improve the efficiency of the next stage);
- Electromagnetic cleaning is carried out (iron compounds are retained by a magnet);
- The purified stream passes through a mechanical fine-mesh filter, which retains the remaining solid impurities.
The cost of filters of this type starts from 10-12 thousand rubles. They should be used only in cases where the main impurity in the water is iron. If, in addition to iron, there are other unnecessary impurities, it is better to use other types of filter systems.
Briefly about water in general
Resource extraction is carried out from different layers of soil
- Verkhovodka
- Water from sandy soil (the well is drilled to a shallow depth)
- Artesian water
Surface water
- Verkhodka contains organic iron.
- Lignins and tannins
- Compounds with humic salts
- Bacterial substance (bacteria transform divalent particles into trivalent ones)
The amount of iron impurities in perishable water does not exceed the norm too much, but is higher than the MPC (maximum permissible concentration). Remove humic iron compounds from such a liquid.
Well on sandy soil
The soil layers of this type of source contain oxygen, with the help of which bacteria change the valence of iron. The resource extracted from sandy soil layers is close in composition to perched water, which allows it to contain humates.
Limestone wells (artesian)
The resource from the artesian basin is environmentally superior to water extracted from sandy soil and high water. The impact of the environment on it is minimal. Depth of occurrence is from 50m to 200m. However, the water contains iron salts and minerals in excess quantities. This happens due to the interaction of water with certain types of soil. Considering the depth, and it is not small, the access of oxygen is limited, and accordingly the source is filled with divalent iron.
There are these types of chemical compounds in the water layer
- Iron bicarbonate – Fe(HCO3)2
- Carbonate – FeCO3
- Sulfate – FeSO4
- Sulfide – FeS
- Trivalent sulfate Fe2(SO4)3 and organic iron are extremely rare in the limestone layer.
- To determine the presence of ferrous iron in a resource, it is enough to give it free exposure to air and leave it for a while. Oxygen will create oxidation, which will cause the iron to settle to the bottom.
- In centralized and private water supplies, cloudiness of the water with a yellowish or brown tint is also observed - this is a characteristic sign of the presence of ferric iron. When the liquid settles, a precipitate forms.
- The yellow tint is also a sign of organic iron, only in this embodiment there is no formation of particle sedimentation.
- A rainbow film covering the water indicates the presence of organic iron.
- It happens that the smell of metal can be heard from the liquid, which is also considered a sign of an increase in the maximum permissible concentration of iron.
How to remove lime from water
The choice of softening method depends on the location of liquid collection and intended use. When purifying water from a well, use:
- Advocacy. The filled containers are kept for several days, during which time the lime particles sink to the bottom, and as a result the liquid is purified and ready for use (minus - there remains the threat of infection and the presence of heavy metals).
- Boiling. At high temperatures, the structure of the molecule changes, turning into a solid state (this is how scale forms). The disadvantage of this method is the duration of the process and the possibility of solid particles of limescale entering the body.
Chlorine, when boiled, forms a dangerous compound - chloroform, which, with prolonged exposure to the body, promotes the activation of cancer cells.
Household jugs with a filter for “hard” water. The liquid flows down and passes through a device consisting of activated carbon, freeing itself from impurities.
If there is running water, it is effective to use:
- Mechanical method. Flowing water passes through a bulk filter (quartz sand, coal, shungite, and silicon are used as fillers). The disadvantages include the bulkiness of the structure (1.5 m) and the removal of only large, more than 20 microns, particles of harmful impurities.
- Disc filters with replaceable cartridge. The devices operate automatically (foamed polystyrene serves as the filter material). The disadvantages of this cleaning method are the cost of the method (cartridges are changed as they become dirty), as well as the fact that high pressure is required.
Water from a well has many impurities that come from groundwater, but it is easier to purify than from a well.
What professional methods exist for removing iron from water?
Let's look at the main ways to purify water from iron:
Method No. 1. Aeration
The basis of this method, as we discussed above, is the natural transformation of iron from a divalent form to a trivalent one by saturating water with oxygen.
The issue of oxygen supply to water can be solved in several ways:
- Simple settling of water in a tank.
- Spraying water using a shower head or fountain.
- The use of elements such as injectors and ejectors that create a dispersion of gas and water.
- Sparging is the injection of oxygen by a compressor (usually an aquarium type).
If the iron content is slightly exceeded, this method may be sufficient to obtain water suitable for drinking.
In practice, the use of only one method of purifying water from iron by aeration is used quite rarely. More often it is used as the first barrier in a large system for removing iron from well water.
Method No. 2. Purifying water from iron using reagents
To speed up the process of transforming iron from one form to another, chemicals (reagents) that have a strong oxidizing effect are used to facilitate filtration.
Such reagents, as a rule, are sodium hypochlorite - NaOCl and potassium permanganate - KMnO4 (potassium permanganate).
Due to the large number of shortcomings of this technology, it is used extremely rarely.
The only advantage of this method is the ease of the process. It is enough to add a reagent to the water and soon you will get “purified” water. Why is this method so bad?
- In the case of constant use of water, the reagent will need to be constantly replenished, incurring costs.
- Incorrect dosage of the reagent can lead to serious consequences for human health.
- The dosage should correspond to the amount of iron in the water. But this parameter can change more than once throughout the season. This creates a danger of intoxication of the body with reagents or insufficient degree of water purification.
Creating a system for controlling the level of reagent dosage will entail significant costs and make this method absolutely unprofitable.
The method is quite applicable for household and technical needs, but not for drinking or cooking.
Method No. 3. Reagent-free water purification from iron
This method does not have the disadvantages of the previous one. To deferrize water, special backfills are used here, which act as a catalyst for the oxidation process and a filter that absorbs the resulting solid iron precipitate. The role of backfill can be performed by synthetic-based substances or natural minerals.
Natural minerals used for these purposes include glauconite, dolomite, and zeolite. Complex (synthetic) backfills include MFO-47, MZhF, BIRM, MGS, Pyrolox, etc.
A feature of the method is that the backfill only acts as an “initiator” of the oxidation process of divalent iron, using the oxygen contained in the water. The backfills themselves do not react. The sediment accumulates in the backfill and is collected by backwashing the filtration system. The properties of the catalyst allow it to be used for a fairly long period.
This method of purifying drinking water from iron also has its disadvantages:
- For the catalyst to function, a certain amount of oxygen in the water is required. Therefore, before reagent-free water purification from iron, the process of water aeration is often used.
- The method depends on the chemical composition of water, its acid-base balance.
- Oxidation is impossible if hydrogen sulfide molecules are present in the water. In such cases, additional cleaning must be done.
- High cost of backfill material. Although it lasts quite a long time, it periodically requires replacement. And this is a significant expense item.
- This filtration system requires constant cleaning and washing of filters. If you neglect these recommendations, the system will quickly become clogged and will not perform its functions.
- Despite the high-quality purification of water from divalent iron, the method is not able to disinfect water. To use such water as drinking water, it will be necessary to use additional purification methods - UV irradiation or use aseptic reagents.
In addition to the described method, the reagent-free category includes:
- Distillation.
With this method, water is evaporated and fed into an additional purification system. The steam is cooled in condensers and the output is absolutely distilled water. But such water is unsuitable for constant use, since along with harmful substances, useful ones are also removed. The taste of this water is not very pleasant. It is more applicable in production or research centers.
- Cleaning using an electromagnet.
Water is driven through an electromagnet under the influence of ultrasonic waves. Iron-containing elements are attracted by the magnetic field and remain on the walls of the mechanical filter. This method helps protect pipes from corrosion and does not contain consumables, which is very beneficial. The filter must be replaced as it demagnetizes.
- Membrane cleaning method.
Membrane filters are used both to purify water from ferrous iron and harmful salts, and to fight viruses and bacteria. In this method, there are several variations of filters: nanomembranes do an excellent job of removing colloidal impurities and bacteria, a microfilter stops rust residues, and a reverse osmosis filter removes all forms of iron from water. Among the disadvantages of the method are the high cost of a water purification system for removing iron for the home and the need for frequent filter replacement.
UV radiation is also used to purify water from iron, but this method is not always effective and is used as an addition to any purification method.
Method No. 4. Ionic technology
This method uses ion exchange resins. In this case, not only the water is purified from divalent iron, but also from soluble forms of potassium and magnesium. In this case, the oxidation process is not needed, since iron ions are replaced by sodium ions.
In theory, this method has no disadvantages, but in real conditions its application is difficult. The iron oxidation process still takes place in the container, converting divalent iron into solid residues of ferric iron, which clogs the surface of the cationic resins. A film appears on the surface of the resin, on which bacteria actively multiply, reducing the overall efficiency of the filter system. As a result, the system cannot fulfill its main task - to purify water from calcium and magnesium ions.
Ion exchange filters in our catalog
- Aquapro mini-cabinet-S 0817 (up to 0.5 m³/h
14,142 rub. - Runlucky B1500 softener cabinet assembled
RUB 33,612
- Ion exchange resin cartridges
from 221 rub.
- Ion exchange resin “ALFAsoft” (1 liter; 0.76 kg)
168 rub.
Such filters for purifying iron from a water system require preliminary filtration, otherwise the method will be unprofitable.
This cleaning method is more popular at thermal power plants and boiler houses when neutralizing the effects of substances that contribute to the rapid appearance of scale.
Method No. 5. Reverse osmosis method
Water is forced through a semi-permeable membrane by applying pressure. Thus, it moves from a concentrated state to a less concentrated one. This purification method is the reverse of the classic osmotic system (hence the name).
The diameter of the membrane micropores is measured in thousandths of microns. Such an insignificantly small size of micropores makes it possible to retain both solid suspensions of metals and molecules of other substances contained in water. Bacteria and viruses are also retained by such a membrane, making the water completely disinfected.
In this case, there is no need for preliminary oxidation of divalent iron, since the membrane also retains these molecules.
To prevent the appearance of trivalent forms of iron (rust) in the water, the filter is made hermetically sealed and oxygen practically does not enter inside.
Reverse osmosis systems
- Ecosoft ROBUST (300GPD)
RUB 41,800 - Reverse osmosis water treatment system Ecosoft
RUB 5,476
- Ecosoft MO6000LPD
RUB 148,094
- Reverse osmosis system Ecosoft PURE
RUB 12,999
This method also has its disadvantages:
- The degree of demineralization is so high that the water is, in fact, close to distilled, and, as we wrote above, is not suitable for regular use.
- Low system performance with high energy consumption.
- The cost of membranes is very high, and ignoring timely replacement will lead to overgrowing of its surface with remnants of mineral elements and organic matter, and, as a result, a significant reduction in throughput.
- This system for purifying water from iron for the home will only be effective in combination with pre-filtration, which adds considerable costs.
As you can see, of all the listed methods, there is not a single one that is universal, suitable for any conditions and without disadvantages. A complete iron removal system for water at home should include a whole range of measures and synthesize all the advantages of each technology.
Read material on the topic: Drinking water safety
How to purify water
You can reduce the concentration of iron compounds yourself in several ways. The cleaning method depends on the volume of liquid consumed and how many impurities it contains.
Advocacy
The easiest way to clean a resource extracted from a well. An additional water reservoir is built, designed for the volume of expected liquid consumption per day, and sedimentation occurs in it.
pros
A simple method that does not require large expenses- There is always a supply of clean water.
- Installing the tank in the attic will create a gravity flow. And it will rid the water of hydrogen sulfide.