Without proper organization of the drainage system, a flat roof will quickly require unscheduled repairs. Stagnation of rain and melt water on the surface will gradually erode the protective outer layer of the coating. As a result, the bare base will rapidly deteriorate from the sun's rays. And when freezing, water crystals can easily tear the material apart.
A properly constructed flat roof drain can prevent and prevent negative impacts. The rules and principles of the design of such an important drainage system should be carefully studied by the owner who cares about the effective and long service of his country property.
Calculation of components
Based on the size and shape of the roof, you can independently calculate how many pipes, gutters, brackets and other parts of the drainage system you will need.
Based on the size of the roof, we select the diameter of the gutters:
- If the roof area is less than 50 m2, gutters 100 mm wide and pipes 75 mm in diameter are used.
- Up to 100 m2, 125 mm gutters and 87 mm pipes are used.
- More than 100 m2 - gutters 150 mm and pipes 100 mm (the use of gutters 190 mm and pipes 120 mm is allowed).
In the case of a complex roof structure, gutters and pipes are determined by the largest projection size of the roof part.
The roof area, consisting of parts, is 160 m2. Considering that one drain pipe is enough to service 100 m2 of roofing in projection, for the roof in the example you will need 2 drain pipes located at the corners of the house. The number of funnels corresponds to the number of pipes, i.e. - 2 pieces.
The number of vertical pipes is determined depending on the distance from the cornice to the blind area. Subtract 30 cm from this distance - the height of the drain elbow above ground level.
For example, the height to the cornice is 7.5 m. Then 7.5 m -0.3 m = 7.2 m.
We will need 3 pipes of 3 m each on each side, which means 6 pipes on both sides.
The number of clamps will be 5 for each side (between the elbow and the pipe, between the pipe and the ebb, and between the pipes) and, accordingly, 10 pieces for the entire roof.
Calculation of the number of gutters
The most commonly used gutter size is 3 meters. The length of cornice A and cornice B is 10.3 m. This means we need:
- There are 4 gutters on cornice A (3m + 3m + 3m + 1.3m). This will leave us with another 1.7 m of unused gutter.
- On cornice B there are 3 gutters and the remainder (1.7 m) from cornice A.
- For eaves C and D we use 2 gutters each, that is 4 pieces on both sides.
- In total, 11 gutters of 3 m each for the entire roof.
The number of gutter corners corresponds to the number of roof corners, in our example there are 4.
Calculation of the number of brackets and gutter locks
The brackets are installed at the rate of 1 piece per approximately 50-60 cm. We take 50 cm and carry out the calculations.
Having summed up the numbers in the last column, we find out that in order to attach the gutters, we will need 58 brackets.
The number of locks between the gutters is equal to the number of joints. In our case, this is 16 pcs.
The number of ebbs (marks) is equal to the number of funnels. In this case, you need 2 times more knees for each funnel. Then for 2 funnels you need:
- 4 knees;
- Low tide 2.
If the facade is not level, but has protrusions, you need to purchase elbows to go around it. The figure below will help you determine their number.
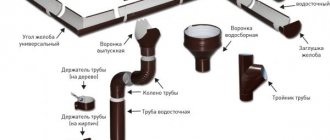
List of required items
In total for this drainage system you will need:
- Gutter (3 m) – 8 pcs.
- Gutter (2.5 m) – 2 pcs.
- Gutter (1.3 m) – 2 pcs.
- Gutter lock – 16 pcs.
- Gutter angle – 4 pcs.
- Bracket – 58 pcs.
- Knee – 4 pcs.
- Drain elbow (mark) – 2 pcs.
- Pipe (3m) – 6 pcs.
- Funnel – 2 pcs.
- Clamp (with pin) – 10 pcs.
Pro tip:
Riser (siphon) drain
As for this siphon, it consists of several types of elements: the main part of the funnel and an additional pipe mounted on the facade. The presence of a riser is not always necessary; it is present in a siphon drainage system. Such a siphon looks like a curved tube, despite the fact that the material used is the same as all pipes.
Note! The siphon resembles the one found in the design of a regular toilet.
Why is it needed? Such a riser plays an important role: it constantly maintains a certain level of liquid in the drainage system, which, when the pressure rises, rises and moves further through the system. This allows you to create a suction effect without additional tools. In this case, the water will not accumulate at the funnel, but will constantly flow through the pipes at speed.
Internal cold and hot water supply systems
20. Internal drains
20.1. Internal drains must ensure the removal of rain and melt water from the roofs of buildings.
Note. When installing internal drains in unheated buildings, measures should be taken to ensure a positive temperature in pipelines and drain funnels at negative outdoor temperatures (electric heating, heating with steam, etc.). The feasibility of installing heated internal drains should be justified by technical and economic calculations.
20.2. Water from internal drainage systems should be discharged into external networks of rainwater or common sewerage systems.
Notes: 1. When justified, it is allowed to provide for the drainage of water from the internal drainage system into the industrial sewerage system of uncontaminated or reused wastewater.
2. It is not allowed to drain water from internal drains into the domestic sewer system and to connect sanitary fixtures to the internal drain system.
20.3. In the absence of rainwater drainage, the discharge of rainwater from internal drains should be received openly into trays near the building (open discharge); in this case, measures should be taken to prevent erosion of the ground surface near the building.
Note. When installing an open outlet on a riser inside the building, a hydraulic seal should be provided to drain melt water into the domestic sewer system in the winter.
20.4. At least two drainage funnels must be installed on the flat roof of the building and in one valley.
Drainage funnels on the roof should be placed taking into account its topography, the permissible drainage area per funnel and the structure of the building.
The maximum distance between drainage funnels for any type of roof should not exceed 48 m.
Note. On flat roofs of residential and public buildings, it is allowed to install one drainage funnel for each section.
20.5. The connection of funnels located at different levels to one riser is permitted in cases where the total estimated flow rate along the riser does not exceed the values given in Table. 10.
Diameter of the drain riser, mm
20.6. The minimum slopes of branch pipelines should be accepted: for overhead pipelines 0.005, for underground pipelines - in accordance with the requirements of section. 18.
20.7. To clean the network of internal drains, it is necessary to provide for the installation of inspections, cleanings and inspection wells, taking into account the requirements of Section. 17. On risers, inspections must be installed in the lower floor of buildings, and if there are indentations, above them.
Note. If the length of suspended horizontal lines is up to 24 m, cleaning at the beginning of the section may not be provided.
20.8. The connection of drainage funnels to risers should be provided using expansion sockets with elastic sealing.
20.9. The estimated flow rate of rainwater Q, l/s, from the catchment area should be determined using the formulas:
for roofs with a slope of up to 1.5% inclusive
for roofs with a slope over 1.5%
In formulas (34) and (35):
F
— drainage area, sq.m;
— rain intensity, l/s per 1 hectare (for a given area), lasting 20 minutes with a period of one-time excess of the calculated intensity equal to 1 year (accepted in accordance with SNiP 2.04.03-85);
— rain intensity, l/s per 1 hectare (for a given area), lasting 5 minutes with a period of one-time excess of the calculated intensity equal to 1 year, determined by the formula
here n is a parameter adopted in accordance with SNiP 2.04.03-85.
20.10. The estimated flow of rainwater per drainage riser should not exceed the values given in table. 10, and for a drainage funnel is determined by the passport data of the accepted type of funnel.
20.11. When determining the estimated drainage area, an additional 30% of the total area of vertical walls adjacent to the roof and rising above it should be taken into account.
20.12. Drainage risers, as well as all drainage pipelines, including those laid below the floor of the first floor, should be designed at a pressure that can withstand hydrostatic pressure in the event of blockages and overflows.
20.13. For internal drains, plastic, asbestos-cement and cast iron pipes should be used, taking into account the requirements of paragraphs. 17.7, 17.9.
On horizontal suspension lines in the presence of vibration loads, it is allowed to use steel pipes.
Purpose of internal drainage
Internal drainage is designed individually for each multi-storey building. Communication performs the most important function of removing precipitation from the roof of the building directly into the storm drain. In addition to this direct function, the internal drains of buildings perform a number of indirect tasks:
- the system prevents soil erosion at the base of the building and maintains the integrity of the foundation;
- drainage of wastewater to a considerable distance from the building, does not allow water flows to negatively affect the paving surface (asphalt, tiles);
- hidden flows do not affect the walls and their finishing coating, preserving the appearance of the building and the favorable humidity regime of the wall material;
- There is no need to place gutters on the facades of the house, allowing you to maintain the ideal appearance of the building.
A hidden, internal drainage system allows you to maintain a favorable microclimate in the apartments of multi-apartment buildings. Communication extends the life cycle of a building, preventing runoff from having a detrimental effect on the foundation and walls. However, it is worth understanding that errors made during installation can not only disrupt the efficiency of utility lines, but also cause significant damage to the structure and render a multi-story building unusable. That is why all work on installing internal drainage must be carried out by professionals in accordance with architectural and construction documentation.
Installation of the figured part and drainage pipes
Laying a drain involves installing pipes from top to bottom, with the elbow, coupling and drain installed with the socket towards the top.
Installation is done as follows:
- A piece of straight pipe of at least 60 mm is inserted into the knee-knee joint (depending on the distance between the front board and the wall).
- Next, the necessary shaped part is assembled into which the upper end of the pipe is inserted.
- The system is attached to the wall using clamps, the distance between which is up to 1.8 m. Only one clamp is fixing, the second is a guide. In some systems, the manufacturer recommends the use of clamps - thermal expansion compensators. The clamp is attached under the connector.
- The pipe is positioned strictly vertically using a plumb line.
- A drain elbow is installed at the lower end of the pipe secured with clamps (the lower edge is at a distance of 25-30 cm from the blind area).
- If there is a drainage system or storm drain, then the lower end of the pipe goes there. The pipes are connected using a coupling (connector).
- Each subsequent pipe is inserted into the connector installed on the previous one.
- A clamp is attached under each connection.
- Depending on the design features of the installation site, an elbow of the desired shape or coupling is attached to the funnel. If the roof protrudes beyond the facade, two elbows and a piece of pipe are used. If the roof does not have a protrusion, then use a coupling.
Installation of roof drains is carried out taking into account compensation for thermal expansion. For this function, manufacturers use expansion gaps. Thus, pipe connectors in some systems have installation lines. The edge of the pipe is set along these lines depending on the air temperature at the time of installation. Silicone-treated seals allow elements to slide smoothly during expansion. When using a pipe connector, leave an air gap of at least 0.6-2 cm.
Pro tip:
It is not recommended to assemble the drainage system at temperatures below -5.
This completes the installation of the drainage system. It is necessary to audit all installed elements. If the configuration of the drainage system fully complies with the design, is calculated and installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations, then all the water falling on the roof will exit only through the pipes, without splashing or overflowing over the edges of the gutters.
At the end of each season, it is advisable to inspect and flush the system (using a hose with water). When clearing any obstructions (leaves, debris), do not use sharp metal objects.
The drainage system is one of the main protective measures, which helps to extend the life of roofing materials, facade and foundation of the building. Correct and competent calculation of the roof drainage system is the key to long-term and reliable operation of the entire building as a whole. Knowledge of the basic principles of calculating the components of a drainage system will help optimize the costs of its arrangement.
Depending on the type, size and slope of the roof, the drainage system can be of several types
:
- organized;
- unorganized.
External calculations are carried out taking into account the following requirements
:
- suspended or wall gutters must be installed on roofs with a slope angle of at least 15°;
- longitudinal is maintained at a level of at least 2%;
- gutters must have sides with a height of more than 120 mm;
- the distance between drainage pipes is no more than 24 meters;
- The diameter of the drainpipe is taken at the rate of 1.5 cm 2 sections per 1 m 2 of roof.
These rules are valid for drainage systems in climate zones with a low probability of water freezing.
- riser;
- funnel;
- outlet pipe;
- release.
Depending on the required configuration and functions performed, the water drainage system can be supplemented with a variety of accessories and components.
Point drainage
When the drainage system is used to wash away dirt when washing a room or liquid is discharged from only one installation, it is not economically feasible to install trays. In such cases, stainless steel ladders are used. These are free-standing receiving devices with horizontal or vertical outlets of various diameters (from 50 mm to 200 mm), having a water seal that prevents unpleasant odors and bacteria from sewer pipes from entering the room. To collect large debris contained in drains, the drains are equipped with mechanical impurity traps. The gratings ensure the safety of movement indoors and protect the components of the ladders from damage.
When choosing sets of stainless drains, you should take into account the expected volume and intensity of the discharged liquid, the location and depth of the sewer pipes. It is advisable to use a vertical drain when the sewer system is deep, and a horizontal drain when it is shallow, in interfloor ceilings.
When a layer of waterproofing is provided in the structure of the floor covering, it is recommended to use double-body drains that collect both surface and drainage runoff.
Not always standard options can satisfy the customer's needs. In this case, Standardpark is ready to develop and produce unique products, taking into account the needs of the client.
What is a flat roof with an internal drain and why is it needed?
The absence of roof slopes deprives the roof of a natural slope for
so that precipitation can be drained. This primarily concerns rain, melting snow or hail.
In such cases, internal or external drains can be installed on buildings.
The arrangement of internal water drainage is a rather complex system when compared with external means intended for the same purposes.
But due to the mass of advantages, owners of various buildings choose exactly the system that is located inside the house. This solution to the issue of removing atmospheric precipitation can be compared to the way water drains from an ordinary bathtub.
The fluid finds the only path of least resistance, where it is directed through the flow. First, it enters the sewer pipe, and then into the sewer riser. In some cases, it is possible to make a system in such a way that water will be collected in a special reservoir, from which it can be used as a technical fluid.
The main advantages of flat roofs with internal drainage are:
- increasing the aesthetics of the building itself, since pipes or other precipitation drainage systems will not be visible on its facades;
- no freezing of wastewater in winter, since it is hidden inside and warmed by the building itself;
- higher efficiency of water removal.
IMPORTANT!
The biggest problem that owners of flat roofs with internal drains face is clogging. Cleaning in such cases is very difficult. But at the moment, special technical means have been created that maximally prevent the occurrence of such situations.
It is also very important to consider the internal drainage before construction begins or before roofing work begins. After construction is completed, installation of an atmospheric water drainage system is possible only in cases where part of the house will be dismantled
Drainage device
Classification of internal drainage
In construction, there are two types of internal drainage of storm water from the roofs of apartment buildings:
- gravity;
- siphon-vacuum.
The gravity system is simple. It is represented by a funnel, which is located directly on the roof, and a riser through which water flows from the roof vertically into the storm collector. This internal drainage system has a low throughput capacity, since water enters it mixed with air. This feature of the system is its disadvantage, due to which it requires the installation of a large number of drainage systems with an increased pipe diameter.
Siphon-vacuum internal drainage, due to its design, allows the pipes to be completely filled with storm water. The system is represented by a complex of drainage funnels, which are connected by gutters into a single horizontal drain. In turn, the horizontal section of the pipe moves to a vertical position with the help of an elbow. After water enters the drain, it moves under the influence of vacuum, filling the entire volume of the pipe. This allows you to increase the throughput of the system, reduce the number of drains, reducing financial costs for materials and installation work.
It is worth noting that creating a flat roof with internal drainage of any type costs the developer less than any other option (single or gable roof with external drainage provided).
What is an internal drain?
You can describe the internal drainage in just one sentence. It is installed on a flat roof, while the external one is mounted on a classic sloping roof.
This drain got its name mainly due to the fact that it is part of the structure itself, and not a separate system from it.
Also, the difference between external and internal drains can be understood at the system design stage. If you take a roof project, then the internal drainage is outlined within its perimeter, and the external drainage is outlined behind them.
Relatively recently, internal drainage was used only to protect apartment buildings, because flat roofing was common in this type of construction. Today, more and more people choose flat roofing when building private houses. At the same time, internal drainage has become more popular.
The main tasks of such a drain, like any other similar system, are to protect the roof and facade of the building from the negative effects of moisture. Without a properly installed drain like this, a building can last much less than its intended life. In addition, it will require constant cosmetic repairs, because facing materials deteriorate much faster than the main ones.
In a building with a flat roof, drainage is even more important, because the roof itself does not have any structural features to protect it from rain and melt water. In standard types of roofing, this is achieved due to the slope and covering of the roof itself.
If you paid attention, all materials used for roofing usually have a corrugated surface
The internal drain uses all the same elements as the external one, but they can differ significantly from them in design and function.
This is interesting: How to make a drain: let's learn all the nuances
Material for construction
Previously, various materials were used for this purpose: metal and several types of plastic. Polyvinyl chloride and galvanized steel have stood the test of time - these are the most common materials. It is from them that all structural elements are made. Steel is resistant to high loads and influence, and a protective zinc layer will protect the metal from corrosion. The choice in favor of galvanized steel is made when the roof is used as additional space. For example, more and more often developers are making a place for relaxation, a platform with a garden, etc. on the roof. All these are additional loads that steel copes well with.
As for polyvinyl chloride, it is not inferior in quality and has average performance, but the price of the material is much cheaper. It is chosen when no special loads on the drain are expected.
Note! Each type has its own pros and cons. That is why these materials are often combined. For example, pipes can be made of metal, and funnels and protective grilles can be made of plastic.
How to calculate gutters for a flat roof
Flat roofs are gaining popularity in private construction. Often these are used roofs. The drainage system in such houses is internal - storm and melt water flows into water intake funnels installed on the roof, from them into gutters, and then into the storm drainage pipeline.
Flat roof. No gutters. During the rainy season, you can release turtles into this pool, but sooner or later the roof will leak, and then you will have to repair not only the roof, but also the ceilings (and save innocent animals)
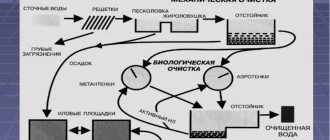
According to SP 32.13330.2012, when developing a project, it is necessary to consider the possibility of cooperating sewer systems. The same code stipulates mandatory consideration of the use of surface water for irrigation, which is quite possible if a septic tank with several chambers for multi-stage treatment is installed on the site (the treated wastewater is used for irrigation). That is, nothing prevents the internal pipeline of the drainage system from being connected to the sewer (this is the cooperation of systems). The pipeline is located in the attic space (if there is none, laying along the ceiling is acceptable). Funnels are connected to it. The pipeline is connected to the riser. To connect parts, shaped elements equipped with sealing rings are used. Be sure to include inspection and cleaning. Another option (not the best) is standard gutters if the roof has a parapet. Holes are made in this parapet and pipes are connected to them.
Installation of external drainage
- no matter how flat the roof is, a slope (towards the funnels) of 1–2% is necessary;
- the drainage collector is installed in a recessed part of the building (or underground: underground structures are insulated; open installation is permissible in the room), and the spillway is connected to the sewer there;
- permissible pipe sizes: length - 700–1380 mm, diameter - 100, 140, 180;
- the diameter of the pipes is determined on the basis that 1.5 cm2 of cross-section removes water from the square of the roof;
- the number of funnels is determined on the basis that 1 cm2 of the cross-section of the water intake is capable of draining water from 0.75 m2 of the roof;
- funnels must be located in insulated (heated) places;
- the inclusion of funnels must be completely sealed - the waterproofing carpet is glued to the sides of the funnels;
- the usual number of funnels is one per roof section;
- water can be discharged into storm drains without connecting networks.
Water will find a hole - however, it is better when this hole is planned and in the right place.
How this should not be done under any circumstances (it’s just that no one sued the municipality)
Some owners of houses with flat roofs with a slight slope (barely allowing water to escape by gravity) are tempted to arrange an unorganized drain. They make a hole in the parapet and the water goes through it. We strongly recommend not to engage in amateur activities of this kind: even if there is a powerful blind area below, and close to it there are rain drainage trays. The water engulfs the facade so much that the famous “Brezhnevka” in comparison with the damaged walls will seem like a masterpiece of architectural thought. The internal drainage system is not at all the prerogative of flat roofs - it can be connected to the gutters of a pitched roof, but this task is for professionals. Such a system must be installed at the construction stage, having previously developed the project in parallel with the rest of the design documentation.
Types of internal drainage systems
Structurally, internal drains are divided into gravity and siphon:
- Gravity drainage collects and freely drains sediment through sloped gutters. In this case, the drainage system is only partially filled with water.
Gravity system
- The siphon system is based on its complete filling with sediment. In this case, when it is completely filled with water, a permanent water column is created, the beginning of which is the funnel of the internal drain, and the end is the exit to the sewer. When the level of precipitation in the vertical part decreases, a vacuum sucks sediment from the funnel and moves it into the vertical riser. As a result, water is removed from the roof by force, which is more efficient.
Siphon systems for internal drainage
Internal drainage - units are installed exclusively using welding, which ensures the tightness of the entire system. Then it will be capable of effective operation in any amount of precipitation.
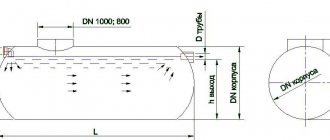
Calculation of the internal drainage system
This calculation is carried out by engineers at the design stage of the building itself:
- The main condition is the possibility of removing moisture - the feasibility of this operation even when the moisture is located relative to the level of the roof, when air cannot get inside the funnel.
- When calculating, it is mandatory to take into account:
- climatic features of a certain region;
- precipitation numbers;
- roof design features;
- building dimensions;
- reverse water pressure
Features of the functioning of siphon systems of internal drainage
To prevent the need for repairs, the internal drainage system requires:
- Thermal insulation of pipelines, in some cases - electric heating.
- To reduce the noise level of flowing water, pipelines must be laid with insulation with noise-absorbing materials.
Storm drainage scheme
Calculation of the number of external drain funnels and pipe diameter
There is a gable roof, the length of the slope is 24 m, the distance from the eaves to the ridge is 10.5 m. It is necessary to calculate the number of funnels and the diameter of the drainpipes for each slope. There are conflicting data on the number of funnels and the diameter of the waters. pipes: 1-SP 17 Roofs
9.7 “For external organized drainage of water from the roof, the distance between drainpipes should be no more than 24 m, the cross-sectional area of drainpipes should be taken at the rate of
1.5 cm2 per 1 m2
of roof area.”
Calculation: For a gable roof with an area of one slope of 24 * 10.5 = 252 m2 With a pipe with a diameter of 10 cm - the transverse area. pipe cross-section: S=Pi*R(squared)= 3.14*25=78.5 cm2 Required. cross-sectional area of drainpipes: 1.5*252=378 cm2 Number of pipes with a diameter of 10 cm: 378/78.5=4.81. Those. 5 pipes 2.-
The vast majority of sources on the Internet talk about a smaller number of pipes: either about 100 m2 per 1 pipe.
It turns out 252/100 = 2.52 = 3 pipes.
Or they provide tables according to which there are generally
2 pipes with a diameter of 10 cm
.
In the technical documentation of the Grand Line company (they refer to calculations according to DIN EN 612-2005) the Grand Line system 150mm-dia. funnels/100mm-dia. pipes - designed for 178 m2 i.e.
for 250 m2 2 pipes are enough. Where is the truth? in the joint venture or in the overwhelming number of Internet sites? How many gutters should I take?
Last edited by MaxKad on 02/08/2017 at 21:34.
Where is the truth? in the joint venture or in the overwhelming number of Internet sites? How many gutters should I take?
I believe that the truth is in SP, but not only in SP 17.13330.2011, but also in SP 30.13330.2012 and SP 32.13330.2012: 9.2. The number of funnels, depending on its throughput capacity, roof area and construction area, is determined according to SP 30.13330 and SP 32.13330. I believe that the number of funnels, either internal or external, and the diameter of the pipe (riser) primarily depends on the estimated rainfall flow rate (l/s), and not just on the roof area. SP 17 for external drainage provides a calculation method that is too approximate and does not take into account the intensity of rain for a specific construction area. (Clause 8.6.9 SP 30.13330.2012).
DIN EN 612-2005 is good, but “what is good for a German is death for a Russian” (c) Gutter manufacturers have the right to refer to anything, especially if they provide the buyer with a guarantee that there will be no overflows during rain. And the designer must justify his decisions himself, referring to the standards in force in the country.
__________________Architecture is a diagnosis.
Gutter rules
The gutter must be installed in such a way that, regardless of temperature, it ensures the removal of water from the roof surface. Water intakes should not be placed near external walls - they will freeze in cold weather. It is recommended to place them longitudinally to the roof.
Tips for creating a drain:
- the roof surface must be divided into zones;
- about 150-200 sq.m. there should be 1 riser per roof;
- the slope to the water intake is made by 1-2%;
- for proper organization of internal drainage, it is necessary to install a collector underground with its outlet to the general sewer system;
- when installing a drain, pipes d = 10, 14, 18 cm are used, the length should be 70 or 138 cm (established by standards);
- determination of the cross-section of the pipe is carried out taking into account the fact that 1-1.5 sq.cm. communication system can remove water from 1 sq.m. surfaces;
- moisture is removed to the outer part of the storm drain;
- the area of the roof area for which one funnel is intended should not be more than 0.75 sq.m. per 1 sq.cm. drainage sections;
- all sections of the riser must be located in areas where there is heating;
- It is necessary to have a sealed and insulated connection between the water supply system and the roof; the blood flooring must be waterproof.
You should think through the cleaning system and inspection arrangements in advance. It is recommended to place risers in an apartment building in sewer and ventilation shafts.
Organization of water drainage
Choosing the material of manufacture and which gutters to install
Galvanized steel products should not be considered for installation on a residential building. The low cost of materials will not make the installation cheaper: installation will take a lot of time, and it is almost impossible to hermetically assemble homemade parts. Steel coated with a thin protective layer of galvanization will begin to rust after 2–3 years, and a new system will have to be installed. Modern budget gutters are made by:
Made of plastic – PVC.
Made of metal with a polymer protective coating.
Aesthetic appearance and reasonable price: advantages of plastic gutters
Plastic drains: in what cases should you install a PVC system?
Inexpensive plastic parts can last for decades without breaking. The components are made from polyvinyl chloride, a polymer based on acrylic resins. Gutters and pipes are ultra-light weight, easy to transport and do not require special skills for installation.
Plastic system elements
Plastic systems are perfect for installation on low one-story residential buildings, outbuildings, garages, and country houses. Mounted on old roofs with fasteners on a wind board. Manufacturers recommend PVC for organizing drainage on the roofs of attic floors: plastic trays are almost silent, unlike metal ones.
The material is quite fragile and not durable. Susceptible to mechanical damage, especially at low air temperatures. Therefore, when choosing a system for installing a plastic roof drain in a region with a cold climate, it is worth considering the simultaneous installation of a heating cable. The roof covering is equipped with the mandatory presence of snow retainers in order to reduce the risk of gutter failure when snow melts.
Gutters made of metal with a polymer layer belong to the middle price category. The parts are made from a steel alloy; several layers of polymer are applied on top to protect the box from exposure to water. When calculating a drainage system, you should also take into account the cost of installation: it is difficult to install metal-plastic parts yourself. Gutters are quite heavy; it is impossible to install trays at height alone.
Metal-plastic drain: details
When assembling, you need special tools and skills in working with metal: metal-plastic parts cannot be cut with a grinder or a drill attachment. The polymer coating is temperature sensitive and peels off when overheated. Also, metal-plastic products require careful handling during loading and transportation: the surface must be covered. Scratches on the polymer are conductors of water to the metal base; accordingly, rust quickly forms at points of damage.
Metal-plastic is the best choice for:
Drainage assemblies for country cottages of large area and height.
Installation of trays on rafter boards - it is allowed to increase the interval between fastenings to 90 cm.
Installations in difficult climatic conditions.
Material for drainage elements
At the moment, the industry produces many configurations of gutters, which differ in the shape of the gutters, material, and so on. The simplest and cheapest are drainage systems, the elements of which are made of ordinary galvanized steel. Such drains are used when installing a drainage system in multi-storey buildings. You can often see them on private residential buildings.
Drainage funnel installation diagram.
Plastic, which is also now becoming fashionable, can also be used as a material for the manufacture of elements of drainage systems. On some houses you can find gutters made of copper. Of course, such a system costs a lot of money, so not everyone can afford it. Very often they cannot do it for one simple reason - there is no harmony with the rest of the facade. A copper gutter and riser will fit perfectly under a copper roof, but will look very unsightly against the backdrop of metal shingles. In most cases, private homes use elements painted in any color or coated with a layer of polymer.
As for the material, copper will be the best option in terms of reliability and durability. When considering cheaper options such as steel and plastic, there are many factors to consider. For example, both plastic and metal elements are perfect for internal drainage, but for external drainage it is best to use metal ones, since steel is less susceptible to low temperatures. The choice of material also depends on the roofing covering. For example, PVC elements are perfect for flexible tiles, but metal ones are suitable for ordinary slate.
How does a drainage system work on a flat roof?
The main purpose of the roof drainage system is to drain water that forms on the surface of the roofing as a result of precipitation in the form of rain, as well as when snow melts in the autumn-spring period of the year.
There are three types of drainage roofing systems:
- external unorganized - when water drains from the roof surface spontaneously, due to its slope to one side;
- external organized - assumes the presence of gutters for collecting water located along the edge of the roof, with its subsequent transfer to drainpipes mounted along the facade of the building;
- internal - consists of receiving funnels placed on the roof surface, serving to collect water through slopes made on its surface, and vertical risers mounted inside the building or structure.
Schematic illustration of an internal and external organized drainage system on a flat roof
Selection of drainage systems
When choosing drainage systems, you need to take into account the roof structure, statistical data on the amount of precipitation in a given region, and the characteristics of the materials from which drainage systems are made.
offers a wide range of drainage system elements for individual and industrial construction from the European company Plastmo.
Plastmo models are made of modified thermoplastic PVC, meet all the requirements of technical standards and are adapted to Russian climatic conditions. They have a rigid design with reliable protection against overflow. Available in 10 colors. Can be made to order in any color from the RAL palette.
The catalog of Plastmo system elements includes more than 30 items of standard and non-standard parts, the main ones:
- gutters 4 and 6 meters long;
- hooks of various sizes and configurations;
- movable funnels;
- universal plugs;
- internal and external corners;
- drainpipes;
- various connectors and clamps;
- elbows, couplings, branches.
Special elements are represented by a wide range of non-standard parts.
On special orders, the company produces drainage system kits for individual projects.
Figure 5. The ratio of the sizes of gutters and pipes depending on the area of the slope.
Required materials and tools
To install an internal drainage system, all its elements are first required. The material usually chosen is plastic or galvanized steel. A PVC drainage system is cheaper and is installed when large loads are not expected on the roof. If the flat roof will be used as a terrace, then it is better to take metal parts.
Tools needed:
- Measuring instruments (roulette)
- Level, vertical plumb
- Hammer, drill
- A hacksaw for metal or plastic, depending on the type of drain chosen, construction scissors
Advice from professionals
If you are installing internal drainage for the first time, pay attention to your specialists.
- Installation starts from the bottom, gradually you need to go up.
- All channels and shafts inside the building intended for water supply must be covered with panels after its installation. This will help maintain the temperature.
- When choosing a water inlet, keep in mind that it must match the roofing material of the roof.
- The places where the funnels are installed should be slightly lower than the rest of the surface. a slight slope can be made on purpose.
- Metal pipes in the internal system must be equipped with electric heating, otherwise in winter they will freeze and may burst.
The design of the internal drainage system is more complex than the external one. It is important to pay attention to the accuracy of the calculations, and during installation - to the tightness of the connections.
Classification of internal water drainage system
The main separation occurs due to the method of collecting water from a flat surface:
- Gravity flow. The most economical, but also ineffective option. The simple funnel used assumes the natural flow of water due to the slope of the roof. This method requires precise calculations to avoid flooding during heavy rain. Although even a thorough calculation cannot guarantee complete drying.
- Siphon. This method already includes the physical laws of pressure drop. Funnels are selected of a more modern type with flow stabilizers. That is, the entire riser assumes complete filling with water, and when the level drops, a zone of low pressure is created around the funnel. Once in a discharged area, water is simply sucked inside. A significant advantage is the high speed of flow passing through the riser, simultaneously carrying away possible blockages.
An important external element of the entire system, the funnel, has its own varieties:
- by design: flat and bell-shaped;
- by material of manufacture: copper, budget plastic, stainless steel;
- by size: according to the cross-sectional diameter of the outlet pipe (an accurately selected size largely determines the tightness of the connection);
- according to additional equipment: heated, with protective barriers, with stabilizers.
According to the material of the drainage pipe:
- PVC is an excellent economical solution for small buildings with low water flow. They are durable and have a fairly reliable and simple connection.
- Metal. Basically, a metal is selected that can remain resistant to constant exposure to moisture for a long time. These are stainless steel and aluminum. The main disadvantage of such raw materials is the need for high-quality sound insulation.
- Cast iron. Pipes that are gradually becoming a thing of the past due to their heaviness.
- Copper. Rarely used raw materials due to their high cost. The main advantage is resistance to acid rain in an industrial area.
- Asbestos-cement. They have many advantages, including safety, durability and lower cost compared to their metal counterpart.