Drainage pipes with perforation. Features of use
Perforated drainage pipes are the main functional element of installing an efficient drainage system. Removing excess moisture by draining the land is an important part in landscaping. The soil, oversaturated with moisture, changes its properties, over time destroys the foundations of buildings, and upsets the ecological balance in the area. To eliminate such a significant drawback, drainage work is being carried out in the required area. Their modern basis is the use of special pipes to create a drainage system that reduces or minimizes the balance of groundwater.
Pipes for arranging a drainage system must have holes, and today you can purchase products with ready-made perforations
Useful tips
- Perforated pipes without a filter are cheaper, but have a significant drawback. Their installation becomes more complicated, since a number of technological operations will have to be performed to prevent siltation of holes (cracks) in the walls. You will need to buy geofabric and backfill the filter layer (river sand, crushed stone). And this is not only extra time, but also additional expenses. The use of jacketed pipes eliminates many problems, and the total cost of installation work is even somewhat reduced.
- When choosing a product version, price should not be the main criterion. The drainage system is closed, and therefore its repair and maintenance is fraught with certain difficulties. In this regard, the material from which the pipes are made becomes of great importance. Ceramics and asbestos cement are characterized by impressive weight and are difficult to connect with each other. In addition, ceramic products, although durable, are quite expensive. Plastic products for the drainage system are the optimal solution. Simplicity of installation and joining, durability, variety of assortments, the ability to install according to the most complex scheme - and these are not all the advantages of polymer products.
- Trying to save on purchasing conventional pipes and then perforating them yourself will not lead to anything good. The location of the slots and their number are calculated by the manufacturer with extreme accuracy. The result of self-treatment of walls is easy to predict: low efficiency of the system, excessive dampness in the area, or even waterlogging.
Geotextiles are considered the most durable protective coating. Unlike coconut fibers, it successfully combines elasticity and strength. This coating of drainage pipes is not damaged even with strong soil movements. And it’s easy to update it yourself.
The effectiveness of the drainage system is determined by the correct choice of pipes. For products with perforation, in addition to the internal diameter, the location of the slots (holes), their sizes and number per unit surface area are of no small importance. Considering the installation features, it is better to consult a specialist in advance.
Drainage pipes with and without perforation, connection elements, consumables: the online store alfatep.ru has everything you need to set up a system for removing moisture from the territory. The assortment is impressive, the quality is confirmed by certificates, manufacturer prices are without surcharges. The company’s specialists provide assistance in developing a drainage scheme and selecting pipes according to type and parameters. Delivery of goods to regions by our own forces. We offer preferential loans and a choice of payment methods. Regular customers and wholesalers receive impressive discounts and individual terms of cooperation. We are always in touch: telephone or the “Contacts” section of the website. Contact us, you won't regret it.
Drainage systems. Their purpose and work
Drainage is a whole complex of measures, including the study of a given site, the design of ditches for laying pipes, and their correct embedding into the soil. The subtleties of arranging drainage systems include knowledge of soils, the installation of filter layers, and the correct installation of products, such as perforated drainage pipes.
As you know, the basis of building structures is their reliable foundation. The durability and well-being of any structure depends on it. The basis for the building foundation is soil. Only durable soil, not oversaturated with moisture, can be a reliable support for any structure. Drainage of the land plot where construction work will be carried out is an important event, the implementation of which largely determines the successful start of all work. The design of a water drainage system with the installation of modern drainage pipes always contributes to the quality of such work, ensuring success.
There are several ways to install drainage:
- deep drainage, where perforated pipes are used, which are designed to remove groundwater;
- open surface, a relatively simple version of a drainage system designed to remove wastewater that accumulates during rain and snowfall.
Drainage pipe installation
Installing a closed deep drainage is not the most difficult job; it can be done on your own. The work itself is quite banal: dig a trench, fill it with crushed stone and sand, install pipes, fill the trench. The difficulty in installing drainage is the choice of diameter, slope and other design intricacies.
It is advisable to install water drainage from the foundation simultaneously with the construction of the house (and in the case of long-term construction, with laying the foundation).
Types of drainage pipes. Their properties, classification
The main type of work during the construction of a drainage system is the correct installation of the pipeline. Auxiliary work includes the implementation of the necessary measures for the installation of a technically and technologically correctly designed drainage system.
Pipes for drainage systems are made of different materials and have different characteristics
In the process of drainage construction, pipes are used:
- without perforation, which remove soil moisture and rainfall;
- with perforation, which allows not only drainage, but also collecting moisture from the site and transporting it;
- with perforation and an installed filter, which protects the pipeline from clogging the holes with dirt.
Note! The use of pipes without a filter requires the installation of a filter layer by filling the pipe with crushed stone of different fractions.
The use of an industrial filter, which is, for example, geotextiles or other materials that are not quickly decomposed, is preferable due to the quality of the operational properties of such a pipe.
In the process of manufacturing drainage pipes, advanced technical and technological innovations and materials are used. The main difference between a drainage pipe and a conventional stormwater pipe is the presence of perforations through which excess groundwater is collected into a pipeline and, thanks to the slope, flows into collection wells and then removed outside the site. The main types of pipes that are used in drainage systems are as follows:
- Asbestos cement pipes have been produced by industry for many years and are used in a wide variety of conditions.
- Ceramic pipes, which are characterized by increased mechanical strength and durability, but are quite expensive.
- Polymer pipes of various modifications: modern, widely used, economical, profitable to install and operate.
Modern drainage systems are most often assembled from polymer pipes
Asbestos-cement pipes are products of the previous generation. They are environmentally unsafe, heavy, requiring physical effort when organizing work and using special equipment. The same applies to ceramic products. Often, drainage holes are made at the installation site; the required quality of pipeline preparation is lacking. All this predetermines increased costs of money and time, which does not suit customers.
Plastic systems have great advantages and promise. We list the main advantages of such products:
- long period of operation, no influence of moisture on the structure of the pipe material;
- have excellent strength characteristics, due to their structural abilities to bear and withstand mechanical loads;
- light weight of products, which facilitates quick installation and facilitates delivery of pipes;
- polymer pipes have good price indicators with corresponding product quality;
- simple and reliable in operation, do not require maintenance or inspection for many years;
- A wide range of products are manufactured, such as perforated pipes for drainage of different diameters, equipped with specialized connecting and sealing elements.
Types of drainage perforated pipes
To arrange drainage drainage, suction drains are used - perforated pipes. Perforation allows you to collect excess moisture directly from the soil, filtering it.
Suction drain pipes can be made of the following materials:
- polyvinyl chloride (PVC),
- low pressure polyethylene (HDPE),
- polypropylene (PP),
- ceramics,
- asbestos cement.
Polymer pipes are lightweight, highly flexible and have a service life of half a century and are distinguished by a variety of standard sizes and low prices, but polymers are afraid of ultraviolet radiation and can lose their shape if severely frozen or heated.
The advantages of ceramic products are a long service life - about 30 years, retention of shape in any conditions and resistance to sunlight, disadvantages - fragility, high price and heavy weight, which complicates delivery and installation.
Asbestos-cement pipes are used less and less, since their strength is negatively affected by moisture and temperature changes, and delivery and installation are difficult due to the large weight of the drains.
In addition, perforations are applied to polymer pipes in the form of narrow and long slots, which are not clogged with small debris, unlike round holes in ceramic and asbestos-cement pipes.
Polymer drains are either smooth-walled or corrugated:
- Smooth pipes are cheaper, but are only suitable for installing drainage in small areas where a pipeline with a large internal cross-section is not needed. Smooth-walled pipes more than 10 cm in diameter are easily deformed under the pressure of the backfill layer.
- Corrugated walls provide additional rigidity, which allows them to withstand the pressure of transported water and soil backfill even with high pipe capacity.
We recommend that you read: What is a vent pipe and is it needed in a private home?
Drains with perforation can be made with your own hands. To do this, holes are drilled in a plastic pipe, then polymer shavings are removed and the edges of the resulting perforation are cleaned. However, round holes are easily clogged, so the artisanal method of making perforated pipes is applicable only if it is impossible to purchase factory-made products.
Plastic perforated pipe. Its advantages and applications
Plastic pipes are used almost everywhere. This also applies to drainage systems, which are based effectively on polymer products. Easy to use, effective in operation, they quickly proved their indisputable advantage. The industry produces many types of polymer pipe products according to established standards. They are made from different polymer compositions: polyvinyl chloride, high and low pressure polyethylene, polypropylene.
Drainage pipes made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are manufactured in the following versions:
- single-layer and two-layer products;
- rigid and flexible pipes;
- pipes equipped with filter material;
- pipes without filter elements.
Drainage pipes can be rigid or flexible, supplied in coils or lengths
Rigid pipes are produced in lengths of 6 meters and 12 meters. Flexible, relatively small in diameter, packaged in coils of approximately 50 meters, depending on the diameter.
Important! Please note that drainage pipes are manufactured in accordance with strength classes from SN2 to SN16. Products are used depending on their ability to withstand specified loads and their purpose.
Polypropylene pipes can have a flat, smooth surface or corrugated, with stiffeners, depending on the functional purpose. Typically, such a pipe is made with a diameter of 50 mm, with a fairly high strength class - SN8.
LDPE and HDPE pipes are widely used in drainage systems. They are low-cost, efficient in installation and operation. The following varieties can be distinguished:
- a simple single-layer pipe with perforation or without drainage holes, used in surface systems;
- polyethylene pipe, with corrugated ribs on the outside and smooth on the inside, with a higher rigidity class, which allows it to be buried up to 4 meters;
- the same design, but with a higher strength class for use at depths of up to 10 meters;
- double-layer pipes made of low-density polyethylene, corrugated, with a high rigidity class for deep burial.
Another highly efficient type of corrugated drainage pipe is the Perfokor polyethylene pipe. Mineral components are used for its production. This composite creates high strength of the product, which facilitates its use in a variety of options for constructing a drainage system. Pipe type – two-layer, perforated in the following versions:
- has perforations along the entire length and works mainly in deep systems;
- perforations are located along the top of the pipe and are used to collect and remove water from the surface of the site.
“Perfokor” pipe is a two-layer product with high technical characteristics
Such pipes are manufactured in both measured lengths of 6 meters and 12 meters, and in rolls. Typical diameters of such pipes are 110 mm, 160 mm, 200 mm. Typically, such pipelines are equipped with a geofilter.
Pipe selection
To choose the right perforated pipes for making your own drainage system, you need to consider:
- material of manufacture;
- type of pipes;
- technical specifications.
What materials are they made from?
For the construction of drainage systems, perforated pipes made of the following materials are used:
- asbestos cement. The material is quite strong and durable. However, factors such as a low level of environmental safety and heavy weight, which complicates transportation and installation processes, reduce the demand for these products;
Asbestos cement is almost never used for drainage
- ceramics. Ceramic pipes are also used extremely rarely, since the relatively high cost is complemented by the fragility and heaviness of the material. Among the positive qualities are durability and long service life (more than 30 years);
Ceramics are highly brittle
- plastic. In most cases, perforated pipes are made of polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), and low-density polyethylene (HDPE).
Polymer ones are characterized by low cost, long service life (more than 50 years), variety, low weight, and flexibility, which greatly simplifies the process of self-installation. However, they react negatively to ultraviolet rays and large temperature differences, which can lead to deformation.
Plastic is the most popular material
Plastic pipes are most often used to organize drainage systems.
Types of perforated pipes
Depending on the type of perforated pipe wall, there may be:
- smooth-walled.
They can be made from different materials, and only this type is made from ceramics and asbestos cement. Plastic ones are characterized by low strength and can be deformed under mechanical stress. Therefore, the area of application for smooth-walled perforated pipes made of plastic is the manufacture of a drainage system in small areas with a sufficient diameter of 10 cm;
Perforated smooth wall type (plastic)
- corrugated. Corrugated perforated pipe is the most common type of product made from plastic, which has a high level of strength. Products of this type can be used in any area, including the location of a highway, a parking lot, and so on.
Polyethylene pipes can also be:
- two-layer, made of HDPE and PVC, which increases the margin of safety;
Dual material product for drainage systems
- supplemented with a filter. A pipe with a filter made of coconut shavings allows you to extend the service life of the drainage system, since the protective layer prevents waste, pollutants and other elements from entering the system;
Protective coconut filter
- supplemented with geotextiles. Pipes with geofabric are also designed to extend the service life of the drainage system and protect communications from various contaminants.
Protective geotextiles
Determination of technical parameters
Corrugated perforated drainage pipe is also selected depending on the following parameters:
- diameter To equip a drainage system for an area of 6–10 acres, pipes with a diameter of 110 mm are sufficient. For large areas, a preliminary calculation of the diameter is required. As a rule, the work is performed by professionals using special programs;
- hardness class. In order for the pipes to withstand the pressure of the soil located on top of the drainage system, it is necessary to select the appropriate stiffness class in accordance with GOST. The averages are shown in the following table:
| Depth of the drainage system, m | Hardness class (SN) |
| Until 3 | 2-4 |
| 3 – 4 | 6 |
| To 10 | 8 |
- type of perforation. To manufacture a drainage system with a high level of groundwater, as well as in regions with a large amount of precipitation, pipes with perforations along the entire diameter are used. To organize surface drainage only during periods of heavy rain, you can use products with partial perforations applied to 1/2 or 2/3 of the circumference.
All technical parameters are indicated in the markings and accompanying documentation.
How to choose the right drainage pipes with perforation, watch the video.
Technological features of drainage pipeline installation
Installation of drainage involves excavation work to dig trenches into which drainage pipes will be laid. The depth and location of the trenches depends on the water saturation of the soil and the geodesy of the site itself. The pipes are prepared, equipped with connecting elements, accessories, filter fabric, and other necessary accessories.
As a rule, a perforated pipeline is laid on a sand bed. Then the pipes are filled with crushed stone, which plays the role of a filter. As an additional filter element, filter fabric or other means are used to filter wastewater. Then they backfill with a sand mixture and cover the trenches with ordinary soil.
In places where the system changes the direction of installation, inspection wells are installed to monitor the operation of the drainage system. In the lowest location on the territory where construction work on the installation of a drainage system is being carried out, a well is installed to collect water.
Note! Wells are also installed in straight sections of the drainage system, approximately every 50–60 meters.
The installation of drainage pipes creates a kind of network of capillaries that direct moisture to the place of its collection. Using modern polymer perforated pipes and auxiliary materials, such drainage can be done independently. To carry out work over large areas, as well as in places of large excess moisture, design work is carried out, which involves the development of a drainage system plan, regulating the use of the appropriate type of pipes, methods of filtration and moisture removal.
Features of drainage pipes and their use
Properly organized drainage allows you to remove groundwater, melt or rainwater from the foundation of buildings and redistribute the level of humidity on the site. The drainage system is assembled from drains - pipes or channels that collect and transport water in the right direction. The installation of a drainage system is simple and is often done by hand: drains are laid in the ground with a slope towards a reservoir, collection well or irrigation tank.
Drainage tasks may vary and the pipes that need to be used to install the system depend on them:
- if you only need to collect water from individual areas and transport it to the discharge site, use pipes and gutters with solid walls - such drains are called prefabricated drains;
- To drain the area and lower the groundwater level, perforated pipes are used, called drainage, suction or filter pipes.
Note! Regardless of the water disposal tasks, only pipes with smooth inner walls that are resistant to moisture, water hammer and temperature changes are used for the drainage system.
Drying systems
If you get an area with high humidity, then don’t despair. Modern equipment makes it possible to build drainage that will save you from all problems. It may differ from each other not only in design, but also in the installation method.
The following types of drainage structures are distinguished:
- Closed. It is used to protect the foundation of a building or to drain nearby groundwater.
- Superficial. Installed to get rid of water that forms after snow melts or heavy precipitation.
If you are going to make an open system, then you will not need equipment, just dig grooves or trenches.
If you need to build an underground system, you will need:
- Perforated pipes for drainage.
- Connecting elements.
- Drainage wells.
- Filters and hatches so that the system can be serviced.
If you have all the preparations, then you can safely begin installing the drainage.
Purpose of the water drainage system
In another way it is also called dehumidifying; the name itself speaks for itself. If we approach this issue thoroughly, then installation of such a structure is necessary in almost every area. You just need to carefully consider the choice, based on the distinctive features of your site, soil type and other conditions.
In what cases is drainage necessary:
- Groundwater is too close.
- Your soil is clay, so water pooling is inevitable, especially after heavy rains.
- If the plot is flat, then you simply cannot do without a good drainage system, otherwise all the water will stand on your beds.
- If your property is located on or below a slope, you will need to install a dehumidification system to prevent the accumulation of liquids draining from the upper levels.
Installing high-quality drainage will allow you to solve all these problems painlessly.
Types of perforated pipes
Almost all pipes in this system must have holes through which water would leak inside. To allow liquid to drain, they must be placed at some angle.
The following pipes are used for installation:
- Asbestos-cement.
- Ceramic.
- Plastic.
The first two varieties are used quite rarely, as they have a lot of disadvantages:
- Too heavy, requires special equipment for transportation.
- Manufacturers produce such products without drainage holes, so you have to make them yourself, and this only prolongs the installation process.
- In terms of their performance characteristics, they are not good enough. Holes made by yourself quickly become clogged, so you have to clean them periodically.
- The service life is relatively short.
- The cost of the equipment is quite high.
Because of all these shortcomings, when constructing a drainage system with your own hands, plastic pipes are used.
Advantages of plastic drainage pipes
The great popularity of perforated pipes is explained by their advantages over other varieties. Among them the following can be noted:
Installation of drainage pipes
- The service life reaches 50 years.
- The material is quite resistant to various external factors.
- High anti-corrosion properties.
- Great flexibility makes it possible to equip absolutely any configuration.
- They do not pose an environmental hazard to humans and all living organisms.
- Great strength.
- Low weight facilitates installation and transportation.
- Even a beginner in this matter can easily carry out the installation on their own.
- Due to the smooth inner surface, no blockages are formed during operation, that is, they are capable of self-cleaning.
- Fairly affordable price.
All these advantages make drainage pipes made of polyethylene very popular.
Types of plastic pipes
Such products are made from polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride or polypropylene. The classification includes the following types of structures:
- Double or single layer.
- Hard and soft.
- Flexible, more like hoses, or rigid.
- With or without filter.
If we take into account other parameters, we can distinguish the following groups:
- Flexible pipes in one layer with perforation. They are usually used for laying at shallow depths.
- Two-layer, having a smooth inner surface and corrugation on top.
- Corrugated pipes of high rigidity. Stacked to a depth of 10 meters.
- Double-layer hard.
Perforations are usually performed in several ways:
- The holes are located only on the top side. They are installed to eliminate melt water.
- There is perforation over the entire surface. Used when installing a closed system.
How to choose perforated pipes for drainage
Depending on the characteristics of the area, pipes of different diameters are used: for small areas 10 cm is enough, but the larger the size of the area to be drained and its humidity, the larger the diameter of the drains. The largest pipes used for drainage have a diameter of 16 cm.
In addition to sizes, the criteria for choosing pipes are:
- hardness class;
- location of perforation.
Depending on the depth of installation, the systems use drainage pipes with different wall rigidities so that the drains can withstand the pressure of the soil layer laid on top.
| Depth, m | Hardness class |
| up to 2-3 | SN 2-4 |
| up to 4 | SN 6 |
| to 10 | SN 8 |
When choosing pipes, the level of groundwater, the amount of precipitation and the method of laying drainage are also taken into account. The purpose of the drains determines exactly how the perforation should be applied: along the entire circumference or partially only in the upper part of the pipe.
| Perforation of the drain | Purpose |
| around the entire surface | lowering the groundwater level, draining excess groundwater, rain and melt water, |
| ⅓ circle segment | surface drainage, storm drainage, |
| ½ circle segment | universal pipe, |
| ⅔ circle segment | organized drainage. |
Installation of a drainage system
Installation of drying equipment on site includes several stages. The technology for carrying out all the work is not particularly difficult. Therefore, it is quite possible for any man.
You can note the following steps that must be performed in a specific order:
- Carry out earthworks, including digging ditches and trenches. The width should be approximately 40-50 centimeters wider than the diameter of the PVC. All large stones and blocks of earth must be removed from the trench; when digging, it is necessary to ensure that there is a slope in the direction where water is supposed to be collected.
- Equipment for shock-absorbing layer. To do this, pour a layer of sand into the trench and compact it well, and add crushed stone on top. If there is no filter layer, it is recommended to lay geo-textile fabric after the sand layer to prevent clogging of the perforations.
- Pipe laying. The process depends on the location of the holes. If they are only on one side, then they must be laid with this part down. Where the pipes turn, it is advisable to install wells. Fittings are used to connect to each other.
- Backfilling the trench is done in the reverse order: crushed stone is poured first, then the sand mixture. The soil that was formed during digging is already laid on top and can be covered with additional turf.
- If you want to protect the foundation of your house from exposure to water, then it is worth laying drainage pipes around the perimeter of the building.
Laying pipes for land drainage
Plastic drainage pipes must be laid at a depth where the soil will not freeze in frosty winters. In order for you to be able to periodically service the system, you need to build inspection wells. They must be installed on a straight section, at a distance of approximately 50 meters, as well as on turns.
We hope that these installation instructions will provide you with the necessary assistance in installing drainage.
Basic rules for laying perforated drainage pipes
The device for draining water from the foundation is not as simple as it seems at first glance. Here we will describe all the features of the drain installation process.
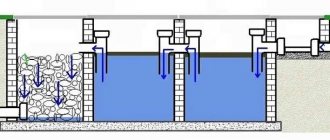
Wall deep drainage around the house is located below the depth of soil freezing, below the foundation and in any case, no higher than 1.2 m from the ground level. It is located at a distance from the walls of at least 1.5 m, from the blind area - 0. -1.2 m. Ditches are dug at least three pipe diameters wide. To the required calculated depth, it is necessary to add 0.3 m - the thickness of the bedding made of crushed stone and sand (crushed stone carries out primary filtration of groundwater).
The first step is to pour bedding onto the bottom of the ditch. First, wide and narrow geotextile tapes are laid to wrap crushed stone and sand.
Then a layer of sand 100-150 mm thick is poured, compacted, and wrapped in textiles. Fill the crushed stone with a filter layer equal to the diameter of the drain and level it with a piece of board nailed to a stick. Crushed stone fraction – 16-32 mm. Before backfilling, wash the crushed stone with high-pressure water from a hose for 10-15 minutes. It is convenient to do this by pouring crushed stone into small piles. Then it is either used or packaged in bags and stored for no more than a week.
You can't dry it!
Starting from the collector well, perforated pipes are laid. They fill it with washed crushed stone to the height of one pipe diameter and wrap it with a large piece of geotextile. Cover with fine unwashed crushed stone of fraction 8-40 mm in a layer of 100-200 mm. Covered with earth.
The slope of the drainage system is determined by SNIP 2.04.03 and varies between 2-10 mm per linear meter. The slope should increase slightly towards the collector well. With a uniform slope, the system silts up faster.
Wells must be installed at every second turn of the pipes and at their connections. Pipeline outlets must be at least 250 mm above the bottom of the well.
Watch our video - it will help you see all the intricacies of the drainage installation process.
Laying ceramic drainage pipes
Despite the fact that plastic drains are most often used to install such systems, in some cases instructions for laying ceramic pipes may be needed. It does not differ greatly from the previous method, but differs in some subtleties:
- Getting started includes the same steps - digging ditches and trenches.
- Ceramic pipes can only be used with a diameter of at least 5 centimeters.
- The polyethylene must be laid in the ditch, pressing well to the ground.
- Moss or matting should be used at the joints to prevent seepage through the joints.
- At the transition point to the areas for collecting drainage water, you need to install a wooden pipe with a slightly smaller size inserted into it.
- Backfill the ditch in the following sequence:
- The pipe must be covered with moss.
- Cover with gravel or crushed stone.
- Lay the removed turf on top, grass side down.
- Cover the entire trench with soil.