In summer cottages with fruit trees, shrubs, vegetable gardens and berries, remote from large populated areas, the problem of recycling not only household waste, but also rotten fruit and vegetable products is always relevant. In this situation, the solution to the problem of getting rid of organic residues is often a self-made compost bin, the manufacturing options of which are distinguished by their design simplicity and availability of materials.
Before building a composter, they usually look through numerous photographic materials on the Internet, selecting the desired design option with available budget components. With proper installation in compliance with the following technologies for assembling and using the container, waste composting will occur with high efficiency, and the garden composter will last for quite a long time.
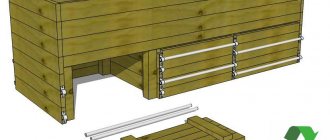
Rice. 1 Composters on the site with the finished product
Operating principle and purpose
Composting is an aerobic (with access to air) process of rotting (re-rotting) plant and household organic waste of animal origin with the help of: bacteria; microorganisms; decomposers (bacteria and fungi that destroy the remains of living beings); detritivores (animals and protozoa that eat decaying organic matter); mushrooms; worms (vermicomposting). The end result of the biodegradation occurring in the compost pit (destruction of complex compounds as a result of the activity of living organisms) is the formation of a useful nutrient mass for plants - humus (humus).
In households, a compost bin performs two main functions: recycling organic waste and processing it into useful fertilizer. During composting, the following processes occur in the stored mass:
- the quantitative indicator of chemical elements useful for plant nutrition—phosphorus, potassium, nitrogen and others—increases;
- the content of hemicellulose, cellulose and pectin components in humus decreases, causing the transition of nitrogen-phosphorus compounds that are well absorbed by vegetation into another organic state that is not absorbed by plants;
- microflora harmful to human health that causes pathogenic bacterial diseases is neutralized, helminth oviposition is destroyed;
- the formed finished mass becomes free-flowing, its introduction into the ground is significantly simplified.
Rice. 2 Compost laying scheme
Raw materials for composting
In households, the main components for putting into compost containers are the following types of waste:
- organic matter of animal origin: manure and its slurry, spoiled feed, bird droppings, feces;
- vegetable - weeds from gardens, parts of garden plants after processing (tomato shoots), grass cut from lawns, vegetable, fruit and berry peelings that are unsuitable for food;
- after processing agricultural products - tops from root crops, corn cobs, sunflower stems, flax and hemp stalks;
- from woodworking and trees: shavings, bark, sawdust, leaves, small twigs;
- household - residues from processing plant foods (vegetable and fruit peels, seed husks, coffee and tea cakes), egg shells;
- peat.
All raw materials for composting are conventionally divided into two categories (table Fig. 3):
- brown - has a high carbon content (leaves and needles of trees, wood waste, straw and plant stems).
- green - with a high concentration of nitrogen (all plants and plant waste, food debris, manure).
The optimal ratio of green and brown mass for effective rotting has been calculated experimentally; it is 25 - 30 units to 1. For example, if we take one part of leaves with a ratio of 60:1 and two parts of manure with a ratio of 15:1, we get three parts humus 90:3, that is, the best ratio of components is 30:1.
To improve the quality of compost, phosphate and dolomite flour, mineral-based fertilizers, ash are added to it, and sometimes soil is used, pouring layers of waste into it.
Rice. 3 Table of carbon to nitrogen ratios for organic matter
You should not put the following in the compost container:
- plants with sprouted seeds, freshly dug roots of wheatgrass and horsetail crops;
- potato and tomato tops infected with powdery mildew and late blight, herbicide-coated vegetation;
- fruit tree seeds;
- garbage that does not contain organic matter;
- unsuitable organic residues from the slaughter of animals, protein waste;
- excrement of some domestic animals.
Requirements and recommendations for making compost bins
When constructing a compost bin, owners of summer cottages and household plots must take into account the factors necessary for effective waste treatment; microorganisms require:
- carbon - contributes to the formation of energy during oxidative and reduction processes with the release of thermal energy;
- nitrogen - participates in the nitrogen metabolism of the soil, converting toxic ammonia into less harmful nitrates and biologically inert atmospheric nitrogen;
- oxygen - required for carrying out oxidative processes involving carbon and carrying out chemical reactions of decomposition of organic matter;
- water is the necessary and best medium for the occurrence of biological processes involving microorganisms.
The rate of reactions and, accordingly, the maturation of compost depends on the presence and ratio of these chemical elements.
Important: Since the processes occur with the participation of aerobic bacteria that need good air access, to obtain compost it requires regular aeration - mixing (shovelling) with a fork or shovel.
When the moisture and oxygen content in the compost mass is close to optimal, its temperature is 50 - 70 ° C; usually, during maturation, the standard temperature indicator is 40 - 50 ° C until all components are processed.
The average time to obtain the finished product is about 2 years from the moment of laying; when using acceleration methods (organic destructors or aeration), the compost matures within 1 season.
Rice. 4 Operating principle of the composter
Taking into account the above, the compost bin must meet the following requirements:
- Since the vital activity of aerobic bacteria, which carry out the main work of decomposing organic matter, requires oxygen, the box is not hermetically sealed. Its walls and bottom should have cracks or holes for ventilation and air access to, if possible, a larger area of humus.
- Excess moisture leads to leaching of humus from the container, so it is equipped with a protective lid.
- To saturate the compost mass with air, it must be stirred periodically - for easy access to the lower layers, the box is not too deep or narrow.
- The process of humus formation takes at least 1 season, while the material used to make the box is constantly in a humid environment with microorganisms. It is desirable that the parts of its design have as long a service life as possible.
- Since a compost heap is usually constantly replenished with organic waste poured through the top, and the humus that has been below for a long time is often ripe and can be ready for use, the design should provide for the possibility of removing the lower layers of fertilizer. To do this, install retractable strips in the bottom or in the front of the drawer from below.
Rice. 5 Composter wooden boxes
Compost bin - humus reactor
Composting is the decomposition or decomposition of organic residues, plant waste with the help of earthworms, bacteria, microorganisms with the formation of the final product of humus or, in other words, humus. The decay period is about 12–18 months and depends entirely on the number of microorganisms, temperature, humidity, oxygen enrichment (air access).
In order for the reheating of organic matter to proceed steadily, it is necessary to provide conditions for the growth and vital activity of microorganisms and the creation of a microclimate. The most complete compliance with these factors can be achieved by using a container for these purposes. It can be a box, box, barrel or pit. Let's focus on the most common option - a box.
A compost bin is designed and necessary for the correct and compact placement of organic waste and the activity of microorganisms. The use of the design allows the biomass of microorganisms that “eat” plant residues to be protected from rain and wind, and a temperature favorable for the reaction to be created.
A compost box is a box with side holes for air access measuring 1.5–3 cm. The design can be solid or have several sections or departments. The size of the box also varies, but it is advisable to adhere to the following standard: 2 x 1 x 1.5 m (height).
Divide the box into sections in order to separate last year's compost from fresh one. The bottom is covered with a mesh, and the box itself is installed on a pallet with an opening lower door or a drawer that can be pulled out.
The idea of using a “reactor” is that raw materials - plant residues, manure, leaves and tree branches - are loaded into a container with a rotting environment through the top lid. As expected, not without the help of living microorganisms, the mixture begins to rot, rot, decreasing in size and breaking up into smaller fractions.
After a certain period of time, crushed rotted plant waste, which has turned into humus, is selected for the needs of the gardener
After a certain period of time, the crushed plant waste falls through a mesh installed inside the box and is picked up with a shovel through the bottom door for application as fertilizer to the garden. The process is somewhat reminiscent of the combustion of wood in a stove, followed by the settling and removal of ash.
Manufacturing materials
Before making a compost bin for recycling waste with your own hands, select the material for its manufacture, most often consider the following options:
Wood
To make a wooden box, they use boards that are unnecessary in the household, ready-made pallets, timber; there is no point in using plywood, fiberboard or chipboard sheets that have too low resistance to moisture. Since untreated wood will not last too long, it is coated with moisture-repellent materials - various types of paints, varnishes, hydrophobic impregnations, waterproofing mixtures, bitumen mastics.
Note: Economical and effective ways to process wood are to impregnate it with machine or waste oil, you can simply wrap individual boards with plastic wrap and nail them to the frame.
Metal
Using regular steel for a box with high moisture and fertilizer that will be added to the soil to feed edible crops is not a good option, given that rust will contaminate the compost. Therefore, the best option is to use corrosion-resistant materials in the construction of the box, the most inexpensive of which are galvanized sheet (metal profile) and aluminum.
A metal box can be assembled from separate narrow plates or corners (to increase strength), screwed to a wooden frame made of timber treated with water-repellent compounds.
Rice. 6 Polymer composters
Polymers
Making a compost bin or barrel from polymers is the most successful option in terms of corrosion resistance and service life of plastics, reaching up to 50 years. The retail chain sells factory-made composters for dachas that have an aesthetic appearance, a variety of design and color solutions, and a convenient system for accessing the lower layers of humus. The price of plastic composters is not so low, a rather inconspicuous product can be bought for 2,000 rubles, the cost of imported boxes or large-volume products reaches 15,000 rubles.
Other materials
In addition to traditional components, a compost bin can be built from the following materials:
Net . Mesh types of compost containers are sold on the market, providing the best air exchange; similar devices can be made yourself from a chain-link type mesh. During operation, the mesh box will have to be closed on top with a waterproof lid, and during operation it will be difficult to mix the compost mass.
Note: When constructing a composter bin, a synthetic mesh is often used, which closes the gaps between the wooden boards, preventing the contents from falling out; with this design, the distance between the slats can be increased to 50 mm.
Rice.
Slate mesh boxes . Recently, slate has significantly lost its position when used as a roofing material; one of the ways to use it is to construct waste recycling containers from sheets. In many versions of boxes, the walls are made of solid sheets, which prevents air exchange.
Brick .
A reliable and durable box can be made of brick or any building blocks; when laying, it is possible to make cells for air exchange; the main disadvantage of a monolithic structure is the difficulty in mixing and removing ripened masses.
Advantages and disadvantages of this type of pit
A compost pit made from slate, like a compost pit made from pallets, has its own advantages and disadvantages.
- Easy installation and operation.
- You can use the resulting humus to fertilize the soil in your summer cottage. The humus is of high quality.
- Cheap materials for making a tank. No specific tools are required.
- High-quality compost will be produced within two years. If you add special impurities, the time frame will be reduced to six months or even two months.
- No unpleasant aroma if there is a lid on the container, which prevents the spread of stench throughout the area.
- you need to correctly place the structure on the site so that the humus rots effectively;
- Regular stirring of the humus is required (once a week).
How to make a wooden composter
It is not so difficult to make a compost box with your own hands, having studied the corresponding drawings and photos on the Internet. To build a wooden composter, boards of small width up to 100 mm of arbitrary length are suitable; to fasten them you will need a beam with a cross-section of about 50x50 mm. To increase service life, it is advisable to treat all wooden parts with water-repellent agents before installation.
Before making a garden composter, an assembly diagram is drawn, after which the building materials are cut into pieces of the required length in accordance with a pre-drawn drawing. To assemble the boxes you will need a tape measure, a hacksaw (jigsaw) or a circular saw for wood, self-tapping screws, a screwdriver (Phillips screwdriver), a crowbar and a shovel for digging holes in the ground.
Rice. 8 Metal containers
Step-by-step instructions for assembling a wooden box are as follows:
- Dig 4 holes in the ground at the required distances to a depth of at least 30 cm, insert pre-cut bars about 130 cm long into them, fill the holes tightly with stones and compact the soil.
- Screw the horizontal wooden planks to the vertical bars around the perimeter using self-tapping screws, leaving a distance of 2 - 5 cm between them. Another option is to assemble the box on the ground and then immerse it in the dug holes.
- To prevent precipitation from penetrating into the box, a light, removable frame is made from wooden planks knocked down around the perimeter of the container (they can be fastened together with flat corners), and a stretched plastic film or a thin sheet of tin is nailed to it on top.
- In the lower part, to extract ripened humus, two strips are made removable by inserting them into the grooves of a curved rigid metal plate.
Even faster, you can make a wooden box from 4 ready-made pallets (transport pallets), for this they are installed vertically or horizontally close to each other and connected to each other in the corners with self-tapping screws or using wooden planks. The design usually provides for the possibility of removing one of the trays for mixing and extracting the compost mass.
Rice. 9 Wooden box assembly drawing
Domestic composters
The Volushka composter is in great demand among gardeners. This is a domestic model with a cone shape. The four sidewalls are bolted together. Product volume is 1000 liters.
The composter is made of propylene with wavy walls. The structure is easy to assemble and disassemble. The appearance of the product allows it to be placed anywhere on the site. The compost it produces is of good quality. The stores have a large selection of composters of different shapes and designs.
So, the useful accumulation of waste will help solve the problem of disposal and enrich the site with valuable fertilizer. It should be remembered that according to sanitary standards, composters must be located at a distance of 20 m from water supplies and 10 m from residential buildings.
There are many options for making and purchasing garden products for obtaining fertilizer. Decide for yourself which composter to choose.
Adviсe
The following tips may be helpful when making your compost bin:
- The easiest way is to make a container from wooden beams and slats; before installation, they should be impregnated with a water-repellent composition; it is cheaper to use used machine oil.
- Since the ripening time of humus when adding accelerators takes 1 year, it is better to apply them in early spring so that the fertilizer is laid out before planting crops.
- During the ripening process, the compost heap must be periodically moistened and mixed; cow manure, chamomile, dandelion, and yarrow infused in water are used as a homemade ripening accelerator.
- The composter must be located in a shaded place at the maximum distance from water intake sources (wells, wells) if they are available on the site, the optimal height of the box is 1 m.
Rice.
10 Types of compost facilities The use of compost technologies in households allows not only to recycle a significant amount of waste, but also to obtain environmentally friendly fertilizer based on it for feeding garden crops. If you have the financial resources, it is not at all necessary to make a composter container yourself from available components - the retail chain sells a number of easy-to-use models made from durable, corrosion-resistant polymers that have an aesthetic appearance and colors suitable for most areas.
Where to start making compost pits
The pits should be as far as possible from residential buildings and located on the leeward side, since organic waste has an unpleasant appearance and smell. The recommended distance is at least 30 m from housing.
Do not place pits close to drinking water sources. The optimal distance is 25 meters.
Consider the terrain features. Pits should not be placed on high ground: along with precipitation, its contents will be spread throughout the area. You should not choose places on the slopes: excess water reduces the fermentation rate. A flat piece of land is best.
Pay attention to the trees next to the holes. Alder and birch will be good neighbors, but it is better not to place holes next to evergreen trees.
To maintain the correct moisture content of the compost, choose an area in the shade.
Don't forget about ease of access to the pit and choose the most suitable location for you.