Description
Tin-lead solder POS 61 is ideal for use in domestic conditions . This is facilitated by the low fusibility of the composition due to the high tin content. Its melting point does not exceed 200 degrees Celsius.
Due to the high fluidity of the molten composition, the solder fills all cracks and cavities, providing high-quality joint characteristics. The composition used belongs to the universal category. It can be used to solder products made from the following metals:
- steel;
- copper;
- brass;
- bronze;
There is an analogue of this solder on the domestic market - POS 60. The mass fraction of tin in its composition is only one percent less.
The foreign analogue is Sn63Pb37, which contains 63% tin and 37% lead. The technical characteristics and scope of application of the material are practically no different from POS 61.
Description of solder
The main requirement for the solder used is a lower melting temperature than the melting temperature of the workpiece. different together . In this regard, there are different types of materials that differ from each other in physical and chemical properties and are part of the alloy components.
So, there are two groups of solders: soft and hard. Soft ones are those whose melting point is below 300 degrees, therefore, the melting of hard solders will be above this value.
One of the most common filler materials is POS - tin-lead. There are several materials in this category, depending on the percentage composition of tin in the alloy, which is indicated by a number. They are characterized by a relatively low melting point and low strength.
This somewhat limits their scope of application. For example, these solders are convenient to use in radio installation and are undesirable for use in parts that experience great physical stress.
Material characteristics
Let's look at the main technical characteristics of POS 61 solder:
- density – 8.5 g/cm3;
- impact strength – 3.9 kg/cm2;
- tensile mechanical strength – 43 MPa;
- relative elongation – 45%;
Chemical composition
The main chemical elements of solder are:
- Tin . Under ideal manufacturing conditions, the tin content in the composition is 61% of the total mass. According to the requirements of regulatory documents, its mass fraction must be at least 59%.
- Lead . Its percentage is 38-39%, depending on the presence of auxiliary additives. For example, POSSU 61-05 solder, in addition to tin and lead, contains only 0.5% antimony.
In addition to antimony, the composition may include the following chemical elements that improve the quality of the compound:
- iron;
- bismuth;
- nickel;
- sulfur;
- zinc;
- aluminum.
Temperature parameters
The soldering temperature of POS 61 is 240 Cº . In this case, the composition begins to melt at a temperature of 184 Cº, and complete transition to the liquid state of aggregation occurs at 194 Cº (± 2 Cº, depending on the content of auxiliary chemical elements).
Of all the lead-tin solders, POS-61 is the lowest melting point.
About the composition of solder
The name of the solder of the tin-lead group indicates the tin content in it. For example, POS-40 contains 40% tin, and POS-61 contains almost 61% tin. The rest consists of lead and additional impurities. By appearance, you can estimate the composition . If the PIC solder is more matte and dark, then it contains more lead. If it is lighter and shiny, then there is more tin. This is best understood by comparison. Look at the photo to see what a sheet of tin and a sheet of lead look like.
The strength of solder depends not only on the alloy alloy, but also on the metal being soldered. For example, to solder copper or zinc, several percent of copper or zinc are added to the POS solder, respectively. This reduces chemical erosion of the metal and increases the surface strength of the joint.
Solder alloying
To improve performance characteristics, alloying of solder with the following substances is used:
- adhesion is improved by the addition of copper, cadmium, antimony, aluminum, silver and zinc;
- ductility and resistance to thermal cycling are improved by the addition of indium, silver, manganese, bismuth, and lithium;
- Nickel, cobalt, zinc, silicon, boron, iron add strength
- The corrosion resistance of solder is increased by nickel and copper;
- Heat resistance is increased by silicon, zirconium, tungsten, vanadium, cobalt, niobium, hafnium.
Varieties
Regardless of the release form, the composition of the material and the ratio of the main components remain unchanged. The most common varieties are:
- Wire. Its diameter ranges from 1 to 7 mm, depending on the application. The step size is 0.5 mm. Delivery is carried out in compact coils or coils, which are unwound during operation. This form of release is the most popular.
- Solder with rosin POS 61 is produced in the form of thin tubes with filler, twisted in a spiral. Pine rosin plays the role of flux during soldering work. Its advantage is its neutral composition, which does not require removal after completion of the working cycle, unlike acid-based fluxes. Other types of POS 61 solders are produced without rosin.
- Ribbon. A distinctive feature is the ability to quickly repair cable and wire materials. Tape solder is characterized by a low antimony content.
- Rods. Their length does not exceed 40 cm. The maximum diameter is 8 mm. This release form is ideal for tinning the temperature rod of a soldering iron. Some craftsmen prefer to make rods themselves, casting them into special molds.
For large production enterprises, POS 61 is supplied in the form of massive ingots weighing up to 25 kg. This reduces the cost of consumables and soldering work.
Characteristics of POS 10
POS 10 has the following chemical composition: 9-10% tin, about 89% lead, 0.2% bismuth, 0.1% antimony and other impurities in small quantities. POS-10 is used for tinning and soldering contact surfaces of electronics. For example, it is used to fill control plugs in radio electronics housings and solder relays.
Soldering temperature POS 10 - 299 °C. The solidus point is 268 °C.
Pros of POS 10
- high melting point is useful when soldering equipment cases.
Cons of POS 10
- high resistivity - 0.2 Ohm•mm2/m;
- high content of lead, which is hazardous to health;
- low strength and tensile strength of about 3.2 kgf/mm2.
Use in everyday life and at work
In addition to unique technical characteristics and high performance qualities, POS 61 solder has another advantage - affordable price .
These factors caused the spread of this material, which has found many applications, both in everyday life and in industry. Among radio amateurs, solder has long established itself as a reliable assistant. The low melting point eliminates the possibility of overheating of radio components and microcircuit elements, which is a decisive factor when choosing a suitable consumable material.
At various enterprises, POS 61 is used for soldering strands of copper wires. The solder contains copper, which has a beneficial effect on the intensity of wire dissolution.
When sealing cracks in metal vessels, a gas burner is used as a working tool. The molten composition easily penetrates into all cracks, reliably sealing the holes.
The low melting point leaves its mark on the work front. Solder cannot be used to repair products whose operation is associated with high-temperature influences. This will cause rapid wear of the connection.
Characteristics of POS and POSS
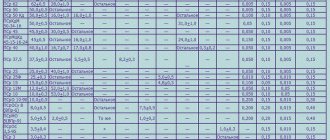
The characteristics of solders of the tin-lead group are shown in the parameters table. Here you can see such characteristics as electrical resistivity, melting point, tensile strength, density, impact strength and Brinell hardness, thermal conductivity, relative elongation of existing varieties of POS and POSSU.
The table shows the lowest melting point solder (cadmium POSK 50-18) with a melting point of 145 °C, and the strongest solder for soldering (POSSu 4-6) with a tensile strength of 6.5 kgf/mm2.
Specifications
Solder for soldering POS 61 is quite common in our country. It is widely used both at the industrial level and in domestic conditions. Its distinctive feature is that due to the high percentage of tin in the chemical composition, its temperature point at which the material begins to melt is very low. It is worth noting that this solder can be classified as one of the most fusible consumables for soldering. This category includes all filler materials whose melting point is less than 450 degrees Celsius. POS 61 melts at temperatures below 200 degrees Celsius. This model is produced in our country in strict accordance with government standards.
Due to the properties described above, the filler material of this model has increased fluidity. In some cases, this property is considered a disadvantage, but not in this case. Due to the low melting point and high fluidity of solder, you can work with it with almost any equipment, from an ordinary household soldering iron to professional specialized units. During the soldering process, solder is able to penetrate even the smallest cracks and recesses, which, of course, allows you to raise the level of quality of the final result of the connection, in particular its strength.
The filler material also interacts well with water. Due to good wetting, soldering using solder of this model does not cause any difficulties during operation. All chemical, physical and mechanical properties of a consumable material are determined by its chemical composition, or rather by a certain ratio of elements in it. Even if you change this value by just one percent, all the characteristics of the material can change dramatically. In addition to the main elements in the composition, additional substances can be added to its structure, which can improve one or another specific characteristic of the solder.
This filler material can be used when working with microcircuits, since the low melting point will not cause technical problems, and most importantly, it minimizes the risk of damage to the thin surface. Unlike other solder models, which work with high temperatures, which can damage the condition of the working surface, using POS 61, with the proper skill and equipment, is absolutely safe even for the thinnest metal.
The low temperature point at which the material begins to melt helps achieve another important property of the material. It lies in the fact that in addition to its main use as a consumable for soldering, it can be used as a substance for tinning a soldering iron and working surface.
There is a characteristic feature, the essence of which is that the less lead is present in the chemical composition of the solder, the more various additional elements there are. The rarest element, which is found quite rarely in alternative models, is antimony. Its presence makes it possible to obtain connections with the maximum level of tightness, which significantly improves the quality of the final result of the connection as a whole.
Read also: Properties of some alloy steels and their applications
Solder POS 61 GOST 21931 76 is very often used in the process of repairing pipelines and other products whose working activities are carried out in constant contact with water and other various liquids. The high level of popularity is due to the ease of use of this material model.
Nomenclature
The material is produced in a fairly wide range of sizes, which makes it easy to choose the right one. It can take the following values.
- 1 mm;
- from 1.2 to 1.8 mm in increments of three tenths of a millimeter;
- from 2 to 4 mm in half a millimeter increments;
- 5 mm.
- 8 mm;
- from 11 to 15 mm in increments of two millimeters.
3. Tube (outer diameter values):
- from 1 to 4 mm in increments of five tenths of a millimeter;
- 5 mm.
- 0.8 and 1 mm, with a material width of eight to ten millimeters;
- from 1 to 3 mm in steps of half a millimeter, as well as 4 and 5 mm, with a material width of ten to fifteen millimeters.
The model name is deciphered as follows:
- the abbreviation “POS” means that the solder belongs to the category of tin-lead filler materials with dominant elements in the form of tin and lead;
- the number 61 indicates the percentage of tin in the chemical composition of the substance.
Solder of this model, as well as all its modifications, are quite popular both in the industrial sphere and in domestic conditions. The most famous brands involved in its production are Arsenal, Technoscrap, KievTsvetMet and others.
POS 61 solder is the most popular filler material made on the basis of a tin-lead mixture. Its low melting point makes it popular for repairing electronic circuits, printed circuit boards and other devices that do not tolerate significant temperature changes.
Read also: Do-it-yourself manual riveter repair
In addition, the composition has proven itself well as a means for sealing cracks and holes in various metal products.
Characteristics of POSSu-61-0.5
POSSu-61-0.5 designates a type of antimony solder containing 61% tin, up to 0.5% antimony and about 38% lead. It is used for soldering and tinning of printed circuit boards and galvanized radio components with increased operating temperature requirements. The melting point is 189 degrees. Pros of POSSu-61-0.5
- increased adhesion to the metal surface due to the antimony content;
- characteristics are identical to POS-61.
Cons POSSu-61-0.5
- difficult to find on sale;
- increased cost.
Characteristics of POS-40
POS 40 consists of 39-41% tin, 59% lead. The remaining impurities are in the same ratio as in POS-10. POS-40 is usually used for soldering and tinning of radio equipment casings made of galvanized iron with galvanized seams.
The soldering temperature of POS-40 solder is 238 °C, and the solidus is 183 °C.
Pros of POS 40
- more resistant to thermal cycling than POS-61;
- good ratio of ductility and melting point.
Cons of POS 40
- elevated liquidus temperature;
- high lead content, which is harmful to health.
Modifications of filler material for soldering POS-61
Model solder POS-61 is produced in various versions. Most often, they differ from each other solely in size, but there are also modifications with the presence of additional chemical elements and substances in the composition. It is worth considering the most commonly used modifications.
1. Solder in wire form. The minimum thickness of the material is one millimeter, the maximum is seven. This version is used most often when soldering anything.
2. Filler material in the form of tubes. Its distinctive feature among the entire range of versions of the POS-61 model is that it contains an additional element - rosin. This makes it possible to significantly simplify all work performed, since there is no need to use various additional substances in addition to filler material.
3. Rod version - solder takes the form of small rods. Most often used during work in domestic conditions.
4. The tape version is the least used. The composition of this substance does not contain any additional elements other than those included in the main composition of the material.
Characteristics of POS 30
POS 30 is an intermediate link between POS 10 and POS 40. POS 30 consists of: 30% tin and 69.5% lead. The rest is doping and impurities. POS 30 can be replaced without hesitation by POS 40. The melting point (liquidus) is 238 °C, and the plasticity temperature (solidus) is 183 °C. POS 30 is usually used for soldering and tinning of radiators and zinc sheets.
Pros of POS 30
- good adhesion;
- high strength.
Cons of POS 30
- high lead content;
- often produced in rods.
Characteristics of POS-90
POS-90 consists of 90% tin and 10% lead. It also contains about 0.1% antimony and 0.05% copper. Most often used for soldering and tinning internal seams of medical equipment and food utensils . The melting point of POS 90 is 220 degrees.
Pros of POS 90
- low lead content;
- rarely counterfeited;
- low resistance;
- high strength.
Cons of POS 90
- high cost (higher than POS-61);
- low plasticity.