Specifications
Silver solders are used for high-temperature soldering above 400⁰C . PSR grade materials create a strong, permanent connection of parts made of various steels, copper and its alloys, silver, and other refractory metals.
Solder resistivity 90 – 120 Ohm. Density 8500 – 10000 kg/m3. Heat capacity 18 – 26 J/kg*deg.
Parts soldered using silver solders can withstand dynamic loads, vibration and high temperatures. They can work in hostile environments.
Release form
Silver solder used for home and industrial soldering is produced:
- wire;
- sheets of various thicknesses;
- hollow tubes filled with rosin.
Wire of various thicknesses makes up the majority of the products. It is easy to select PSR for any type of soldering, choosing from a large number the desired diameter within the range of 0.13 - 6 mm.
The use of plates for soldering additives is possible only in a large enterprise. Home equipment is simply not capable of melting them.
Head of the welding wire and solder shop of the DonMet plant Evtyushenko V.P.: “PSR plates are used in the electrical industry for tin-plating the ends of copper multi-core cables of high-voltage lines and for the protective coating of large parts operating in aggressive gases and liquids. A layer of silver, a chemically inert material, applied on top protects the steel surface from oxidation, the destructive action of acids. They mainly use PSR 40 or PSR 45.”
Varieties
PSR solder contains from 1% to 72% silver.
Depending on its composition and qualities, it is used to join various metals and solder tools, such as a diamond drill bit and a circular saw segment. Soldering of silver parts and tinning is carried out using a material with the lowest silver content - PSR 1. The elements are connected at medium temperatures. Non-ferrous metals require a little more silver to solder them well. For them, solder with a silver content of 2.5 to 40% is used.
Tinning of copper and soldering of its alloys, as well as nickel, kovar, low-siberian steel, is carried out with wire with a high silver content of 50 - 72%, as well as PSR 10 and PSR 15.
The PSR 40 with its wide capabilities is in greatest demand among amateurs . Solder is used for soldering high-alloy steels, including stainless steel, heat-resistant alloys, corrosion-resistant materials, and lead-tin bronzes.
When working with jewelry, PSr 45 is used. The melting point of 700⁰ allows soldered products to work at high temperatures. The copper content of 30% allows joining refractory alloys and heat-resistant steels. After tinning, copper, nickel, and bronze acquire a bright shine and do not oxidize for a long time.
Chemical composition
| Element | Percentage |
| Silver | 45 |
| Zinc | 24 |
| Copper | 29 |
| Nickel | 0,5 |
| Iron | 0,1 |
| Lead | 0,05 |
| Bismuth | 0,005 |
Physical properties
Physical characteristics of PSR 45 solder
| Property name | Symbol | Meaning |
| Solder PSR 40 melting point | T | 720 degrees Celsius |
| Resistivity | R | 100 Ohm |
| Solder Specific Heat Capacity | WITH | 20 J/kg degrees |
| Solder Density | 9100 kg/cm3 |
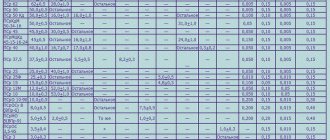
Assortment
| Wire | ||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
Explanation of markings
Each material that is created for soldering has its own unique marking. As a rule, the markings indicate the type of solder, as well as its composition. This helps to select the options required for soldering. Here it is worth noting such points as:
- PSR is a solder that contains silver. Here it acts as the main element that sets the properties of the alloy;
- 40 – silver content in percent. So it contains 40%.
Physical properties
Solders with a high silver content have high fluidity . They penetrate into the small pores of the parts being connected. Low-melting materials PSR 62, PSR 40 are recommended for soldering parts that cannot withstand high temperatures.
Silver solders are universal and suitable for soldering almost all steels and alloys, including non-metallic materials such as ceramics. The main condition for a strong connection is that the melting temperature of the wire must be lower than that of the parts being connected.
The low resistivity of the consumable material allows you to solder micro and electrical circuits.
What is silver solder?
Modern metal working involves stepwise soldering technology. It requires special attention as some silver alloys have a high melting point. This property ensures the high quality of the resulting compound.
Silver solder for soldering in its pure form is extremely rare, which is due to the high cost of the non-ferrous alloy. Compositions with other impurities are more effective in use. The following are often used as additional components:
- Nickel.
- Copper.
- Lead.
- Zinc
Pure silver alloy is used only in jewelry. The properties of solder primarily depend on the proportion of precious metal in the composition:
- At a concentration of more than 50%, the metal becomes ductile and resistant to increased loads.
- Other components can change the basic properties of the alloy, expanding its range of applications.
All possible options are indicated in GOST 19738-74. In the technical documentation there is a table of brands indicating the percentage of all elements. You can save significantly on soldering by making your own alloy. The advantages of most alloys include the following:
- High degree of fluidity. This simplifies the distribution of the composition over the surface.
- Strength. The resulting connections can withstand high loads.
- Corrosion resistance. When exposed to high humidity, metal becomes corroded. When silver is included in the composition, corrosion resistance is ensured.
- The basic properties allow the composition to be used for joining a wide variety of metals.
- Low resistance to electric current allows the use of solder in the creation of electrical equipment.
The only significant drawback is the high cost of the composition. Therefore, it is used much less frequently compared to other alloys.
Melting temperature
Silver solders are used in high-temperature soldering. The melting temperature of rods is very different. It depends on the amount of silver and the presence of other alloying components . Solder of the PSR 1, PSR 2-58 grades most easily passes into the liquid state at 508 – 511⁰C. It contains 30 – 58% tin or lead and up to 2% silver.
They stand out sharply for their refractoriness, among materials similar in silver content, PSR 10 and PSR 12. They contain bismuth 2 times more than other brands of solder and copper up to 52%. Their melting points are 1123⁰ and 1103⁰C, respectively.
Silver solder PSR 45 contains 30% copper from additional substances. Melts at a temperature of 938⁰C, becomes completely liquid at 1003⁰C.
The silver solder PSR 40 next to it on the list has a copper and zinc content of 17% each. Melting until complete transition to a liquid state is carried out at a temperature of 863⁰ – 883⁰C.
Wire grades PSr 71 and PSr 72 contain less than 3% copper. A large amount of silver makes them refractory, with a transition temperature into a liquid state of 1068⁰ and 1052⁰C.
The presence of fluxes affects the melting temperature of silver alloys during soldering and it is lower than that of pure alloy in a furnace.
Soldering process
If you have the appropriate tools, you can carry out soldering yourself. The most difficulties arise when working with stainless steel. The recommendations are as follows:
- To begin with, the surface is cleaned from various contaminants; any mechanical method can be used. Most often, paint and dirt are removed with a brush, after which the surface is degreased using a special composition.
- Selected flux is laid out on the future soldering area. Application technology largely depends on what material is used. The flux must be distributed evenly, otherwise the quality of the connection may be poor.
- To process a large area, a special torch is used to heat the metal to the required temperature. The first sign that the material is ready for soldering is a change in its temperature.
- After reaching the required state of the workpiece, the selected solder is supplied. It should be spread over the surface in an even layer.
- The entire seam is passed from start to finish. A little time is given for the material to cool, after which the workpiece is heated a little more to gradually reduce the temperature.
If the connection area is small, then you can use a small soldering iron. In this case, there is no need to preheat the base.
Assortment
For soldering, silver solder wire with a diameter of 0.15 mm is available . The maximum thickness of consumables is 6 mm. The step in size up to 0.4 mm is 0.05 mm, from 0.6 mm to 2 mm, the difference in the cross-section of adjacent rods is 0.2 mm. The largest dimensions 4 - 6 mm are an integer.
The minimum cross-section is limited to silver wire containing more than 50% lead and antimony. The figure is taken as a total if both substances are present in the composition. Solder is available from a size of 0.5 mm.
Silver solder is available in unannealed form . Annealing can be carried out for wire with a diameter of 2 mm or more by agreement with the customer. the technical characteristics of soldering. The rod becomes softer, more flexible, and fits better in dense rows when wound on a reel.
PSR solder up to 0.5 mm is wound onto coils. Above this section it is wound into skeins. The maximum packing weight of 6 mm wire is kg. The winding must consist of one solid piece without soldering or joining by other means.
For household use, spools of wire are sold:
- 200 g up to Ф 0.35 mm;
- 300 g up to Ф 0.60 mm;
- A rolled product with a diameter of 0.8 mm weighs 500 g;
- up to a diameter of 1.6 mm, solder weight in a roll is 1600 g.
Hobbyists use mostly small-diameter solder . 200 - 300 grams of consumables are enough to solder and tin at home circuit boards and jewelry for several years. Large skeins are suitable for production work.
Soldering strips are available in thicknesses from 0.1 mm to 5 mm. Material width 5 – 200 mm. The length can be standardized or free. Strips of the same size are collected in packs.
Explanation of markings
The wire marking indicates its main characteristics. For example, the designation of solder with 40 percent silver in the composition and a diameter of 5 mm looks like this:
Wire PSr 40 5.0 GOST 19746-74.
This marking is deciphered as follows:
- Silver wire, solder for soldering. Not annealed.
- Contains silver 40%.
- Rolled diameter 5 mm.
- Manufactured in accordance with GOST 19746-74 - silver wire for solder, of the highest quality.
Regulatory documents regulate: production technology, section dimensions, control methods and permissible defects . Each document has its own requirements for different categories of silver solder.
The chemical composition is the same for all categories and sizes of rolled silver. It is regulated by GOST and the corresponding international standard.
Marking
Like other soldering materials, this solder has a unique marking that allows you to judge its type and components. Its name is deciphered as follows:
- PSR is a solder that contains silver. It is this element that is the main one in the composition and generally determines the properties of the alloy.
- 45 – this number indicates the quantity of the main element, that is, silver, contained in the solder. This brand includes 45 percent of the valuable element.