An air compressor, used both in production and for household work, can safely be called the most common type of compressor equipment. According to their design features, compressors are divided into two types.
- A screw compressor, the main element of which is shafts that pump air. They are located close to each other, however, ensuring maximum tightness and eliminating the outflow of air from the chamber is only possible by using the appropriate oil, which forms the much-needed oil film.
- Piston compressor. This compressor has more “moving” parts, which means that the issue of reducing friction is especially relevant. The injection of compressed air into the receiver ensures the forward movement of the piston.
However, despite the differences in technical components, for maximum performance and safety, both types of compressor equipment require the correct selection of oil (in accordance with the characteristics specified by the manufacturer) and its timely replacement.
Alternative option
vacuum in the compressor
This method is less effective than the previous one and is more suitable for partially draining the oil for analysis.
Manufacturers test on their own equipment, so their recommendations are based on experience. That is why it is necessary to always try to adhere to their recommendations, especially in cases where the compressor is under warranty. You can lose it if you use oil not recommended by the manufacturer. So, some manufacturers provide the following frequency of oil sampling: 1 month after starting the installation, every 3 months if it operates continuously and after 4 months if it operates intermittently.
Some useful tips
When to change the oil? How often should this be done? Is it possible to change compressor oil to oil for piston internal combustion engines? How to properly drain old compressor oil? Where to put used oil? This is a list of the most frequently asked questions by compressor equipment owners. We offer you some tips and recommendations to help answer these questions.
After purchasing a compressor, carefully read the accompanying documentation, paying special attention to the section where the rules for operating the equipment are indicated. The frequency of oil changes (an indicator based on the number of hours worked) is indicated in the operating documents
Strictly follow these recommendations, this will significantly extend the life of the compressor. When starting work, check the oil level in the inspection window every time, it is important to ensure its proper level. In the operating instructions, the manufacturer must indicate the brand of oil that can be poured into a specific type of compressor. If you do not have the opportunity to purchase just such an oil, you can use oils from other manufacturers, but with absolutely identical characteristics. Under no circumstances should you fill a piston compressor with oil for piston internal combustion engines! This is a recipe for equipment failure. The container, after draining the compressor oil, will be unsuitable for further use.
Therefore, you can use a simple plastic bottle for this. Pay attention to the color of the used oil; if it is very dark, then it is safe to say that the equipment has regularly overheated. Do not throw away used compressor oil, it is quite toxic! It can be handed over to a collection point without any problems, after which it will be processed. There is no need to mix used oil with new oil, this can negatively affect not only the operation of the compressor, but also lead to an emergency. To be sure that the used oil has completely drained out, tilt the piston head. This will avoid mixing new oil with used oil. Try to use the same base oil, choosing, for example, “synthetic”; in the future, you should not change its base. Do not neglect flushing the unit with special flushing liquids. This will increase the service life of the compressor and help, despite the intensity of work, to maintain its performance characteristics. The frequency of such a procedure should be indicated in the accompanying instructions.
Helpful information
Content
One of the conditions for the uninterrupted operation of a screw compressor is timely oil change. This equipment is characterized by an optimal balance of ease of use and durability. The working part of the unit consists of a compression chamber, a pair of specially shaped screws and a motor.
Lubrication value for screw compressor
The service life of a screw compressor depends on the quality and regularity of oil changes more than in other types of devices. Increased requirements for the properties of the lubricating fluid are due to the specific operation of the equipment. Air injection is carried out by a pair of screws, during the rotation of which the cavity between them moves from the suction point to the compression chamber. The screws do not touch, leaving a microscopic gap between them. During operation, this gap is filled with an oil film, so air leakage is excluded. During compressor operation, the oil composition gradually changes. Wear products from parts, dust and moisture from the incoming air enter the process fluid. A change in composition leads to a deterioration in technical parameters. For screw compressors, timely oil change is one of the most important operating requirements.
How often does a screw compressor require an oil change?
The standard service life of the lubricating fluid is from 2500 to 3000 working hours, but at least once a year. It is not recommended to exceed this time. For some models, the developer may set other deadlines, which must be reported in the instruction manual.
External factors also influence the period of permissible work:
level of pollution and humidity of captured air.
ambient temperature.
The reason for the reduction in oil life may be a malfunction of the air filter or another structural element of the screw compressor.
When operating a new screw compressor, the first oil change should be carried out at shorter intervals. As a rule, the oil product needs to be completely replaced after 500 hours of operation. This is due to the fact that during the running-in stage of the unit, moving parts are ground in and wear products are released.
Also, residual molding sand gets into the oil, which can remain on the surfaces of new parts made by casting. All these factors lead to the fact that the composition of the lubricating fluid in a new compressor unit changes faster than in a run-in and well-tuned unit.
Procedure for changing oil in a screw compressor
Make sure that the pressure in the system and receiver is “0” and disconnect from the power supply.
Remove the compressor housing wall.
Visually check the absence of oil leaks, the condition of the radiator, the strength of fastening of the components, the tension of the belts, and the clogging of the air filter. If problems are identified, fix them.
Completely drain the entire volume of lubricating fluid. The old grease is drained through the oil drain valve. The operator should ensure that the system is empty.
Replace the oil filter and filter separator (oil separator). As a rule, during this maintenance the air filter is also changed.
After this, new oil is poured in the quantity recommended by the manufacturer.
Check the oil level through the oil indicator sight glass
After checking that the oil filler holes are closed, turn on the compressor for a few minutes. Then you need to recheck the oil level and add if necessary.
Important! You can fill only those brands of oil recommended by the manufacturer. You cannot mix different brands. If the compressor has not been used for a long time: before starting after changing the oil, it is necessary to add a portion of oil to the screw pair (through the air filter pipe or otherwise).
Tags: procedure for changing oil in a screw compressor, changing oil in a screw compressor, changing oil in a screw compressor step by step
www.compressor-mash.ru
Characteristics that determine which oil can be poured into the compressor
It is the discharge temperature that is one of the main parameters (relating to the safety of the compressor).
- category 1 – gentle operating conditions, up to 160°C;
- category 2 – standard operating conditions, up to 180°C;
- category 3 – heavy duty for continuous operation of compressor stations, up to 200°C;
- category 4 – harsh working conditions, including in aggressive environments, over 200°C.
A number of other parameters depend on the lubrication method used in specific compressor models. This list is determined by the equipment manufacturer.
- Oil is supplied under pressure using nozzles. This is an entire system that has a separate capacity (replenishment and replacement are carried out directly during operation). Viscosity is selected in strict accordance with operating conditions, including ambient temperature.
- Discharge using an internal gear pump also requires low viscosity, but is not dependent on the degree of oil heating.
- Natural splashing from the crankcase oil bath does not require special characteristics; standard values for transformer oils are sufficient.
As an example, an illustration of the parameters of Lukoil KS-19 motor oil.
Basic requirements for the characteristics of compressor oil
Due to the fact that compressor lubricants must be separated from the gases pumped into the cylinders, volatility is an important parameter. This characteristic is measured when the liquid is heated to operating temperature, which occurs after 10-15 minutes of operation of the unit. Characteristics of Ravenol compressor oil - video
- When creating oils, manufacturers are forced to compromise. On the one hand, a minimum viscosity is required, on the other hand, oil that is too thin is prone to evaporation. Therefore, binders must be added to the composition.
- Another requirement that compressor manufacturers make is a low oxidation coefficient. With prolonged use, the oil may burn. Soot and soot are formed, which gets on the cylinder walls and leads to the formation of scratches and scoring.
- The degree of wear resistance characterizes the ability to maintain specified characteristics until the oil is changed. If the parameters gradually decrease, it is impossible to ensure stable operation of the compressor.
- After short-term heating to a critical temperature, the basic indicators should return to their original state.
- Additives must be added to prevent foaming. The crank mechanism works like a mixer. The oil will simply whip up in the crankcase without creating a strong working film.
The complex of properties of compressor oil, from any manufacturer, must ensure:
- reliable start-up of equipment regardless of external temperature;
- if possible, reduce energy costs for operating units;
- at high loads on the piston group, there should be no prerequisites for jamming of the rubbing pairs;
- prevention of emulsion formation: with a sharp change in pressure in the piston group, condensate forms, which must be bound by demulsifiers.
Compressor oil characteristics
When choosing, you need to take into account not only the brand and manufacturer of the oil, but also its main characteristics:
- oil base (synthetic, semi-synthetic, mineral);
- oil viscosity (the criterion depends on the operating conditions of the equipment);
- the presence of additives (the oil may contain additives - substances that improve the performance characteristics of compressor equipment);
- pressure (at what operating pressure of the compressor: low, medium, or high - this oil is used).
Why is there smoke coming from the breather?
There can be only one malfunction of the breather: it began to poorly pass accumulated gases, comparing the pressure inside the engine with atmospheric pressure. But the smoke coming from it can say a lot:
- The cylinder oil scraper rings were stuck or worn out. Simple decarbonization using traditional methods or special chemicals will not help here, so you will have to disassemble the engine.
- Likewise, if one/several exhaust valves burn out. A simple compression test will help determine this.
- Oil seals. Just replace them when it's time or they show signs of increased wear.
- The shaft seals, which allowed oil vapors to pass through, were worn out. Change them without hesitation, preferably without shelving them.
- The oil in the engine is old and needs replacing for a long time. No comments: as practice shows, repairing the “heart” of a car is tens of times more expensive than replacing it.
- White smoke on a hot engine - coolant enters the lubrication system. You'll have to look for where exactly the leak is.
- Oil overflow. In an internal combustion engine, it is just as dangerous as underfilling: engine wear/fuel consumption increases significantly, so check its level with a dipstick on a level surface when the engine is well warmed up. Then you will see how well the technicians at the service station (or you yourself) performed its replacement/topping up.
- The oil is of poor quality/not suitable for the car/counterfeit. There is only one way out - replace it. Likewise, if you filled up with fuel at an unknown gas station: just don’t do it again.
- Finally, the breather itself clogged from time to time, not working at 100%. Simple cleaning and preventive maintenance will eliminate this.
An impressive list of different situations. And there is no doubt that if your car’s breather is smoking, you have definitely found your case among them.
Compressor oil for piston compressors - what is its feature?
The ideal conditions for lubrication of any working mechanism are a sealed housing and a closed internal oil line. A piston compressor only half satisfies these conditions.
The lower part of the mechanism (connecting rod and rear of the piston group) are located in the so-called crankcase. An air compressor is characterized by the design of a conventional internal combustion engine, only the opposite is true. The crankshaft receives torque from the outside, and the piston group is a consumer of energy and does the work.
So, the upper part of the piston and cylinder directly interacts with the atmosphere, and everything that gets into this zone is thrown out. That is, oil for piston compressors, which enters the piston chamber, will inevitably be present in the composition of the compressed air.
Of course, at the outlet there are filters - separators, and piston rings, if possible, remove the layer of lubricant from the cylinder walls. This is where the manufacturer's headache begins.
- on the one hand, it is necessary to limit the amount of oil to achieve clean air;
- on the other hand, a mechanism with an insufficient amount of anti-friction agents will quickly fail.
It is impossible to organize a mechanical separation of the lubrication zone and the production of compressed air. Therefore, the oil in a piston air compressor must have special properties:
- strong adhesion: the liquid must be retained in the lubrication zone and not penetrate into the working area of the cylinders;
- high load-bearing capacity;
- the characteristics of the composition should not change under conditions of temperature changes: the compressor can become very hot during operation;
- good thermal conductivity: the reason is indicated in the previous paragraph;
- high flash point: a potential fire in the compressor is very dangerous;
- thermal-oxidative stability;
- great importance is attached to antioxidant parameters: due to the characteristics of the compressor, condensation forms in it;
- high ability for water separation (water displacement);
- accordingly, the oil should not be hygroscopic;
- viscosity characteristics are a compromise: thick oil is ineffective, and too thin oil will penetrate into the working area of the cylinder;
- minimum coke number (carbon deposits are formed at high temperatures);
- Compressor lubricant should not contain toxic or environmentally hazardous additives.
Automotive lubricants used for internal combustion engines do not have such properties in their entirety. Therefore, they can only be used to drive a compressor. You cannot fill the working block (in which air pressure is created).
Compressor equipment is known for its ability to produce low-level performance, however, the process of producing compressed air occurs at fairly high pressures. The combination of these two factors allows the use of oil-free and oil piston compressors in appropriate conditions when the use of other types of devices is impractical.
Why pour oil into the compressor?
At first glance, it may seem that the pistons in the compressor can operate without oil. There are modern materials that have a minimum coefficient of friction (Teflon, fluoroplastic, etc.).
For example, piston-type automotive compressors do not use separate lubricant. However, there is a huge difference in the volume of air pumped. Let us remember the elementary laws of physics: when gases are compressed, a large amount of thermal energy is released.
Simply put, the piston group gets very hot during operation: the higher the pressure in the receiver, the stronger the heating. It is for this reason that the compressor cylinders are equipped with air cooling fins.
- Oil has good thermal conductivity (albeit less than ordinary water), so washing the piston group to some extent helps remove heat.
- No matter how low the coefficient of friction of the piston rings, heating still occurs. If you leave the compressor without lubrication, the metal may become hot, it will “lead”, and the geometry will be disrupted.
- In addition to the pistons and cylinders themselves, the piston group consists of many elements: connecting rods, crankshaft, and possibly a gearbox. These elements require lubrication, and according to the classical method (as in an internal combustion engine). That is, the compressor has a crankcase in which lubricant splashes.
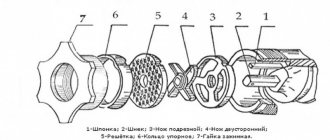
To understand the principle of operation of a piston compressor, consider its structure:
The crankshaft (1) rotates freely using bearings (2) . The need to lubricate these components is not even discussed: without it, work is impossible. The connecting rod (3) and piston pin (4) do not have rolling bearings. Just like in an internal combustion engine, liners are installed. If these friction pairs are not lubricated, the compressor will seize within a few minutes.
To prevent air compressor oil from leaking out of the housing, a seal (8) . What about the piston (5) ? If the rings are not sealed, fumes from the lubricant will enter the working chamber (6) . And then through the valves (7) the contaminated air will enter the working line.
With such a lubrication system, the cylinder walls are sufficiently washed with oil to ensure normal sliding and additional cooling. To clean the air from possible vapors, filters are installed.
It is usually a porous material that retains any liquids. To obtain breathing air (for example, when filling scuba tanks), more advanced cleaning systems are used.
There is another design of the piston group, which is used in compressors with guaranteed purity of the pumped air. Only the crank mechanism is lubricated; a slider is installed between the piston and the crankcase, guaranteeing complete dryness in the working chamber. True, such systems cannot provide high performance: loads are contraindicated.
Foreign standards, but not alien
The existing range of compressor oils is wide. Its increase is due to the growing demand for compressed air, the development of compressor designs, and tightening requirements for their performance, reliability and energy efficiency.
Compressor oils of various viscosity classes are offered by the main players in the Russian oil industry (compressor oil LUKOIL, ROSNEFT).
As foreign trade liberalized, foreign-made products appeared on the domestic market, manufactured taking into account the latest advances in oil refining technologies (SHELL compressor oil, MOBIL compressor oil).
It is not surprising that today in Russia brands of compressor oil have become widespread, the production of which is regulated by European standards (DIN 51506-2017, ISO 6743-3A).
In DIN 51506-2017, compressor oils are classified into groups depending on the final temperature of the compressed air:
- VB, VB-L – up to 140°C;
- VC, VC-L – up to 160°C;
- VD, VD-L – up to 220°C.
They differ in their aging resistance (VDL compressor oil is especially resistant). “V” means compressor oil, “L” indicates the presence of additives.
Manufacturers, in order for their products to be easily recognizable on the market, give them their own names (SHELL CORENA compressor oil, MOBIL RARUS compressor oil, LUKOIL STABIO compressor oil). If the name contains (or implies, ─ as indicated by the reference to DIN 51506-2017) a combination of the letters VD, VDL (VD-L), VB, VBL (VB-L), VC, VCL (VC-L), present in Brand numbers in most cases indicate the kinematic viscosity of the oil at 40 OC. It is equal to the ISO viscosity grade with relatively small deviations (± 10%).
Examples: compressor oil 32, compressor oil 46, compressor oil 100 (for example, compressor oil VDL 100 or compressor oil VG 100), compressor oil 150.
The brand of compressor oil may contain a direct reference to its ISO viscosity ─ compressor oil ISO 100. Or a more specific example ─ Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 100.
Mannol Compressor Oil
Compressor oils Mannol Compressor Oil ─ one of the products of the company Sudheimer Car Technik-Vertriebs GmbH ─ is represented in Russia by the company BITECH (https://bi-teh.ru/). The German manufacturer produces a wide range of products, including lubricants and oils ─ industrial, motor, and transmission. Including compressor oil brands:
- Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 46;
- Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 100;
- Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 150.
Mineral compressor oil Mannol Compressor Oil based on paraffin oils is used to lubricate piston, screw, and centrifugal air compressors, and Mannol Compressor Oil ISO 46 is also used for pneumatic tools. Its effectiveness is enhanced by the presence of ashless additives.
Mannol Compressor Oil has vital properties for compressors:
- thermal stability;
- oxidation resistance;
- anti-corrosion properties;
- low volatility;
- leaves a minimum of deposits.
All of them help to guarantee stable, reliable operation of the equipment.
Buying compressor oil Mannol Compressor Oil means making the right choice for the correct operation of compressors.
Compressor oil manufactured in northern Germany is distinguished by high quality and compliance with the requirements set by consumers for this type of product.
A few lines below about the requirements, but now we list the main functions of compressor oil.
Compressor oil functions:
lubrication;
lubrication of rubbing surfaces reduces abrasive wear of parts, reduces energy losses caused by friction, ensures the cleanliness of rubbing surfaces, helps prevent scuffing, jamming and other defects fraught with serious breakdowns and rapid wear;
cooling;
removal of excess heat is a necessary condition for the functioning of the compressor;
- corrosion protection;
- sealing gaps;
Having several orders of magnitude less fluidity than air, oil fills gaps, promoting better sealing of cavities.
The piston compressor lubrication system includes a pump, oil filter, thermostat, and oil cooler. Compressor oil for reciprocating compressors lubricates pistons, valves, bearings and crank mechanism. It forms a stable liquid layer between the rubbing surfaces (cylinder liner and piston ring).
Compressor oil for screw compressors lubricates shaft bearings, screws and gears (or just gears), helps reduce the temperature in the compression chamber, and seals the gaps between rotors.
Enemies of pneumatic equipment
It is very important that the air used when operating compressors is as clean as possible. Unfortunately, ideally clean air does not exist. Even electronics manufacturers cannot achieve a complete absence of foreign inclusions.
Types of contamination of painting units:
- moisture (water vapor);
- solid pollutants (dust);
- friction products of parts (metal particles);
- rust and scale;
- oil.
Compressors are capable of compressing air several times. Accordingly, the content of contaminants, in particular moisture and dust, increases in proportion to compression. Air inlet filters are primarily designed to protect the compressor itself. They retain relatively large particles of solid inclusions.
But water vapor is no less a problem. Normal air humidity is considered to be in the range of 35-65%. In production shops where professional pneumatic equipment is used, complex systems with multi-stage air purification are used, incl. and from moisture. In everyday life, the quality of air entering compressors is controlled almost exclusively by its own filters.
When air is compressed in the receiver, moisture is concentrated and can turn into condensation. Moreover, the moment of condensation occurs not only in the receiver itself, but also in the pneumatic line. In this case, water may get onto the surface to be painted along with air and paint, which is unacceptable.
It is possible to minimize the formation of condensation. To do this, it is recommended to create conditions under which the temperature of the air entering the receiver will be as low as possible.
During the cold season, at negative outside temperatures, air humidity is minimal. If the compressor takes in cold outside air, then practically no condensation forms.
If the problem of moisture and condensation is critical, it is recommended to use special dehumidifiers.
As already mentioned, mechanical filters at the entrance to the unit protect against solid particles. Manufacturers do not install filters that are too dense (thin) because they have significant air resistance and reduce compressor performance.
Solid particles can not only enter the apparatus from the outside, but also form inside it. These are elements of wear of rubbing parts, scale and rust that form in the receiver. To prevent these particles from being fed into the spray gun, separate filters are used, which also need to be changed periodically.
The degree of air purification is indicated in the compressor passport. Everything about cleaning classes can be found in GOST 17433-80.
Read also: Hammering a dowel into concrete
Operating principle of the crankcase ventilation system
Oil smells like gasoline reasons In order to understand why oil is squeezed out of the breather, I propose to briefly consider the principle of operation of the oil system. Not many people know, but for proper operation of the engine, ventilation is necessary, since during its operation gases collect in the crankcase, and now we are not talking about exhaust gases. To ensure the removal of these gases, old cars used a so-called crankcase ventilation system, which after some time became known as a “breather.” With the help of a breather, engineers were able to ventilate the crankcase and thereby relieve the pressure that forms during engine operation. However, the system turned out to be ineffective, since tiny oil particles penetrated the breather along with excess pressure and gases.
The issue of penetration of “oil dust” into the breather was partially resolved by means of a special mesh that traps oil particles and does not let them into the breather. However, despite this, some of the oil vapors still penetrate into the breather, creating certain difficulties for owners. A small amount of oil that has penetrated into the breather is not considered anything terrible, however, if oil flows out of the breather in large quantities, this is a reason to seriously think about the technical condition of the engine.
Oil change process
To drain the used oil faster, let the compressor run for several minutes, this will allow the oil in the crankcase to warm up to 50-60 degrees, so it becomes less viscous. Before draining, be sure to ensure that the compressor is unplugged. Bleed all the air in the receiver, then check the pressure gauges, they should be “zero”. Prepare a container to drain the used oil. Remove the breather (upper plug) and unscrew the drain bolt in the crankcase (at the drain hole), while simultaneously placing a waste container. After completely draining the used oil, tighten the crankcase drain bolt and you can start filling in new oil. Be careful, the composition of the oil must comply with the manufacturer’s recommendations!
Using the sight glass, check that the oil level is correct and close the breather. Do not exceed the permissible oil level! When everything necessary for changing the oil is done, let the compressor run for 5-7 minutes
Pay attention to the sound of the operating equipment; normally the sound should change.
*Periodically, before changing the oil, flush the compressor. To do this, it is necessary to use a special flushing liquid, the main task of which is to remove carbon deposits.
Compressor oil: what kind and how much to pour, what to replace with, why does it foam?
Compressor oils are lubricants with special technical characteristics (low volatility, low tendency to foam, coking, self-ignition), which ensure correct operation and significantly extend the service life of air compressors, reduce the risk of explosion and fire in production.
Based on the type of base they are divided into:
- mineral - the cheapest, used for light and medium-load devices used indoors;
- synthetic - retain viscosity properties over a wide range of temperatures and pressures, due to which they provide easy start-up and the longest service life of heavily loaded equipment operating in the open air. Their only drawback is the high initial costs;
- semi-synthetic - at an affordable price, they have good viscosity-temperature characteristics and effectively protect lubricated surfaces from corrosion and premature wear.
Compressor oil compatibility table
| Ether* | PAG | PJSC | Group III synthetic oil | Mineral oils of group I and group II | Silicone base oil | |
| Ether* | Yes | No | Maybe | Maybe | Maybe | No |
| PAG | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| PJSC | Maybe | No | Yes | Maybe | Maybe | No |
| Group III synthetic oil | Maybe | No | Maybe | Yes | Maybe | No |
| Mineral oils of group I and group II | Maybe | No | Maybe | Maybe | Yes | No |
| Silicone base oil | No | No | No | No | No | Yes |
It is impossible to answer for sure whether one oil will be compatible with another, since it is always worth considering incompatibility with additives and the degree of contamination of the oil during operation. When changing oil in compressors, we strongly recommend draining the old oil and flushing the system, regardless of what base oils are included in the old and new oils, since there is always the possibility of incompatibility. This conservative recommendation is also based on a risk-benefit model when it comes to tank size; tanks tend to be small in size. So, due to the fact that the container contains a small volume of oil, i.e., its loss in the process of removing its residues will be minimal, draining the oil and flushing the system should be carried out taking into account all risks and compatibility aspects.
This procedure not only reduces risks, but also improves equipment performance.
In some cases, the services of technical specialists may be required. If the question arises about removing carbon deposits and varnish deposits, it is worth thinking about the incompatibility of oils. In this case, it is necessary to flush, possibly using solvents, replace seals, etc.
We bring to your attention recommendations for washing. These can be used as requirements to complement OEM requirements.
Using Procedure B
Recommended when replacing incompatible products (for example, when replacing a PAG-based oil with another type of oil that does not contain PAG) and compatible products/base oils, if there is a possibility of incompatibility with additives or contamination, including water . So Procedure B is used if deposits have accumulated in the system. Often at this level of incompatibility when replacing PAG based oils with PAO, etc., OEMs require seal replacement and contact them for advice.
Classification of compressor oils and their scope
All modern compressors are divided into two main types, differing in their design and operating features. These include:
- Volumetric. In such equipment, the distilled gaseous substance is sucked into the working chamber, compressed and thrown out under pressure by the forward-return movement of the piston system;
- Dynamic. The compression of the medium they distill is carried out using turbine mechanisms. The intake gas is accelerated by the turbine rotors, after which it suddenly slows down, causing it to be dynamically compressed.
In volumetric piston compressors, oil provides lubrication of moving parts - piston group, valves, bearings. Traditionally, such models use mineral oil that meets international certificates DIN-51506-VGL, VDL. The viscosity class for them corresponds to ISO/VG standards from 68 to 150. In positive displacement rotary or screw compressors, the moving parts are lubricated using an oil bath. As a result, the oil is constantly mixed with the forced air, heating to a temperature of about 90-100ºC.
At the outlet of the compressor chamber, a filter device is installed that separates the oil from the gaseous substance. Therefore, for use in rotary and screw compressors, oils with increased deaeration and demulsification characteristics are used.
Special requirements are also imposed on increased anti-corrosion properties and the maximum amount of deposits during operation. Most manufacturers of such equipment provide instructions in the accompanying instructions regarding the selection of a suitable lubricant.
In dynamic modifications of compressor units, lubrication is provided through a forced supply circuit: gears, shaft seals, bearings. It is recommended to use the same type of oil for the compressor operating mechanism and its drive system. It is recommended to use special turbine oils of the following grades in dynamic installations that comply with the ISO/DP-6521 standard:
- DIN-51-515 TDL-32;
- TDL-46;
- TDL-68;
- TDL-EP with extreme pressure additives.
Conventional motor oils are classified according to their flash point.
Compressor lubricants are divided, unlike motor lubricants, according to the temperature of the pumped substance.
In Russia, along with the international classification of compressor oils, the domestic classification adopted by Gostekhnadzor back in Soviet times is still often used.
According to it, all compressor oils are divided into 4 groups:
- Lubricant intended for operation under moderate loads. The temperature of the discharge gas does not exceed 160ºC.
- The second group is intended for operation under moderate loads, but with a discharge gas temperature of up to 180 degrees.
- Compressor lubricant of the third group is designed for mechanisms operating under increased loads and temperatures up to 200ºC.
- The last group includes oils intended for operation in extremely difficult conditions, with increased pressure and temperatures up to 200ºC.
Each group has a special list of operational and technical properties that must be taken into account when choosing the type of oil for the compressor.
It should be noted that foreign manufacturers have not developed a unified classification for operating temperature, and each large company uses its own standards.
Device characteristics
- Productivity shows how many liters of compressed air the equipment produces per minute. For small auto repair shops, a compressor of 300 l/min or higher is sufficient. Such equipment makes it possible to connect 4–5 units of pneumatic tools.
- Power. The performance of the equipment depends on this indicator. It is measured in kW or horsepower. Give preference to equipment with more power, all other parameters being equal.
- Air pressure is an important indicator of functionality. It is indicated in the passport for the compressor. For most car services, models with values of 8–10 atmospheres are suitable. Manufacturers equip modern compressors with regulators to increase or decrease pressure depending on the situation.
- Voltage. Compact compressors are connected to a 220 V network, and large industrial compressors are connected to 380 V. If there is no need to connect to high voltage networks, choose small models - this is a universal option for a car service center.
- Receiver volume. For a professional auto repair shop, you will need a receiver with a capacity of at least 25–50 liters. The air collector helps to level out pressure surges that invariably occur when using the tool.
Choose a compressor for a car service center based on the characteristics you need. The company's catalog includes models of any type, power and volume. Each piece of equipment meets high requirements for quality and reliability.
Why is a screw compressor better than a piston compressor?
When choosing compressed air equipment, the buyer is forced to evaluate many models. The most common types of compressors are screw and piston. Let's understand the operating principles of the first type and find out why a screw compressor is preferable to a piston compressor.
Compressors are used in everyday life and professional activities to operate pneumatic tools. The equipment prepares air - cleans and compresses it due to a special design. The belt-driven compressor is equipped with an electric motor. The screw block admits air through the valve. There it is compressed due to the reduction in space between the driving and driven rotors.
Compressed air enters the tank of the air-oil separator, in which the primary separation of oil occurs. The liquid is discharged out through the valve. After this, the pre-cleaned air enters the cyclone separator, where it is re-processed - 99% of the oil remains here. The clean air enters the dehumidifier, where all existing moisture is separated and removed.
Read also: What is hot melt adhesive?
Oil change, rules and recommendations
Do not use machine oil unless absolutely necessary. Due to its properties, it is not suitable for air compressors and can damage its components.
Many manufacturers indicate specific requirements in the operating instructions and give recommendations on what kind of oil is poured into the compressor. But some nuances are not described in the instructions. It is best to pour a little more than the maximum oil level into a piston compressor, since they do not have a separate lubrication system - it comes by capturing a certain amount of it directly from the crankcase. But a similar system is provided in the design of an oil-free piston compressor. In turn, if replacement is necessary in such a compressor, it is necessary to flush the entire tank. To do this, you need to fill in oil with a very low viscosity level and let the compressor run for about 15 minutes. Then it must be completely removed by slightly tilting the piston head.
Do not pour processed products, especially on the ground. It is better to hand it over to a collection point for further processing.
Also, do not mix several types of products. No matter what the condition of the air compressor, even the most worn and old one needs to be filled with good and fresh material. The reason for this increased attention may be the occurrence of an emergency.
Fire is especially dangerous when the compressor is running. Over time, it wears out and loses all its properties; in addition, in most structures it evaporates, its level decreases, and the density of pollution increases. To avoid the consequences of such operation, regularly change the oil in accordance with the recommendations.
Good afternoon, how much oil is poured into the compressor if there is no control window?
Which compressor - rotary or piston? Centrifugal, radial-axial or axial? What brand is the compressor? To answer your question, it must be supplemented with clarifying information.
How does a freezer work at sub-zero temperatures? Freezers have appeared that operate at an outside temperature of minus 15°C
A freezer placed on a balcony, which can operate at a temperature of - 15°C, differs in design from a conventional freezer in the following parameters, which make conventional freezers vulnerable to sudden temperature changes or sub-zero temperatures. Namely, conventional freezers have the following disadvantages when installed outdoors:
1) Deformation of rubber seals due to temperature changes;
2) Risk of electrical wiring failure;
3) The process of rusting unprotected metal parts;
4) Deterioration in the quality of plastic parts for the same reasons;
5) General deterioration in the operation of the freezer;
Freezers that can operate at high negative temperatures do not have these disadvantages, or they are minimized, in the following way: the use of rubber and plastic parts that are resistant to temperature changes, the use of corrosion-resistant metal parts, protected electrical wiring, including short-circuit protection, protection from temperature differences of the compressor and other main parts.
9 Good answer
Why bleed air from the compressor?
Air is bled from compressors with a receiver to make it possible to drain the water (condensate) accumulated in the receiver.
In addition, constant pressure can cause so-called “fatigue” of the metal (accumulation of minor damage) from which the receiver is made, but this is rare. The main reason is the need to drain condensate.
3 Good answer
What is the best oil to use for filling an air compressor?
It all depends on the type of compressor action.
If it is a screw type, then it is advisable to fill it with oil with a viscosity of 46.
If RPC (rotary vane) - viscosity 68.
For piston engines, oil with a viscosity of 100 is usually used.
There are many manufacturers: Shell, Mobil, Lukoil, Fuchs.
You can select oil using a convenient form on the PressAer website.
5 Good answer
How to choose a compressor for industrial equipment?
For industrial equipment, the best choice is a screw compressor. Unlike a piston, it is designed for continuous operation and can work around the clock, which is especially important for large metal and woodworking industries.
When selecting a compressor for industrial equipment, the main criteria are:
- Performance – depends on the power of the compressor, it shows how much air the equipment can compress in a minute. It is necessary to find out the compressed air requirement of each of the machines, sum up the amount of air for each unit and add 25-30% to this. Data on how much air your machine needs can be found in the instructions for the equipment or on its nameplate.
- Maximum operating pressure is the maximum pressure that the compressor is capable of maintaining in the pneumatic network. Minimum pressure is the lower limit. If the equipment indicates a working pressure of 6 bar, a compressor with a maximum pressure of 8 bar will be sufficient. (10 bar is possible, but the performance of such a compressor is lower) The minimum pressure of a screw compressor is usually 4.5-6 bar, depending on the model. The choice of maximum operating pressure depends on the pressure required for stable operation of compressed air consumers. It is necessary to take into account pressure losses in the pneumatic line, as well as losses during the passage of compressed air through equipment for its preparation (driers and filters). It is important to remember that each extra bar of “pumping” increases energy consumption by 6-8%. Therefore, you should not choose too much pressure.