Design of a die for sheet metal stamping, selection of equipment
Volumetric stamping is the process of metal forming, which consists in deforming the workpiece, as a result of which the metal fills the cavity of the tool - a stamp called a stream...
Manufacturing of RES parts using powder metallurgy and pressure methods
2.2.1. Separation operations of sheet stamping
Cutting is the separation of a part of the material along an open contour with scissors or in stamps. Shears for cutting sheet material are parallel, guillotine, roller, disk and vibrating (Fig. 9.1). Parallel…
Forging and stamping of products
4.1 DESIGN OF THE KGSHP DIE
The dies of crank hot stamping presses have a prefabricated design, which simplifies the production of replaceable tools and creates conditions for saving expensive tool steels. Dies consist of die inserts...
Increasing the technical performance of stamping the “Piston” part by reducing the number of technological transitions and operations, increasing metal savings
f2. Selection and justification of technological process options for sheet stamping of parts
According to the basic technology, the “Piston” part is manufactured using the following technological process: 1. Cutting the sheet into strips; 2. Control; 3. Varnishing; 4. Felling; 5.Vacquering; 6. First hood; 7. Firing; 8. Hardening; 9. Locksmith; 10.Vacquering; eleven…
Development and technological process of manufacturing the “lid” part
3.3 Obtaining the initial blank for cold sheet stamping
The initial blank for this part will be a sheet 10mm thick. Rolled sheets are produced at rolling mills. The essence of rolling production is that the metal is plastically deformed by rotating rolls...
Development and technological process of manufacturing the “lid” part
3.4 Description of equipment and tools for cold sheet forming
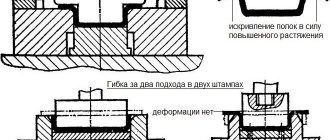
For cold sheet metal stamping equipment, a die with a spring buffer should be used to ensure constant force. The figure shows a diagram of the stamp and a sketch of the workpiece. Figure 5 4…
Development of technology and equipment for manufacturing the “Plank” part
f1. Analysis of the constructability of the form and the manufacturability of the manufacture of part elements using sheet stamping operations
Manufacturability should be understood as such a combination of structural elements that ensures the simplest and most economical production of parts while observing the technology and operational requirements for them...
Development of a technological process for sheet stamping of a lid and design of a die
f2. Die design, equipment selection
Development of a technological process for sheet stamping of a lid and design of a die
f2.4 Die design, sequence of die production and assembly
technological stamping press pressure Selection of stamp parts. Based on the dimensions of the working area, we select the overall dimensions of the matrix and calculate its thickness using empirical formulas. Using the obtained matrix dimensions...
Development of a technological process for processing the “Lid” part
2.2.1 Obtaining the initial blank for cold sheet stamping
The initial blank for this part will be a sheet 10mm thick. Rolled sheets are produced at rolling mills. The essence of rolling production is that the metal is plastically deformed by rotating rolls...
Development of a technological process for processing the “Lid” part
Description of equipment and tools for cold sheet stamping
For cold sheet metal stamping equipment, a die with a spring buffer should be used to ensure constant force. The figure shows a diagram of the stamp and a sketch of the workpiece...
Development of a universal machine for cutting, creasing and perforating paper
1.2 Features of the equipment and process of creasing sheet products
Creasing is the operation of applying a straight groove to a sheet of paper. It is necessary for subsequent folding along the line of paper with a density of more than 175 g/m² or cardboard. The groove itself is called big. Creasing is performed...
Technological process for manufacturing round broaches
f6. Design of operations, selection of bases and equipment
Operations design is the materialization of cost-effective processing methods. The choice of equipment is carried out taking into account the type of production. We select technological bases...
Technological process of assembling the die matrix of cold die forging of the VAZ 2108 internal hinge body
f1 technological process of assembling the die matrix of cold die forging of the body of the internal hinge of the VAZ 2108
Sheet stamping technology
f4. Mechanization and automation of the sheet stamping process
Source: https://prod.bobrodobro.ru/11239
Description of stamps
Our own design department and nine years of experience allow us to produce a stamp of any complexity in a short time. A stamp is equipment for presses, with the help of which the part itself is made. The principle of operation of stamps is the plastic deformation of parts using stamping equipment . Stamping equipment consists of a matrix and a punch, which are made of wear-resistant and hard material. Metal blanks are placed between the matrix and the punch. Using a press, the workpiece is given the required shape. Thus, the workpiece is deformed according to the shape of the matrix. Stamping equipment includes special presses and hammers, which drive the entire mechanism.
INTRODUCTION
workpiece stamping fasteners cutting
Cold stamping is a type of metal forming that combines a number of processes carried out by cold plastic deformation using various types of dies that directly deform the metal and perform the required operations.
Technologically, cold stamping allows:
— to obtain parts of complex shapes, the production of which is very difficult by other methods;
— create parts that are strong and rigid, but lightweight in terms of their mass characteristics, with little material consumption;
— obtain interchangeable parts with high dimensional accuracy.
Economically, the advantages are:
- economical use of material and low waste;
— low cost of manufacturing products;
- high performance.
The development of the technological process for sheet stamping will be carried out using the KOMPAS-Stamp computer-aided design system, which is implemented in the Windows environment with the KOMPAS-Graph drawing and design editor. The KOMPAS-Stamp system is focused on automating the design of dies for various cold sheet stamping operations and provides automation of the design of dies of original and standard designs.
Volume stamping
, a technological process
of forging and stamping production
, which consists in changing the simplest volumetric blanks (cylindrical, prismatic, etc.) into more complex products, the shape of which corresponds to the cavity of specialized tools -
dies
.
O. sh. how the process of redistribution of the metal of the workpiece occurs as a result of plastic deformation (see Metal forming
).
The main operations of O. sh. - upsetting, upsetting, broaching, extrusion, bending, flattening, calibration, formation of protrusions, thickenings, depressions, carried out on forging and pressing machines - hammers
,
presses
and special purpose machines. From stamped forgings, after cutting and heat treatment, various parts are obtained: connecting rods, crankshafts, levers, gears, turbine blades, fasteners, balls, rollers and bearing rings, etc.
There are cold and hot O. sh. Cold stamping is carried out without heating. The starting material is calibrated rods, cut into measured (piece) blanks, or wire in coils. The mass of the resulting products is from several g
up to several
kg
;
accuracy in grades 3-2; surface roughness corresponds to 7-10 classes of cleanliness. Kholodnoy O. sh. critical parts with high and stable mechanical properties are obtained, which is explained by the absence of recrystallization in the metal and hardening. Since the workpieces do not heat up, the formation of scale, decarburization, dezincification, etc. does not occur on the surface of the forgings, which improves the quality of the forgings in general and reduces allowances for further processing. In some cases, forgings do not require additional processing, being finished parts (the metal utilization factor is 1). However, to implement cold O. sh. significant forces are required - up to 2500 Mn/m2
(1
Mn =
100
tf
) and more, which negatively affects the durability of the dies. Heating the workpieces, i.e., hot O. can significantly reduce the effort (by 10–15 times).
Hot stamping is carried out with heating to a temperature of 200-1300 ° C, depending on the composition of the alloy and processing conditions. The starting material is rolled rods, divided into measured blanks, equal in volume to the future forging (taking into account the inevitable waste). The mass of the resulting products is from several g
up to 6-8
t
;
the dimensional accuracy of forgings depends on their mass and configuration and can be increased by subsequent cold calibration; surface roughness corresponds to cleanliness classes 3–7. Process of hot O. sh. similar in physical essence to free forging
, but carried out in dies. Hot O. sh. they obtain forgings that are homogeneous in structure, have relatively high accuracy, and have a complex configuration that cannot be achieved with free forging. However, the average coefficient of metal utilization during hot O. sh. 0.5–0.6 (i.e., up to 50–40% of the metal goes to waste), during cold stamping this coefficient is much higher.
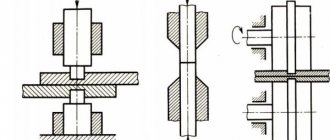
Stamps for O. sh. most often consist of 2 halves - upper and lower ( Fig. 1
, left) or from a punch and die (
Fig. 1
, right).
Typically, when stamping on hammers and vertical presses, the lower part of the die is stationary, and the upper part is movable. O. sh. performed in open dies - with a parting plane perpendicular to the direction of stamping (see Fig. 1
, left), or in closed dies - with a parting plane along the perimeter of the forging (
see
Fig. 1 , right). An open stamp is distinguished by its simplicity of design and versatility of use, but hot stamping in it is associated with the formation of a burr, which ensures the filling of the complex relief of the stamp cavity. A special groove is provided in the die to accommodate the burr. After stamping, the burr is trimmed in a die on a trimming press. Metal waste in this case is 5-20%, sometimes reaching 50-80%. In closed dies used for hot and cold cutting, the burr is either very small (no more than 1%) or completely absent, because the forging is formed from the entire volume of metal. However, these dies are less universal; for example, they cannot produce ball-shaped forgings. In cases where it is necessary to obtain initial workpieces of sufficiently high volume accuracy, closed dies with compensators are used - additional cavities into which excess metal of the workpiece flows. Compensators are located at the last location in the die to receive metal to prevent premature and excessive metal from entering the compensator. However, this method is uneconomical, because the metal entering the compensator goes to waste. Another technological method for hot O. sh. is the use of stamping slopes, which are made in the cavity of the stamps in order to facilitate the ejection of finished products. The forging results in a distorted shape, for example, instead of a cylinder there is a truncated cone. Typically, hammer dies have slopes of 5-7°. Excess metal on the forging (lap) is also waste. To implement O. sh. With a smaller slope (1-2°), ejectors are used in dies: when stamping on hammers - only lower ones, on presses - upper and lower ones.
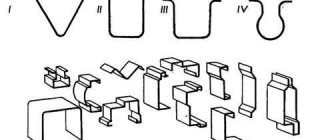
One of the rational solutions is hot O. sh. in split dies, i.e. in dies with 2 or several split planes, most often on horizontal forging machines. The matrices of these stamps do not have slopes; they can even stamp forgings that expand towards the bottom of the matrix. In split dies, stamping can also be carried out on hydraulic screw and crank presses. Forgings for the same part can be produced using hot cutting methods. both on the hammer and on the press. In these two cases, the workpieces will look different and have different allowances ( Fig. 2
).
O. sh. It is used as a single-pass process for producing the simplest forgings and a multi-pass process for parts with complex shapes. With multi-junction O. sh. They carry out a preparatory operation (the so-called shaping of blanks), and then carry out final stamping. Multi-junction O. sh. produced using mechanized means or on automatic machines, on hydraulic presses with a force of 750 Mn
, hammers with a mass of falling parts up to 20-25
tf
, crank hot stamping presses with a force of up to 80
Mn
, on automatic machines for single and multi-position stamping, on cold extrusion presses, rolling machines, forging rollers and other specialized equipment.
When stamping on hydraulic screw presses and high-speed hammers, it is possible to obtain forgings with thin sections. On multi-position cold and hot stamping machines, O. is carried out.
:
for cold stamping up to 50 mm
with a productivity of up to 500 pcs./min , for hot stamping - up to 120
mm
with a productivity of up to 70 pcs.
/min
.
Stamps are precise, complex and expensive tools, so the use of O. sh. Suitable mainly for large-scale and mass production.
Prospects for further development of O. sh. are determined by the expansion of the use of dies for hot low-waste stamping and the design of powerful equipment for cold stamping, as well as the introduction of new metal deformation processes using superplasticity phenomena, the use of hydrostatic methods, etc.
Lit
.
see under art. Forging and stamping production
.
Y. M. Okhrimenko, G. A. Navrotsky.
Contents TSB
Sheet stamping
Since ancient times, people have made thin-walled products, vessels and jewelry from metal. They were made from a sheet of metal by hammering - giving shape to a cold or heated sheet of ductile metal by tapping it with a hammer around a wooden model of the future product. The seams were soldered or embossed. Copper was most often subjected to this treatment, less often silver or gold. The products obtained in this way were extremely highly valued, since all operations were manual and it took the craftsman more than one day to make one jug.
Sheet stamping
The inquisitive human mind was looking for ways to speed up and reduce the cost of production until the mid-19th century, when such a powerful source of energy as steam appeared. Since then, the technology for producing thin-walled metal sheet products by deforming it under pressure, or sheet stamping, has improved significantly. Today, billions of different parts are produced using this method, from phone parts to car bodies.
Design and production of dies
One of the company's activities is the design and production of dies, molds and technological equipment. Machine Tool Association "PRESSMASH" offers design services for cold sheet metal
, including large dies for automotive body parts.
Designing stamps begins with you providing initial information, which can be in the form of:
• mathematical model of the part imported from any 3D CAD system;
• drawing of the part - in this case, our specialists will build a three-dimensional model of it;
• sample part
Based on the information received, we offer stamp manufacturing
, molds and repair of products manufactured by us. When developing a die design, the company places high demands on manufacturability, durability, strength, and reliability of the die design and part fastening. And the ability to quickly replace a worn part, conveniently load a workpiece into a die and easily remove waste will ensure safe operation and cost-effective production of parts.
Our company designs and manufactures all types of cold stamping dies:
– dies for cutting, punching, notching, trimming, stripping,
– dies for bending, forming, drawing, die forging,
– multi-position dies, combined,
– dies for automatic metal stamping on stamping complexes.
Our advantages
Modern metalworking equipment is used in the manufacture of dies and molds. We produce dies for cutting, drawing, and bending of any complexity. Mold making
and stamps takes a minimum amount of time, since our company has the ability to carry out a full range of work
in its own production
, which significantly reduces the time from the customer’s application to the final testing of the stamps, or until receiving a batch of stamped parts according to the drawing.
Designs of cold metal stamping
and their parts are diverse (Separating, Shaping, Relief-molding, straightening, embossing, Combined), and the cost of the part depends on the correctness and accuracy of their production. Our company is ready to accept your order for the design and manufacture of dies and molds according to your technological requirements.