To view the video, you need a modern browser that supports HTML5 video.
The invention of the sheet was a real breakthrough in metalworking. And almost immediately, having assessed the plastic properties of the resulting product, the craftsmen began to think that it could be given different shapes. The first example of cold metal stamping was the simplest embossing: a sheet was placed on a mold made of wood, and then systematically tapped with a hammer.
The technology was complex and labor-intensive. But hundreds of years had to pass before the invention of mechanisms that would make work easier...
Features of cold stamping of sheet metal parts
The “first sign” of serial stamping technology arrived in metalworking shops in the mid-19th century.
It was then that the first machine tools were invented and put into operation. But stamping reached a truly outstanding scale with the advent of the automobile industry, and in the 30s of the last century - aircraft and rocket manufacturing. The production of parts using the cold stamping method began to be used for the production of housings and internal components. Technology has developed rapidly and, perhaps, even now has not reached its peak in everything.
Modern stamping without heating to high temperatures is capable of creating parts of any shape and size - as a finished product or “semi-finished products” for subsequent processing. The manufactured products are distinguished by precision and increased strength.
History of the process
Metal stamping has undergone changes throughout history. The first upsurge in this process was noted in the 1850s. From this period of time, machines began to be used in metal stamping, which improved the quality of the finished product.
The next advance in the stamping process occurred in the 20th century. Thanks to the development of new technologies, the automotive industry began to actively develop. Using stamping, parts of the body and internal mechanisms of the car were made.
In the 1930s, the stamping process began to be used in ship and aircraft construction. 20 years later, this technology gained popularity in the field of rocket science.
There are several reasons explaining the growing popularity of this part processing technology:
- It is possible to produce both finished parts and blanks for further processing. The shape and parameters can be any.
- The stamping process can produce parts with low mass and high strength.
- High precision of work eliminates the need for additional processing of the part with other tools.
- The rotary conveyor line, operating automatically, facilitated and accelerated the production process.
Cold stamping can produce structures and parts of various shapes, but there are limitations regarding dimensions. This technology is designed for the production of workpieces weighing up to 1 ton. If you need a part of greater mass, it is not advisable to use a cold metal processing method.
Cold metal stamping: technology
In the stamping process, the most important role is played by the preparatory stage—the production of tooling.
It is produced in the workshop, but originates in the design bureau, where technologists and designers are involved in the process. They evaluate what final shape the product should achieve, how many stamping operations should take place and in what sequence. The result of the collaboration of these specialists is the creation of a matrix-punch pair. Next, the project goes to the workshop, where cold metal stamping occurs: under the influence of pressure, the matrix and punch stamp the required number of parts from sheets or strips. Cold stamping is called such with some convention: after obtaining impressions of the desired shape, in order to strengthen them, a final heat treatment can be carried out - recrystallization annealing.
Sometimes the stamping operation can be supplemented by simultaneous punching or drawing. For this purpose, an insert made of particularly hard metals or alloys is added to the matrix and punch. But the possibility of such work must be calculated at the design stage.
Stages of stamp manufacturing
A major role in ensuring the required quality of the finished product is played by the design of dies for cold stamping, due to which the part is formed with the required geometric parameters. Working drawings of such working tools installed on stamping presses can be made in both two- and three-dimensional formats. To solve this problem, appropriate knowledge and skills are required.
The development of a drawing and the subsequent production of a stamp used for cold stamping are carried out in several stages:
- drawing up a sketch of the future stamp;
- studying the scheme according to which the material will be cut, checking such a scheme using a special computer program;
- editing the sketch, if necessary;
- final verification of the dimensions of the developed stamp;
- designation of the position and exact dimensions of the holes that will be made on the working surface of the stamp.
When developing dies, you often have to choose between the quality of the future part and the cost of production.
When developing dies for cold stamping, it is necessary to break the drawing of the finished product into separate parts and carefully study them. After this procedure is completed, the production of stamps is carried out. In this case, it is necessary to pay special attention to the requirements for the parameters of the finished product. For each stage of the cold stamping technological process, a route map is developed, which takes into account both the execution time of individual operations and the characteristics of forgings at individual processing stages.
Most dies are made of carbon or alloy steel, but aluminum and copper alloys are sometimes used
In such a matter as cold stamping of a metal workpiece, many parameters are important, which, in particular, include the sequence of technological operations, the distribution of material in the cavity of the working tool, the equipment used and processing modes.
The process of manufacturing dies for cold stamping also imposes serious requirements, since the quality of the formed product depends on the accuracy of this tool.
Stamping of parts, in which sheet metal is used as a workpiece, can include a whole list of mechanical operations. Such operations include, but are not limited to, cutting, punching, extruding, bending, cold heading, forming, crimping and drawing. In this case, cutting, punching and a number of other technological operations are classified as separation operations, and cold heading, molding, bending, etc. are classified as shape-changing operations.
Types of Sheet Forming Separation Operations
Types of sheet metal forming operations
Have a question?
Our services
Cold stamping of parts in Moscow
The demand for cold stamping services in the capital has remained quite unstable over the past 30 years. Unexpected declines in the number of orders, usually associated with economic crises, are followed by equally unexpected periods of recovery. There is no doubt about one thing: Moscow stamped steel is sold to metropolitan enterprises in hundreds of thousands of tons. Customers are attracted by:
- high accuracy of product dimensions;
- elimination of surface defects;
- Compared to “hot” technology, there are no traces of heat treatment, such as scale.
Working using cold metal stamping technology is also beneficial for the performers, since it is less labor-intensive and more productive. Finally, both customers and contractors note the fact that this production method uses less material.
Hot stamping with hammers
The technology uses the phenomenon of converting the kinetic energy of a falling massive hammer into the energy of impact deformation of the workpiece. Hammers are raised to their original state by compressed air or steam and have a mass of 0.5 to 25 tons.
Hot stamping with hammers
By changing the height of the hammer, you can adjust the impact force. The stroke of the hammer is also adjustable, this makes it possible to rotate the workpiece during the next lifting of the hammer and more accurate stamping. All preparatory operations are available, including broaching and rolling.
The accuracy of manufacturing parts using hammers leaves much to be desired, which is explained by the inevitable shift of parts of the die relative to each other at the moment of impact. Tolerances when using hammers have to be given large, and to ensure the possibility of removing products from the press, large stamping slopes are made.
Types and methods of modern metal processing
Cold stamping, along with hot stamping, is considered one of the oldest technologies for processing sheet blanks.
Along with them, modern production can use more advanced, but at the same time expensive ones. For materials with high plasticity, hard rubber stamping is used. Its disadvantage is that it is impossible to process a large series of rolled products in this way. Also interesting is the technique in which metal changes shape due to liquid pressure. In this process, a liquid substance acts as a punch, pressing the sheet tightly against the die. This technology is used if it is necessary to obtain products of complex shapes.
Blast wave stamping is considered quite “aggressive”, but effective. As a result of the mini-explosion, the material is pressed into the matrix.
The choice of method is determined by the complexity of the final part, as well as its size.
Design and principle of operation of pressing equipment
Stamping machines are not divided by technological operations. Hot and cold types of deformation are performed on the same equipment. Presses are selected according to the following parameters:
- power;
- performance;
- slider stroke;
- availability of additional equipment for heating and cutting nearby;
- table size.
The main tool involved in deformation is a stamp. Its working parts: a matrix and a punch, which are designed for a specific part and operation. The slider and table have standard grooves for fastening:
- T-shaped;
- dovetail.
To create flat parts from a sheet with a large number of identical holes, a sheet metal stamping machine is used. Small parts with a figured configuration are made on crank-type presses. Hydraulic equipment is used to make car bodies and aircraft parts.
Metalworking press
Crank type presses
The equipment is based on a crank mechanism. It converts the rotational movement of the drive into translational movement of the slider. Presses are classified by the number of sliders - 1, 2 and 4. In production, single-column machines with 1 and 2 cranks are mainly in demand. Operating synchronously from a single drive and distribution gearbox, 4 units are installed on large equipment designed for the production of large parts with a large degree of deformation, for example, fenders, hoods and trunks of cars.
To make holes without deforming the workpiece on conveyors, sheet metal stamping machines are used. They are the simplest crank-type presses.
Advantages of crank presses:
- easy adjustment;
- high performance;
- small error.
The main disadvantage of the crank is its possible jamming. If there is not enough power, the slider stops at the lowest point. To lift it, you need to disassemble half of the mechanism.
Hydraulic presses
Hydraulic presses are among the most powerful stamping units. The largest of them produce car bodies, wings and fuselages of aircraft. In the cylinder, under oil pressure from below and above, a piston moves, to which a slider and other elements of the working mechanism are attached. The stroke length of the working tool is adjusted by switches. Having reached them, the stop turns off the oil supply.
The hydraulic press can be stopped at any point in the working path. Its disadvantages include:
- complex hydraulic system;
- low performance.
The punch presses evenly along the entire length of the working stroke with great force, but moves slowly.
Hydraulic Press
Radial forging presses
To create cylinders from a flat sheet with a longitudinal connection of the ends, radial type equipment is used. The workpiece is deformed on a shaft, which rotates and presses the sheet against the working tool that produces the deformation. As a result, the workpiece takes the shape of a cylinder. The diameter is determined by the size of the shaft.
Induction heating is used for rolling thick sheets.
Radial type equipment is unsuitable for other types of technological operations.
Electromechanical presses
The operation of an electromagnetic press is based on the force created by an electric magnetic field. In a mechanical machine, the movement of the working tool is carried out due to the movement of the electric core. He moves the slider.
The advantage of electromechanical machines is power supply and high productivity. There is no need for complex mechanisms and hydraulics.
Disadvantages include low power, low efficiency and uneven force at different points in the power stroke.
Stamping greatly simplifies the production of thin-walled parts with complex configurations and minimizes material consumption. It is advantageous to use in mass production of parts starting from 1000 pieces. Single production will not pay for the production of expensive stamps with complex and time-consuming manufacturing technology.
Cold sheet stamping is a guarantee of high-precision parts
Despite its apparent archaic nature, the production of parts using the cold stamping method has no equal in demand. Customers are attracted by:
- impeccable accuracy of the obtained impressions,
- high process automation,
- low costs for the production process,
- little waste,
- completeness.
In fact, the most difficult stage of the work is not the production of a part that can be produced quickly and in any quantity, but the design.
Stamping streams and their types
For simple product configurations, hot die forging is performed in a single pass.
Stamping streams and their types
If you have to stamp an intricate product with differences in thickness and height, protrusions and bends, production is carried out in several passes, in each of which the molding is done by a separate depression on the stamp - a stream. They are divided into two types:
Procurement
They are used for shaping, bringing the blank material to a spatial configuration that allows hot die forging operations to be carried out with minimal loss of material.
Procurement streams
Types of harvesting streams:
- Drawing - stretches certain parts of the blank, narrowing their cross-section. A series of gentle blows is used with the blank turned over
- Taxable - thickens the cross-section of the blank, “driving” material from neighboring areas to this place. A series of gentle blows with turning the blank over is also used.
- Pinch - flattens the blank at the point of application, causing an increase in the local width. 1-3 strong blows are used,
- Bending – used for parts with a curved axis
- Sedimentary - used for products close to round shape. Reduces the height of the blank, achieving the desired height and radius
Stamping
They are used in final molding and come in roughing and finishing.
Roughing is used for products with complex configurations and to reduce finishing wear. Designed to bring the dimensions and configuration of the blank closer to the final product. It is deeper and narrower than the finishing stream, and has larger radii and slopes. These measures are used to freely place the blank in the finishing stream.
Stamping streams
The finishing stream is used for molding the final product and is manufactured with an allowance for shrinkage during cooling. It is installed in the middle of the die, since the pressure and stress generated during finishing stamping are maximum. To drain the extruded metal, a flash groove is located around the stream.
Materials used in cold metal stamping
Stamping operations are possible on all metals and alloys that have sufficient ductility.
But parts made from them may have a limited scope of use. Simple carbon steels are suitable for the production of manufactured goods and products that do not need to withstand heavy loads. Alloyed structural steels withstand not only stamping, but also operations combined with welding. Stamped aluminum blanks are in demand in the assembly of equipment and instrument making, copper - in electronics, nickel-plated - in the production of tableware and jewelry.
Equipment
Sheet metal stamping is done using a press and a stamp. The press is used to create pressure, that is, the stamping process itself, and the stamp gives the product the desired shape. The stamp is made of tool steel and consists of a punch and a matrix.
The deformation process occurs with the help of a punch and a matrix at the moment of their approach. The movable part is the upper half of the stamp, fixed on the press, namely on its slider.
The lower half remains motionless and is located on the working surface of the equipment. If it is not steel that is being stamped, but the material is soft, then the working parts of the stamp can be made of polymer alloys or wood.
When producing a single, particularly large-sized product by stamping, it is usually not a press that is used, but a special device made of a cast iron or concrete matrix and a container with liquid (usually water). A sheet of metal is placed on the matrix, and above it is a liquid punch.
Concrete matrix fixture
To create the pressure in the liquid necessary to deform the metal into the desired shape, a gunpowder-based charge is detonated in the container or an electric discharge of sufficient power is provided to the water.
For cutting sheet metal, scissors, rather than a press, are used. They come in several types:
- with parallel knives;
- disk;
- guillotine;
- vibration.
Vibrating type scissors are most often used.
For high-quality manufacturing of products, you need to carefully select a press for each type of operation and material being processed. There are several types of presses:
- Hammer (maximum speed up to 20 m/s).
- Hydraulic press (maximum speed up to 0.3 m/s);
- Crank machine (maximum speed up to 0.5 m/s);
- Rotary type machine (maximum speed 8 m/s);
- Pulse stamping machine (maximum speed up to 300 m/s).
Crank machines are suitable for most types of operations. They can have from one to four crank mechanisms. The operating principle of the crank mechanism can be described according to the following diagram:
- The drive electric motor transmits motion to the crank shaft through a kinematic chain, which consists of a friction clutch and a V-belt drive.
- An adjustable length connecting rod drives the crank slider.
- The foot pedal through the clutch starts the working stroke of the press.
Equipment for stamping products with complex configurations may have several sliders.
Cold and hot sheet metal stamping
Hot sheet stamping also accounts for a significant share of the metalworking market. In contrast to cold metal stamping:
- there is less risk of workpiece destruction;
- deformation does not require much effort, and therefore not much equipment power;
- the processed material can acquire a granular structure, and with it increased strength.
But this technique also has disadvantages, and significant ones:
- much higher production costs;
- less accuracy, including due to temperature fluctuations;
- scale formed on the surface of a metal.
- deterioration of some mechanical characteristics of the material.
Types of stamping technological operations and equipment
Cold stamping is widely used for the manufacture of various volumetric body and flat parts and holes with a complex configuration around the perimeter. The stamping technology includes the following operations:
- felling;
- firmware;
- pruning;
- flexible;
- hood;
- flange.
Various types of tools and equipment are used for metal stamping. Basically, these are stamps consisting of two parts:
- fixedly fixed matrix;
- punch moving perpendicular to the parting plane.
A stamp for piercing and cutting may have clamps that the slide lowers along with the punch. They fix the workpiece, preventing it from moving.
Tools and devices for deforming parts are installed on special equipment - presses. The matrix with the stamp body is fixed on the table. The punch and other elements at the top of the tool move along with the machine slide. The clearance is provided by the die guides. They prevent the parts from moving relative to each other and provide the necessary clearance.
Types of sheet metal stamping equipment
The mechanical process of manufacturing parts by stamping is quite simple, but it can be produced on machines of different types and classes.
Let's consider the types of pressing equipment for stamping operations. Crank presses
named after the type of drive. They are considered the simplest in the line of machines for this purpose. With their help, you can process sheets with a small cross-section and produce parts of very modest sizes.
Compared to this technique, hydraulic presses
much more powerful. Just imagine: they can exert pressure equal to two thousand tons on the workpiece! In addition to the potential, the advantages of these machines are considered to be greater control over the controls and more accurate debugging. If you need to turn sheets of considerable thickness into parts, a crank press will be useless, but a hydraulic one will do the job.
Radial forging presses have a more specific application.
. They are used to produce products with the shape of a body of revolution.
Electromagnetic presses are considered the latest invention in the machine tool industry.
, which operate on the basis of an electromagnetic field. The key “tools” of the process are the core and the punch, which interact based on electromagnetic pulses. The technique is quite effective, and yet electromagnetic equipment is inferior to hydraulic equipment in power.
Let's consider how some separation operations are carried out.
cutting
When cutting, a certain part is separated from a part by cutting it along a curly or straight line. This separation operation is performed using a press made in the form of scissors of different designs.
This operation is intended mainly to prepare the workpiece for other processing methods.
Punching
An operation called punching is used to create holes of different shapes in a workpiece. During punching, part of the metal is completely removed from the workpiece, and its weight decreases.
The figure shows a diagram of the punching process.
Felling
Using the process of cutting out a metal part, a finished product has a closed contour.
The figure shows a diagram for manufacturing a part using cutting.
2. Form-forming deformations include changes in the shape and size of a product when its individual areas are moved, without leading to its general destruction. These include drawing, bending, relief molding, twisting, crimping and other operations.
Let's consider some types of operations that do not lead to physical destruction of the form.
Hood
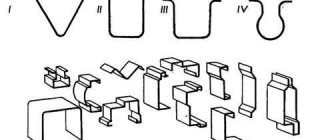
Using drawing, hollow volumetric products are obtained from flat sheet blanks. For example, in this way parts are made in the shape of a hemisphere, cylinder, cone, cube and other types. The figure shows different hood options.
Bending
Using the bending operation, a sheet product is given a given bending shape. Depending on the type of bending, this operation makes it possible to obtain curved products of different configurations. Some of them are shown in the figure.
Technology for stamping parts from metal sheets
Pressing equipment uses pressure force, but the operations based on this force vary significantly depending on the type of workpiece. Extrusion technology is used to produce rod-shaped parts. In the production of hardware products - studs, screws, bolts, etc. - the cold heading technique is used. Sheet blanks are processed using the molding method described above, which guarantees the production of three-dimensional products.
Cold die stamping of sheets to order
Do you have sheet metal and ideas about what it should be transformed into? We are ready to take on your project in the coming days and complete it turnkey - from creating drawings and developing equipment to the actual cold stamping of metal. Modern technologies and equipment allow us to process workpieces from any materials:
- gland,
- become,
- aluminum,
- copper,
- titanium and others.
During the production cycle, we will carry out all the necessary operations on your rolled products: cutting, bending, drawing, forming, crimping and others. Additional advantages of working with us are low prices, the ability to order stamping at a discount and always high quality work.
Features of the technology
The raw material for stamping can be a metal sheet, steel strip or thin tape. Cold sheet stamping has become most widespread for a number of reasons. Hot stamping technology is used in cases where the power of the equipment used is not enough to deform the metal in a cold state or when it is necessary to process a part made of metal with low ductility. As a rule, hot stamping technology is used to process sheet blanks whose thickness does not exceed 5 mm.
Depending on what needs to be done with sheet metal during the stamping process, separation and form-changing technological operations are distinguished. As a result of the first, a part of the metal is separated from the workpiece, which can occur along straight or curved lines, as well as along a certain contour. The separation of metal in such cases occurs due to the displacement of its parts relative to each other.
There are a number of separation stamping operations, which are performed using a press equipped with a special tool.
Cutting
During the cutting process, parts of a metal part are separated from each other along a straight or curly line. The press with which such an operation is performed is more correctly called scissors, which can be disk, vibrating or guillotine. Using cutting, products ready for further use are obtained or blanks are formed for their further processing by other methods.
Schemes for cutting sheet metal with scissors
Punching
This operation is used to form holes of various configurations in a sheet workpiece.
During the punching process, part of the material is removed as waste.
Punching
With the help of punching, a finished product with a closed contour is formed from a metal part.
An example of a part made from strip by cutting
Form-changing stamping operations, in full accordance with their name, are used to change the shape of a sheet metal workpiece, as well as its dimensions, without mechanical destruction.
Flanging
This is a technological operation of stamping sheet metal, as a result of which edges of the required size and shape are formed around the holes in the metal workpiece, as well as along its contour. Most often, the ends of pipes are flanged, on which flanges are subsequently planned to be fixed.
Scheme of flanging a part around a pre-punched hole
Drawing
This is truly volumetric stamping, the purpose of which is to obtain hollow spatial products from a flat metal sheet. Using this technological operation, it is possible to produce objects of box-shaped, hemispherical, cylindrical, conical and other shapes.
Instrumental drawing methods
Crimping
This operation is performed using a conical-type matrix. The purpose of crimping is to narrow the ends of hollow parts made of sheet metal.
When crimping, the end of the workpiece is pushed into the funnel-shaped hole of the matrix.
Bending
Using this technological operation, stamping gives sheet metal workpieces the required bend.
Bending allows you to obtain parts of various shapes, depending on which types of bending are distinguished.
Molding
This is a change in the shape and size of local sections of the workpiece, in which the external contour of the product remains unchanged.
Forming patterns
Not only sheets made of carbon and alloy steels, but also parts made of copper, aluminum and their alloys can be processed using cold stamping technology. Moreover, using a press and corresponding sheet metal stamping dies, it is possible to process materials such as leather, cardboard, rubber, and polymer alloys.
Parts for the production of which cold stamping was used are distinguished not only by the accuracy of their geometric parameters, but also by their high surface quality. The cleanliness of the latter in some cases may correspond to the 8th class. On average, the surface cleanliness of stamped products is in the range of 2–6 classes, which is quite satisfactory for consumers of such products.
Production workshop in which the sheet stamping process is carried out
It should be borne in mind that cold stamping of sheet metal is accompanied by an increase in its strength characteristics.
When choosing a press to perform such a technological operation, as well as when designing sheet metal stamping dies, you should take into account a number of parameters of the feedstock. This is the only way to ensure high quality of finished products. Such parameters, in particular, include:
- electrical and magnetic conductivity of the material to be processed;
- hardness and mechanical strength of metal;
- workpiece mass;
- impact strength possessed by the metal being processed;
- thermal conductivity of the metal, as well as its heat resistance;
- the degree of resistance of the metal to corrosion and its wear resistance, which will affect the durability that the stamped sheet will have.
Hot stamping on presses
Hot stamping of metal is also carried out on crank presses. The main characteristic of the equipment is the force it develops, varying from 6 to 110 MN.
Hot stamping on presses
The design of the crank hot stamping press has a rigid drive and does not make it possible to regulate the press stroke and its force. These factors exclude broaching and rolling from the list of permissible operations, since they require gradually increasing pressure.
The absence of impacts, the constant stroke of the die and the use of guides eliminates shifting, which makes it possible to achieve precision processing that is fundamentally unattainable with hammers.
Accordingly, it is possible to set significantly smaller tolerances, stamping radii and slopes, which reduces material losses and increases equipment productivity.
In addition, static deformation penetrates deeper into the blank than dynamic deformation, and this makes materials with low ductility accessible for processing.
The negative features of crank hot stamping presses are:
- scale is pressed into the surface; to combat this, heating in an inert atmosphere or deep cleaning of the blank is used;
- Due to prolonged contact with the punch, the blank cools down, its ductility and fillability decrease.