OPEN DRAINAGE DEVICE
Surface, open drainage is a system of ditches of various sizes, tree-shaped. Everyone has a rough idea of how to make this kind of drainage. To create it, all you need from tools is a shovel and a wheelbarrow.
The largest - the central ditch - serves as an exit channel. Adjacent to it are smaller side “branches” into which smaller grooves “flow”. It is better to place them at right angles to each other. Often the grooves are filled with crushed stone, sand or other material that allows water to pass through well, and covered with turf or mesh. This type of drainage is called reservoir drainage. The slope of the canal should be about 3 cm per m.
If there are many areas of accumulation and stagnation of water on the site, you can make parallel ditches (for example, along paths or near a pool). Cleaning large areas of water is called linear. If you have one or two places where a large amount of water gets in, it is enough to make local, or point, drainage. For example, to drain water coming from a storm gutter in front of the terrace or at the entrance.
If your site is exposed exclusively to external “attacks”, that is, water flows onto it from neighboring areas, you can use open drainage, limiting yourself to ditches near the fence that prevent water penetration.
At first glance, this type of drainage system is quite simple. However, there are some pitfalls here. This system is suitable for places with a natural slope, and also requires careful organization of the site. It is necessary to level it thoroughly, filling in all the depressions and depressions and leveling the hills and elevations that can organize the reverse flow of water.
How to properly make closed drainage around the house with your own hands
Such a device for protecting a house from water can be done independently even after the construction of the building is completed. First of all, you need to prepare working tools and all the necessary materials:
- two types of shovels (bayonet and shovel);
- spirit level for checking the slope;
- manual rammer;
- a device for removing excess soil from the site (stretcher or wheelbarrow);
- roulette;
- geotextiles;
- backfill for the moisture collection layer (crushed granite stone is best suited);
- sand;
- inspection and drainage wells;
- drainage pump;
- drains and fittings for connecting them to each other and to wells.
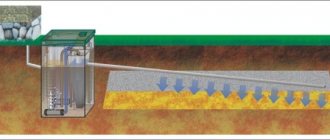
DEEP DRAINAGE SYSTEM
Deep closed, or tubular, drainage is most common these days. It is used in densely built-up areas where it is not possible to build an open system, in places where there is no natural slope, in areas with an extensive system of paths, in gardens with complex landscape design using numerous plant species.
A deep tubular system is a linear type of drainage; its point use is rare. Drains can be made from asbestos-cement, ceramic or plastic perforated pipes. Their diameter is 8-11 cm and above. Smaller diameter pipes are not suitable for these purposes.
If for some reason it is not possible to buy perforated pipes, you can use ordinary plastic pipes for external sewerage. To do this, make cuts on them in a checkerboard pattern for half the diameter of the pipe. The distance between the slots is no more than 50 cm. Or drill 5 mm holes on all sides, the distance between which will be about 1 cm.
Deep drainage begins with digging trenches according to a previously drawn up project. In garden plots, a system of canals forms a kind of Christmas tree. It is necessary to make ring drainage around the house.
The depth of the trenches depends on the degree of your problem and varies from 50 cm to 3 m. It is better to lay pipes below the freezing level of the soil - 110-130 cm. Near the house below the foundation level. To drain water from the root systems of trees, drains are deepened by more than 1.5 m. The distance between drainage trenches on the site is 5-10 m. When calculating the depth, 20 cm should be added to the required dimensions for the installation of a “cushion”. The slope of the trench bottom is made towards the collector (0.5-1 cm - near the house and up to 3 cm per m - on the site).
Summary
In some cases, it will be necessary to install a reservoir drainage system. The main reason for this is the presence of clay soils. In such a situation, the installation of the drainage system is carried out when laying the foundation directly under it. The general scheme is the same as described for the ring system, but there are nuances regarding collector wells, which are often constructed with a filter bottom.
Recommended Posts
Bituminous mastic for waterproofing the foundation.
What kind of foundation is needed for a house made of aerated concrete?
How to choose roofing felt for foundation waterproofing
Do-it-yourself USHP foundation
DIY strip foundation
Pile foundation with grillage
WHY ARE WELLS NEEDED?
At every 90° turn, inspection wells are installed (sometimes, to save money, they are made at every second corner).
On straight sections they are installed every 50 meters.
They are made from large diameter pipes. You can also find ready-made prefabricated wells on the market.
It is recommended to create a sludge collector at the bottom so that small particles that fall into the pipe can settle in it without clogging the pipe.
To do this, the drainage pipe is fixed at a level of 20 cm above the bottom of the well.
When there is quite a lot of sludge, it is removed with a special pump. The pump is lowered into the well, then, after agitating the water at the bottom with a pressure jet, it is turned on.
Calculation work
If you want to build a drainage system yourself, you can follow a few simple rules. The first of these states that drainage pipes must be placed below the base of the foundation. You will have to go deeper another 50 cm from the extreme point of the sole. Therefore, if the foundation is laid at 2 meters, you will have to work hard. The pipes must be laid with a slope so that water can flow freely into the collector wells. A slope of two degrees is maintained. To make it easier to measure, the level should change every two centimeters every meter. The ideal place to locate the collector well of the drainage system is the lowest point of the site. Therefore, it is first necessary to carefully examine the site and sketch out a diagram of the future drainage system.
Advice! By placing the storage well at the lowest point of the site, it will be possible to avoid the installation of several elements with pumping pumps.
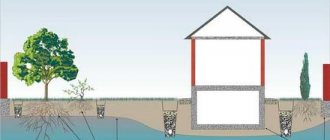
Foundation ring drainage
Ring drainage is an excellent solution to eliminate the problem when groundwater and rainwater seep into the soil next to the foundation wall, have a destructive effect on it, and also penetrate into the basement.
Most often, this problem manifests itself during spring floods, when the snow melts and the soil thaws. This disturbs the peace of the house's residents, forcing them to pump out water from the basement. Ring drainage is a network of perforated pipes suitably laid around foundations and draining groundwater accumulating in this place.
What is important to consider when choosing this type of drainage:
- the action of such drainage implies a ring, the inside of which will be isolated from water;
- if water comes from one specific side, then such drainage can be laid in the form of an open circle;
- such a system is installed below the floor level of the basement room that must be protected from moisture;
- Such a system should be laid at a distance of 5-8 meters from the wall itself. If this distance is less, then care must be taken to remove, weaken or settle the soil of the building itself.
Necessary materials
The main elements that form the entire drainage system are pipes, inspection and collector wells. Products made from the following materials can be used as pipes:
- asbestos cement;
- ceramics;
- plastic.
The first and second options were quite common until a certain time. Their advantage can be considered accessibility and low price. But ceramic pipes are quite fragile, which introduces certain difficulties during installation and also limits the maximum pressure that can be applied from above. Asbestos-cement solutions quickly become clogged and destroyed by constant exposure to moisture. Another disadvantage is the need to independently drill holes along the entire length of the pipe, which also causes some inconvenience and takes a lot of time.
The best solution at the moment can be considered plastic products. Users choose these pipes due to the following advantages:
- long service life;
- resistance to biological and chemical influences;
- presence of holes;
- high strength;
- smooth inner walls;
- affordable price.
The service life of such pipes reaches several decades, so you don’t have to worry about the performance of the system for a long time. The polymer from which drainage pipes are made is inert to most chemicals. The latter often enter the system along with rainwater, which washes them off the ground surface. Bacteria that are in the soil are also unable to cope with plastic, so you don’t have to worry about corrosion processes. The manufacturer provides holes through which water seeps into the pipes, so you don’t have to make them yourself. Corrugated pipes are considered the best solution for constructing the system. Thanks to the stiffening ribs, they are able to withstand significant loads exerted by the soil. The inner walls of such products are smooth, so blockages are not a problem, because there is simply nothing for contaminants to cling to. Due to the ease of production, the price remains affordable for the end user.
Along with the pipes, inspection and collection wells are installed. The first are plastic containers that have bends for connecting pipes to them. These wells are used to control clogging and for system maintenance. If there is a suspicion of a blockage, it can always be cleared through the inspection well. They are usually installed at pipe joints that run parallel to different walls. Collector wells have a larger capacity compared to inspection wells. Their task is to accumulate water that comes from the drainage and stormwater systems. Emptying of collector wells occurs through the use of drainage pumps, which discharge liquid from them into drains or sewer systems. In some cases, it is possible to connect collector wells to the sewer system so that when it overflows, the water will automatically drain.
Note! Gravel, sand and geotextiles are used as auxiliary materials for the drainage system.
Wall foundation drainage
Today, one of the most effective is the drainage of the foundation of a wall-type house. This type of drainage removes water from the base and protects against the extreme rise of moisture contained in the soil. As a result, the durability of the building increases; there are no puddles, fungus, mold and other destructive organisms in the basements.
A wall drain is a structure typically constructed below the basement floor level. A foundation drainage system is especially necessary if the house has a basement or ground floor. And it is advisable to take care of it at the initial stage of construction - at the stage of laying the foundation pit.
If drainage was not provided for during the design, then the existing house will have to be protected from groundwater. And you should start by digging a pit around the house again.
Drainage pipes are installed around the perimeter of the house. In the places where they connect, in the corners, inspection wells are installed. At the lowest point of the site there is a pumping well. It must discharge excess water off-site into a storm drain or a nearby body of water. In order to properly drain the foundation, a number of components should be taken into account. The depth at which the foundation is laid.
Regardless of the material used to organize water drainage, the entire drainage system is laid 30-50 cm below the location of the base cushion. The slope should also be taken into account. Lowering the drainage system towards the collecting collector at an angle with a coefficient of 0.02 (2 cm per 1 m) will ensure uninterrupted drainage of excess water and prevent it from stagnating in the pipes. Remember that in any case, the drainage of the foundation slab should be located no closer than 3 m from the house. It is also necessary to provide for a concrete blind area, which should extend at least 1 m from the foundation of the building.
What is important to know when choosing this type:
- It is often used as a preventative against water;
- This drainage system is often used with a mixed source of groundwater;
- Such drainage is laid outside the building. The distance from the wall to the drainage system is equal to the width of the foundation of the building itself.
- Such a system is laid no lower than the level of the base of the foundation;
- If the foundation depth is too deep, the drainage may be slightly higher.
Kinds
There are several main types of drainage systems. The choice of one or the other directly depends on the characteristics of the site, the degree of its susceptibility to flooding, and the groundwater level.
Open drainage
This is a truly budget option. The system is based on a series of open channels dug into the site, which drain excess water away from the building. This scheme cannot protect against groundwater, but it collects rain and melt water quite effectively.
It is rational to use such a system only in the case of an area where the aquifer lies deep enough, but the clay soil contributes to the stagnation of rainwater.
Storm drain
Since the open system itself is ineffective, it should be supplemented with a storm drain. Its task is to collect and remove rainwater outside the site.
Structurally, a storm drain consists of a network of pipes laid underground and water collectors brought to its surface. Depending on the owner’s preferences, several point collectors or belt collection channels can be installed.
Ring system
Both previous designs cannot be considered as complete drainage. They only remove moisture from the surface without regulating the water level in the soil.
Note! The ring system is a good foundation protection; if installed correctly, it will ensure the durability and reliability of the building.
The system includes two parts - storm protection and groundwater drainage pipelines. Storm protection consists of pipes into which water collected from the roofs of buildings is supplied, it is transported to storage wells and accumulated in them. The second part is a closed network of special pipelines with holes (tubular drains). They collect water from the soil and send it to the same storage tanks.
If it is necessary to significantly lower the groundwater level, drainage wells are used. Excess moisture, which is collected by all these devices, is discharged outside the site in case of a slope or collected in a collector for subsequent removal.
Formative drainage
Perhaps the most effective way to protect the foundation is reservoir drainage. It does its job perfectly on any soil, collecting and removing water. This is an excellent drainage for strip foundations, foundations made of solid concrete blocks and other similar structures. Its only drawback is that pipelines can only be laid before construction begins.
The basis of the system is perforated pipes, which are laid below the base of the foundation at the level of the sand backfill. The water they collect is accumulated in a receiving well. Then it is drained into the sewer, and in case of its absence, it is periodically removed.
Foundation waterproofing device
This is a necessary measure not only when there is a risk of flooding or when arranging a used basement floor. Protecting the foundation of the building will extend its service life, maintain its original characteristics and eliminate dampness on the ground floor. Traditionally, there are two ways to insulate the foundation from moisture:
- Treatment with bitumen mastic. The thickness of the layer depends on the depth of the foundation: up to 2 meters - 2 mm, more - up to 4 mm.
- Laying membrane film. It is a more modern, but at the same time expensive method. After treatment with mastic, a roll of membrane (polymer profiled film with corrugation) is rolled out over the entire surface of the base. Its two- or three-layer varieties are equipped with an additional layer of geotextile. The principle of operation comes down to the drainage of moisture that has seeped through the fabric to the drainage pipes.
Additionally, it is worth insulating the foundation.
Consequences of prolonged exposure to excess moisture
Water has an extremely aggressive effect on the foundations of buildings; its excess is also detrimental to cultural plantings. Neglecting the design of the water drainage system can lead to the following:
- the appearance of dampness and the spread of harmful fungus on the floor of the first floor;
- erosion of the foundation, its destruction and distortion of the entire structure;
- waterlogging of the local area and the appearance of an unpleasant odor;
- decreased aesthetics due to the death of ornamental plants and the presence of dirt on paved areas.
Also prerequisites for installing wall drainage
can serve:
- from the basement floor to the groundwater level is less than half a meter or the base is below this level;
- the house is located on clay or loamy soils, which are not capable of absorbing excess moisture, but the use of the ground floor is planned.