Semi-automatic welding (MIG) is a kind of evolution of manual arc welding (MMA). Even despite the availability of MMA inverters, it is better to use MIG welding for home use. But to fully appreciate its advantages, you need to know how to cook with a semi-automatic device. In fact, there is nothing complicated about it.
What is semi-automatic welding
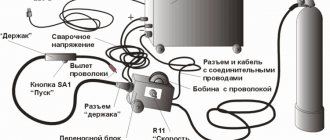
Before starting practical classes on mastering the technology of working with semi-automatic stations, you should study the theory in detail. The equipment consists of the following main components:
- the main block through which filler wire and power are supplied;
- a burner with a wire located inside it;
- welding sleeve;
- shielding gas supply system;
- conductive tip.
Large enterprises often use stationary semi-automatic installations for welding parts on assembly lines. Such equipment ensures good quality of the welded joint, uniform distribution of weld deposits along the entire length of the seam, high speed of work and low energy consumption. Depending on the principle of operation, semi-automatic models are divided into several groups:
- for welding edges in a protective environment;
- performing work using flux;
- welding with flux-cored wire;
- universal automatic devices.
Without exception, all installations do an excellent job of joining workpieces made of non-ferrous or ferrous metals. Depending on the type of filler wire feeding, semi-automatic machines are:
- stationary. The housing is installed on a special console or other base and is rigidly fixed;
- portable. The device has relatively small dimensions and weight. Can be moved effortlessly by one person;
- mobile. The unit is mounted on a trolley and moved within one room - usually a workshop or assembly area.
There is also a classification of equipment depending on the type of feed rollers: pulling, pushing or push-pull.
Education
Training in semi-automatic welding can be completed at special courses. The program includes theoretical and practical classes. You can choose individual training according to a schedule convenient for the student and also learn everything about semi-automatic welding. After graduation, you must pass an exam and prove that all knowledge has been acquired.
A certificate of the established form is issued, which lists the subjects taken, practical classes and indicates that the title “Electric and gas welder” has been awarded. It is possible to obtain an international diploma, which makes it possible to apply the acquired knowledge in other countries.
Training in semi-automatic welding gives an idea of the types of semi-automatic machines, the choice of welding mode and wire diameter, and the technology of the welding process. The lessons learned on the theory of “semi-automatic welding machines” will allow you to understand the designations of the materials used and the markings of the wire. The basics of semi-automatic welding include information about the design of semi-automatic devices, the principle of their operation, ensuring the safety of the welder, carrying out preparatory work, and choosing welding modes.
At the courses you can not only learn everything about semi-automatic welding, but also apply the acquired knowledge in practice. They are conducted under the guidance of a mentor, who will point out errors and explain how to eliminate them. Group classes have the advantage of being able to hear other students' questions and learn the correct answers. During practical classes, you should listen to the analysis of all situations, from which you can learn a lot of useful things.
Semi-automatic welding lessons are taught by professionals with extensive experience. The acquired profession is in demand and highly paid. Those who already have a welding profession, but who want to improve their skills, can also enroll in the courses. Training in a specialized course will help you understand what semi-automatic welding is. The knowledge gained will help you easily read drawings and understand technological materials.
Semi-automatic welding technology
Semi-automatic welding with gas
Using a semi-automatic machine, you can weld parts made of galvanized or rusted metal. When connecting difficult-to-weld parts, aluminum or copper wire is used as an additive. This makes it possible to obtain a strong weld with a uniform distribution of the weld.
When you plan to weld materials in a protective environment or using flux, preparatory work is carried out first:
- Using a solvent, the surface of the joints is degreased and cleaned of mechanical impurities;
- the operation of gas equipment is checked;
- a small section of the joint is welded. At this point, the basic settings are adjusted;
- a fine selection of voltage and current is performed.
The simplest option for using a semi-automatic machine is considered to be working in a protective environment. Any inert gas that is available is used: argon, helium, carbon dioxide or nitrogen. The welding technique does not depend on the choice of gas and remains unchanged. Carbon dioxide, which has good protective properties and a relatively low cost, is most often in demand.
Advantages of using semi-automatic welding machines in a protective environment:
- the appearance of the structure remains unchanged;
- even the most inaccessible areas of the product are processed;
- the output is a thin and fairly strong weld;
- minimum waste;
- all work is completed quickly.
How well the seam will be formed depends on three main factors: compliance with the interval between the surfaces being welded, the method of guiding the wire along the joint, compliance with the technology and standards for performing welding work.
Welding of profile pipes with a wall of 2 mm
- Log in to reply to this topic
#1 Space77
Friends, hello everyone! Just learning how to weld, the question arose: is it necessary to leave a gap when welding profile pipes (2 mm)?? I will cook at an angle of 90 degrees and end to end. I looked at the GOST standards, and it seems that the tables say 1-1.5 mm gap . I plan to cook with an inverter or semi-automatic wire.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#2 Susanin
- 3
- Top
- Insert nickname
#3 Alexey Trunov
Good health! Welding a 2 mm profile is not a thick-walled pipe with a “clearance” root weld, where a gap is needed for full penetration and the formation of a back bead.
When you weld thin metal, you are almost always on the verge of “burning through”, everything depends on the speed of movement of the electrode, its angle of inclination and, most importantly, the diameter of the electrode and the set welding current.
Because I don’t have a PA yet, I weld the entire profile with 1.6-2 mm electrodes, mostly Plazmatec. Don’t even bother with 3mm electrodes, you’ll waste more time.
Of course, if there is a PA then everything is easier)
- 2
- Top
- Insert nickname
#4 Susanin
Good health! Welding a 2 mm profile is not a thick-walled pipe
Don’t even bother with 3mm electrodes, you’ll waste more time.
Of course, if there is a PA then everything is easier)
well, about 3mm it’s in vain, they have more deposited metal
- 6
- Top
- Insert nickname
#5 Space77
Thank you, I read the Notes, yes, a lot of good information. I think this topic will still be of interest to many, since I think many people want to learn how to cook a professional pipe. Well, thanks to Alexey for the detailed answer.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#6 Space77
Another question for experts: I want to learn how to make beautiful facial seams on a professional pipe. If there is a semi-automatic machine, will they be ideal only with gas, or will it also work out beautifully with cored wire?
- Top
- Insert nickname
#7 AVN
It depends on what kind of powder. Actually, it doesn’t depend on the welding method, but on the skill and only then on the skill. materials.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#8 Alexey Trunov
well, about 3mm it’s in vain, they have more deposited metal
It's right. But we take into account that a novice welder is asking for advice. And one more thing - if the product, let’s say, should be “exemplary”, then the welds must be treated with “Bulgarian”. And from a “C” the seam will be thicker.
- Top
- Insert nickname
#9 Alexey Trunov
Another question for experts: I want to learn how to make beautiful facial seams on a professional pipe. If there is a semi-automatic machine, will they be ideal only with gas, or will it also work out beautifully with cored wire?
Of course, the most ideal welds on a profile pipe, without taking into account the ADS, are obtained on P/A.
I haven’t welded with flux-cored wire myself, but it is known that semi-automatic welding with regular wire in the “Ar+Co2” mixture produces very beautiful seams in appearance.
To eliminate “extra” metal on the walls of the professional pipe, you need, of course, a “chameleon” type welding helmet in order to accurately see the initial position of the torch and the welding site.
Well, of course, it is important that your hand does not shake)) during welding, which will greatly affect the appearance of the seam. And for this it is necessary to use various methods of fixing the hand that holds the burner: wrist - you hold the working hand with the other hand, ulna - you rest the elbow of the working hand on the table or knee if you cook in a semi-squat, and shoulder fixation - when the shoulder of the working hand rests on some or a surface near the welding site, if of course it is nearby)
Go for it! Everything will work out! And remember that we all went through “snot” and clumsy stitches. Any failures only move you towards success, the main thing is not to give up!
- 1
- Top
- Insert nickname
#10 Simfer
- Participant
- Messages: 762
- City: Simferopol
And one more thing - if the product, let’s say, should be “exemplary”, then the welds must be treated with “Bulgarian”. And from a “C” the seam will be thicker
Setting up a semi-automatic welding machine
Fine-tuning of a semi-automatic welding machine is a prerequisite for obtaining a high-quality welded joint. Before operating the equipment, the welder must select:
- filler material feed rate;
- current strength;
- optimal inert gas pressure.
Installations for automatic welding are supplied complete with documentation, which also contains information on adjusting the basic welding parameters. Based on the data in the tables, an experienced welder will be able to accurately select the most suitable parameters for working with a particular material.
How well the unit is configured can be checked on unnecessary pieces of metal. If the seam turns out even, smooth, without drips or interruptions, then the settings are chosen correctly. The optimal shielding gas pressure should vary in the range of 1-2 atmospheres.
To prepare semi-automatic welding for work, you should:
- Select the wire of the most suitable size. Most of the popular consumables have a diameter from 3 to 6 mm. For semi-automatic welding, in most cases, wire with a diameter of 4 mm is selected.
- Pull the additive to the burner so that it comes out and adjust the degree of its pressure.
- Prepare protective gas for use. The most commonly used is argon or carbon dioxide. The first ensures the stability of the electric arc and minimizes the formation of spatter. And the second one has the advantage of low cost and is perfect for working with steel workpieces.
- A gas cylinder is connected to the equipment.
When setting up equipment, you must follow established rules. Compliance with them will be the key to obtaining a high-quality and even seam. First of all, you need to achieve uniform and stable combustion of the electric arc. It is important to thoroughly clean the joints from slag, grease, paint and other contaminants. An equally important condition is the optimal wire feed speed. All settings can be found in the accompanying literature that comes with the installation. Factory parameters should not be taken as dogma. They can serve as a basis from which the welder will start in search of the most suitable option.
The fact is that each time the settings can vary greatly depending on:
- selected operating mode;
- quality of energy supply;
- differences in the composition of the metal being welded;
- air temperature;
- composition and diameter of filler material;
- spatial location of the joint;
- type and composition of the protective environment.
Most often, when setting up a semi-automatic welding machine, welders make mistakes, which can be identified by the following symptoms:
- Extraneous sounds that resemble a loud dry crackling sound. These symptoms occur when the filler wire is fed slowly. Simply increasing the wire feed speed is enough to completely correct the situation.
- When performing work, there is a lot of splashing. This is possible in cases where too little inert gas is supplied. To fix the problem, you need to check the gearbox - often the problem is its malfunction. Sometimes simply increasing the gas flow is enough.
- Poor welding of the metal and, as a result, poor weld quality. Most likely, the inductance and voltage are selected incorrectly.
- The roller is of unequal thickness. The defect occurs due to the fact that the burner speed is selected incorrectly.
Electric arc welding with argon
Welding of profile pipes in a protective gas environment is often used today. The thing is that this technology is usually used to connect thin-walled workpieces, which include electric-welded profile pipes.
What you need to pay attention to when carrying out this process.
- Before welding a profile pipe, it must be cleaned and degreased.
- Next, the diameter of the tungsten electrode is selected. It depends on the thickness of the parts being welded. If their thickness does not exceed 2 mm, then a non-consumable electrode with a diameter of 1 mm can be installed. If it is more than 2 mm, then it is better to take a tungsten rod with a thickness of 1.6 mm.
- Now you need to select the diameter of the filler wire. Firstly, it must be made of the same material as the pipes being welded. Secondly, its diameter also depends on the thickness of the pipes. The ratio here is: thickness 1 mm – diameter 1-1.5 mm, thickness 2 mm – diameter 2-2.5 mm.
- The electrode must be kept closer to the weld pool. The shorter the arc, the better the welding, the better the quality of the seam.
- The electrode and additive should move only along the seam, no lateral movements. They must always be in the shielding gas area.
- The wire is fed into the welding zone smoothly; when fed sharply, splashes are formed.
- It is optimal if the filler wire goes in front of the torch.
- The end of welding is carried out by decreasing the current strength, and not by the release of the non-consumable electrode from the weld pool. Be sure to turn off the supply of protective gas 10-15 seconds after turning off the power supply. In this way, the electrode itself is cooled; oxidation reactions will not occur on it, which increases its service life. And the seam is also cooled.
Now to the question of how to cook correctly, this refers to the modes and nuances of welding. Steel products are usually welded with direct current of straight polarity. The magnitude of the welding current depends on the thickness of the parts being welded, within the range of 50-120 amperes. Gas consumption should not exceed 12 liters per minute. It would be nice if the welding equipment is equipped with an oscillator, with which you can ignite the arc without touching the metal surface.
Types of welding seams when welding semi-automatically
By manipulating the settings of semi-automatic welding, a specialist can obtain a variety of types of seams. According to their appearance, they are divided into several types: T-bar, butt, corner, overlap. There are several types of connections that differ in their spatial position: bottom, ceiling, horizontal and vertical.
The formation of the ceiling seam is divided into two stages:
- Boiling the base. The root suture is formed, as a rule, with three-millimeter electrodes with a low current strength.
- Final formation of the seam.
The second stage can be performed in different ways:
- Connecting workpieces by applying short intermittent seams or by spot welding. With this approach, the likelihood that drops of molten metal will fall on the welder is minimal. This technology involves additional boiling of the workpieces at the beginning and end of the joint.
- Performing work with a minimum arc. The peculiarity of the method is that the seam cools down very quickly: immediately after the arc is interrupted.
Bottom connection is the main method of joining metals, which forms the basis of the industrial production of welded structures. It can be performed either by manual arc or semi-automatic welding. Such seams are characterized by high mechanical strength, which is ensured by the uniform distribution of the melt.
For corner joints, semi-automatic welding modes can be very different. The location of the blanks is also variable:
- The connecting surfaces are placed perpendicularly. With this placement, only the internal joint is welded. In cases where tubes are welded, a concentric weld around the circumference is required.
- The angle between the connecting surfaces is less than 60 degrees. This is an ideal arrangement: the parts are perfectly welded from all sides.
When joining pipes or sheet metal, a butt weld is used. With this option, welding can be: one-sided, one-sided with processing, two-sided. One-sided welding is acceptable if the thickness of the workpieces does not exceed 4 millimeters. With thicker edges, it is advisable to process the joint on both sides.
When single-sided welding, special attention should be paid to the preliminary preparation of the metal. Thorough preparation of edges is an important precondition for the formation of a high-quality seam during semi-automatic welding in a protective environment. The edge is cut using a file or grinder. During processing, the tool is held so that the angle at the edge of the workpiece is approximately 45 degrees.
The overlapping connection of workpieces is chosen when it is necessary to ensure high tensile strength of the seam. To prevent moisture accumulation, you need to place seams on both sides of the joined surfaces. The T-joint is excellent for connecting the base of a metal structure.
Advantages of automatic welding machine
The automatic welding machine has many advantages. One of them is the lack of the human factor. It can work for 24 hours with equally stable results. It is unlikely that any person will boast of such productivity.
It makes no difference to the machine which welding takes place. It copes equally with small elements with thin seams and with structures of significant dimensions. The machine will not get tired, it does not need sick leave, a break or a day off.
If the wizard makes a mistake with the parameters, this situation can be corrected without any problems. And if the master, due to, for example, physical or mental well-being, performs the work poorly, the workpiece will be rejected.
Vertical seam
The technology for forming a vertical seam using a semi-automatic machine has several features:
- The melt should cool much faster than with horizontal welding. This is necessary to prevent molten drops from dripping onto the floor. Droplet size can be reduced by minimizing the size of the welding arc.
- Vertical welding is performed in the direction from bottom to top. In this case, it is possible to lay an even seam, without sagging or unevenness.
To achieve a good result when vertically welding workpieces in the top-down direction, you should adhere to several basic rules. The first is to use an extremely short arc to reduce spatter and minimize melt volume. Secondly, at the beginning of welding, the electrode must be positioned strictly perpendicular to the working surface. Third, the electrode is then placed at an acute angle. But you shouldn't expect a perfect result. As practice shows, seams have very poor characteristics. It is recommended to resort to this welding method only in extreme cases.
There are several basic techniques for forming a vertical seam using semi-automatic welding:
- Triangle. The method is used in cases where workpieces with edge thicknesses of up to two millimeters are connected. Its essence lies in the fact that movement from bottom to top causes liquid metal to float onto already frozen metal. It hardens fairly quickly without dripping onto the floor or onto the operator. In this case, the slag moves at a certain angle, forming some semblance of a triangle.
- Herringbone. The technique is used for welding joints 2-3 mm deep. The movement of the electrode begins at one of the edges. The metal melts throughout its entire thickness, and the arc gradually moves deeper into the joint.
- Ladder. The optimal way to connect two workpieces with a large gap between them. The electrode moves from one edge to the opposite in a zigzag manner.
Difference from automatic welding
Automatic and semi-automatic welding have much in common and are very different from the manual method. The main difference between automatic welding and semi-automatic welding is that the semi-automatic machine mechanically feeds the wire, which acts as an electrode, to the work site, but then it is moved manually. This allows you to correctly form the seam and monitor its quality.
It is advisable to use automatic welding in mass or large-scale production. On welding forums the question is sometimes asked: how to weld semi-automatically with electrodes. Experienced welders answer that for this they will have to radically redo the machine, but this does not guarantee a high-quality weld.
Horizontal seam
Semi-automatic welding makes it possible to produce horizontal seams of the highest quality, regardless of the direction of movement. To obtain a high-quality seam, you need to take into account some features:
- it is necessary to balance the gravity of drops of molten metal and the burning force of the electric arc;
- it is important to choose the optimal speed of moving the electrode along the joint;
- To control the melt, welding work should be carried out continuously.
In some cases, it is not possible to complete the seam in one pass. Then you can resort to a technique that involves periodically extinguishing the arc. Various welding patterns can be used on workpieces with edges up to 4 mm. In all other respects, the quality of the seam will depend on the experience and skill of the welder.
A horizontal weld is created in four stages:
- Formation of the root roll. It is performed with a short electric arc. The electrode is held at an angle of 80 degrees in relation to the working surface. The primary roller is formed, as a rule, at maximum current.
- Secondary roller application. Before starting the process, the average current strength is set. The roller is performed in one pass using an electrode of the largest possible diameter. When forming a roller, the forward angle technology is used.
- Creating the third roller. Depending on the previously obtained results, one of two methods is used to form the third roller. The area of the secondary roller is large - the third one lies in the center. When the dimensions of the secondary correspond to the norm, then the third stage is performed in two approaches.
- Checking the quality of work.
Welding defects most often form in the upper part of the seam. Therefore, you should carefully monitor the quality of work at this stage.
general information
An automatic welding machine is a type of welding equipment. The machine is used for automatic welding. Automatic welding does not even require welding skills from the welder. All that is needed is to configure the device correctly. He will do the rest of the work without outside help.
An automatic welding machine for welding is a complex unit, which, however, is capable of operating stably even under significant loads. At the same time, the quality of the seams largely depends on the correctly selected settings. Well, since with this technology the welder does not participate in the welding process itself, he is called an operator.
The automatic welding machine performs a whole range of tasks at once. It not only ignites the arc and conducts the seam, but also protects the welding zone from oxygen (this is done by submerged arc welding machines), and also feeds the welding wire into the weld pool.
Welding thin metal semi-automatically
Depending on the type of metal, welding can be performed in one of two ways:
- Conventional sheet blanks can be welded using any method.
- Thin rivet material should be overlapped. It is boiled through the holes that were previously prepared in the top sheet.
When performing work, you need to pay special attention to some nuances:
- wire feed speed, voltage and current are reduced to the minimum permissible parameters;
- It is not allowed to delay the electric arc in one place. This may cause burnt to the workpiece or bead overflow;
- It is advisable to start welding the rivet material from the center of the lower workpiece. Otherwise, you can fill the previously prepared holes.
In cases where tightness is not a prerequisite, you can resort to a point connection. The distance between welding points can be from 1 to 5 centimeters.
Preparation of semi-automatic machine, wire and gas
- turn on the gas supply if a high-pressure cylinder is installed;
- excite the arc by touching the wire to the workpiece;
- press the button that feeds the wire.
The following rules must be followed:
- cook so that you can see the weld pool, that is, hold the wire, and therefore the burner, straight or at a slight angle;
- maintain the same gap between the parts (if the parts are 1 cm thick, it should be at least 1 mm, then it is calculated based on the thickness of the metal being welded - 10% of the thickness);
- If it is necessary to make a connection on a lining, it is placed tightly to the parts from below.
Attention! The setting of the semi-automatic welding machine depends on the model of the device and must correspond to the thickness of the product and the grade of metal. Therefore, it is necessary to read the manufacturer’s instructions, which he describes in the accompanying documents, and only then cook.
Welding thick metal semi-automatically
Metal with a wall thickness of more than 4 millimeters requires preliminary preparation: chamfers are removed from both edges. This allows you to form an even and at the same time very strong seam.
When working with thick workpieces, you should perform oscillating movements with the torch so that a large area of the edges is heated. The manufacturer encloses documentation with semi-automatic welding machines that contains useful reference information. Among other data, there are tables with recommended parameters for welding thick metal workpieces.
Basic rules for performing work:
- the gap between the edges should not exceed two millimeters;
- the width of the weld must correspond to the thickness of the metal;
- When choosing consumables, you should take into account the recommendations of the equipment manufacturer.
If a specialist is tasked with boiling a workpiece with a thickness of more than five millimeters as best as possible, then the work must be completed in several approaches. The first step is to weld the center of the joint. After this, the part is boiled on top and bottom. It is advisable to weld workpieces in an open area or in a spacious, well-ventilated room.
Possible adjustments during the welding process
In order for the seam to turn out smooth and beautiful, you need to feel the semi-automatic machine and be able to adjust it correctly. It is necessary to set the necessary parameters according to the setting tables that are attached to the technical documentation for the device of a particular type. You cannot cook at a low operating current: this will affect the quality of the seam, and in some cases it will not even be possible to connect the parts together. The following principle is observed: the thicker the metal, the higher the operating current or voltage (depending on the operating principle of the semiautomatic device).
More details about the adjustment in the video:
Semi-automatic wire welding
Filler wires
When joining metals semi-automatically using filler wire, it is necessary to take into account some nuances:
- correspondence in chemical composition between the filler material and the material being welded is required;
- the wire must be from a trusted manufacturer, that is, high-quality and certified;
- The terms and conditions for storing the additive must be observed.
It so happens that in production and at home you most often need to cook steel or manganese. It is for these purposes that the wire supplied for welding work is most in demand.
The following types of material are used to work with ferrous metals:
- Sv-08GS. Applicable to alloy or low carbon steel;
- Sv-08G2s. Designed to work with high carbon steel.
Very often, flux-cored wire is used to make ferrous metal structures. The material is advantageous in that it makes it possible to work without supplying shielding gas to the welding area. There is no need to carry a cylinder of inert gas to the site. This is important when speed of work combined with mobility is required: you need to quickly visit several sites.
The material is a tube made of low-carbon steel, the cavity of which is filled with a special powdery composition. The metal melts, releasing powder. As a result of its combustion, a gas cloud is created, which protects the working area from atmospheric air. In the vast majority of cases, the powder contains metal dust and rutile.
To connect stainless steel, wire Sv.-06Х19Н9Т, Sv.-01Х19Н9 or Sv.-04Х18Н9 is used. These materials provide high weld strength. SV-AK5 wire is intended for aluminum workpieces. Its characteristic feature is the original color of the seam.
Preparation for the welding process
Preliminary preparation is required before starting welding work. It consists of four stages:
- Bevels or chamfers are created on the edges.
- The surface is cleaned of dirt.
- The welding zone is treated with a caustic substance, which will prevent the rapid formation of a refractory film of aluminum oxide.
- The Teflon channel is treated to reduce friction of the filler wire on its walls.
A novice welder must learn that in any situation, before starting work, in addition to those listed, the following manipulations must be performed:
- remove currently unnecessary tools and other items from the workplace;
- provide maximum flow of lighting to the workplace;
- arrange the tools and auxiliary equipment necessary for work;
- check the integrity of the cable and the readiness of the extension cords.
After this, you can begin preparing the equipment. Procedure for performing manipulations:
- carefully lay out the welding sleeve;
- check the condition of the burner nozzle;
- connect the gas cylinder;
- secure the parts to be connected on the table. If the work is carried out directly on the structure, then ensure the immobility of the welded surfaces using accessible methods;
- put on overalls and other welder’s equipment;
- give power to the semi-automatic machine;
- bring the burner to the joint.
After completing the work
After completing the work you must:
- shut off the supply of wire and inert gas;
- disconnect the device from the power source;
- allow the seam to cool;
- carefully inspect it and if defects are found, repeat the welding.
The semi-automatic machine makes it possible to use different types of filler wire.
It is important to use available protective equipment to the maximum. Complete equipment consists of the following functional components:
- Eye protection. Ideally, when performing welding work, use a special mask. It is also permissible to wear safety glasses or use a face shield.
- Respiratory protection. There are special filter masks that are useful in conditions of poor or no ventilation.
- Splash protection. A special suit made of heat-resistant material helps to avoid burns.
Safety precautions
To avoid injury, follow simple safety rules:
- When performing work, you should constantly be on wooden scaffolds.
- To illuminate the workplace, use light from 12 volt power sources.
- At heights it is mandatory to take insurance. The size of the insurance string must be at least two meters.
- Welding work in enclosed spaces should only be carried out with effective exhaust hood. In cases where ventilation is not possible, the welder must use a hose gas mask. In low smoke conditions, working in a respirator is allowed.
- It is strictly forbidden to handle parts to be welded with bare hands.
- Work in open areas is prohibited during precipitation.
Preparing the welding machine for work
Like any type of activity, carrying out welding work requires compliance with the rules of preparation for the process, this will ensure the safety and quality of the process itself.
Before starting work, you need to prepare the welding surface to avoid the appearance of pores. To do this, you need to remove dust, debris, dirt, moisture, oil, as well as rust up to 30 mm from the edge of the gap from the surface.
The surface can be cleaned with a metal brush, a steel brush for metal, rags, or a sandblaster, then it must be degreased and etched.
It is also necessary to prepare the welding machine; for this, the following preparation steps must be followed:
- Check the grounding of the device. Any cooking equipment must be checked for connection to the grounding conductor. Missing or malfunctioning jeopardizes the safety of the welding process.
- Checking the network voltage. Many devices are sensitive to power surges and may fail. Therefore, the voltage in the network must be stable.
- Select the welding machine mode. Modern semi-automatic machines have many welding modes and its adjustment. With their help, you can adjust the welding to the material being welded and the nature of the welding.
- Before starting work, you need to adjust the diameter of the tip; it should be several millimeters larger than the size of the wire.
- Check the adjustment of the tip and feed mechanism. If these elements are upset and configured incorrectly, this can lead to operational errors or damage to the material being welded.
- Checking the quality of the wire. It should be smooth without burrs, dents and various kinds of scratches.
Solaris MULTIMIG-225
The first semi-automatic machine in our rating is the MULTIMIG-225 model from the Solaris brand. The device is not cheap, but it boasts excellent technical characteristics. The semi-automatic machine produces an honest 220 Amps when welding in MIG mode and 200 Amps when welding in MMA mode. This is enough to perform most welding work in a country house or small workshop.
MULTIMIG-225 works perfectly even with unstable or low voltage, which is very important when welding in the country. The heart of the device is modern IGBT transistors, thanks to which the semi-automatic machine can boast of great functionality. For example, the machine is capable of not only MMA and MIG welding, but also spot welding under certain settings. In short, a universal assistant in everyday life and during repairs.
The device comes with a burner with a Euro connector. The body has a convenient metal carrying handle. The body itself is also made of metal and is resistant to corrosion.
Below is one of the real reviews from a welder:
I spent a long time choosing a welding machine and noticed that my neighbor had this exact model. I used it a couple of times and was pleased with the results. I bought myself exactly the same Solaris. I am 100% confident in him! The seams turn out neat, just as needed. The metal does not spatter, the arc burns well. I use it and enjoy the work.