Stainless steel is used in many industries, as well as in everyday life. When eliminating possible breakdowns of parts and connecting individual parts, semi-automatic stainless steel welding is used. Special equipment and a protective gas environment will help avoid the appearance of defects at the joint.
Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel
Features of stainless steel
The process of joining stainless steel by welding is considered complex. This is due to the composition of stainless alloys, as well as their characteristic properties.
Types of stainless steels
The material is classified into:
- Ferritic structure. Such alloys contain chromium in amounts up to 20%. Used in heavy industry for the manufacture of heating systems. Resistant to corrosion and also capable of magnetization, this metal is considered in demand.
- Austenitic structure. Contains nickel and chromium. They make up up to 70% of all stainless alloys in industry. They are resistant to corrosion and have high strength, unlike analogues.
- Ferrite-martensite structure. They have a needle-like carbon structure, which is why they are considered a durable type of stainless alloy. Resistant to premature wear and able to withstand elevated temperatures. The composition contains a minimal amount of foreign impurities.
- Combined structure. This category is obtained by combining the main types. Manufactured using new technologies. Contains all the beneficial qualities of the materials used.
Properties and weldability of stainless steel
Stainless alloys have the following properties that can affect the welding process:
- The thermal conductivity of the material is 2 times lower than that of carbon steels. Because of this property, the weld pool overheats and corrosion resistance decreases. To prevent this, the junction is cooled.
- The low melting point promotes the formation of metal at the welding site with a melt temperature of 500°C. This phenomenon will subsequently lead to the appearance of seam defects and cracks will form. Forced cooling must be used.
- High thermal expansion will lead to mechanical deformation at the weld. To prevent this, it is recommended to leave a gap of a certain size between the parts.
- Reduced electrical conductivity is the main characteristic of stainless steel. This property leads to critical heating of alloyed electrodes.
Intrinsic characteristics make stainless alloys difficult to weld. For a normal connection, it is necessary to use forced cooling of the seam.
Preparatory work
Before cooking stainless steel with a semi-automatic machine, careful preparation is required:
- Clean work surfaces until shiny;
- degrease parts with acetone or any organic solvent;
- if the metal thickness is more than 4 mm, process the ends so that a small space is formed between them for filling with metal;
- warming up the parts to 100, remove excess moisture;
- heat the metal to 200 to relieve internal stress.
In production, to remove surface contaminants: carbon deposits, traces of grease, rust, parts and wires are etched with a solution of hydrochloric or sulfuric acid. After this, rinse with hot and cold water and dry.
The flow rate of the gas mixture at an operating pressure of 0.2 atmospheres using a reducer is set within the range of 6-12 m3/min. Failure to comply with these indicators reduces the quality of the seam.
Adjustment of current and voltage depends on the power of the device.
The penetration depth, arc length, and weld shape depend on these parameters. As the current increases, the deposited weld becomes wider, and the welding depth decreases.
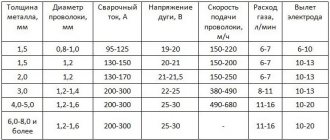
Some settings for a semi-automatic welding machine:
| Metal thickness, mm | Wire diameter, mm | Gap when butt welding parts, mm | Current strength, A | Welding voltage, V |
| 1 | 0,8 | 0 | 65 | 17 |
| 1,5 | 0,8 | 0 | 115 | 17 |
| 2 | 0,8 | 0,5 | 130 | 17,5 |
| 3 | 1 | 1 | 210 –215 | 18 |
| 4 | 1 – 1,2 | 1,5 – 2,5 | 220 – 280 | 20 |
| 5 | 1,2 | 2,5 | 190 – 300 | 21 |
| 6 | 1,2 | 2,5 | 300 | 22 |
Each machine is supplied with a table of welding modes. The master selects the semi-automatic operating mode, depending on the welding parameters. After setting up the machine, weld on a test piece. If necessary, adjust the settings.
Semi-automatic stainless steel welding technology
To improve the quality of the connection, as well as reduce the level of falsity in the welding process of stainless alloys, semi-automatic devices are used. The equipment gives:
- providing the weld pool with gas to protect it from outside influences;
- feed of filler wire;
- forced cooling;
- the ability to perform work in hard-to-reach places.
During the welding process, areas of increased internal stress are formed on the metal surface. To prevent this phenomenon, it is recommended to carry out processing by heating the part to a temperature of 760°C and further self-cooling.
Shielding gas - how to use and is it always necessary?
It has already been mentioned that there are three options for inert gas that can be used when welding stainless steel with a semi-automatic machine. Namely:
- In an argon environment. The advantage of this method is that the seam is aesthetically pleasing. The disadvantage is a large amount of splashes of molten metal. The arc burns unstable, and the cost of argon is high.
- In a carbon dioxide environment. The most budget-friendly welding method of the three options. However, the resulting splashes are even greater than when working with argon. And the seam turns out very rough and unattractive.
- A mixture of carbon dioxide and argon. The best option that allows you to combine the advantages of both inert gases is high quality welds combined with low cost.
If the requirements for the quality of the weld are not high, then the percentage of carbon dioxide in the mixture can be increased to 30. But most often, combinations of argon and carbon dioxide are used in ratios of 95-98% and 5-2%, respectively.
Regarding the question of whether it is always necessary to use an inert gas, there is a clear answer - no, not always. A protective environment is needed, but it can be provided without gas. An alternative solution is cored wire. It is a thin-walled narrow tube containing flux inside. The flux, coated with a protective metal layer, is released during welding and provides protection to the molten metal from atmospheric oxygen.
It should be borne in mind that the degree of protection of the working area when using wire with flux is less than when working with gas. The seams are not as reliable and aesthetically pleasing. Therefore, this welding method is less in demand and is used less frequently.
To summarize, we can emphasize that among the advantages of using shielding gas with filler wire (let's call this option classic) are high productivity and a minimal amount of molten metal splashes. Its disadvantages are the need to carry a cylinder with the gas itself and some associated restrictions when used outside stationary welding stations.
Flux-cored wire makes it possible to get rid of these shortcomings. You can carry out welding work anywhere and there is no need to drag a heavy cylinder of inert gas with you. But this method has its drawbacks. And they consist in the high cost of consumables, the abundant formation of slag on the surface of the seam and the need for additional protection against corrosion after completion of welding work.
Materials and equipment
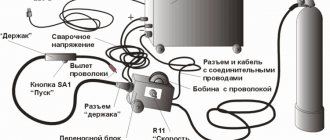
Semi-automatic machines are used in the welding process. They are provided with a wire feed system as well as shielding gas. A semi-automatic welding machine must have the ability to switch polarity, as well as control and adjust basic parameters.
Wire for welding stainless steel
To ensure a reliable seam, it is necessary to use semi-automatic stainless steel welding wire. It is also made from stainless steel materials. If it is not possible to use a gas environment, it is recommended to use cored wire; it has a hollow structure, the void is filled with flux. The disadvantage of the latter is the subsequent appearance of cracks in the structure of the seam.
Gas selection
The use of gas is due to the need to protect the joint from harmful oxidation. In this case, the substance should not enter into chemical reactions with the metal, which could reduce the characteristics of the stainless steel. In this case, inert gases with added carbon dioxide are used.
Gas cylinders
Gas selection
Semi-automatic welding without the use of shielding gas is only possible if we are talking about the use of flux-cored filler wire. In this case, the seam protection is created from the powder with which the wire is coated, which prevents air from entering the weld seam.
If welding occurs using wire made without a special coating, then it becomes necessary to select a special shielding gas, which will also protect the weld from air ingress.
Two gases can currently be used for welding stainless steel:
- carbon dioxide;
- argon.
Experienced welders use a special mixture for this type of welding, which combines argon and carbon dioxide. The most common percentage of such gases is: 98% argon, 2% carbon dioxide.
However, each welder, depending on his work experience, preferences and technological requirements for the quality and appearance of the weld, selects the mixture parameters in his own way. The main condition for this is to ensure maximum protection of the welding zone.
Approximate cost of argon cylinders of different volumes on Yandex.market
How to cook stainless steel semi-automatically
Often, connection parts may be located in hard-to-reach places. Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel provides a reliable seam that is protected from premature wear.
Metal preparation
Before performing work on connecting with filler wire, it is necessary to prepare the parts:
- remove all contaminants at the connection point;
- degreasing the metal is carried out to ensure the reliability of the seam and protection from cracks; solvents will help with this;
- To remove excess moisture, it is recommended to heat the parts to 100°C.
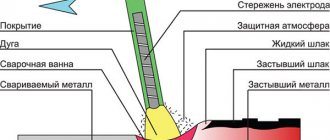
Welding technical diagram
Three methods are used to join stainless alloys by welding:
- for parts of small thickness, the short arc method is required;
- with jet transfer, a welded stainless steel joint is obtained for parts of large thickness;
- The impulse method is considered universal.
The technological process requires following certain rules:
- for a good view it is necessary to place the burner at a negative angle to the seam;
- the head should be kept at a distance of 12 mm from the metal surface;
- the wire should melt in small portions, without large drops.
The welder is recommended to fulfill a number of requirements:
- welding is carried out with reverse polarity of the terminals;
- the angle value regulates the quality and width of the seam;
- the extension length of the filler wire should be no more than 12 mm;
- dried gas must be supplied to the weld site at a flow rate of up to 12 m3/min;
- to prevent splashes, the surfaces are treated with a chalk solution;
- It is recommended to make the beginning and end of the seam at some distance from the edge of the parts.
Correction of defects
When performing welding work, deformations may occur at the joints; this occurs as a result of heating. To resolve this, do the following:
- when bubbles form at the seam, use the method of tapping with a hammer from the edge of the parts;
- warped metal must be straightened by heating the part with a torch, as well as tapping with a hammer.
To obtain a seam, it is necessary to study the theoretical part, as well as perform test welding on samples.
Options for setting welding machine modes
In order for the quality of the welded joint to be maximum, and the joint itself to be extremely strong and not to be destroyed soon after the product starts to be used, it is necessary to correctly select the welding machine modes.
When selecting the parameters in which the device will operate, it is necessary to rely on the following initial data:
- connection design option (angular bottom connection, bottom butt connection or vertical spatial);
- thickness of the welded joint parts (the thicker the metal, the higher the parameters of welding current and welding voltage);
- wire thickness (the rule of direct dependence of welding current and welding voltage on wire thickness also applies here);
- the presence or absence of a gap when butt welding parts and the size of such a gap.
If we are talking about welding parts, where the metal thickness of each part is 0.8 mm, and which is carried out end-to-end with zero gap using wire also 0.8 mm thick, then the welding current is in the range from 50 to 80 A, the welding voltage is not may be higher than 16 V.
All main welding modes can be seen in the table.
Sequence of work progress
Stainless steel welding can be carried out in three main ways:
- Using a short arc - semi-automatic gas welding, especially suitable for working with thin workpieces;
- with jet transfer - cored wire is used;
- The pulse method is the most accurate and efficient, when the wire is fed into the welding zone by pulses in the form of small drops.
Before cooking stainless steel semi-automatically in carbon dioxide, you need to take into account the general provisions:
- Set reverse polarity - turn on the burner in the positive terminal, and the workpiece in the negative terminal;
- the current should be approximately 20% lower than for conventional welding;
- departure, i.e. distance from tip to tip of wire, no more than 12mm;
- To remove water vapor, the gas passes through a dryer located before or after the reducer.
- fill the device with a coil of wire. Using the broaching mechanism, its tension is adjusted.
What you need for welding
- Current source (semi-automatic);
- welding wire;
- shielding gas.
The welding wire must be identical to the metal being welded. In our case, choose stainless steel for a semi-automatic machine.
Stainless steel welding wire for semi-automatic machine
There is wire from Russian and foreign manufacturers on the market, which is divided into flux-cored and solid wire. Diameter from 0.13 to 6.0 mm. At home, diameters of 0.6 and 0.8 mm are used, and over 1.0 mm in production.
- Solid wire is used for gas shielded and submerged arc connections. This method eliminates the entry of air into the welding zone, thereby improving the quality of the weld.
- Corroded stainless steel wire (self-shielding) is a thin-walled tube filled with flux and gas. The mixture of components allows you to weld products without protective gases (carbon dioxide and argon).
Wire for welding stainless steel semi-automatically, produced with heat treatment or cold drawn. And it is divided into oxidized (T) and light (white, TS).
Stainless steel wire is available in 2 accuracy classes:
- increased accuracy (P);
- normal accuracy.
Wire with increased precision is used to improve the quality of the seam.
Stainless steels are divided into different grades based on their chemical composition, and the wire also has different markings. The table (below) will introduce the brands, diameter and weight of stainless steel wires:
Cost of stainless wire for semi-automatic machine
The price varies depending on the manufacturer and the region of residence of the buyer.
- ER 308 LSI 0.8mm 1kg - 825 RUR;
- ER 308 LSI 0.8mm 5kg — 4237 rub.
Video:
Gas selection
Semi-automatic cooking without gas is prohibited, except when using cored wires. Semi-automatic welding of stainless steel can be performed in an environment of carbon dioxide or a mixture of carbon dioxide and argon.
Carbon dioxide is a readily available and cheap gas for joining stainless steels. When used cleanly, the welder is faced with excessive spattering of metal and a clumsy weld.
It is more convenient to use a mixture of argon and carbon dioxide, percentage ratio 98/2 (Ar-98%, CO2-2%). Experienced welders vary the composition of the mixture depending on the brand of stainless steel and their preferences.
The percentage of carbon dioxide and argon can be adjusted using two separate cylinders. Connect the outputs from the two gearboxes using a tee taken from the windshield wiper of a domestic car. Details of this design are in the video:
That's it, all you have to do is select the shielding gas and connect the wire to the device. Be aware: the conductive tip must be the same diameter as the wire.
Buy tips with a reserve; during operation they burn out and the device then cooks worse.
Video: how to set up a semi-automatic machine for operation (for beginners).
How to weld stainless steel in a carbon dioxide environment
Use a grinder to clean the working surface of the product, and when connecting metal with a thickness of 4 mm or more, make edges (grooves for depositing metal). This article talks about marking stainless steels and preparing surfaces.
After cutting the chamfers, join the parts together using clamping pliers, leaving a gap between the products (at least 1.5 mm).
The gap should be along the entire length of the workpiece; it will allow the metal to be welded to its full thickness. Connect the ground and set your settings on a semi-automatic device depending on the design of your device and the thickness of the metal.
Simple semi-automatic machines on the front panel have 2 adjustments:
- welding voltage;
- wire feed speed.
Advanced models are equipped with an inductance adjustment knob. Also, the wire feed speed depending on the diameter can be adjusted by a switch.
Setting the inductance changes the arc rigidity, penetration depth and bead shape:
- With low inductance: the arc is cold - we get a thin bead with deep penetration;
- With high inductance: the arc is hot - a wide bead with shallow penetration.
Holding the torch with a slope of 20-60 degrees (the distance from the nozzle to the weld pool is 10-20 mm), use short tacks to make a stainless steel connection. They pulled the trigger, released it, pressed it and released it, and this is how the cut edges are slowly filled with metal. You can cook either with an angle back (toward you) or with an angle forward (away from you).
The tables (below) will help you decide on the settings of the semi-automatic machine:
When welding with an overlap, there is no need to cut chamfers; it is enough to clean the surface, place the parts on top of each other and make the connection.
During the welding process, before making a new seam, bite off the weld bead at the tip of the wire.
In the process of joining stainless steel semi-automatically in a carbon dioxide environment, change the wire feed speed, with such manipulations you will achieve a high-quality seam.
Video:
Stainless steel, due to the chemical elements it contains (for example, chromium), is slightly susceptible to corrosive environmental influences. However, such properties of this metal require a careful approach to the process of its welding, which is expressed in the subtleties of selecting filler materials with which the welding process is carried out.
Read also: Gasoline motor pump for water characteristics