Anyone who owns their own home knows how often they have to do repairs, design or build something. Therefore, the farm must have various tools. Often you have to perform operations with metal: cut it, connect it. Sometimes you can get by with simple twists and bolted connections, but in some cases welding remains the only option. The simplest method in this case is electric arc welding, and the most affordable and reliable machine is a welding transformer.
The transformer unit is good because it works from any outlet where there is a standard alternating voltage, and the internal circuit of the welder is so simple that there is absolutely nothing to break.
Types of welding transformers
On sale you can find the following transformer-type welding machines, mass-produced:
- Units with amplitude control, which have normal magnetic dissipation, and the choke has an air gap.
- AC welders with amplitude control, which have increased magnetic dissipation - windings in a moving state or spaced apart, having a reactive nature, a moving magnet or a shunt that is magnetized, with capacitor or pulse type stabilization.
- Thyristor models where the phase is regulated - stabilization is carried out using a pulse type or by the make-up method.
In the first two categories of welding transformers for household or professional configurations, amplitude adjustment is carried out by changing the transformer resistance or by adjusting the voltage when idling. The shape of a single-phase signal, namely a sine wave, remains unchanged.
Welding thyristor transformers have phase regulation in their circuit. The main types of such units operate on the principle of converting a sinusoidal signal into a form close to pulses of different alternating polarities.
Equipment design
With the classic design of a welding transformer with a moving winding, it contains the following elements:
- The metal case is rectangular in shape, with longitudinal holes on all sides for air circulation during cooling.
- The cover on which the welding current adjustment element is located.
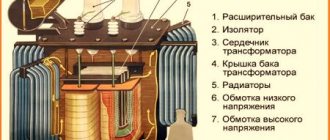
- The transformer itself has two windings of primary and secondary purposes with a magnetic circuit or core of a closed structure, an adjusting screw, along the tape thread of which a running nut with a winding fixed to it moves.
- A handle connected to an adjusting screw and used to control the clearance.
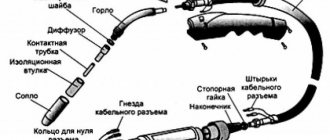
- Terminals or clamps for connecting power cables to the welding unit with an electrode holder and a common terminal.
Magnetic core
Since the magnetic circuit in a welding transformer is one of the main elements, we should talk about it separately. The main task of the magnetic circuit is to transmit the magnetic field from the primary winding to the secondary. Moreover, the closed core itself is not an element that can in any way affect the current strength. The material from which it is made is electrical steel. The core does not have an all-metal shape, but is assembled from individual plates isolated from each other with a special varnish.
The purpose of combining the plates into one group is to prevent the occurrence of currents in the core that counteract the magnetic induction and thus weaken it.
How to reduce the noise of a welding transformer? When large currents pass through the windings of the transformer, due to the strong magnetic field, the core plates begin to emit a hum. To reduce it, you need to tighten the plates as much as possible.
Repairing DC devices
The simplest diagram of a welding machine allows you to study the device and make the necessary repairs when a breakdown is detected.
The device is powered strictly from the mains and is standard 220 Volts. A 10 A fuse is connected to the primary winding (burnout of the part allows you to quickly eliminate the malfunction by ensuring a simple replacement). The SA1 16A machine is also additionally supplied.
The power part of the device becomes faulty for the same reasons as transformers. The electronic part includes a rectifier and control unit. It may indicate a malfunction of the diode bridge or other parts.
Rewind
Repairing welding transformers in the current mode when rewinding the device requires performing certain preparatory actions to select the necessary materials:
- wire for primary and secondary rewinding (the quantity and grade of material can only be found out after complete disassembly of the device);
- shellac (replaced with tsaponlac, PF paint);
- a mandrel or block to provide a secondary winding (according to the dimensions of the measured coil frame), made of special wedges. The required values are obtained after unwinding;
- varnished fabric
During repairs, the windings are unwinded, turns and layers are counted, and the obtained values are recorded on paper.
Calculation of the length of the required distance:
- obtaining the length of the “average turn” (the average number between the maximum value of the turn length in the outer and inner layers);
- number of layers obtained, turns.
Determining the distance of the required wire involves multiplying the length of the “middle temple” by their number and the number of layers.
Based on the surviving part of the winding, the required cross-sectional diameter and type of wire are determined. The primary winding of thin wire is wound directly onto the frame, and the secondary winding onto the mandrel with preliminary winding of one layer of varnished cloth.
The turns are wound tightly to each other and the number of turns is strictly observed. Each layer of winding is carefully treated with shellac and a layer of varnished cloth is applied. Drying the materials prevents the movement of wires that can occur when the insulation heats up and breaks down.
After winding, collect the coils of the repaired device and dry them thoroughly. Using a tester, the integrity of the winding is checked.
Important! The primary winding should have a resistance value of about 20 Ohms, and the secondary winding should not exceed 0 Ohms.
The serviceability of the device is checked by measuring voltage values and simultaneously connecting the device to the mains. If all data matches, the repair was successful and the transformer can be used for its intended purpose.
Do-it-yourself welding transformer repair
Before you independently carry out repairs on the design and maintenance of welding machines, you need to check some important aspects:
- compliance of the necessary parameters (selected polarity, current value, materials being processed, electrodes used (diameter, size);
- required cable contact and clamping;
- possible detection of excess continuous operation time or cable breakage.
If the above malfunctions have not been identified, then the protective housing of the transformer should be removed and an external inspection should be carried out to identify visual damage:
- changing the appearance of the contact block;
- violation of the insulation of one of the supply wires;
- weakening of the fastening contact;
- the absence of voltage on the secondary winding requires rewinding the transformer (this process is discussed in detail above).
Important! If you do not have the skills to properly repair and maintain welding transformers, you must contact a service center and get qualified advice from specialists.
Carrying out a complete renovation
Overhaul of a welding transformer involves performing the following actions:
- complete disassembly of the device;
- installation of new parts that need to be replaced.
Parts to be replaced:
- primary or secondary winding coil;
- capacitors, choke;
- contact units (pads, clamps);
- moving mechanisms, components.
When carrying out a major overhaul, all technical characteristics after replacing parts must correspond to the device. The agreement with the customer involves a complete repair of this device to ensure a longer service life and avoid repeated breakdowns.
Repair prices
The cost of repairing such devices is based on 2 important aspects:
- the cost of parts that need to be replaced;
- payment for services performed.
In order to profitably repair a device, you must first take into account the cost of repair and compare it with the price of a new transformer. In some cases, it is more profitable to buy a new device and not waste extra time troubleshooting.
Important! A damaged transformer can be disassembled and the copper winding can be sold for scrap, and the proceeds can be used to purchase a new device.
Welding transformers are devices that require ongoing repairs as needed and regular maintenance. If these standards are observed, serious malfunctions in the device can be easily prevented.
Operating principle of a welding transformer
The welding type transformer is a step-down type device. It converts high voltage to lower voltage. Due to this, the current strength in the secondary winding increases, which is capable of melting the metal during welding. There is nothing complicated in the physical process itself - the principle of operation in a transformer with a moving winding:
- When a high-voltage alternating voltage is applied to the primary winding, a magnetic field flux is formed in it, which is of an alternating nature.
- This magnetic flux penetrates the core. The latter, in turn, transmits the field to the second winding, while reducing the loss of magnetic induction in space.
- Magnetic induction induces an electromotive force (EMF) in the secondary winding, which causes the electrons of the metal to move, that is, an electric current is obtained.
- Since there are fewer turns in the secondary winding than in the primary coil, the voltage at the transformer output drops and the current increases.
- When the electrode is connected to the workpiece, an electric arc occurs, which transfers metal particles from the electrode to the parts being welded.
In addition to the welding mode, when the welding transformer is under load, the welding transformer circuit can be in idle mode.
Idling
Idling does not mean that there is no current flowing in the secondary coil wire.
It can arise due to magnetic leakage fluxes. This is not always safe for the welder, since the voltage at the terminals of the secondary winding of the transformer increases more during idle than under load, and you can get an electric shock. To avoid this, the metal body of the unit must always be grounded. Also, some models of welding transformers are equipped with a protection unit against increasing no-load current. This unit is switched on immediately upon completion of the welding operation.
What malfunctions can there be
When working with a welding transformer, the following problems often arise:
- No arcing, cooling fan failure to start. The main reason is a violation of the integrity of the power cable. It is less common to detect damage to other equipment components or activation of overheating protection.
- No welding arc when the fan is running. It is observed when there is a breakdown in communication between the internal components of the system.
- No electric arc when the warning light is on. This problem occurs when the protective mode is triggered.
- Formation of a large amount of splashes. The seam quality remains low. It is worth checking that the wires are connected correctly and changing the polarity.
What characteristics to consider when purchasing
Remember! When buying a welding machine based on a transformer, you need to realize that this device is good for its simplicity, but it is rarely possible to get a beautiful weld on it. Therefore, inexpensive devices of this type are suitable only for domestic needs without claims for professional welding. If we take serious transformer units with an arc stabilization system, then they will cost a decent amount and should justify themselves.
When choosing welding equipment, look at the following parameters:
- The value of the welding current, which for weak household models is no more than 200 amperes, for semi-professional ones will reach 300 amperes, for powerful production models it exceeds 300 amperes.
- The thickness of the electrode and the type with which the device is capable of working. For welding thin-walled and medium-thick metal workpieces, a welder working with 2- and 5-mm electrodes is suitable; for welding thick walls, the unit must be able to melt electrodes with a diameter of over 5 mm.
- Power consumption and output efficiency. More powerful three-phase units are more often used as industrial equipment.
Tools
0 votes
+
Vote for!
—
Vote against!
Today you won’t surprise anyone with a manual arc welding machine. Thanks to this invention, welding of sheets, pipes, channels and other elements and structures made of ferrous metals, both in industry and in private households, became widely available. The most widespread among all welding equipment are AC welding transformers. These simple, unpretentious and reliable units for manual arc welding are powered by a conventional 220 or 380 Volt network and are capable of working in difficult conditions. The development of electrical engineering and electronics has made it possible to create welding transformers of various modifications, which has significantly expanded their range on the market. But there are no particular difficulties in how to choose a welding transformer. The main thing is to understand the types of welding transformers, know why and how the device will be used, and also understand what characteristics you should pay attention to when choosing and purchasing.
- Types of welding transformers
- Transformers with minimal and normal magnetic leakage
- Transformers with increased magnetic dissipation
- Thyristor transformers
- Characteristics of welding transformers
- Marking of welding transformers
- Welding current control limits, A (min-max)
- Electrode diameter
- Mains voltage and number of phases
- Rated welding current of the transformer
- Rated operating voltage
- Nominal operating mode PN %
- Power consumption and output (efficiency)
- Open circuit voltage
- Number of serviced workplaces
- AC/DC
- Cooling type
- Weight and dimensions of the welding transformer
Those who are going to purchase this unit for the first time and work with it need to know and understand how everything works. The transformer itself consists of two windings - a primary and a step-down secondary, wound on a core. The principle of operation of the welding transformer is quite simple and consists in converting the incoming voltage of 220 or 380 Volts into a lower one, about 30 - 60 Volts. At the same time, the current can reach 700 Amperes, which allows metal products to melt and weld together. All types of welding transformers operate on this principle. But thanks to developments in the field of electrical engineering, it was possible to create more advanced and easy-to-use models of welding transformers.
Types of welding transformers
Quite a long time has passed since the creation of the first welding transformer. During this period, new technologies appeared and new modifications of welding machines were created. Today there are three main types of welding transformers. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. When choosing a welding transformer, it is important to understand the differences between the models and for what purposes each is more suitable.
Transformers with minimal and normal magnetic leakage
STE welding transformers are designed in such a way that the windings have minimal magnetic dissipation. The current strength is adjusted by a screw choke mechanism, which is located separately. This welding transformer circuit is used in models STE-85 and STE-24U.
Transformers with normal magnetic leakage are similar in their design to those described above. The difference lies in the presence of an additional reactive coil located on the main rods of the magnetic core of the primary and secondary windings, as well as on the additional inductor winding. The inductor itself is mounted on a magnetic core. The current strength is adjusted in the same way as for STE transformers. Welding transformers with normal magnetic dispersion are represented by models such as STN and TSD. The windings of such transformers are made of copper and aluminum.
Models STE , STN and TSD are used for manual arc welding; they are simple and trouble-free in operation. But, despite their simple and reliable design, these transformers have a number of significant disadvantages. Firstly, the vibration of the inductor core disrupts the current setting during operation. Secondly, welding transformers with normal and low magnetic leakage have high power consumption from 25 kW to 78 kW. Thirdly, large mass - more than 120 kg. Also among these transformers there are models such as TSD-1000-4 and TSD-2000-2, capable of delivering a rated welding current of 1000 A and 2000 A. But the mass of these transformers, as well as STN-700, STN-500-1 , STN-350, TSD-500 from 220 kg to 675 kg, which makes them very inconvenient for private use.
Transformers with increased magnetic dissipation
The fundamental difference between transformers with increased magnetic dissipation and welding transformers with low and normal dissipation is the movable design of the windings or shunts. This approach made it possible to achieve higher performance characteristics with a relatively small mass of the transformer itself. For comparison, you need to look at the SGE-34U model and the TDM 503 welding transformer. With almost equal performance characteristics, the difference in weight is almost half as much in favor of the TDM.
Transformers with increased magnetic dissipation include models with moving windings, such as the TS-500, TSK-300 welding transformer and TD-300 welding transformer. There are also models with movable magnetic shunts, such as STSh-250 and welding transformer TDM-317. In addition to those listed, there are those with fixed magnetizing shunts and windings - TDF-1001 and TDF-2001, as well as transformers with complex magnetic commutation. For example, a welding transformer VDU-506 or a welding transformer VD-306. Today, for private use, the most common models of welding transformers are TD, TS and their modifications TDM , TDE and others. Welding transformers with increased magnetic dissipation are used for arc and automatic welding, as well as for submerged arc welding.
Thyristor transformers
Another type of welding transformers are thyristor welding transformers. This is a relatively new type of welding equipment. Its operation is based on the principle of phase regulation of current strength using thyristors, which convert the incoming alternating current into alternating pulses. Such transformers were originally used for slag and resistance welding due to arc instability. Today, with the development of semiconductor technologies, thyristor welding transformers have gotten rid of their main drawback and are the latest generation of welding machines. They are widely used for both manual arc welding and spot and slag welding. An example of a thyristor transformer is Deltapower 400E.
Characteristics of welding transformers
Regardless of the type of welding transformer, any welding machine has a number of specific characteristics that determine its operating efficiency and ease of use. When choosing a welding transformer, it is important to know and understand what each characteristic is responsible for and which of them you should pay attention to first.
Marking of welding transformers
The first thing that catches your eye is the name of the welding transformer. For example, the welding transformer TDM-401, the name of which encodes the basic characteristics. This is done so that without a technical passport it is possible to determine what kind of device it is, how it is designed and what its rated current is. Today, the unified system of designation and classification of power sources for welding contains the following rules:
- type of power source: T – transformer, G – generator, A – unit, B – rectifier, U – specialized source-installation;
- type of welding: D – arc, P – plasma;
- welding method: G – in shielding gases, F – submerged arc, U – universal. If there are only two letters, it means that welding is carried out with coated electrodes;
- type of external characteristics: F – rigid, P – falling;
- number of welding posts: M – multi-station, without designation indicates one post;
Important! Sometimes the letter “M” denotes a mechanical method of adjusting the current strength. Also, instead of it there may be the letter “T” or “P”, indicating a thyristor welding transformer.
- rated current is indicated by one or two numbers, rounded to tens or hundreds of Amperes.
- the last one or two digits indicate the registration number in development;
- after the numbers there is a letter designation of permissible climatic use: HL - cold climate, U - moderate, T - tropical;
- the final number indicates acceptable placement: 1 – outdoors, 2 – under a canopy, 3 – in an unheated room, 4 – in a heated room.
For example, the TDM-401 welding transformer tells us that it is an arc welding transformer with mechanical regulation and one welding station, with a rated current of 400 A. Older models, such as the TS or STS welding transformer, carry older markings . So “W” means adjustment using shunts, and “C” means that the device is intended for welding.
Also, the technical data sheet of the welding transformer indicates the protection class according to the international IP system. The tables below provide detailed transcripts.
Welding current control limits, A (min-max)
Perhaps this characteristic is the main one for any welding transformer. Adjusting the welding current indicates two important points at once. Firstly, the fact that adjustment is generally possible, which means that electrodes of different diameters can be used. Secondly, you can see the maximum possible current strength, which will allow the use of large diameter electrodes, which in turn affects labor productivity. This is especially important for those who choose a welding transformer for a workshop or workshop that requires high welding current, more than 200 A. For domestic use, a lower welding current will be sufficient.
Electrode diameter
One of the secondary, but very important characteristics is the used electrode diameter. The table below shows the main electrode diameters depending on the current strength of the welding transformer.
It is necessary to note such an important point as that electrodes of a slightly smaller diameter should be used, despite the given indicators. As practice shows, an electrode selected to the maximum for its current strength will not weld the seam well enough.
Mains voltage and number of phases
This characteristic is one of the main ones. It indicates the required network voltage for normal operation of the welding transformer. It is necessary to know in advance what voltage will be at the place of operation of the welding transformer in order to select the appropriate one. The number of phases of the transformer itself also depends on this. So for a single-phase welding transformer a current of 220 V will be required, for a two-phase one 380 V, but the TD-500 welding transformer, operating both from a 220 V network and from a 380 V network, is three-phase.
Rated welding current of the transformer
One of the most important parameters when choosing a welding transformer. It indicates the maximum value of welding current that the transformer is capable of delivering. Its value determines both the possibility of melting and cutting metal and the electrodes used for the work. It is this parameter that is indicated in one or another model of welding transformer in the form of a two-digit number, such as, for example, in the TS-200 welding transformer, where “200” means that the rated welding current is 200 A.
Rated operating voltage
This parameter indicates the output voltage from the secondary winding, which is necessary to maintain a stable welding arc. As noted earlier, this voltage is in the range of 30 – 60 Volts. The value of this parameter affects the ability to work with metal of a certain thickness. The lower the nominal value, the thinner the metal elements can be welded together. This indicator will be especially important for those who are going to weld car bodies.
Nominal operating mode PN %
This characteristic does not particularly affect the choice of a particular welding machine. But you still need to know and understand what it is responsible for, since the safety of the welding transformer during operation depends on this. The rated operating mode, or as it is also called, the on-time, indicates how long the transformer can be in welding mode. For example, the welding transformer TD-300 has a nominal operating mode of 40%. This means that out of 10 minutes you can work for 4 minutes without a break and rest for 6 minutes, allowing the transformer to cool. Otherwise, you risk damaging the device.
Power consumption and output (efficiency)
With this indicator everything is quite simple. It indicates how much energy is required per hour of operation of the transformer. The lower this figure, the better. But it is also necessary to pay attention to the power output when welding. If the difference between them is too large, then it is better to look for another transformer, the efficiency of which is much higher. Otherwise, you risk wasting many kilowatts of energy while performing a tiny fraction of the required amount of work. Many manufacturers immediately display efficiency, while some only indicate power consumption and output. You should be careful and, when you come across the second option, remember the minimum difference between power consumption and output power.
Open circuit voltage
Another important characteristic is the open circuit voltage, which is responsible for the appearance of the welding arc. The higher this characteristic, the easier it is to create an arc. But there are certain safety restrictions for the operator. So for a network with direct current the threshold is 100 V, for alternating current 80 V.
Number of serviced workplaces
With this parameter everything is quite simple. It indicates the number of welders simultaneously working from the transformer. In fact, this parameter is important for workshops where there is a need for several people to work simultaneously. Household models are limited to one workplace.
AC/DC
This abbreviation indicates the ability of the welding transformer to operate on direct or alternating current. There are transformers that operate only on alternating current, and there are those that only operate on direct current. For example, the Fubag TR-300 welding transformer operates from an alternating current network. Or a welding transformer VD-306, which also consumes alternating current. But both of these devices produce direct current. Their second name is welding rectifiers. It is also necessary to highlight the DECA MMA PRIMUS 250E AC/DC, which is a prominent representative among welding transformers labeled AC/DC.
Cooling type
Another minor, but at the same time quite important characteristic is the type of cooling of the transformer. It doesn’t affect anything, but it can tip the scales in favor of one device or another. There are welding transformers with natural cooling and forced cooling. Essentially, forced cooling is better because it allows you to more effectively get rid of excess heat during operation. But not all transformers are equipped with fans.
Weight and dimensions of the welding transformer
The weight and dimensions of the welding transformer do not affect the performance of the welding transformer. But, nevertheless, these characteristics can influence the choice. After all, it depends on the mass and dimensions of the transformer whether it will be mobile or stationary, whether it will be on wheels or with handles for carrying. Today there are various models on the market and there is plenty to choose from. But it is necessary to immediately make a reservation that high-power and productive welding transformers will be very bulky and heavy, created for industrial conditions. At the same time, more compact and lightweight ones are intended for the common man. Today, the development of technologies in the field of electrical engineering has made it possible to create welding machines with excellent performance characteristics, relatively low weight and rather modest dimensions.
Choosing a welding transformer for a welding novice can seem like a nightmare. Especially if there is no understanding of what this or that characteristic is responsible for. To make the right decision, you should invite a specialist who can help you choose. But if you prepare in advance by studying all the necessary materials about welding transformers, the choice will not be such a difficult matter.
Popular models
BISON ZTS-200 is a compact transformer that can be used to weld low-carbon steel. The installation can take power from both three-phase and single-phase networks, which is selected with a special switch. The device provides welding current in the range from 60 to 200 amperes, which is enough to solve everyday problems when working with metals no more than 6 mm thick. To avoid overheating, the model is equipped with a thermal fuse.
PRORAB FORWARD 180 is a cheap low-power welding transformer for working with cast iron and steel. It uses electrodes with a diameter of no more than 4 mm, the welding current power does not exceed 180 amperes. The device can be powered from 380 and 220 V. The manufacturer equipped the welder with power cables with a crocodile and electrode holder, a face shield, a metal brush and a slag remover.
ELITECH AC 200T is a semi-professional welding transformer powered by any type of network. A powerful model (within 10 kW), which is designed for long-term continuous operation with a maximum current of 200 amperes. It is permissible to work with thin electrodes from 1.6 to 4 mm in thickness. Users describe the welder as a very unpretentious device.
Explore the product! The best thing when choosing a welding transformer is to study the most successful technical parameters for this category of devices and compare them with the parameters of real models offered on the market.
Advantages and disadvantages
The positive qualities of transformer equipment include:
- High efficiency, ease of operation and maintenance. Repairing the device does not involve large expenses, which allows it to be used at home.
- Low cost.
The disadvantages include:
- Arc instability. This is due to the AC parameters. To work with such devices, specialized electrodes are used.
- Changes in output voltage, which negatively affect the quality of the weld.
- Inability to use for joining parts made of non-ferrous metals or stainless steel.
- Dimensions and heavy weight, causing difficulties when moving.
We recommend reading: How to choose a gasoline welding generator
Homemade device options
It is not necessary to buy a welder; you can assemble the design of a welding transformer with your own hands. To do this, use one of the following methods:
- They use an old LATR (autotransformer). The most important thing about LATR is its powerful toroidal core. Two copies of such magnetic cores are taken and a winding is wound on each ring. One will act as a primary, the other as a secondary. The most suitable autotransformer model for such processing is LATR 1M, the original winding of which can withstand current up to 10 amperes.
- A magnetic circuit from an old electric motor is used. What can be taken from an engine to make a welder is its stator. It only needs to be freed from the old winding by removing it from the grooves and removed from the housing by breaking or cutting the latter. The core plates should then be fastened with pins and a new winding wound over it. Those engine magnetic cores that have a large diameter and small thickness are better suited for such operations.
- Transformers from old color TVs such as TS-310 or TS-270 are converted into welding transformers. These network converters are convenient because they are large in size and have an easily disassembled U-shaped core.
Anyone who knows which welding transformer is best to choose among the models on the market, or has experience in making such a device, share your skills in the comments!