Among the various machines for electric arc welding, there are devices that can not only increase the current required to melt the edges of metals, but also equalize the variable voltage frequency to a constant value. This allows for better seam formation, reduces splashing of liquid metal, and produces a more durable connection. This unit is called a welding rectifier. How does it work and how does current conversion occur? What types of devices are there?
What is a welding rectifier
The device is a converter unit with the ability to adjust current (amperage) and voltage (voltage). At the output of the welding rectifier there are wires with terminals - positive and negative. One of them is connected to the electrode, and the other is in contact with the workpiece. As a result of closing the circuit, an electric arc is formed. Its high temperature allows it to melt metals and weld them.
Depending on their purpose, rectifiers differ in their level of complexity and functionality. However, the basic operating diagram remains standard. It is based on a converter - a transformer that modulates the voltage required for a specific situation. In addition, the circuit contains a certain number of semiconductors that cut off the negative part of the AC sine wave, allowing only the positive charge to pass through.
Current adjustment
The operating parameters of the rectifier are regulated electrically or electromechanically. In the second case, the operation is performed by elements located before the main block. The valves are supplied with alternating current having the characteristics required for welding. Electrical adjustment is possible with thyristors.
We recommend reading: How to make a welding machine yourself
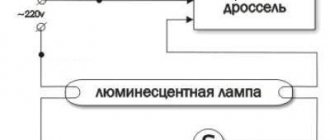
Ballast connection
A ballast rheostat included in the electrical circuit allows the welder to configure the machine in accordance with the selected technology.
The principle of operation is based on a change in resistance.
The higher it is, the lower the current strength. The ballast rheostat is a spring; the nature of its operation depends on the size of the coil, the total length of the part, and the material of manufacture. The element is connected to the contact of the regulator, the movement of which changes the resistance.
Design and principle of operation of a welding rectifier
Listed below are the main elements that are included in any equipment design of this kind. So, the welding rectifier consists of:
- transformer - a unit that allows you to regulate voltage. The mains current passes through the transformer and is converted. As a result, the power load is reduced;
- a rectification unit, which consists of a set of semiconductors that converts alternating current into direct current;
- frequency and current regulators;
- drives – smooth out impulses.
To understand the operating principle of equipment, you need to pay attention to the mechanics of semiconductors. They are open to the passage of electrodes exclusively in the positive half-cycle. Provided that the circuit contains several semiconductors, an appropriate number of half-wave curves are generated. They overlap each other, creating constant tension.
Common options for rectifier devices
Among the models of rectifier devices for welding on the market, the VDM 1202C device can be distinguished - it has a high current-voltage property. 1202C is used for arc welding in the construction and energy sectors.
In the welding process using device 1202, any type of electrode can be used, both DC products and universal or special ones.
According to experts, the VDM 1202 device is considered reliable, high-quality and durable.
The rectifier device model 1202 is increasingly preferred by professionals, since it can be used with doubling the voltage power.
A feature of rectifiers with doubling voltage power is the ability of capacitors to accumulate and save electricity.
At the moment, the price of a rectifier for welding 1202 is about $1000.
Rectifier devices VDU 506C are intended for the assembly of arc welding units and semi-automatic devices, for arc welding carried out by hand using coated electrodes.
VDU 506S, assembled with a semi-automatic device, is used during semi-automatic welding using consumable wire in a shielding gas environment. VDU 506S is an analogue of devices of the VDU 506 type, their production was carried out in Lithuania and in Russia.
Unlike model 506, version 506C has a light weight of 250g and smaller dimensions - 740x600x920.
In turn, the VDU 506 rectifier is capable of welding with simple electrodes, working in a protective gas environment, and welding with powder material.
And also the ability to cut molten metal with your own hands.
The welding rectifier VD 301 UZ is used to maintain the electric arc during do-it-yourself arc welding, for cutting and welding metal products.
Russian production has provided the VD 301 UZ model with effective operating properties; the VD 301 UZ can be used in various climatic conditions.
The VD 306 M1 device is used for welding with coated electrodes. The VD 306 M1 device allows you to process steel parts.
The version of the rectifying device for welding VD 306 C1 is designed for manual welding using direct current for welding various types of steels, including corrosion-resistant ones.
IMPORTANT TO KNOW: Tips for choosing a hose for gas welding
The material used for the transformer winding is copper. The VD 306 C1 is operated from 380V, at the moment the price for the rectifier device 306 reaches $300.
VD 313 UZ is used for manual welding of steel products using coated electrodes. The VD 313 rectifier has a simple but reliable design. In terms of mobility, the 313 model competes with the VD 306.
The welding rectifier VD 313 UZ is equipped with a shunt control device, due to which the period of change in the welding mode is reduced.
The classic rectifier VD 401 is indispensable for supplying direct current to a welding electric arc, for welding and cutting metals, and is also used for manual welding.
Video:
The rectifier model for welding VD 401 is powered by a 3-phase network. The design consists of a power type transformer, an equalizing block, a magnetic shunt, a cooling system, an auto switch and a housing.
The 401 welding rectifier is intended for use in enclosed but naturally ventilated spaces. The use of VD 401 in hazardous areas is prohibited.
The VD-16-Ch rectifier is used for manual electric arc welding on direct current. VD-16-Ch has a protective sensor against overload, and VD-16 can be used at temperatures from -10 to +40ºС.
The operation of the VD-16 under the influence of prolonged vibrations, rain and snow is prohibited; it is also prohibited to operate the VD-16 in a chemical environment.
Using welding rectifiers
Welding rectifiers are used in work with direct and reverse polarity, with low and high currents. When choosing power parameters, the thickness of the workpiece, ductility and refractoriness of the material are taken into account.
The devices are suitable for connection:
- refractory tungsten electrodes;
- low-melting coal consumables;
- attachments for automatic and semi-automatic machines.
A schematic diagram of a welding rectifier is always included with the equipment. It is used by specialists when it is necessary to repair a welding machine.
Main types of welding rectifiers
Welding current converters differ in two respects: the type of design and the method of adjusting the power parameters of the connection.
Main types of rectifiers:
- adjustment is carried out through changes in the operation of the transformer;
- models with throttle. An induction coil is used, eliminating sudden voltage changes;
- thyristor. Thyristors are used as regulators that change voltage.
- transistor. The equipment circuit includes semiconductors that smooth out the amplitude of current pulses;
- inverter The device is equipped with a frequency boost converter and a current regulator.
The main differences between welding machines depending on the power indicators and the features of their adjustment:
- Models for electric arc welding, connected to a three-phase network. Characterized by large sizes. The operation of the converter is associated with significant losses of electricity. The capabilities of the device are limited by the power of the transformer and the parameters of additional resistance.
- Automatic and semi-automatic machines. The output current depends on the power of the magnetic field, which in turn is controlled by a rheostat. It allows you to change the number of turns of the secondary winding (using the principle of current-voltage regulation). In addition, an oscilloscope is installed to monitor pulse adjustment. Initially, the current is rectified, after which it is converted into high-frequency alternating current.
- Three-phase choke-type rectifiers are installed in argon arc welding. Their design provides an additional core with a winding. Its role is to accumulate charge supplied to the rectifier capacitor.
Dynamic response
Schematic diagram of a bridge rectifier for a welding machine.
Another useful technical parameter characterizing the operation of the device is the dynamic characteristic (DC) of your power supply, which must have a quick response to changes in the electrical parameters of the arc (current, voltage). This depends on the time it takes for the voltage to recover from zero readings in short circuit mode to the arc reappearance voltage.
This time is the DH of the power supply. It should not be more than 25 Volts/0.05 seconds. This dynamic effect occurs when the hot metal is short-circuited to the part, at the moment the transformer goes into short-circuited mode. In this case, the short-circuit current strength in the secondary winding can reach double the value, and welding machines for manual welding, due to this ratio, can have a negative factor.
For stable burning of a welding arc, the so-called elasticity of the arc has an important property. It continues to burn as its length increases
The elasticity of the arc is a quantitative value; its criterion is its maximum length at which the arc is capable of existing.
The arc ignites only when the required voltage is reached in the initial half-cycle. The alternating current arc goes out and lights up 100 times/sec with separate flashes. This can be changed by the open circuit potential and the phase shift between the open circuit potential and the arc current. You can reduce pauses in the duration of electric arc burning by increasing the idle potential.
But it is not recommended (due to electrical safety) to increase it above 80 V. This can be solved by using circuitry, for example, by turning on inductors that create a phase shift in voltage and current. The electric arc, after modification, maintained by self-induction, may not be interrupted.
Advantages and disadvantages
Modern welding machines are distinguished by good functionality and high power in a modest size. The most compact models are inverter. Experts place them in a separate group. The transformer in such devices occupies no more than a fifth of the total volume.
The main difference between other rectifiers and transformers is that they can generate direct current, while this function is not available for transformers. It is this feature that is the foundation of a large list of advantages of devices with rectifiers:
- the electrode heats up much faster when direct current is applied to it instead of alternating current;
- Unproductive electricity consumption is significantly reduced and, accordingly, the efficiency value increases;
- the arc is characterized by combustion stability;
- uniform melting of consumables is accompanied by a minimum amount of melt splashes. This reduces the likelihood of injury among welders;
- arc stability makes it possible to better control the seam. It turns out to be as smooth and durable as possible;
- The functionality of a welding machine with a rectifier is richer than that of an analogue with a transformer;
- consumption of filler material is reduced. The savings become more noticeable the larger the amount of work performed.
In addition to the advantages, rectifiers also have disadvantages:
- it was not possible to completely eliminate power loss;
- devices with rectifiers perform worse than transformer ones in the event of a drop in network voltage;
- very sensitive to short circuits in the power supply network. They fail at the slightest short circuit in the wiring;
- Most models are not recommended for use in conditions of increased dust or humidity.
Basic malfunctions and maintenance of welding machines
Before connecting to the network for the first time, new converters must be purged. An ordinary household hair dryer is suitable for these purposes. It is turned on at maximum speed at an average warm-up level. This is done in order to dry any possible accumulation of moisture inside and remove dust that reduces the resistance of the copper winding. Blowing should be repeated approximately once a quarter.
If there was a long break in the operation of the equipment (up to 1 year), then before turning it on you need to “pump” the semiconductors. The essence of the procedure is to let the rectifier operate in different modes, starting with idle. This “break-in” lasts approximately two hours. After this, the welding machine will work flawlessly and stably under different conditions. It is necessary to monitor the condition of the main components and prevent the equipment from overheating.
The most common malfunctions of welding equipment and ways to eliminate them:
- The equipment does not work when connected to the power supply. Possible reasons:
- fracture of the supply wiring strand. In this case, the contacts in the plug “dangle”. The plug needs to be replaced;
- no voltage in the network. You should check the switch at the entrance and make sure it is turned on;
- One of the system nodes has failed. It will be very difficult to repair it yourself without proper training. It is better to take the device to a workshop;
- The semiconductor resource has been exhausted. The circuit needs to be re-soldered.
- The electrodes stick and at this moment the hum of the converter is heard. What you can do:
- check the serviceability of the capacitor and semiconductors;
- measure the performance of the power supply network and make sure that the voltage corresponds to the nominal value;
- make sure the throttle wiring is intact.
- During operation, the inverter switches off unexpectedly. This may happen:
- in case of overheating. You should make sure that the cooling system and fan are in good working order;
- if the integrity of the winding of the built-in transformer is damaged. You need to replace the old one with a new one.
- The voltage is unstable when operating under load or at idle speed. You should check:
- regulator knob;
- fuse installed on the primary winding;
- reliability of starter terminal contacts.
If the welding machine no longer maintains the required operating parameters, overheating may be the likely cause. To verify this, just touch the body. If it is hot, then you need to give the generator a break and check how freely air flows to the fan.