What is alternating current
This type of current represents the organized oscillatory movement of charged particles. The cause of the phenomenon is electrical voltage varying according to a sinusoidal law. The electric current is related to it by a direct relationship: I=U/R. So it is constantly changing in the same way.
Current and voltage of this type are characterized by the following parameters:
- Instant value. This is the current i and voltage u at the current time.
- Maximum value. This is the largest deviation from the zero value (Imax and Umax).
- Amplitude. This is the difference between the largest deviations.
- Frequency. This is the number of oscillations per unit time (f). For mains current, the figure is 50 Hz (cycles per second).
- Period. This is the duration of one oscillation cycle in seconds (T). The value is related to frequency: T=1/f.
The fact that current and voltage are constantly changing makes calculations very difficult. To simplify them, the so-called effective value. This is a direct current (voltage) equivalent to a given alternating current, i.e. causing the release of the same amount of heat in a linear conductor.
For example, the current value is the voltage of 220 V in a household outlet. In fact, the voltage in it constantly changes according to a sinusoidal law from +311 to -311 V.
What is direct current
Direct current is the ordered movement of charged particles that meets 2 conditions:
- the direction does not change;
- the amperage varies so smoothly that the inductive properties of the circuit do not manifest themselves at all.
One pole of the DC voltage source is negative (-), the other is positive (+). It is generally accepted that the current moves in the direction from “+” to “-”. But in metals, where free particles are negatively charged electrons, they move the other way around - from “-” to “+”.
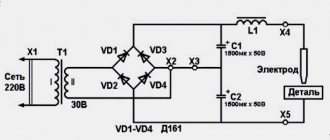
Direct electric current for welding is obtained by rectifying alternating current. They use a circuit of diodes (valves) - semiconductor devices that transmit electricity in only one direction. To smooth out ripples, the diode bridge is supplemented with a capacitive filter.
DC welding machine (diagram).
Features of application
The work of electric current in conductors consists of 2 phenomena:
- Heat release. Its amount is proportional to the square of the current: Q=(I^2)*R, where R is the resistance of the conductor.
- Creation of a magnetic field. Its intensity increases if the conductor is wound into a coil.
Welding is based on the first phenomenon. When an electric current moves through an air gap, an arc discharge is formed, characterized by a high temperature. It causes the metal to melt, as a result of which the edges of the workpieces merge together.
The ability of electric current to create a magnetic field is used to reduce voltage using a transformer. It consists of 2 unconnected coils. The primary is connected to the network, and the electric current flowing in it through an alternating magnetic field induces an emf in the secondary. The voltage reduction factor depends on the ratio of the number of turns in the coils.
We recommend reading: How to treat an eye burn from welding
What is a regular welding machine?
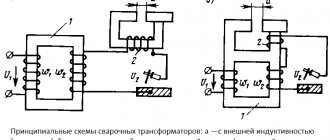
The classic current source for generating an electric arc is a transformer. The welder lowers the mains voltage, and the current increases accordingly. Such equipment was used for manual welding everywhere until the beginning of the 21st century.
The operating principle of the transformer is based on the magnetic induction method. Electric current passing through the first winding magnetizes the core. An electromagnetic field arises, and under the influence of waves an electric current is formed in the wire of the secondary transformer winding. The output voltage depends on the number of secondary turns. The equipment generates high-ampere current with parameters necessary for welding.
Welding transformer layout
Advantages and disadvantages of welding transformers
First, about the advantages of transformer devices:
- simplicity of the device, the scheme of operation is clear to the student;
- maintainability, in case of breakdown the transformer can be repaired independently;
- the ability to work for a long time is ensured by low sensitivity to overheating during operation;
- impact resistance – the risk of mechanical damage during transportation is minimal;
- accessible service;
- low price;
- versatility, the device is used for welding various metals;
- there are no special storage requirements, the transformer is resistant to high humidity and dust.
The disadvantages of traditional welders are obvious:
- when the network sags, the transformer turns off; a stable voltage is needed for power supply;
- lack of precise adjustment of current parameters, large adjustment steps, difficult to set up equipment for welding thin-walled workpieces;
- heavy weight, it is difficult to move the equipment independently;
- significant dimensions;
- high power consumption.
It is worth considering that most transformers operate from a three-phase network. Beginners working with a transformer have problems with arc ignition and sticking. Seams are difficult to form without experience.
Effect of welding current on welding
According to the formula Q=I²xR, heat input in the electric welding process depends on the current strength. The higher its value, the deeper the metal melts.
It is necessary to select the optimal value, otherwise the following defects arise:
- If the current is too low, there is a lack of penetration.
- If it is too high, there is a burn through of the metal, an extensive weld pool, and deformation of the workpieces.
In both cases, the seam becomes less durable.
Factors influencing the choice of indicators
The welding current value is selected according to 2 criteria:
- Electrode diameter. The thicker the consumable, the higher the amperage.
- Coating material. For example, rutile electrodes are used to cook at a lower electric current than basic electrodes.
The diameter of the consumable is selected depending on the thickness of the workpieces.
Table of the influence of welding current on various indicators.
Features of the work
Electric arc welding of cast iron and other types of metal must be carried out correctly. Compliance with all principles and rules will allow you to obtain a strong and high-quality weld.
Manual electric arc welding technology includes several features:
- At the initial stage, the workpieces are cleaned and degreased, and they can be cut. You need to attach a hot electrode to them. The end part of the electrode divides the surface area of the element being welded into ions and electrons;
- In order for welding to be faster and the result to be of high quality, special elements should be applied to the surface of the welded material (electrode). It is recommended to use calcium, potassium, sodium. They accelerate the separation of metal into particles;
- The welding process can be carried out using an open or closed arc. When open, a lot of nitrogen will penetrate into the metal base, this will have a detrimental effect on the structure of the weld. To reduce this negative impact, a layer of metal must be applied to the electrodes. In industrial conditions, the best option would be to use a closed method, during which the welding zone will be protected from exposure to oxygen;
- Next, you need to install the electrode in the equipment for electric arc welding - an inverter. Using the end of the rod, you need to pass it twice along the ends of the metal components being welded - this will ignite the arc. After the welding machine is turned on, it is necessary to set the current at the required level;
- During the welding process, the electrode rests on the surface of the parts being welded and is slowly moved across the gap area. Liquid metal enters the weld pool, which, when solidified, forms a strong and even weld. The use of a special technological map will allow you to accurately calculate the power, current and duration of arc exposure;
- Welding of vertical seams is carried out using an arc. The level of the contact angle between the electrode and the surface to be welded must be straight. A slight deviation of 10 degrees is allowed;
- To prevent the deposition of liquid metal in one area, the herringbone, triangle, or multi-layer thin arc technique can be used.
Important! During electric arc welding, the welder must follow all the rules and steps. Each welding method is selected depending on the metal used and the welding conditions (in industrial or domestic conditions).
Selecting current for welding materials
The recommended range is given on the packaging with consumables. The exact value is determined experimentally.
Electrode 4 mm
These consumables are used to cook workpieces 4-6 mm thick. Set the electric current strength within 120-200 A.
Electrode 3 mm
Consumables with this thickness are used to connect parts to a wall of 3-4 mm. The optimal welding current values are in the range of 80-160 A.
Electrode 2 mm
Thin consumables are used to cook steel 2-3 mm thick. Choose an amperage between 40 and 80 A.
AC and DC Welding Equipment
Welding work is carried out using the following equipment:
- Transformers. The simplest, cheapest and most reliable devices. They produce alternating voltage at the output.
- Rectifiers. They differ from the previous ones by the presence of a diode or thyristor bridge that converts alternating current into direct current. Compared to the previous version, they are larger in size and weight, more complex in design and more expensive.
- Inverters. They produce a constant electric current at the output. They are compact in size.
The inverter converts the mains current in the following order:
- Straightens.
- Converts to high frequency AC (60-80 kHz). This function is performed by a special electronic unit with fast-switching transistors, controlled by a microcircuit.
- Using a converter, it lowers the voltage to the operating value.
- Straightens again.
Increasing the frequency of the electric current can significantly reduce the size and weight of the transformer. As a result, the cost of the device and losses in it are reduced.
Equipping the inverter with electronics provides additional benefits in the form of the following functions:
- Hot start. Facilitates arc ignition by briefly increasing voltage.
- Anti-sticking. Voltage relief in situations where the consumable has touched the workpiece for a long time (often observed during ignition).
- Arc force. It consists of a short-term increase in the strength of the electric current in cases where there is a risk of arc extinction. Most often this occurs when the electrode and the workpiece are short-circuited by a drop of molten metal.
- Stabilization. Provides preservation of welding mode parameters under conditions of input voltage fluctuations.
Inverters are more expensive than other types, but the ease of operation and high quality of the seam justifies the price difference.
There are devices for the following types of electric welding:
- Refractory consumable in a protective gas environment. Use a torch with a tungsten or graphite electrode and a nozzle for injecting argon. Filler material in the form of wire is fed into the welding zone. The device can be operated without gas supply. Then a hollow wire filled with flux is used as a filler material. When burned, it turns into gas.
- Consumable electrode. Such consumables are equipped with their own flux in the form of a coating (coating). In addition to protective components, it contains easily ionized arcs that improve combustion.
Devices for welding with consumable consumables are equipped with an electrode holder.
According to their purpose, devices are divided into types:
- For manual welding - argon and consumable electrode.
- Semi-automatic devices. Designed for welding with a refractory consumable, the filler material is supplied mechanically.
- Automatic machines. Work is carried out without human intervention in accordance with user-specified settings. The unit is equipped with a refractory electrode.
We recommend reading: How to weld exhaust manifolds
Polarity forward and reverse: what is the difference
Polarity in welding on an inverter machine is an extremely important thing that you need to understand.
If the welding current is constant, then the movement of electrons is also constant. And in this situation, there is almost no splashing of drops and pieces of molten metal, as a result of which the seam comes out neat and of high quality.
At its core, polarity is the direction of electron flow, which depends on the order in which the cables are connected to two different connectors on the device. Inverters have the ability to select the type of polarity. The welding current can also be adjusted.
Reverse polarity
Types of polarity for welding.
This is the negative pole on the metal workpiece, and the positive pole on the electrode. The current thus moves from minus to plus, that is, from the metal to the electrode. With this method, the electrode gets quite hot. The method is good when welding thin metals as the risk of burn-through is reduced.
Straight polarity
Here it’s the other way around: the negative pole is on the electrode, and the positive pole is on the metal of the workpiece. The current now flows from the electrode to the part being welded, which in this case heats up more than the electrode. This is how they work with thick metal edges.
It should be noted that the polarity is always indicated in the instructions on the packs of electrodes.
One of the main “inverter” questions from debutants is what is the most optimal polarity when welding with an inverter? The answer depends on many criteria, but from the point of view of cutting metal, the polarity should be straight.
The fact is that with this type of polarity, the molten area turns out to be deep and narrow - just what is needed when cutting.
With reverse polarity, the opposite is true: the melting zone is shallow and quite wide.
What are DC and AC electrodes
An electrode is a piece of metal wire designed to supply electricity to a workpiece. Products are divided into 2 types:
- melting;
- refractory.
Products of the first type are equipped with coating. It performs the following functions:
- Forms a protective gas.
- Serves as a source of alloying elements.
- Supports arc combustion due to easily ionized elements. For electric current to flow, free charge carriers are needed. The presence of other ions in the gap between the consumable and the workpiece, in addition to electrons, stabilizes the process.
Consumable electrodes are divided into types:
- universal – work on any type of electricity;
- for welding at constant voltage.
Refractory electrodes are also universal.
Welding electrodes.
Differences between DC and AC electrodes
Based on the type of coating, consumables are divided into types:
- Sour.
- Cellulose.
- Rutile.
- Basic (calcium fluoride).
The first 3 types are universal, the fourth is intended for welding only at constant voltage. Basic and rutile electrodes are the most common.
The peculiarity of welding with alternating current is that the arc burns less stable. It is extremely sensitive to the number of free charge carriers. The main type of coating contains fluorine, which acts as a deionizing element. It makes it difficult to burn an arc, so such consumables do not work well at alternating voltage.
The advantage of calcium fluoride coating is the absence of organics, which eliminates the saturation of the metal with hydrogen and provides it with good protection against oxidation. As a result, the seam is strong and flexible.
It is also necessary to pay attention to the characteristics of the welding machine. To start an arc on alternating current, some electrodes require an increased open circuit voltage - 70 or 90 V versus the standard 50. This is especially necessary when re-igniting when the consumable is covered with slag. Most transformers have an open circuit voltage of 50 V. There are models with an additional output that generates an open circuit voltage of 70 (V). They cost more. For an inverter, this figure is 89-93 (V).
When choosing electrodes, you should consider the type of welding machine.
Selecting the type of current. AC Welding
Currently, alternating current welding is more widespread. This is mainly due to the operational and economic advantages of this type of welding, which are as follows.
1. Equipment for welding with alternating current (transformers and regulators) is much cheaper than for welding with direct current, has less weight and dimensions, and is simpler in terms of maintenance, care and operation.
2. The efficiency factor (efficiency) of welding transformers with regulators is 0.8–0.85, and units for single-station DC welding are 0.3–0.6. When multi-station welding on direct current, a significant part of the energy is lost in the ballast rheostat, so the average efficiency of the station is only 0.24-0.43. Different efficiencies of equipment determine different energy consumption per 1 kg of deposited metal: 3-4 kW-hour/kg for alternating current welding, 6-8 kW-hour/kg for single-station welding and 8-10 kW-hour/ kg for multi-station DC welding. In addition, when welding with alternating current, the magnetic blowback of the arc is much less than when welding with direct current.
The disadvantages of AC welding include:
1) low power factor of the welding station, usually equal to 0.3-0.4; cos f of the electric motor for the converter for DC welding is 0.6–0.7;
2) less stability of the AC welding arc when welding with electrodes of small diameters;
3) in practice, electrodes are sometimes used that can only be used with reverse polarity of direct current (for example, UONI-13, etc.), as well as electrodes intended for welding on alternating and direct current, but giving better quality of seams when welding on direct current current (for example, K-5, etc.). The use of such electrodes limits alternating current welding.
The choice of the type of current is made based on the above comparison of welding with alternating and direct current.
www.prosvarky.ru
Electrode brands for AC and DC current
You can cook using alternating current with the following consumables:
- OZS-4, OZS-6, OZS-12 (rutile). Designed for welding carbon steels.
- MP-3. Designed for joining low carbon steels. Recommended for beginner welders. Provide high quality connections even when the workpieces contain dirt, rust and moisture. The MP-3S variety is intended for high-carbon and low-alloy steels.
- ANO-4, ANO-6, ANO-21. The first grade is created for low-carbon steels, the middle one for carbon steels, the third for high-carbon and low-alloy steels.
- W.P. Tungsten consumables.
- WL-15 and WL-20. Alloyed tungsten consumables.
Recommended reading: Choosing polarity when welding
The following electrodes are used to cook only with constant electric current:
- UONI-13/55. They are considered the best for the manufacture of critical structures made of carbon steel. When the arc extinguishes, the molten coating immediately solidifies at the end of the electrode, so it must be cleaned to re-ignite.
- OZL-8. Designed for steels alloyed with chromium and nickel. Used in the manufacture of units experiencing high loads; create a durable, oxidation-resistant seam. It is necessary to ensure smooth cooling of the metal, otherwise it may crack.
- Kobelco LB-52U (Japan). Designed for the manufacture of critical structures from low-carbon steel. They are often used when it is not possible to perform double-sided scalding, for example when installing pipelines. They are sensitive to the humidity of the coating, therefore they require preliminary calcination at a temperature of 300°C.
- ESAB OK 61.30 (Sweden). Electrode for stainless steel.
Difference between AC and DC welding
AC transformers have the following advantages:
- low cost;
- simple design;
- high efficiency;
- reliability;
- great resource.
Flaws:
- Poor seam quality. It turns out wide and uneven due to arc fluctuations.
- Large metal losses due to strong splashing.
- Poor arcing.
- Ability to weld only carbon steel.
AC welding is used in the following situations:
- There are low quality requirements.
- A large input of heat is required, for example in the construction of ships.
Direct current devices are more complex and more expensive. They are characterized by relatively large power losses, but provide high connection quality and arc stability. In addition to carbon steel, they can be used to weld stainless steel, as well as non-ferrous metals (using appropriate electrodes).
In DC welding, there are 2 connection methods:
- With straight polarity. The negative pole (cathode) is connected to the electrode, the positive pole (anode) is connected to the workpiece.
- With reverse polarity. The anode is connected to the consumable, the cathode to the workpiece.
Difference in currents.
Inverter design
Inverters are sometimes called DC welding machines because during their operation, the first stage is the conversion of alternating voltage to direct current.
Inverters are actively replacing transformer-based devices due to their light weight, compact size and high performance.
The welding inverter consists of a high-voltage rectifier diode bridge and a low-pass filter, a frequency generator in the range of 30-70 kHz, high-voltage power switches, an isolation capacitor and a step-down transformer. It performs the function of a low-frequency alternating current to high-frequency converter.
A voltage of 220 V 50 Hz is supplied to the rectifier bridge, where it is rectified, the filter reduces ripple and is supplied to electronic switches made on bipolar transistors with an insulated gate or field-effect transistors.
At the output of the keys, thanks to a control unit based on a frequency generator, a signal with a frequency of 30-70 kHz is obtained. Passing through the separating capacitor, the electric current gets rid of the constant component and enters the primary winding of the step-down transformer.
The output of the secondary winding produces high-frequency alternating current, which is used for welding. Essentially, AC welding inverters are designed as switching power supplies without a rectifier unit at the output .
Due to the rapid transition through zero, AC inverter welding machines have a stable, uniform arc, which has a positive effect on the quality of the seam.
Using an inverter allows you to get a small-sized device with high power. A disadvantage of the inverter can be considered its high sensitivity to voltage surges.
Welding current designations for electrodes
The marking of consumables is in the form of a fraction. The last digit in the denominator indicates the type of current. “0” stands for “DC only with reverse polarity.” Other numbers mean that the consumable is universal, i.e. can cook with any type of current. At the same time, the polarity is encrypted for constant, and for alternating - the minimum required value of the no-load voltage.
The data is summarized in the table:
| Recommended DC polarity | Open circuit potential difference of alternating current source, V | Designation |
| Reverse | – | |
| Any | 50±5 | 1 |
| Straight | 2 | |
| Reverse | 3 | |
| Any | 70±10 | 4 |
| Straight | 5 | |
| Reverse | 6 | |
| Any | 90±5 | 7 |
| Straight | 8 | |
| Reverse | 9 |
Thus, the number “5” in the marking means that the electrode can be used to cook:
- Direct current of straight polarity.
- Variable if the no-load voltage of the source is at least 70 V.
Types of devices
Typically, when carrying out electric arc welding, a simple welding machine is used - a transformer one. It works on the principle of a conventional transformer, lowering the voltage and increasing the current. This device cooks using alternating current.
However, transformer welding equipment is inconvenient and huge in size. For this reason, problems may arise with its movement. For these purposes, a special device on wheels is required.
If you need a mobile welding machine for electric arc welding, then an inverter is an excellent option. This equipment first converts alternating current from the household network into high-frequency current. And after that it converts it to permanent. In addition, devices of this type are lightweight and compact in size.
Inverter arc welding equipment helps achieve maximum arc stability. This is what has a positive effect on the quality of the seam. In addition, the device allows you to use different modes - with direct and reverse polarity.
Additional Information
When welding with direct current, an uneven distribution of thermal energy is observed between the workpiece and the electrode:
- For consumables that melt. The anode spot is colder than the cathode spot. Therefore, to connect thin-walled workpieces, direct polarity is used (so as not to burn them), for thick-walled ones, reverse polarity is used (for deeper penetration).
- For refractory consumables. The anode spot, on the contrary, is hotter than the cathode spot.
Welding with a refractory electrode is carried out only with straight polarity, regardless of the thickness of the workpieces. When connected in reverse, when the discharge hits the consumable, it quickly becomes clogged.