Filler welding wire and its features
Wire is a metal product that has a small cross-section. Moreover, it is so small that its size is incomparable with its length. For the production of wire, various types of metals are used - ferrous, non-ferrous, and stainless.
Flux Cored Welding Wire
A separate class of products is welding. It is used for automatic and semi-automatic welding. Electrodes, rods and other products used in welding parts manually and automatically are made from it.
In fact, it replaces the electrodes used in welding. Through it, electricity is supplied to the welding zone, which is necessary to ignite and maintain the arc. In addition, the wire takes part in the formation of welds and provides their physical and mechanical parameters.
To produce wire used for welding, various types of metal are used. At the same time, the scope of use of the finished wire may change. For example, aluminum can be used in the production of welding wire. It can be used to work with alloys based on magnesium, aluminum and a number of others. If the wire is made of stainless steel, then it is used when welding parts made of steels resistant to corrosion.
In the construction of ships, cored wire is most often used. In addition, there is copper-plated wire. Its use entails obtaining high-quality seams. Not so long ago, wire without any coating at all was in use.
Copper-plated filler wire
When choosing wire for welding work, you must always remember that there are several types of similar products on the market. They differ from each other not only in chemical composition, but also in structure and the number of alloying components.
The wire must be selected based on the marks on its surface or on the packaging. The marks tell the consumer about the physical and technical parameters of the wire and its scope of application.
For example, in GOST 2246-70, this is a document that normalizes the technical specifications for steel welding wire. So, it says that for the production of this welding material it is permissible to use low-carbon steel (Sv-08AA, Sv-08GA) alloyed (Sv-08KhN2GMYu, Sv-08KhN2G2SMYu) and high-alloy alloys (Sv-10Kh16N25AM6, Sv-09Kh16N25M6AF).
In addition, welding wire is divided into that which is used for welding work, and that from which electrodes are produced. It can be manufactured with or without copper plating. All details regarding diameter, grade of steel alloy, and presence of coating must be specified when placing an order.
What is filler wire
Filler wire is a rod made of a special material with a cross-section of small diameter. Various metals can be used as materials for its manufacture. A separate type is filler wire for argon arc welding. It can be used when using automatic and semi-automatic devices. Rods for argon arc welding play the role of conductors between the current and the arc. They ensure easy ignition of the arc and stability of its combustion.
During welding, the wire material gradually melts and mixes with the main product. When mixed, the characteristics of the seam are improved. Since the additive for argon welding must have the same composition as the base material, the wire can be made of various types of metal. The filler material for argon arc welding does not have any additional coating or coating, since their functions are performed by argon.
General parameters of the welding method using argon
The basis of argon welding, as already noted, is the creation of a weld pool under the protection of argon. Its presence protects the melt from exposure to atmospheric oxygen. The technology of such welding involves the use of at least two welding methods. To implement them, consumable and non-consumable electrodes can be used.
Argon welding
Welding technologies involve two methods, one uses consumable electrodes, the other uses consumable electrodes. By using the latter, a high-quality seam is obtained with uniform melting of both workpieces. This method is used for welding pipes and joining parts made of titanium and aluminum.
An arc is ignited between the working tool and the parts to be welded. When welding parts using argon-arc technology, tools (electrodes) made from tungsten are used. Their main advantage lies in their refractoriness. To improve its performance characteristics, individual chemical compounds are introduced into the tungsten alloy.
If there is a need to use additional filler material, then it is supplied to the weld pool of the assembly and this eliminates contact with the electricity supplied to it.
Basics of welding aluminum with argon (argon arc method)
Aluminum argon arc welding (AC TIG) is performed using special equipment and materials. The standard kit for welding work includes:
- TIG AC/DC inverter (AC source);
- grounding (working without it is unsafe);
- tungsten electrodes;
- filler rod (wire);
- special TIG welding torch;
- burner cooling unit (for large volumes of work);
- collets with holders and nozzles for the burner;
- a gas cylinder (argon or a mixture of argon and helium);
- reliable gas hose;
- reducer to reduce the pressure of the gas used.
In addition, it is worth getting a good welding shield or a “Chameleon” mask with an automatically darkening filter, and also using high-quality leggings. Many welding enthusiasts prefer to use a welding current control pedal in their work, but more often it can be found in the arsenal of a professional welder. For a beginner, it is more important to master the welding technique and correctly set the gas supply volume, prepare materials, set up the machine and adjust the welding current to the desired metal thickness.
What are the benefits of welding aluminum with argon?
Aluminum is a more difficult metal to heat treat than iron. The main reason for this is the instantaneous formation of a thin oxide film on its surface upon contact with oxygen. This film has a melting point several times higher than pure aluminum.
During the welding process, argon prevents the oxidation of aluminum , displacing oxygen. The filler wire, which is made from aluminum, melts under the influence of an arc and forms a weld.
The advantages of using argon arc welding are very significant:
- universality of the method (it is suitable for welding various metals and alloys);
- arc stability;
- possibility of forming a neat thin seam;
- stronger welded joints in critical areas.
The AC TIG welding method truly provides first-class results. In addition, a lot depends on the inverter. Therefore, premium models are always used in production, and a good owner is ready to invest money in the purchase of a reliable device. Even if you have to use it only from time to time.
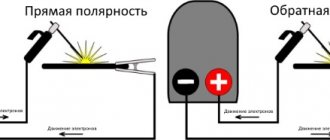
AC or DC – the choice is obvious
When welding aluminum, it is alternating current that has won the love and respect of specialists. In order to understand why this happens, you need to delve a little into the technical details.
When connecting direct current of reverse polarity, cathodic cleaning of the oxide film occurs , but the welding temperature increases significantly. As a result, even such a refractory metal as tungsten, from which the electrode is made, begins to gradually deteriorate. If you connect direct current of direct polarity, it cannot penetrate the oxide film, but provides a more stable arc.
It is switching the polarity of the current that ensures a high-quality result of your work. This means that the choice is obvious - you need to use alternating current.
Aluminum welding with direct current is used much less frequently. It’s much more difficult to work this way; moreover, you need to use pure helium instead of argon, which costs several times more.
Preparing parts for welding - why is it needed?
The quality of the weld directly depends on the thorough preparation of the surface of aluminum products. If you neglect this rule, you risk getting a negative result, even if you use a high-quality inverter and first-class argon.
Therefore, before starting welding work, it is necessary:
- Degrease the surface using a solvent (white spirit, gasoline or acetone).
- Clean the surface from the oxide film mechanically or chemically.
- Allow the treated products to dry after chemical treatment with special compounds.
The mechanical cleaning method using a wire brush or sandpaper is allowed when welding at home.
The production uses a chemical cleaning method, including etching in alkaline solutions, washing in hot and cold water, clarification and final drying.
How to properly weld aluminum with a tungsten electrode with an additive
For welding aluminum, non-consumable electrodes made of refractory tungsten are used. Many models of these products contain additional impurities that improve the quality of the process.
Read also: Wrought iron staircase with wooden steps
The technology of argon arc welding of aluminum has its own characteristics. The main rule that should be strictly adhered to is the following: the filler wire must be in front of the electrode and it must be moved exclusively along the seam.
Welding can be done in various spatial positions. But it is worth remembering that argon is a heavier gas than oxygen. Therefore, the best quality of the seam is ensured when the welded products are positioned horizontally. For welding work on ceilings or walls, it is advisable to use a mixture of argon and very light helium. At the same time, costs inevitably increase, since the cost of helium is much higher than that of argon.
A few more points to note are:
- The length of the arc should be minimal. To do this, the electrode is placed as close as possible to the surface of the work being welded.
- The wire feed must be done smoothly. With experience this happens automatically. It's more difficult for beginners. Sudden jerks lead to metal spattering.
- The vertical position of the electrode provides the most stable arc. Therefore, it is advisable to adhere to it throughout the entire welding process.
- The welding speed should be as high as possible. The higher it is, the better the quality of the seam. Therefore, you can distinguish the result of the work of an experienced welder from the efforts of a beginner with the naked eye.
Equipment for argon welding – what to choose?
The choice of a specific model of welding equipment (inverter) depends on:
- financial capabilities of a particular person or organization;
- type of planned welding work and its frequency;
- diameter of the metal being welded;
- Possibility of permanent connection to a 380V power source.
The universal devices Brima TIG 250 AC/DC 220V or Svarog TECH TIG 200P AC/DC (E101) are perfect for use at home. They can be used for argon arc welding on alternating and direct current, as well as for manual arc welding of iron products on direct current.
By purchasing them, you get at your disposal inexpensive universal devices that are easy to use. They will always help you quickly, and most importantly - efficiently, to carry out welding work even in your own apartment.
The Svarog TECH TIG 315P AC/DC (E103) and Bars Profi TIG 317DP AC/DC models operate at a voltage of 380 Volts and are designed for welding thick metal. They have more impressive technical characteristics.
Therefore, they are often purchased by customers who work in auto repair shops, workshops or forges.
Premium class welding inverters BLUEWELD BEST TIG 252 AC/DC HF/LIFT VRD and EWM Tetrix 230 AC/DC are indispensable for repair work, construction, engineering, and chemical plants. They provide safe operation even in areas with a high risk of electric shock and are designed for use in low temperatures (down to -20° C).
The most functional are premium inverters designed for use on an industrial scale. They have many outstanding characteristics and features.
The Lincoln Electric INVERTEC V205-T AC/DC model has a convenient power recognition function that reliably protects the inverter from overloads. In addition, it also includes a fan control function, reducing power consumption and the amount of dust entering the machine.
The EWM Tetrix 551 AC/DC inverter is equipped with large wheels that make moving the device much easier and a simple control panel.
The Kemppi MasterTIG MLS 2300 ACDC welding machine has maximum welding power of 220V and is compact in size.
The ESAB Origo TIG 4300IW AC/DC model is specially designed for TIG welding of different materials and contains a convenient function for pre-programming modes.
In the Tiberis store you can always count on competent advice when choosing the right inverter model and pleasant service. Call us by phone or! With our help, welding work becomes very convenient.
Video tutorial on welding aluminum for beginners
Go to sections of the article:
What are the characteristics of the ArDS of some metals? How to choose a filler rod? Why do you need a filler rod?
Banal questions that every novice argon welder asks himself, because when doing argon arc welding (read ArDS for dummies), you need to hold the torch in one hand, moving it along the connection line, and with the other, add filler material to the weld pool as it melts. In some cases, for example, when butt welding thin metal, you can do without a rod, but if you need to reinforce the seam in the form of a convex bead or weld a T-joint with a certain leg, you cannot do without an additive. Everything here is the same as in manual arc welding. The filler material must have a similar chemical composition to the base metal of the product, then the mechanical properties of the weld will be high. During the process of melting the rod and the transition of the metal into the weld pool, some burnout of alloying elements occurs, so ideally their percentage in the rod should be slightly higher than that of the metal being welded.
Here are some metals that are widely used today in all sectors of the national economy and in everyday life:
- black ;
- stainless;
- aluminum;
- copper and its alloys.
Let's look at each of them in more detail.
Application nuances
Today, many welding methods have been developed, working on the basis of different principles. But it’s difficult to say which way is better. Each of them has pros and cons. But sometimes it turns out that it makes sense to use only one, specific type of welding. One of these types is welding with powder or flux-cored wire.
Filler wire application process
Essentially, this wire is a tube with flux and metal powder placed inside it.
In the Russian Federation, wire is produced mainly for welding work with black steels.
There are requirements for a material of this class, for example, its use should not create problems when igniting and maintaining the arc. The wire should melt evenly and not create a large number of sparks around the weld pool. The resulting slag is evenly distributed over the entire surface of the seam and as it cools, it should be easily separated.
The seam must meet all the requirements of regulatory documentation and there must be no defects on it - undercuts, lack of fusion, pores and cracks. These properties determine the possibility of using flux-cored wire to perform the work. Meanwhile, to establish some properties of the welding wire, it is necessary to perform experimental welding. To do this, you need to take a roller and weld it onto a metal plate. Welding should be performed evenly, in the lowest position of the working tool. The average welding modes for the metal being welded are taken as welding modes. After conducting such experiments, it will become clear when and under what conditions it makes sense to use such wire.
Welding diagram when using filler wire
This welding can be used frequently as it has many advantages. Thus, welding may be impossible because it is impossible to direct the electrode to the required location. By the way, such problems arise when performing semi-automatic welding.
Under these conditions, it makes sense to use powder welding. The thing is that it combines the positive properties of ordinary electrodes and ordinary welding wire.
It should be noted that flux-cored wire welding does not require gas, a set of gas hoses and equipment for supplying or creating flux.
Stainless steels
Corrosion-resistant steels are more difficult to weld than black steels due to their more complex physicochemical properties. Firstly, stainless steel has a higher electrical conductivity, so higher currents than usual will be needed, approximately 15%. Secondly, alloying with chromium from 13% (which makes steel resistant to corrosion) can cause problems. For example, when welding thin-walled stainless steel, which is more common than thick-walled, it is important to organize gas protection for the reverse side of the seam, the reverse bead. Chromium oxides cause cracks. If you welded an expensive car exhaust system from AISI 304 steel and the seam was protected only from the outside, over time your system will fall apart. To protect the seam inside the pipeline, argon is injected into it, and the open ends are closed with plugs.
Austenitic steels type 12Х18Н10Т (AISI 321); 08Х18Н10 (AISI 304) is welded with stainless steel rod ER-308 (analogues SV-06Х19Н9Т, SV-01Х19Н9, SV-04Х19Н9). Steels of type 12Х18Н10т are also called “food grade stainless steel”, since the optimal proportion of chromium and nickel provides resistance to aggressive environments, such as organic acids formed during the processing of some industrial food crops. Steels of this type are often found in everyday life. The weld metal ER-308, which has a similar chemical composition, is also not afraid of acidic and other “unfriendly” environments. The low carbon content in ER-308 wire reduces the risk of intergranular corrosion, the process of corrosion along the grain boundaries of the metal. The silicon and manganese content has a positive effect on the formation and crystallization of the weld pool.
Mechanical properties of ER-308:
- Yield strength, Rp0.2 390 MPa;
- Tensile strength, Rm 600 MPa
- Elongation A5 42%
- Impact strength, J 120
The next class of steels is chromium-nickel-molybdenum type st.10Х17Н13М3Т, st.03Х17Н14М2; 15Х14Н14М2ВФБГ; 08Х16Н13М2В. They are used more often in industry, in everyday life much less often. Thanks to alloying with molybdenum, they become resistant to even more aggressive acidic environments (sulfuric, orthophosphoric acids, etc.). Molybdenum prevents local corrosion, hot cracking, increases the operating temperature of structures and mechanisms and increases impact strength at ultra-low temperatures. Stainless steel rod ER-316 (domestic analogue Sv-04Х19Н11М3) is used as a filler material for these steels .
Mechanical properties of ER-316:
- Yield strength 480 MPa
- Tensile strength 630 MPa
- Elongation 33% KCV
- +20°С 175 J
- — 110°C 150 J
- -196° C 110 J
A question is often asked about welding stainless steel at home: is it necessary to purchase an expensive inverter-type power source for this? It’s not at all necessary; you can weld stainless steel using a regular MMA welder (see our Review Store). Some of them, however, have an MMA/TIG mode switch, but even those inverters that do not have this feature can be adapted for argon arc welding: purchase an additional valve torch, an argon cylinder and a pressure reducer. Welding on such a homemade argon machine has its own characteristics, but if you take them into account, you can work quite well. The main thing is not to start welding on the product; prepare a graphite backing for this. If you start on a product, the tungsten electrode will be enough for a couple of ignitions, then you will have to sharpen it. It is also necessary to complete the process on graphite.
Advantages
Filler welding wire can be classified as self-shielded and gas-shielded. Wire protection can be provided by various types of gases. The use of welding wire allows you to obtain:
- Due to the high heat flux, the electrode forms a narrow region of thermal action on the metal.
- The necessary effect on the metal of the resulting weld due to changes in the gas composition and grade of wire.
- High labor productivity during welding work.
Self shielding cored wire
The use of welding wire provides great opportunities for mechanization of work.
One of the obvious advantages is that due to the use of wire for electric arc welding, the main and auxiliary time for performing work is reduced, as a result, overhead costs are reduced and the cost of the finished product is reduced.
Filler wire with polished surface
There are two types of welding wire - with a polished and with a copper-plated surface. And the condition of the wire surface has a significant impact on the quality of the arc, the resulting seam, the number of drops of molten metal and, of course, the reliability of the welding equipment.
Copper welding
On the Internet you will find a lot of information on copper welding, but 90% of this information is theory rewritten from Soviet literature or the like. Practical advice has to be collected bit by bit. What is the most important thing in welding? That's right, practice and a little theory.
What is stated not without reason: copper has high thermal and electrical conductivity, high currents are required. There may be a problem with it becoming brittle when hot. Actively dissolves oxygen to form cuprous oxide and hydrogen, even despite protection with argon. Moreover, the surface layer of metal grains is oxidized, Cu+Cu2O is formed. Due to the fact that Cu2O has a melting point 20 degrees higher than Cu, the metal is prone to the formation of hot cracks.
When welding copper, nitrogen-arc welding is also used. Nitrogen, used as an inert medium, provides better protection of the weld pool and deeper penetration at the same current. But there are also disadvantages: arc instability, low welding speed. Therefore, argon is still used for welding copper, since it is easier to work with when compared to nitrogen, and it costs less than helium.
Theoretically, no matter how reliable gas protection is provided, it is still not enough: oxygen and hydrogen still saturate the molten copper. In order to remove these harmful gases, deoxidizers are needed. That is why it is not recommended to use pure copper as a filler material for welding copper, but with the addition of alloying elements. For example, the copper filler rod CuSi3 (CuSi3Mn1; BrKMts3-1; ESAB OK Tigrod 19.30) contains 3.4% silicon and 1.1% manganese, which bind oxygen and remove it from the melt.
Chemical composition of CuSi3 :
- Si 2.8-4.0
- Mn 0.75-1.50
- Fe o C. But in most cases it does not play such a role as annealing at a temperature of 450 - 500 o C after welding. In most cases, this operation is mandatory to relieve internal stresses and “restart” the alloy structure.
Be careful. When tin bronzes are heated to 550 o C, a low-melting component, tin, melts. In this regard, numerous defects (pores, cavities) are formed.
If, despite heat treatment, the seam cracks, it means that the filler material was poorly selected and must be replaced. In this case, you need to remove the deposited metal (cut with a grinder before removing the additive). If the crack passes through the weld crater, it is necessary to move the torch towards the base metal.
Read about welding brass in a separate article.
Flaws
Meanwhile, it should be noted that the use of filler wire for welding has a number of disadvantages that technologists must take into account when choosing a welding method and modes:
- Welding filler material requires constant protection and this has a negative impact on the cost of work.
- To store large volumes of material, it is necessary to provide strictly defined conditions, which are not always possible to use.
- Reels with it are not always convenient to use for work at home, especially when it comes to small volumes of welding.
Additional fluxes for welding
- When performing welding using this product, it is quite problematic to select one universal diameter and therefore you have to keep several standard sizes of products in stock.
- Often, to improve the quality of welds, it is necessary to use additional flux.
Application
Having correctly selected the filler material, it is necessary to follow the welding technology in an argon environment. Automatic and semi-automatic modes can be used. The supply of filler wire must be synchronous with the supply of argon. Typically, constant voltage is used, which requires the use of a rectifier.
Classification
When choosing the necessary welding material, you need to understand what kind of work it will be used for. To facilitate the choice, several types of classification have been developed. Initially, groups are distinguished regarding the amount of alloying elements in the chemical composition of the wire; three main groups are distinguished:
- with a small amount of carbon;
- with a small amount of alloying components;
- with a large number of alloying components.
A separate group includes flux-cored wire, which is used for automatic welding and shows the required quality of the welded joint.
Filler wire structure
Another method of classification determines it by material of manufacture. In this case, the products are divided according to the main material. For the manufacture of welding wire, aluminum, copper, stainless steel, steel, etc. are used.
For welding parts made of ordinary steel, the following grades of welding material are used:
08G1S - it consists of a material coated with copper, it is used when working with steels and materials with a low content of alloying elements. Carbon dioxide or an argon mixture is used as a protective medium. It is used for welding on semi-automatic equipment.
Aluminum welding
Tig welding of aluminum has already been discussed and discussed on various sites and forums on the Internet. Welding aluminum is more difficult than ferrous metal and stainless steel, but if you do everything correctly, the process itself and the result of the work will bring you pleasure.
What aluminum alloys are most often required to be welded?
First, these are well-weldable deformable aluminum-magnesium and aluminum-manganese alloys AMg and AMts, which are not hardened by heat treatment. To weld these alloys, filler rod TIG ER-5356 (domestic analogue of Sv-AMg5 GOST 7871-75) . The rule for selecting a rod is the same: it must have a similar chemical composition to the metal of the product. In this regard, the ER-5356 rod is most consistent with such brands as AMg3, AMg5, AMg6.
Mechanical properties:
Yield strength: 120 MPa, Tensile strength: 265 MPa, Elongation: 26%
Secondly, these are cast aluminum alloys alloyed with silicon (silicon + manganese) such as AK7ch (AL9), AL10, AD35, etc. and so on. They are often used in various structures and assemblies that require reduced weight while maintaining high strength, since all these alloys are strengthened by heat treatment. For example, AK7ch can be aged to a hardness of 70...80 HB.
For such alloys, the additive TIG ER-4043 (AlSi5), a domestic analogue of Sv-AK5 GOST 7871-75, . It is often necessary to correct casting defects or mechanical defects (aluminum car wheels, aircraft asynchronous electric motor housings, etc.).
Mechanical properties of seam welded with ER-4043: Yield strength: 55 MPa, Tensile strength: 65 MPa, Elongation: 18%
As already mentioned, aluminum is a difficult metal. Therefore, it makes sense to talk about the difficulties associated with welding it. Here are some features:
- The surface of aluminum is covered with a refractory oxide film AL2O3; according to some data, its melting point is 2000-2700 degrees Celsius, which is an order of magnitude higher than the melting point of aluminum itself, only 600-650 degrees. Obviously, if you melt an aluminum film, you will inevitably burn through the metal. You need to remove the film in some other way. And they were invented.
Read also: Analysis of chainsaw Shtil 180
The first method is alternating current welding. It is known that alternating current differs from direct current in that it changes the direction of its movement many times per unit of time. The alternating current arc has a destructive effect on aluminum oxide.
The second method is to use a flap wheel to clean the metal to a shine or chemical etching.
- You will also need high-purity argon with the lowest impurity content. Dirt will immediately “craw out” from ordinary argon.
- The high thermal and electrical conductivity of aluminum requires high power from the power source and preheating in electric furnaces.
- It is better to perform large volumes of work on welding inverters specially designed for welding non-ferrous alloys: you can adjust the “aluminum cleaning” and work in 4T mode in the following sequence: adjustable initial current - main current - weld crater.
For welding stainless steel
Stainless steel has some processing difficulties. To perform welding, a material is selected that is as close as possible to the composition of the workpiece. For example, 04×19N11M3.
Wire for welding stainless steel
It is resistant to corrosion. Wire made from this material is used for welding parts that contain chromium, etc. Welding is carried out on automatic equipment under gas protection.
Magnesium welding
Magnesium is a silvery-white metal. In its pure form, without impurities, it is rarely used. But in alloys - often. Magnesium is four times lighter than steel, while magnesium alloys have high strength, making them popular primarily in the automotive and aviation industries, where the primary goal is to reduce the weight of the product. They are also used in household appliances, pneumatic and electric tools, etc.
Ordinary welders do not often encounter magnesium welding, but from time to time they may bring something similar to weld. Therefore, we will briefly talk about how to weld this metal.
Magnesium is often compared to aluminum. These metals do have something in common - a relatively low melting point, about 600 - 650 ° C, and a very refractory oxide: MgO melts at 2800 ° C. However, the melt density of magnesium is lower than that of aluminum.
The additive and parts are prepared by chemical etching.
Magnesium welding is carried out with alternating current on a short arc (this removes oxide better and gas protection is more effective). Its fluidity when melted is high, almost like water. Therefore, steel pads with a groove are used to form the return roller. Welding of parts with a thickness of 5-6 mm is carried out without cutting the edges of the connection with the lining. Above 6 cm, a V-shaped cutting is performed. The strength of welds is 60-80% of the base metal.
Filler material
Magnesium additive is a rare, scarce and expensive thing. It is sold in very few places and is difficult to find. Magnesium cannot be cooked with a simple aluminum rod. What should you do if you bring a product to repair, but you don’t have the necessary materials for this? It would seem that the situation is hopeless and repairs will have to be refused. But don't rush to conclusions. You can get everything you need at your nearest plumbing store. anode there , which can be cut into “noodles”, cleaned - and the additive is ready!
On a note. Where else is Mg:
- Pallets from “Zaporozhets”;
- Chainsaw "Friendship";
- Aviation wheels.
Add a comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Types of wire for stainless steel 12x18n10t
To weld stainless steel parts, it is necessary to use argon arc welding and an additive made of the same material. It may have different properties that may be suitable for other cases. Long products are produced from steel 12×18N10T. The filler material of this grade must meet the requirements of GOST 18143-72.
Welding filler wire has found its use in the mechanical engineering and food industries, construction, etc. It has not only high corrosion resistance, but also resistance to chemically aggressive environments. It contains a sufficient amount of chromium, which protects it from rust.
For welding work, products produced using cold drawing technology are used. It has a fairly low price and at the same time, this treatment preserves all its properties. This wire ensures the quality of the seam when processing any material.
Stainless steel wire 12Х18Н10Т
Thus, water supply systems are often assembled from pipeline fittings made from this grade of steel. When assembling and repairing, it is considered optimal to use a welding additive of the 12Х18Н10Т brand.
This steel grade is available in several versions. For its production, hot or cold rolling technologies are used. They make it possible to obtain a product with a diameter from 0.2 to 6 mm. When using wire of this brand, it is necessary to take into account that it can change some of its parameters based on the diameter.
Welding stainless steel parts is a complex technological process and if its rules are violated, the result can be a large number of substandard products. To avoid this, it is necessary to make the right choice of wire material. Wire made from steel 12Х18Н10Т is a specific product and quite possibly may not be suitable for most types of alloy steel. The main rule for choosing a material for welding is the identity of the chemical composition. The good thing about wire made from this wire is that the industry produces a wide range of products and, as a rule, there are no problems with selection. By the way, when welding, pre-heating and gradual cooling may be required. Heating is carried out using a gas burner.
Black steels
These include not only carbon steels, but also low-alloy steels. They are welded using MMA, but a truly high-quality, durable welded joint can only be achieved with TIG. It is believed that low-carbon steels are the easiest to weld. However, processes occurring in the heat-affected area can lead to strengthening of excessively heated zones during conventional welding, and problems with embrittlement may appear during multilayer welding. In boiling and semi-quenched low-carbon steel, a drop in impact toughness is observed in the heat-affected zone. As is known, black steels containing carbon:
- up to 0.25% are considered well weldable (Article 3, Article 10). But if problems arise, such as those described above, a slight preheating of 150-200 degrees in the SNOL electric furnace is recommended.
- from 0.25 - 0.45% are considered difficult to weld or partially weldable. They need to be heated before welding manipulations with a tungsten electrode and must be heat treated after. If it is possible to carry out complete heat treatment, such as annealing or hardening + aging, this is the best option. But if the product is already ready, and no deformations are allowed in it, you will have to limit yourself to low-temperature tempering (or, as this process is also called, rest).
- from 0.45% carbon and above, steel is not used for welded structures, especially if it is even slightly alloyed. But this is for structures. If the product will not bear any loads, you can try to weld Art. 55, only without sudden temperature changes, using all the “metallurgical” tricks.
Read also: Acetylene water and hg2
And finally, we got to the welding rod. All of the above cases are welded with rod Sv.-08G2S GOST 2246-70 or its minor modifications. The deoxidizers silicon and manganese in its composition have a positive effect on the mechanical properties of the seam, inhibit the development of seam porosity, the appearance of shells, reduce spattering, etc. The rod is used for welding products or structures for critical purposes, such as vessels, high-pressure pipelines, loaded components and parts. Imported analogue of Sv.-08G2S: copper-plated welding rod ER 70S-6. Micron coating of copper is, of course, a big plus, since copper protects the steel rod from pitting corrosion and oxidation - these processes actively take place in warehouse storage conditions. ER 70S-6 rod does not need to be sanded before welding for fear that dirt on its surface will show up as defects in the weld.
Mechanical properties of metal in a weld when using ER 70S-6:
- Yield strength 525 MPa;
- Tensile strength 595 MPa;
- Elongation 26%;
- КV – 30°С 70 J.
Welding Features
Stainless steel was obtained by accident through experimentation. Small additions of chromium, nickel and molybdenum (these components make up only about 15% of the total) led to significant changes in the chemical and physical properties of stainless steel.
It has become resistant to moisture, dirt and sources of corrosion. But at the same time, a number of features have been added that make welding not so easy. We're talking about a high melting point (1800 degrees!). Because of this, it is difficult to choose the optimal welding mode so that lack of penetration or burns do not form.
In our opinion, the optimal technology for welding stainless steel is semi-automatic, using shielding gas. When using this method, the wire is fed in a given mode into the welding zone, freeing the welder’s hands. And the gas protects the metal from oxidation, improves the quality and appearance of the seam.
It is better to use carbon dioxide as a gas. This gas does not affect the chemical properties and structure of the metal in any way, which is very good. All the characteristic features of stainless steel are taken into account, its advantages are not lost and its disadvantages are leveled out.
The most common methods of welding stainless steel
The connection of stainless steel parts with a high chromium content can be performed using different technological methods. For example, in practice the following types of welding are often used:
- argon-arc. Tungsten electrodes are best suited in combination with AC/DC TIG operation;
- MMA. Manual welding or cutting is performed with coated electrodes;
- semi-automatic. Work with electric arc welding machines is carried out in a protected environment. Argon is best. The operating mode is MIG, and stainless steel wire is used as an additive;
- cold welding. A special technological process has been developed for joining stainless steel. It passes under high pressure. The name was chosen based on the fact that metal melting is not provided;
- resistance spot welding and seam welding.
Before welding stainless steel workpieces, it is necessary to thoroughly degrease the joints and adjacent surfaces, and also clean them. For these purposes, acetone or aviation gasoline is most often used. Thanks to preliminary preparation, it is possible to reduce the porosity of the seam, and the welding arc will be stable and quite powerful. Only after careful cleaning of the edges can one hope for a high-quality final result.
What kind of welding, or rather the method of performing work, to use in a particular case is decided by the specialist himself. In addition to the basic methods discussed above, there are other technological methods that are rarely used. In any case, the choice of technology is influenced by the set of requirements for the future design and the characteristics of the materials used in the work.