Last updated April 2, 2021 at 1:37 pm
On January 1, 2015, the new Technical Regulations of the Customs Union “On the safety of wheeled vehicles” came into force in Russia. According to clause 9.8.3 of TR CU 018/2011, gas equipment on cars must be inspected and tested at the same frequency as inspection of gas cylinders.
Service life and verification of gas cylinders
For each container, the manufacturer provides a passport, which, in addition to parameters, indicates the service life, frequency, and date of the next inspection of gas vessels.
The frequency of recertification of vessels is as follows (regulated by Appendix No. 4 to the Federal norms and rules in the field of industrial safety approved by Rostechnadzor Order No. 116 dated March 25, 2014):
- Steel vessels for LPG (liquefied petroleum gas propane-butane) must be checked once every 2 years . Regardless of the type of container (toroidal or cylindrical).
- CNG (compressed natural gas) methane cylinders are checked at intervals:
- carbon steel - 3 years ;
- from alloy steels - 5 years ;
- made of metal composite materials, including with aluminum liner - 3 years ;
- consisting of non-metallic material (carbon fiber plastic) - 2 years .
The service life of the cylinders is determined by the manufacturer; as a rule, it is:
- Propane – 10 years;
- Methane - from 15 to 20 years, depending on the material of manufacture.
If there is no plant information, according to paragraph 485 of the “Industrial Safety Rules for Hazardous Production Facilities that use equipment operating under excess pressure,” the service life of the tank is set to 20 years.
When is Propane Tank Suitability Testing Required?
If the cylinder material is carbon or alloy steel, the inspection frequency is five years. Cylinders installed on a vehicle are certified every three or five years. Thus, from the moment of manufacture, the product must undergo regular certification, which will determine the strength of the container and valve, as well as weight and resistance to high pressure.
Sometimes it is necessary to conduct a survey earlier than planned. This happens in cases where:
- obvious valve failures are detected;
- a leak;
- shoe damage;
- poor quality of painting on the outer surface of the cylinder .
Who and where carries out recertification of gas cylinders and inspection of gas cylinder equipment
In accordance with paragraphs 486-508 of the same rules, re-examination and testing of gas containers is carried out by authorized organizations that have:
- Equipped room (testing point);
- Certified personnel;
- An individual mark with a code, which is assigned along with the issuance of a Rostechnadzor permit for 5 years;
- Equipment for testing gas containers (stands).
Checking gas equipment on cars is carried out by certified installers (service stations).
In other words, the organizations that carry out the inspection of automobile gas cylinders, as well as the inspection of gas equipment in general, are not always the same companies.
If in your locality there are no service centers legally authorized to check the containers of automobile gas equipment, you can contact gas filling stations for help.
Mandatory requirements for vessels subject to inspection
Technical requirements for vessels that are presented for the next inspection are established by the relevant governing documents.
For propane-butane cylinders, this document is RD 03112194-1094-03, and for methane equipment - RD 03112194-1095-03. Both documents were approved by the Ministry of Transport of the Russian Federation in 2002. Before submitting a car cylinder to a specialized inspection point within the prescribed period, you must perform an independent inspection and make sure that it meets the requirements of the governing documents:
- the regulatory expiration date has not expired;
- the outside of the cylinder is cleaned of oil and other contaminants;
- the type of vessel and its design are in accordance with regulatory requirements;
- the automobile cylinder is equipped with standardized filling, consumable and other fittings provided for by design; the tee has the necessary plugs;
- cylinders do not contain gas residues;
- all valves are closed.
RD 03112194-1094-03 and RD 03112194-1095-03 allow cylinders to have parts and fittings of different designs, but only within the limits of changes made by the manufacturer during the period that a particular product was in production.
Removal of vessels from residual gas motor fuel must be carried out at specially equipped sites. The rules do not allow the presence of excess gas pressure in cylinders. If there is excess pressure, the cylinder is not allowed for inspection and is unconditionally returned to its owner.
The basis for refusal to carry out an examination is the presence of cracks, bruises, various types of cavities, scratches on the outer part of the body, exceeding 10% of the structural thickness of the wall. Also, cylinders that are missing all or part of the passport data, have expired the designated certification period, or have expired are not subject to testing.
The inspection of cylinders is accompanied by marking in compliance with the standards governing the rules for applying inscriptions. The stamp of the point that carried out the inspection, the date of the inspection and the scheduled date of the next inspection are applied to the marking plate of the manufacturer using the embossing method. The mark is applied in one line in Arabic numerals, the height of which should not be less than 8 mm. The appointed date for the next inspection can be duplicated in white inscription on the outer part of the cylinder pre-painted with red enamel. In addition, white warning notices must be applied to the outer part of the cylinder.
How much does it cost to re-examine cylinders and check gas equipment on a car?
The price of verification depends on the volume and type of vessel, but on average in the market it starts at 1,200 rubles. Additional operations may affect the final cost:
- Dismantling/installation;
- degassing;
- cleaning/washing;
- primer, painting;
- minor repairs or restoration of the cylinder.
Thus, the cost can reach up to 7,000 rubles per cylinder. Which will often exceed the purchase price of a new container.
A scheduled inspection of gas equipment costs about 500 rubles, here everything also depends on the model of equipment, brand of machine, and elimination of identified problems.
It is worth noting that all procedures take 1-3 days if done according to legal requirements.
Many legitimate service shops will charge the customer a fee and perform a formal inspection of the equipment. Here everyone chooses for themselves.
Gas refill
Modern gas cylinders for fire extinguishing systems are characterized by increased strength and resistance to corrosion. Manufacturers regulate the maximum service life before the first inspection at 15 years, and the total useful life up to 30 years. These indicators are regulated by the following regulations GOST 4.106-83, NPB 22-96, Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 123-FZ of July 22, 2008. The frequency of maintenance and recharging of gas fire extinguishing systems depends on the timing of the survey. For low pressure cylinders (up to 60 bar) with a welded body it is 5 years. For high-pressure tanks (up to 150 bar), seamless, seamless - up to 10 years. The specific period is indicated in the product passport or on the nameplate attached to the cylinder.
The survey is carried out in accordance with the rules of PB 03-576-03:
- An external inspection of all structural elements is carried out;
- Cleaning from dirt and dust;
- Checking the presence of seals, passports, strength of fastenings and completeness of the device;
- The integrity of the cylinder and its locking device is monitored.
- The pressure in the containers is checked, taking into account the temperature inside the room. For low pressure cylinders the limit is 10% reduction, for high pressure containers up to 5%. If the indicators exceed the limit value, then the cylinders must be refilled.
Refilling cylinders of gas fire extinguishing systems with refrigerants is carried out using special equipment in a stationary production line. Before filling, the shut-off valve and the surface of the container are carefully checked. Filling with liquefied gas is carried out to 4/5 of the total volume. For more economical operation, refilling is carried out into a cooled cylinder, this can significantly reduce the pressure drop.
Technical examination of gas cylinders
Work order:
- Analysis of documents, checking them with container markings;
- dismantling (degassing if necessary) and disassembly by removing the multivalve or valve (the owner can remove the cylinder himself);
- washing, cleaning, external inspection;
- internal inspection (except for LPG vessels with a capacity of up to 55 liters);
- checking the mass and capacity by filling with water, weighing the empty and filled containers, then comparing the calculated volume of water with the original data indicated in the passport (steel seamless up to 12 and over 55 liters, as well as seam of all volumes are not checked);
- Carrying out pressure tests on a test bench.
Faulty toroidal cylinder
During inspection, cracks, corrosion, dents, and other damage are revealed, with which operation is prohibited.
Vessels are rejected if:
- The expiration date has expired;
- the depth of the sink, risks, cracks is more than 10% of the wall thickness; thread worn;
- weight of seamless cylinders with a volume of 12-55 litres. reduced by 7.5% and higher, also capacity increased by 1%;
- corrosion occupies more than 10% of the area.
Test technology
Stand for testing gas cylinders
Vessels are checked using special equipment for pressure testing gas cylinders using pneumatic or hydraulic methods. Housings must withstand pressure that exceeds the working load by 2 times. For propane-butane containers, the working pressure is 1.6 MPa, and for methane – 20-25 MPa.
Documents for cylinders
Upon completion of successful tests, the organization applies (knocks out) a stamp on the metal plate of the cylinder, the date of the next, current inspection. The same data is duplicated in the vessel passport.
If the container has a volume of 100 l. and more stamps are not required; the corresponding marks are reflected in the passport.
Types and design of valves
Despite the fact that all cylinders for storing and transporting gases differ from each other in shape, coating color, volume and many other characteristics, they all have the same design. The cylinder includes a faucet, a tank, etc. Faucets may differ from each other in design features and materials that were used for their production. In addition, they are divided by type of application - some are used for oxygen, others for propane, and others for acetylene. Accordingly, the following type of coatings are applied to their surface:
- blue;
- red
- white.
Gas cylinder valves
A typical gas tap consists of:
The body is made in the form of a tee, consisting of three fittings, each of them has a thread. On some models, a safety valve is built into the housing. The main task of this device is to relieve excess pressure that has arisen in the cylinder.
A fitting located at the bottom designed to connect the valve to a gas storage tank. A regulating flywheel (steering wheel) is attached to the top one. External communications are connected to the side fitting or gas is injected. The body and main parts are made of brass or steel.
Valves used for non-flammable gases are made with a right-hand thread on the fittings, for those used for flammable gases, a left-hand thread is cut.
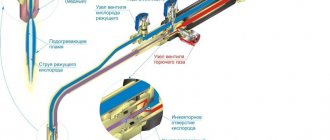
The process of checking HBO on a car
After installing and connecting the cylinder to the car, the gas cylinder equipment is checked, which includes:
- checking the tightness of the system under pressure;
- adjusting the operation of gas equipment;
- CO, CH content of exhaust (smoke in diesel engines).
Based on the test results, a certificate of periodic testing of the gas equipment (form 2b) installed on the vehicle is issued.
Step-by-step instructions for replacing the valve
The new control valve is not fixed to the cylinder with a clean thread. It is imperative to use sealing materials: sealants or fum tape.
Checking tightness and completing work
Upon completion of work to replace the valve on the gas vessel, it is necessary to check the tightness of the newly assembled connections. To do this, they use a method that has been proven for decades - applying soap foam.
Checking tightness and completing work
If the joints are assembled poorly, then bubbles will form at the point of gas leakage and therefore work will need to be done to reassemble them anew.
List of documents that the driver of a vehicle equipped with gas equipment must have with him
The driver is required to present documents for the installed equipment during an inspection by a traffic police inspector, at the request of a gas station employee, when passing a state technical inspection:
- vehicle registration certificate, which contains a note indicating the legal installation of gas equipment;
- certificate form 2b;
- cylinder nameplate with inspection marks;
- passport with data corresponding to the container plate.
Recertification of the cylinder and checking of gas equipment are carried out in order to ensure the safe operation of a vehicle with gas cylinder equipment. The lack of documentary evidence can cause not only fines in the amount of 500 rubles, but also other troubles.
Today we will talk about such maintenance of diving equipment as pressure testing of cylinders. All cylinders must undergo technical inspection at least once every 5 years.
Hydraulic tests of metal-plastic cylinders must be carried out by test pressure, determined by the formula:
Rpr=(1.25*Km+A*(1-Km))*P*S20/st,
where Km is the ratio of the mass of the metal structure to the total mass of the cylinder.
- A=1.3 for non-metallic materials with impact strength more than 20 J/sq.cm.
- A=1.6 for non-metallic materials with an impact strength of 20 J/sq.cm. or less
Hydraulic testing of cylinders made from casting must be carried out with a test pressure determined by the formula
Rpr=1.5*R
The following stamps must be clearly stamped on the upper spherical part of each cylinder:
- -manufacturer's trademark
- - cylinder number
- - date (month and year) of manufacture (test) and year of the next survey
- - designated operating pressure, P, kgf/cm^2 (MPa)
- - test hydraulic pressure, P, kgf/cm^2 (MPa)
- - nominal cylinder capacity in liters, E
- - actual weight of the cylinder in kilograms, V
- - manufacturer's quality control mark
And so, we go to the hydraulic testing point
Today's test subjects are awakened by a 6 liter cylinder with a working pressure of 300a.
First, open the valve completely and release the compressed air remaining in the cylinder. Next, we clamp the cylinder tightly in a vice and begin to unscrew the valve. It is worth noting that for most cylinders the process of unscrewing the valves is not very difficult, however, if old-style cylinders are pressurized, and these are usually cylinders from AVM devices, then to remove such a valve you have to burn the neck of the valve, since litharge (lead oxide) is usually used there ).
Next, we carefully remove the valve from the cylinder
Then the rust is pumped out and knocked out of the cylinder. After that, a cable and various brushes are inserted into the cylinder for more thorough cleaning of the glass and the bottom of the cylinder.
After this, an inspection is carried out. For this purpose, an electric lamp is lowered into the cylinder. When inspecting the outer and inner surfaces of the cylinder, the following defects may be identified, which serve as a basis for rejecting the cylinder: cracks, dents, cavities and scratches with a depth of more than 10% of the nominal wall thickness, tears and gouges, wear of the neck thread, as well as the lack of passport data on balloon.
- Next, we treat the inside of the cylinder with a special composition consisting of:
- -zinc oxide
- -orthophosphoric acid
- -triphosphate
- -sodium dichromate
- -water
We keep this composition in the cylinder for 20-30 minutes, as a result we get a cylinder covered inside with a protective layer, the composition acts in much the same way as a car rust converter, removes traces of corrosion and prevents its further spread. After which the liquid is drained and we proceed directly to hydraulic tests, for which we completely fill the test cylinder with tap water. For hydraulic testing of cylinders, water with a temperature of no lower than 5 degrees Celsius and no higher than 40 degrees is used. The temperature difference between the wall of the cylinder and the surrounding air during testing should not cause condensation of moisture on the walls of the vessel.
Next, a special valve is screwed into the cylinder and connected at the other end to a booster compressor. The container is wiped dry. It is worth noting that during testing the cylinder is located outside the room where the compressor and pressure tester are located.
Then a small bottle containing water with glycerin and an excess pressure of about 100-150 atm is connected to the booster compressor. (glycerin is necessary to lubricate the leather cuffs of the compressor).
We open the can and the pressure in the test cylinder immediately increases to 100 atm, then by pumping the compressor we increase the pressure to the required one. In 10 strokes you can reach a pressure of 400 atm, so you need to be careful. The test pressure should be 1.5 times higher than the working pressure. The test pressure should be monitored by two pressure gauges. Both pressure gauges are selected of the same type, measurement limit, identical accuracy classes, and division values.
For cylinders:
- — with working pressure P-150 kgf/cm^2, test pressure P-225 kgf/cm^2
- — with working pressure P-200 kgf/cm^2, test pressure P-300 kgf/cm^2
- — with working pressure P-232 kgf/cm^2, test pressure P-348 kgf/cm^2
- — with working pressure P-300 kgf/cm^2, test pressure P-450 kgf/cm^2
During hydraulic testing, cylinders must be under test pressure for 1 minute, after which the pressure is gradually reduced to operating pressure, at which the cylinders are inspected. The cylinder is threaded through a special template, which shows that the geometry of the cylinder is not broken. Cylinders are recognized as having passed the hydraulic test if there is no rupture, visible residual deformation, pressure drop on the pressure gauge, leakage, tears or sweating.
Next, the valve is unscrewed, water is poured out, and the bottle is sent to dry. The dryer is a room heated to 80-85 degrees. The container dries within 24 hours.
We proceed to complete disassembly of the valve, remove the gaskets, blow out the filter with compressed air, inspect the valve and internal elements for suitability for further use.
Assembling the valve and applying fum tape
After the drying time has passed, the cylinder is removed from the drying room and, without turning on the valve, a marking is applied indicating the passage of the next hydraulic test and the date of the next test.
Next, screw the valve into the cylinder and clamp it tightly.
At the end of the procedure, fill the cylinder to operating pressure with compressed air.
Hydraulic testing may be replaced by pneumatic testing, provided that this test is controlled by the acoustic emission method. Pneumatic testing is carried out with compressed air or inert gas. The value of the test pressure is assumed to be equal to the value of the test pressure during the hydraulic test. The holding time under test pressure must be at least 5 minutes.
The use of a solution for treating the inner surface of cylinders has proven itself to be the best. The tested cylinder had been treated with this solution many times already, and during each inspection no traces of rust or scale were found on the inner surface. The article was written based on the norms and rules for hydrostatic testing of high pressure vessels in the Republic of Belarus. 04/11/2007.
Fedorenko Konstantin (AVM)
Many thanks to M.F. Stankevich for help in preparing the material.
Discuss on the forum
Regulations
- Technical Regulations of the Customs Union “On the safety of wheeled vehicles”;
- Appendix No. 8 to TR CU 018/2011;
- Methodological recommendations for installing gas equipment on wheeled vehicles in operation in the Russian Federation;
- Methodological recommendations for the technical operation of gas-cylinder wheeled vehicles in operation in the Russian Federation;
- Industrial safety rules for hazardous production facilities that use equipment operating under excess pressure;
- A unified form of certificate of periodic testing of gas equipment installed on a vehicle, and the rules for its registration;
- A unified form of passport for a gas cylinder of a wheeled vehicle and the rules for its registration.
How to check a gas pressure gauge
In general, the test consists only of comparing the data of the pressure gauge being tested with the readings of the control device or calculating the current gas pressure, then measuring it using a pressure gauge and comparing the data. To do this, you only need a control pressure gauge and a thermometer. If we describe this procedure in more detail, it looks like this:
- install the pressure gauge sensor into the container through a special fitting;
- when the pressure value is recorded, remove the pressure gauge and install a control device in its place;
- After comparing the readings of the two instruments, check the accuracy of the instrument readings;
- if the instrument readings do not coincide with the reference pressure gauge, it is necessary to adjust it so that under the same operating conditions the instruments show the same pressure values;
- there are adjusting bolts on the pressure gauge body, with the help of which adjustments need to be made;
- with an electronic analogue the actions are the same, only you need to take into account that this device has inertia, so the readings must be held for 8 to 10 s.
If there is no reference device, you must first calculate the working pressure using the formula P2=T2.P1/T1:
- this will require a vessel of a volume that is known or can be measured, containing air at normal atmospheric pressure and room temperature;
- the vessel is hermetically sealed and gradually heated;
- then the pressure inside the vessel is simply calculated using the formula, where T1 and T2 are the initial and final air temperatures in the vessel, and P1 is the atmospheric pressure.
- if the instrument readings do not coincide with the calculation, then it is necessary to adjust it to the data obtained during the calculation.
Check out the types of pressure gauges sold by our company.
Permissible operation period
This period is determined by GOST 949-73 . For steel tanks with high pressures up to 19.6 MPa, the period is set to 20 years from the date of manufacture. This maximum life may be reduced due to severe operating conditions as well as normal wear and tear.
For plastic composite containers, this period is determined by the manufacturer and is 10 years.
Aluminum containers of the BD type that have recently appeared on the market are also not mentioned in GOST; for them, the period is also defined in the manufacturer’s specifications. It is equal to 20 years
Voluntary verification
In order to increase competitiveness, many entrepreneurs order a voluntary certificate, which confirms compliance with GOST or TU. It is valid for 3 years, is issued at an authorized center and gives the applicant a number of advantages:
- increases confidence in products from buyers, helping to increase demand and, accordingly, profits;
- strengthens the company’s position in the market, allowing it to build profitable relationships with partners;
- increases the chances of winning in government procurement, tenders and auctions.
How is verification carried out?
Checking pressure gauges is identifying inconsistencies or establishing whether the instrument readings are valid. To identify this compliance, readings are taken from the device and compared with the readings of a reference pressure gauge. After comparing the data, the possibility of further use of the device is identified. If the pressure gauge indicators comply with the standard, a verification mark is set, and it is used further. If during the manipulation process significant errors in the readings are revealed, the device is calibrated. If the indicators are very different from the actual ones and calibration cannot solve the problem, then the device is disposed of and is no longer used. Such a device is considered untrusted and cannot be used.
If the verification result is positive, a small stamp is placed on the glass of the device or its body, indicating the year and date of the operation. A similar mark is made in the technical passport of the device. Verification can only be carried out by a special licensed organization supervised by regulatory authorities. She also has the right to set a stamp on the completion of the procedure. A representative of the organization must remove the pressure gauges and bring them to the verification site.