What the article is about:
Choosing a shielding gas for welding: helium, argon, carbon dioxide
Oxygen has a negative effect on the weld pool, which can reduce the resistance of the weld to corrosion processes. In addition, as a result, its strength qualities will decrease.
As a result, pores may appear on the seam. Thanks to the gas flow, the weld pool has a protective shell that protects it from dangerous environmental influences. Moreover, the shielding gas provides the weld with protection from moisture and oxidation.
The quality of the weld depends largely on the shielding gas. This is especially true for such types of welding as MAG - Metal Active Gas, MIG - Metal Inert Gas and TIG - Tungsten Inert Gas.
Shielding gases and their types
Inert protective gases do not have the property of dissolving or interacting with heated metal. Used when welding magnesium, titanium, aluminum. For example, nitrogen, argon, helium.
Active gases, on the contrary, interact with the metal and are able to dissolve in it. For example, oxygen, carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen.
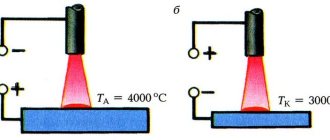
Argon is a non-toxic and explosive gas, tasteless and odorless. Designed for argon-arc TIG welding for all materials, as well as MIG welding of non-ferrous metals. Argon can also be used for welding refractory and chemically active metals.
When using argon, it is possible to obtain a narrow and deep seam. This type of gas is transported and stored in special cylinders, which are decorated in gray and have a green inscription.
Instructions for welding in different ways
There are 2 welding techniques:
- Butt. Before starting, you need to accurately fit the parts so that there are no gaps between them. Used when high precision is needed, for example when replacing part of a sheet. In this case, a single seam is made, then it is cleaned.
- Overlapping. One detail is superimposed on another. You don't have to adjust the edges to each other. Does not require much experience from the welder, unlike the previous method.
We recommend reading: What is submerged arc welding
Manual welding method in a chamber
If direct control of the process is needed, welding takes place in a room filled with gas. The specialist works in a spacesuit with an individual breathing system. This is a difficult job that requires high qualifications.
The manual welding method in the chamber allows you to control the process.
With non-consumable electrode
Inert gases are used as a protective medium: argon, helium. Filler wire can be used to fill the weld. It must be made of the same material as the part. It can be supplied manually or using automatic devices.
With consumable electrode
The wire or metal must be close in chemical composition to the structure being welded. They melt, and a strong, even connection is obtained. This method provides deep penetration with a small weld pool. Due to this, the efficiency increases.
The electrodes melt and a strong connection is obtained.
Pulse arc welding
This method consists of superimposing additional current pulses on the main one. This makes the arc stable, which means that the metal along its entire length after melting has the same quality.
Using a three-phase arc
In this method, an electrical discharge is applied between three electrodes located so close that warm energy acts in the melting space. Each of the three arcs has its own burning duration. The sequence is determined by the alternation of phases of the electric arc.
Three-phase arc welding has a number of technological advantages.
When forced to form a seam
There are devices that hold the weld pool. They are needed to correctly form the junction of the parts. These can be rotating disks, copper sliders. The parts used are cooled with water.
With magnetic field controlled arc
This is a new process control method in which combustion is controlled by the tension around the weld pool. During welding, areas with dense and sparse induction lines are created. The electrical discharge is deflected between them.
Welding with an arc controlled by a magnetic field is widely used to join metals.
With tungsten electrode
This is the most common type of non-consumable electrode materials. Suitable for most metals, including titanium, bronze, gold.
The advantage is that the spatial position and welding mode can be any.
Other welding options
Separately, submerged arc welding can be distinguished. During the smelting process it burns and releases protective gas. After this, a harmless slag is formed.
Helium for welding
Helium is a non-poisonous type of protective gas; it is odorless, tasteless and colorless. Helium is used for argon-arc TIG welding of non-ferrous metals, aluminum, etc. This option is also suitable for welding on ceiling surfaces. In the process, it is possible to obtain a wide weld with wetted edges.
Helium is often used in addition to argon. It is designed for joining magnesium and aluminum alloys, as well as active and chemically pure metals. This gas is found in brown cylinders and has a white lettering.
Carbon dioxide is suitable for welding thicker metals. In this case, you need to be prepared for the formation of splashes during welding. You can only work using a short arc. The gas is used for MAG flux cored wire welding and semi-automatic MAG short arc welding. Available for sale in black cylinders with yellow inscription.
What equipment is used in welding
Semi-automatic class inverters are most often used. You can adjust the current and voltage on them. At the same time they serve as a power source. There is a wide selection of units on the market, differing in power and additional options. If you are welding medium-thick metal from popular alloys, a simple model is sufficient.
We recommend reading Features of carbon dioxide welding
Semi-automatic welding machine
Welding machines with the function of supplying a protective environment are divided into 2 types: local and general. In the first case, gas comes directly from the nozzle. This type is most popular in industry. It is not suitable for all products, but it allows you to get a satisfactory result. If the structure is too large, air can get into the melting zone, then the quality will drop significantly.
For large parts, it is recommended to use units with an atmosphere control function. It works like this:
- air is pumped out from the internal cavity;
- gas is pumped in;
- welding is carried out with remote control.
Semi-automatic welding is one of the most commonly used in professional environments.
Additional components
In addition to the automatic device, the following accessories are used:
- Filler rods. Necessary for creating a neat seam on complex metals - non-ferrous, stainless, steel. The composition is selected depending on the metal alloy. They act as solder paired with a non-consumable electrode.
- Wire. Additional element for electric arc welding with argon. Supplied automatically from a coil installed on the inverter. Like rods, it melts into a smooth path when working with a non-consumable electrode.
- Hoses and fittings. This is a consumable item that periodically wears out and requires replacement. It is recommended to select a hose of such length that there is enough space between the machine and the work area.
Wire feeding systems
With the manual welding method, the master himself is responsible for advancing the rod. But there are also automatic mechanisms where a specialist only needs to control the process. They work independently of the welding machine. The advantage is that they allow you to regulate the speed of movement, which depends on the strength of the current.
The wire feed speed is adjusted in automatic mode.
Wire feed systems can be stationary or mobile. The first ones are installed on the inverter. The latter can be used on different units. The disadvantage of both types is that they require maintenance and have a complex design. A specialist who does not have technical knowledge will not be able to service them.
Gases complementing welding mixtures
Thanks to such welding gases, it is possible to make a better quality weld and reduce metal spattering.
For MIG MAG welding, oxygen is used as an additional component. With its help, you can create a wide seam, while the penetration of the metal is insignificant.
Hydrogen is used to bond austenitic stainless steel. The process creates a wide seam with deep penetration.
Nitrogen is intended more to protect the weld from rust than as a protection.
It is very important to choose the right shielding gas. Not only the quality and geometry of the weld directly depends on this. This way, it will be easier to correct defects and process the seam at the end.
Gases used in operation
In industry, mixtures of several elements are more often used. The following substances can be used separately: hydrogen, nitrogen, helium, argon. The choice depends on the metal alloy and the desired characteristics of the future weld.
Inert substances
These impurities give stability to the arc and allow deep soldering. They protect the metal from environmental influences without causing metallurgical effects. It is advisable to use them for alloy steel and aluminum alloys.
Inert substances allow deep soldering.
Active elements
The peculiarity of welding is that the compounds react with the workpiece and change the properties of the metal. Depending on the type of metal sheet, gas substances and their proportions are selected. For example, nitrogen is active towards aluminum and inert towards copper.
We recommend reading: Choosing a welding inverter
Common gas mixtures
Active substances are mixed with inert ones to increase the stability of the arc, increase productivity, and change the shape of the seam. With this method, part of the electrode metal passes into the melting region.
The following combinations are considered the most popular:
- Argon and 1-5% oxygen. Used for alloy and low carbon steel. At the same time, the critical current decreases, the appearance improves, and the appearance of pores is prevented.
- Carbon dioxide and 20% O2. It is used for carbon steel sheet when working with a consumable electrode. The mixture's high ability to oxidize gives deep penetration and clear boundaries.
- Argon and 10-25% CO2. Used for meltable elements. This combination increases the stability of the arc and reliably protects the process from drafts. Adding CO2 when welding carbon steel allows you to achieve a homogeneous structure without pores. When working with thin sheets, seam formation is improved.
- Argon with CO2 (up to 20%) and O2 (up to 5%). Suitable for alloy and carbon steel structures. Active gases help make the smelting area neat.
Argon and oxygen are the most popular combination of gases for welding.