Carbon steels: grades and brief characteristics
This large group of steels is divided into two main categories: ordinary quality steel (GOST 380-2005) and high-quality steel (GOST 1050-2005).
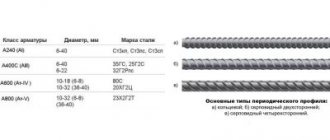
Types of carbon steels for rolled metal
- Ordinary quality steel is the most common and cheapest category, characterized by a large number of impurities. It is used for the production of ordinary hot-rolled steel - I-beams, angles, channels, rods, sheets. The production of thin hot-rolled sheets from steel of ordinary quality is regulated by GOST 16523-97, thick - by GOST 14637-89. Such rolled products are used to create welded, riveted or bolted structures, as well as for lightly loaded machine parts - axles, shafts, gears. For them, hardening by heat treatment is most often used. Such steels are designated by the letters St and a number indicating tenths of a percent of carbon, for example – St1, St2, St3.
- High-quality carbon steels are marked with two numbers indicating hundredths of a percent of carbon content. The main differences between these materials and steels of ordinary quality are more stringent requirements for micro- and macro-structure, setting narrow limits for carbon content, and lower amounts of phosphorus and sulfur. Steels 15, 20, 25 are used without heat treatment or in a normalized state for the manufacture of low-critical parts with surface hardening. Rolled metal from steels 30, 35, 40, 45, 50 is widely used in the production of parts for all branches of mechanical engineering: spindles, rods, friction discs, plungers, traverses.
According to the degree of deoxidation, both of these groups are divided into three categories:
- calm - from which oxygen, as a harmful impurity, is almost completely removed;
- boiling - contain an increased amount of FeO, have a lower cost compared to calm ones, are less weldable, are prone to aging and cold brittleness;
- semi-calm - their quality characteristics and cost occupy a position between calm and boiling.
GOST 535-88: Long-rolled and shaped rolled products made of carbon steel of ordinary quality
Home / GOSTs / GOST 535-88: Long and shaped rolled products made of carbon steel of ordinary quality
GOST 535-88: Long-rolled and shaped rolled products made of carbon steel of ordinary quality
GOST 535-88
| Rolled sections and shapes made of carbon steel of ordinary quality |
This standard applies to hot-rolled sections and shaped steel for general and special purposes made from carbon steel of ordinary quality.
1. Basic parameters
1.1. Rolled products are made from steel grades St0, St3kp, St3ps, St3sp, St4kp, St4ps, St4sp, Stbps, St5sp, Stbps, Stbsp in accordance with GOST 380-88.
1.2. The chemical composition of steel must comply with GOST 380-88; at the same time, for steel StZkp, StZps and StZsp, it is allowed to reduce the lower limit of the mass fraction of one of the elements: carbon - up to 0.11% or manganese - up to 0.25% while ensuring the mechanical properties established for the specified steel grades.
1.3. SVP profiles for supporting mine workings in accordance with GOST 18662-83 are made from steel grades Stbps and Stbsp,
1.4. The method of deoxidation, if not specified in the order, is determined by the manufacturer.
1.5. At the request of the consumer, the mass fraction of sulfur in steel of all grades, except for the STO grade, should be no more than 0.040%, phosphorus - no more than 0.030%.
1.6. Depending on the standardized indicators, rental products are divided into categories: 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
To designate a category, the category number is added to the designation of the steel grade, for example, St3ps1, St3ps5, St5sp2, St4sp3.
The category is indicated in the order. The category, if it is not specified in the order, is determined by the manufacturer.
1.7. Depending on the purpose, long products are divided into groups:
I - for use without surface treatment; II - for cold machining by cutting; Ill-for hot forming;
The group is indicated in the order. The group, if not specified in the order, is determined by the manufacturer.
1.8. In terms of shape, size and maximum deviations, rolled products must meet the requirements:
GOST 2590-71 - for hot-rolled rounds; GOST 2591-71 - for hot-rolled square; GOST 103-76 - for hot-rolled strip; GOST 2879-69 - for hot-rolled hexagonal; GOST 8509-86 - for corner equal-flange; GOST 8510-86 - for unequal corner; GOST 8239-72 - for I-beams; GOST 8240-72 - for channels; GOST 19425-74 - for beams and channels for special purposes; GOST 12492.0-72 - GOST 15492.21 -72 - for profiles of agricultural engineering; GOST 19240-73 - for ground and overhead rails; GOST 18662-83 - for profiles of hot-rolled SVP support for mine workings GOST 5157-83 - for profiles for various purposes; GOST 17152-71 - for blade profiles of earthmoving machines; GOST 21026-75 - for channels with a bent shelf for trolleys; GOST 26020-83 - for I-beams with parallel flange edges;
Examples of symbols are given in the appendix.
Note.
Rolled products are divided into long products and shaped products. Long products are classified as rolled products in which the tangent to any point on the perimeter of the cross section does not intersect this section. Shaped products include rolled products in which the tangent to at least one point of the cross-section perimeter intersects this section. 2. Technical requirements
2.1. Rolled products are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Rolled products are produced in a hot-rolled state. To ensure the required properties, heat treatment can be used.
2.3. At the request of the consumer, the weldability of steel is ensured by complying with the requirements for the chemical composition of steel and the mechanical properties of rolled products.
2.4. Standardized rental indicators by category are given in table. 1.
Table 1
| Category | Chem. compound | Temporary resistance | Yield strength | Relative extension | Cold bending | Impact strength | Steel grades | |||||||||||
| at t in °C | After mechanical aging | |||||||||||||||||
| +20 | -20 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1 2 3 4 5 | — + + + + | + + + + + | — + + + + | — + + + + | + + + + + | — — + — — | — — — + + | — — — + | St.0; St3kp; St3ps; Art. 3sp; St.4kp; St.4ps; St.4sp; St.5ps; St.5sp; St.6ps; St.6sp; St.3kp; St.3ps; Art. 3sp; St.4kp; St.4ps; Art.4sp;Art.5ps; St.5sp; St.3ps; Art. 3sp; St.4ps; St.4sp; St3ps; Art. 3sp; St3ps; Art. 3sp; | |||||||||
Notes
- The “+” sign means that the indicator is normalized.
- For steel grades St0, St3ps and St3sp, the yield strength and bending are not standardized.
- Category 2 rolled products from steel grades St3ps, St3sp, St4ps and St4sp are produced with a thickness of less than 5 mm.
2.5. The mechanical properties of rolled products under tension, as well as bending test conditions, must comply with the standards given in table. 2.
table 2
| steel grade | Tensile strength, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2) for thicknesses, mm | Yield strength, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for thicknesses, mm | Relative elongation,%, for thicknesses, mm | Bending until the sides are parallel (a is the thickness of the sample, d is the diameter of the mandrel) for thicknesses, mm | ||||||||
| to 10 | St.10 | to 10 | St. 10 to 20 | over 20 to 40 | over 40 to 100 | over 100 | up to 20 | over 20 to 40 | St.40 | |||
| no less | up to 20 | St.20 | ||||||||||
| St0 St3kp St3ps St3sp St4kp St4ps St4sp St5ps St5sp St6ps St6sp | Not less than 300(31) 360-460 (37-47) 370-480 (38-49) 380-490| 370-480 (39-50)| (38-49) 400-510 (41-52) 410-530 (42-54) 490-630 (50-64) 490-630 (50-64) Not less than 590 (60) | — 235 (24) 245 (25) 245 (25) 255 (26) 265 (27) 285 (29) 285 (29) 315 (32) | — 235 (24) 245 (25) 245 (25) 255 (26) 265 (27) 285 (29) 285 (29) 315 (32) | — 225 (23) 235 (24) 235 (24) 245 (25) 255 (26) 275 (28) 275 (28) 305 (31) | — 215 (22) 225 (23) 225 (23) 235 (24) 245 (25) 265 (27) 265 (27) 295 (30) | — 185 (20) 205 (21) 205 (21) 225 (23) 235 (24) 256 (26) 255 (26) 295 (30) | 18 27 26 26 25 24 20 20 15 | 18 26 25 25 24 23 19 19 14 | 15 24 23 23 22 21 17 17 12 | — d=ad=ad=ad=2a d=2a d=3a d=3a — | — d=ad=ad=ad=2a d=2a d=3a d=3a — | |
Notes:
- For shaped rolled products with a thickness of over 20 mm, the value of the yield strength is allowed to be 10 N/mm2 (1 kgf/mm2) lower than the specified value.
- It is allowed to reduce the relative elongation for shaped rolled products of all thicknesses by 1% (abs.).
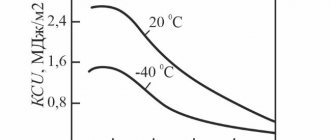
2.6. The impact strength of long and shaped rolled products of categories 3, 4, 5 from steel grades St3ps, St3sp, as well as categories 3 from steel grades St4ps, St4sp must correspond to that given in table. 3.
Table 3
| steel grade | Rolled thickness, mm | Sample type according to GOST 9454-78 | Impact strength KCU, J/cm2 (kgcm/cm2), not less | ||
| at temperature, C° | after mechanical aging | ||||
| +20 | -20 | ||||
| St3ps,St3sp | 5-9 10-25 26-40 | 3 1 1 | 108(11) 98(10) 88(9) | 49(5) 29(3) — | 49(5) 29(3) — |
| St4ps,St4sp | 5-9 10-25 26-40 | 3 1 1 | 98(10) 88(9) 69(7) | — — — | — — — |
Notes:
- The "-" sign means that the test is not carried out.
- Determination of the impact strength of rolled products of round cross-section is carried out starting from a diameter of 12 mm, square, starting from the square side of 11 mm, shaped - from thicknesses from which samples of types 1 and 3 can be cut according to GOST 9454-78.
- When testing rolled products for impact strength, it is allowed to reduce the value of impact strength on one sample by 30%, while the average value must not be lower than the standards indicated in the table.
2.7. Delamination is not allowed at the ends of rolled rods (rods).
2.8. For group I, individual rolled out bubbles, dirt, ripples, imprints, and marks are allowed on the surface of long products without cleaning, without removing the profile dimensions beyond the minus deviation. Other types of defects must be removed by gentle stripping or cutting, which does not take the profile size beyond the limits of minus deviation.
2.9. For group II, defects are allowed without cleaning, the depth of which does not exceed: minus maximum deviation for rods with a size of at least 100 mm; sums of maximum deviations - for bars measuring 100 mm or more. The depth of defects is calculated from the nominal size.
2.10. For group III, individual rolled bubbles, dirt, rippling, imprints, and marks are allowed on the surface of long products without cleaning without cleaning, which do not take the profile dimensions beyond the limits of minus deviation.
Other types of defects must be removed by gentle stripping or cutting, the depth of which should not exceed:
- sums of maximum deviations of diameter or thickness for rods measuring 40 mm or less;
- 5% of diameter or thickness - for rods with sizes over 40 to 140 mm;
- 8% of diameter or thickness - for bars larger than 140 mm.
The depth of stripping or cutting is calculated from the minimum size of the rolled product.
In a cross-section of rolled products (diameter or thickness) of more than 140 mm, no more than two strippings of maximum depth are allowed, which should not be located on the same axis.
2.11. The depth of occurrence, cleaning or cutting out defects on the surface of rolled products that do not have standardized maximum deviations should not exceed 10% of the thickness of the profile element being cleaned.
2.12. Defects are removed by flat sanding or cutting with a width of at least five times the depth.
2.13. The rental must be trimmed. When cutting rolled products in a cold state, waviness and chips are allowed on the cut surface (end), which do not take the length of the profile beyond the nominal size and maximum deviations along the length. When producing shaped rolled products, the cutting angle should not extend the length of the rolled product beyond its nominal size and maximum deviations along the length. Burrs should not exceed 0.5 mm for shaped steel thicknesses up to 10 mm and 0.1 for thicknesses over 10 mm. When cutting long products with a diameter (thickness) of up to 80 mm, the length of the crumpled end should not exceed the diameter of the profile being cut. The bevel of the cut is not controlled. When cutting long products with a diameter (thickness) of more than 80 mm, the cut angle should not exceed 5 mm, and the size of burrs should not exceed 2 mm. When cutting long rolled products with scissors in a hot state, knife imprints up to 0.25 times the diameter (thickness) of the rolled product are allowed. Rolled products with a diameter (thickness, width) up to 40 mm of unmeasured length may be manufactured with uncut ends.
2.14. Marking and packaging - in accordance with GOST 7566-81 with additions. Rods with a diameter (square side) of over 80 mm are subject to piece-by-piece hot stamping. The mark is applied to the end of the rod and contains the steel grade or its symbol indicating the decoding in the quality document, the heat number or its symbol indicating the decoding in the quality document.
2.15. Marking of rolled products is carried out with indelible paint in the colors specified in GOST 380-71.
3. Acceptance
3.1. Rentals are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of rolled products of the same size and one melting ladle. For rolled steel grade St0, the number of changes is c. batches are not limited.
3.1.1 In a batch consisting of rolled products of category I, the presence of several heats is allowed, and the batch must consist of rolled products of the same size and one grade of steel. The weight of the batch is no more than the wagon norm.
3.1.2. The batch must be accompanied by a quality document in accordance with GOST 7566-81 with the additions: rental categories; surface quality groups; if there are several heats in a batch, the number of heats in the batch.
3.2. To check the quality of rolled products by chemical composition and mechanical properties, the following is taken from the batch: for chemical analysis, one sample from the melting ladle; for tensile and bending tests - one rod, coil or strip; for impact strength testing - two rods, coils or strips.
3.2.1. When rolling melts to various thicknesses (diameters, square sides), rods for mechanical testing are selected from the minimum and maximum thickness of the rolled product.
3.3. If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one indicator, a repeat test is carried out in accordance with GOST 7566-81.
3.4. To control the surface quality and dimensions of rolled products, 10% of rods, coils or strips are selected from a batch, but not less than 5 pieces.
3.5. Chemical analysis of finished rolled products and bending testing may not be carried out; the established standards are ensured by the manufacturing technology
4. Control methods
4.1. Sampling methods for determining the chemical composition of steel - according to GOST 7565-81.
4.2. Chemical analysis - according to GOST 22536.0-87; GOST 22536.1-77; GOST 22536.2-87; GOST 22536.3-77; GOST 22536.4-77; GOST 22536.5-87; GOST 22536.6-77; GOST 22536.7-77; GOST 22536.8-87; GOST 22536.9-77; GOST 22536.10-77; GOST 22536.11-87; GOST 22536.13-77; GOST 17745-72; GOST 18895-81 or other methods approved in accordance with the established procedure and ensuring the necessary accuracy of analysis. In case of disagreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, the assessment is carried out using standard methods.
4.3. Sampling methods for mechanical and technological tests - according to GOST 7564-73 (option 1).
4.4. The tensile test is carried out according to GOST 1497-84 on samples of five times the length, one sample from the rod.
4.5. The bending test is carried out according to GOST 14019-80 using one sample from the rod.
4.6. The impact strength test is carried out according to GOST 9454-78 on two samples of types 1 or 3 from the rod for each temperature.
4.7. Determination of the susceptibility to mechanical aging is carried out according to GOST 7268-82 on two samples from the rod.
4.8. Control of mechanical properties is carried out for the minimum and maximum thicknesses (diameter, square side) of rolled products of one heat: for thicknesses up to 10 mm, St. 10 to 20 mm, St. 20 to 40 mm, St. 40 to 100 mm. When monitoring mechanical properties, it is allowed to use statistical and non-destructive testing methods in accordance with the regulatory and technical documentation on methods for testing metal products. When the manufacturer uses statistical control methods in accordance with the regulatory and technical documentation, the control of mechanical properties provided for by this standard may not be performed. The manufacturer ensures that the manufactured products comply with the requirements of this standard. In arbitration cases and during periodic quality checks, the control methods provided for in this standard are applied.
4.9. The quality of the surface is checked by inspection without the use of magnifying devices. Delamination of rolled products is controlled by inspection of the ends of the rolled products.
4.10. The geometric dimensions and shape of the profile are checked using measuring instruments in accordance with GOST 162-80, GOST 166-80, GOST 427-75, GOST 882-75, GOST 3749-77, GOST 5378-66, GOST 6507-78, GOST 7502-80 or tools certified according to GOST 8.326-78 and GOST 2216-84.
4.11. To determine the mass of I-beams with parallel flange edges, a sample of at least 300 mm in length is cut from each selected rod.
4.12. The mass of profiles is checked on samples 1 m long. For I-beams with parallel flange edges, a sample length of less than 1 m, but not less than 300 mm, is allowed.
5. Transportation and storage
5.1. Transportation and storage - according to GOST 7566-81.
Appendix Required
Examples of rental symbols
Rental symbol scheme
X1.. X1_1 X2 GOST X3 . . . ———— X4 X5 X6 GOST 535-88
X1 - type of rolled product (circle, square, hexagon, strip, angle, I-beam and others; X1_1 - Size of rolled product or profile number; X2 - Accuracy of rolled product - A, B, C (GOST 2590-71, GOST 2591-71, GOST 8509 -86 and others); X3 - Number of the standard for the assortment (GOST 2590-71, GOST 2591-71, GOST 8509-86 and others); X4 - Group by purpose - I, II, III (according to GOST 535-88); X5 - Rolled category - 1,2,3,4,5 (according to GOST 535-88); X6 - Steel grade according to GOST 535-88 (St3kp, St3ps and others);
Hot-rolled round steel with a diameter of 30 mm of normal rolling accuracy (B) according to GOST 2590-71. grade St5ps, category 1, group II: 30-V GOST 2590-71 Circle———— St5ps1-II GOST 535-88
Hot-rolled equal-flange corner products, size 50x50x3 mm, high rolling accuracy (A) according to GOST 8509-72, grade StZsp, category 3 group I: 50x50x3-A GOST 8509-86 Angle———— St3ps3-I GOST 535-88
Hot-rolled products, I-beam number 30 according to GOST 8239-72. grade StZps, category 4, group I: 30-GOST 8239-72 I-beam———— St3ps4-I GOST 535-88
T-rail according to GOST 19240-73 steel grade St5sp, category I group I: GOST 19240-73 T-rail ———— St5ps1-I GOST 535-88
I-beam with parallel flange edges, number 40B according to GOST 26020-83, steel grade StZsp, category 5, group I: 40B GOST 26020-83 I-beam———— St3ps5-I GOST 535-88
Rolled metal from alloy steel grades
In the production of rolled metal products intended for the creation of building structures operating under conditions of high loads and low temperatures, low-alloy structural (construction) steels of type 09G2S, 10G2S1, 10G2S1D are used. They also withstand dynamic and vibration loads and weld well. 09G2S is a material widely used in the production of shaped steel.
For work under high loads in chemically active environments, rolled metal made from corrosion-resistant steel grades is in demand.
- Chromium steels of type 12Х12, 20Х13, 30Х13, 40Х13 are widely used in mechanical engineering, production of medical equipment, household items, food and chemical industry equipment.
- Steels containing chromium, nickel and/or manganese. The most popular representatives are 12Х18Н9, 12Х18Н10Т (proven to work well in oxidizing environments, widely used in the food industry and medicine), 12Х18Н12Т. These are expensive materials, therefore, for less critical cases, analogs are used in which part of the nickel is replaced with manganese.
- High-alloy acid-resistant steels. 06ХН28МДТ – used for welded structures operated in contact with hot sulfuric acid.
Application of different types of stainless steel
BETAL sells stainless steel grades that have found their application in industry. For example:
- AISI 304; 304L; 316 is the main raw material for the food industry. They are used in the manufacture of stair railings, light structural elements, arches, decorative parts in architecture and furniture production. Aisi 316 is particularly resistant to aggressive environments.
- AISI 321 (08x18n10t); 316Ti is in demand in mechanical engineering and the petrochemical industry. They are used to produce circles, squares, hexagons, strips, etc., which subsequently become raw materials for various hardware connecting products.
There are also heat-resistant and heat-resistant types of steel on sale.
They are used to make parts for the engineering industry - valves, fasteners, engines, heat exchangers. Grades 30x13 and 40x13 are used to create medical instruments and household items, and 08x181 is the basis for structural elements that will work in oxidizing environments (nitric acid). Often clients are interested in purchasing products made from 14x17xH2 at a price per ton, which are in demand in the aviation and chemical industries. Consultants will advise which grades of stainless steel are most suitable for the customer. Their chemical composition and technical characteristics are regulated according to GOST.
Classification of rolled metal products by section shape
According to the cross-sectional shape, rolled metal is divided into sections, shaped, sheets, and pipes.
Long and shaped rolled products
In accordance with GOST 535-2015, long-rolled metal includes products in which any tangent to the cross section does not intersect it, and shaped metal products include metal products in which at least one tangent to the cross-section intersects it.
Types of rolled metal products:
- Circle . In GOST 2590-2006, the table indicates the assortment and weight of a linear meter of hot-rolled round metal, the range of section sizes is 5-270 mm. The hot-rolled circle serves as the starting material for the production of cold-deformed circles and is used in construction. The range of nominal diameters of cold-rolled wheels is 3-100 mm. The products are in demand in mechanical engineering, in the production of household appliances, in the furniture industry, in the design of facades and interiors.
- Square . The range of sides of hot-rolled squares is 8-200 mm. These metal products are used in the construction of fences, the manufacture of gratings, metal gates, wickets, and in the production of calibrated squares. Cold-deformed squares are produced in a range of side sizes - 3-100 mm. It is used in the automotive industry and mechanical engineering, in interior design, and furniture production.
- Hexagon . The cross section is a regular hexagon. The marking of this type of rolled metal indicates a number equal to the diameter of the inscribed circle in mm. Hot-rolled hexagonal rod is used in the production of hardware and calibrated (cold-drawn) hexagon. Calibrated hexagonal rolled metal is used in the production of parts for the automotive and mechanical engineering industries on high-performance automated machines.
- Strip – hot-rolled and cold-rolled . It is used in construction, in the production of pipe and bent shaped products (angles, channels), welded I-beams.
Types of shaped metal :
- I-beam is a construction metal product with a cross section in the shape of the letter H. Produced only by hot rolling. It is used in the construction of large civil and industrial facilities.
- Channel . The cross section can be equal or unequal. The products are manufactured using hot rolling technology. It is used in the construction of frame structures - canopies, gazebos, street advertising media, and as a frame for facing materials.
- Corner . Hot-rolled corner metal products are produced equal-flanged and unequal-flanged. It is often used to create additional connections in load-bearing and non-load-bearing metal structures, when arranging supports for various purposes, in mechanical engineering and machine tools.
Sheet metal
Hot rolled sheets are produced in a wide range of thicknesses - from 0.5 mm to 160 mm. General purpose products are regulated by GOST 19903-2015. Scale that is present on the surface is removed using sandblasting machines or etching. To give precise dimensions and improve the surface quality of hot-rolled metal products, cold rolling is used.
8 Acceptance rules
8.1 Rentals are accepted in batches. The batch must consist of rolled products of the same size and one melting ladle. For rolled steel grade St0, the number of heats in a batch is not limited.
8.1.1 A batch may contain several heats (prefabricated batches), and the batch must consist of rolled products of the same size (diameter, thickness or number) and the same grade of steel. The chemical composition, tensile strength, yield strength, elongation, impact strength, cold bending and compliance with a given category of rolled products for this batch are determined by the heat that has the lowest carbon equivalent value (). The mass of the batch is no more than 200 tons. The weight of the batch of rolled products from billets produced on continuous casting machines using the “melt-on-melt” method is no more than 500 tons.
8.2 The batch must be accompanied by a quality document in accordance with GOST 7566 with the additions: - the “sb” index and the carbon equivalent value - for the prefabricated batch; — index “sv” — when supplying rolled products with weldability ensured; - index (*) for ladle sample or (S) for finished rolled products - when indicating the chemical composition.
8.3 To check the quality of rolled products by chemical composition, mechanical and technological properties, the following is taken from the batch: - for chemical analysis - one sample from a ladle melt or one sample from the finished rolled product of each ladle melt; - for cold tensile and bending tests - one rod, coil, strip or profile; - for impact bending testing to determine impact strength - two rods, coils, strips or profiles.
8.4 When rolling melts to various thicknesses (diameters, square sides), rods, coils, strips or profiles for mechanical testing are selected from rolled products of minimum and maximum thickness.
8.5 To control the mass of rolled products, one rod, coil, strip or profile is selected from the batch.
8.6 To control the shape, dimensions of rolled products and surface quality, 10% of rods, coils, strips or profiles are selected from the batch, but not less than 5 pieces.
8.7 Chemical analysis of finished rolled products and cold bending testing may not be carried out; the established standards are ensured by the manufacturing technology.
8.8 If unsatisfactory test results are obtained for at least one indicator, a re-check is carried out in accordance with GOST 7566.
Specifications
The table of steel grades presented on the website will help consumers choose the most suitable one not only in terms of properties, but also in cost. If you would like to place an order for metal products made from them, please contact our consultants. Each grade of rolled steel belongs to a specific class, depending on:
- carbon content – low-carbon (up to 0.3%), medium-carbon (from 0.3 to 0.7%) and high-carbon (more than 0.7%);
- purposes – structural (high-strength, spring-spring, upgradeable) and instrumental;
- qualities - ordinary - only carbon, while high-quality and high-quality (A) can be carbon and alloyed;
- degrees of deoxidation – calm, semi-calm, boiling.
Often the consumer is interested in what analogues of steel grades are there and how much does rolled metal from them cost? Check the information by phone.
Various alloy steels, in addition to the numbers in the markings, also have letters that indicate certain impurities in the steel, in particular:
- K - cobalt;
- X - chromium;
- Yu - aluminum;
- N - nickel;
- G (or Mg) - manganese;
- B - tungsten;
- C—silicon;
- F (or Va) - vanadium;
- M - molybdenum.
TECHNICAL REQUIREMENTS
2.1. Rolled products are manufactured in accordance with the requirements of this standard according to technological regulations approved in the prescribed manner.
2.2. Rolled products are produced in a hot-rolled state. To ensure the required properties, heat treatment can be used.
2.3. At the request of the consumer, the weldability of steel is ensured by complying with the requirements for the chemical composition of steel and the mechanical properties of rolled products.
2.4. Standardized rental indicators by category are given in table. 1.
Table 1
| Category | Chemical composition | Temporary resistance | Yield strength | Relative extension | Cold bending | Impact strength | steel grade | ||
| At temperature, °C | After mechanical aging | ||||||||
| +20 | -20 | ||||||||
| 1 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | St0; St3kp; St3ps; St3sp; St4kp; St4ps; St4sp; St5ps; St5sp; St6ps: St6sp |
| 2 | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | — | St3kp; St3ps; St3sp; St4kp; St4ps; St4sp; St6ps; St6sp |
| 3 | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | — | St3ps; St3sp; St4ps; St4sp |
| 4 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | — | St3ps; St3sp |
| 5 | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | St3ps; St3sp |
Notes:
1. The “+” sign means that the indicator is normalized.
2. For steel grade St0, the yield strength and bending strength, for steel grades St6ps and St6sp, bending is not standardized.
3. Shaped and strip products of category 2 from steel grades St3ps, St3sp, St4ps, St4sp are produced with a thickness of less than 3 mm and more than 40 mm. Long products of category 2 from the same steel grades are produced with a diameter of less than 12 mm, a square side of less than 11 mm and a diameter (square side) of more than 40 mm.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 2).
2.5. The mechanical properties of rolled products under tension, as well as bending test conditions, must comply with the standards given in table. 2.
table 2
| steel grade | Tensile strength sв, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for thicknesses, mm | Yield strength st, N/mm2 (kgf/mm2), for thicknesses, mm | Relative elongation d, % for thickness mm | Bend until the sides are parallel (a — sample thickness, | ||||||||
| to 10 | St. 10 | to 10 | St. 10 to 20 | St. 20 to 40 | St. 40 to 100 | St. 100 | up to 20 | St. 20 to 40 | St. 40 | |||
| no less | up to 20 | St. 20 | ||||||||||
| St0 | At least 300 (31) | — | — | — | — | — | 18 | 18 | 15 | — | — | |
| St3kp | 360 — 460 | 235 | 235 | 225 | 115 | 185 | 27 | 26 | 24 | d = | d = 2 | |
| (37 — 47) | (24) | 124) | (23) | (22) | (20) | |||||||
| St3ps | 370 — 480 | 245 | 245 | 235 | 225 | 205 | 26 | 25 | 23 | d = | d = 2 | |
| (38 — 49) | (25) | (25) | (24) | (23) | (21) | |||||||
| St3sp | 380 — 490 | 370 — 480 | 255 | 245 | 235 | 225 | 205 | 26 | 25 | 23 | d = | d = 2 |
| (39 — 50) | (38 — 49) | (26) | (25) | (24) | (23) | (21) | ||||||
| St4kp | 400 — 510 | 265 | 255 | 245 | 235 | 225 | 25 | 21 | 92 | d = 2 | d = 3 | |
| (41 — 52) | (26) | (26) | (25) | (24) | (23) | |||||||
| St4ps | 410 — 530 | 265 | 265 | 265 | 245 | 235 | 24 | 23 | 21 | d = 2 | d = 3 | |
| St4sp | (42 — 54) | (27) | (27) | (26) | (25) | (124) | ||||||
| St5ps | 490 — 630 | 285 | 285 | 275 | 265 | 255 | 20 | 19 | 17 | d = 3 | d = 4 | |
| (50 — 64) | (29) | (29) | (28) | (27) | (26) | |||||||
| St5sp | 490 — 630 | 295 | 285 | 275 | 265 | 255 | 20 | 19 | 17 | d = 3 | d = 4 | |
| (50 — 64) | (30) | (29) | (28; | (27) | (26) | |||||||
| St6ps, | Not less than 590 | 315 | 315 | 305 | 295 | 296 | 15 | 14 | 12 | — | — | |
| St6sp | (60) | (32) | (32) | (31) | (30) | (30) | ||||||
Notes:
1. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, for shaped rolled products with a thickness of over 20 mm, the value of the yield strength is allowed to be 10 N/mm2 (1 kgf/mm2) lower than the specified value.
2. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to reduce the relative elongation for shaped rolled products of all thicknesses by 1% (abs.).
3. By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is allowed to exceed the upper limit of tensile strength by 50 N/mm2 (5 kgf/mm2) compared to the specified limit, provided that other standards are met.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
2.6. The impact strength of long and shaped rolled products of categories 3, 4, 5 from steel grades St3ps, St3sp, as well as category 3 from steel grades St4ps, St4sp must correspond to that given in table. 3.
Table 3
| steel grade | Rolled thickness | Impact strength KSV, J/cm2 (kgf×m/cm2), not less | ||
| at a temperature of 0C | after mechanical aging | |||
| +20 | -20 | |||
| St3ps, | 3,0 — 4,9 | 108(11) | 49(5) | 49(5) |
| St3sp | 5,0 — 9,9 | 108(11) | 49(5) | 49(5) |
| 10 — 25 | 98(10) | 29(3) | 29(3) | |
| 26 — 40 | 88(9) | — | — | |
| St4ps, | 3,0 — 4,9 | 98(10) | — | — |
| St4sp | 5,0 — 9,9 | 98(10) | — | — |
| 10 — 25 | 88(9) | — | — | |
| 26 — 40 | 69(7) | — | — | |
Notes:
1. The “-” sign means that the test is not carried out.
2. Determination of the impact strength of rolled products of round section is carried out starting from a diameter of 1.2 mm, square, starting from the side of the square 11 mm, shaped - from thicknesses from which samples of types 1 and 3 can be cut according to GOST 9454.
3. When testing rolled products for impact strength, it is allowed to reduce the value of impact strength on one sample by 30%, while the average value must not be lower than the standards specified in the table.
2.7. Delamination of rolled products is not allowed.
2.8. For group I, individual rolled bubbles, ripples, imprints, and marks are allowed on the surface of the rolled product without cleaning, without removing the dimensions of the profile beyond the minus deviation. Other types of defects must be removed by gentle stripping or cutting, which does not take the profile size beyond the limits of minus deviation.
2.9. For group II, defects are allowed without cleaning, the depth of which does not exceed:
minus maximum deviation - for rods less than 100 mm in size;
sums of maximum deviations - for bars measuring 100 mm or more.
The depth of defects is calculated from the nominal size.
2.10. For group III, individual rolled bubbles, dirt, ripples, imprints, and marks are allowed on the surface of the rolled product without cleaning, without removing the dimensions of the profile beyond the limits of minus deviation.
Other types of defects must be removed by gentle stripping or cutting, the depth of which should not exceed:
sums of maximum deviations of diameter or thickness for rods measuring 40 mm or less;
5% of diameter or thickness - for rods with sizes over 40 to 140 mm;
8% of diameter or thickness - for bars larger than 140 mm.
The depth of stripping or cutting is calculated from the minimum size of the rolled product.
In a cross-section of rolled products (diameter or thickness) of more than 140 mm, no more than two strippings of maximum depth are allowed, which should not be located on the same axis.
2.11. The depth of occurrence, cleaning or cutting out defects on the surface of rolled products that do not have standardized maximum deviations should not exceed 10% of the thickness of the controlled profile element.
2.7. — 2.11. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).
2.12. Defects are removed by flat sanding or cutting with a width of at least five times the depth.
2.13. The rental must be trimmed. When cutting rolled products in a cold state, waviness and chips are allowed on the cut surface (end), which do not take the length of the profile beyond the nominal size and maximum deviations along the length.
The miter cut of shaped rolled products should not take the length of the rolled product beyond its nominal size and maximum deviations along the length. The height of the burr when cutting with scissors should not exceed 0.5 mm for the thickness of the shaped steel in the direction of movement of the knives up to 5.0 mm inclusive, 1.0 mm for thicknesses over 5.0 to 10 mm inclusive and 0.1 thickness for the thickness of the shaped rolled products more than 10 mm.
The cutting angle of long products with a diameter (thickness) up to 80 mm is not controlled; for long products with a diameter (thickness) over 80 mm, the cutting angle should not exceed 0.1 diameter (thickness), and at the request of the consumer - 5.0 mm.
The height of the burrs when cutting bars with scissors should not exceed 0.1 diameter (thickness).
The height of burrs when cutting shaped and rolled products with saws should not exceed 3 mm.
At the request of the consumer, burrs must be removed.
When cutting long and shaped steel with scissors, tightening of the ends and knife marks up to a depth of 0.25 of the diameter (thickness) of the rolled product are allowed.
Rolled products with a diameter (square side, width) up to 40 mm of unmeasured length may be manufactured with uncut ends. By agreement with the consumer, rolled products with a diameter (square side, width) over 40 mm are manufactured with uncut ends.
(Changed edition, Amendment No. 1, 2).
2.14. Marking and packaging - in accordance with GOST 7566 with additions.
At the consumer's request, rods with a diameter (square side) over 30 mm, packaged in bundles, are marked. The mark is applied to the end of the rod and contains the steel grade or its symbol indicating the decoding in the quality document, the heat number or its symbol indicating the decoding in the quality document.
2.15. Marking of rolled products is carried out with indelible paint in the colors specified in GOST 380.
Rolled products in bundles are marked with color markings in strips no less than 20 mm wide. The paint is applied to the side surface along the circumference (at least 1/2 the circumference) at a distance of no more than 500 mm from the end.
For long products with a diameter (square side, thickness) over 80 mm, it is allowed to apply color markings to the ends of three to five rods in a bundle.
By agreement between the manufacturer and the consumer, it is possible not to mark with paint.
2.14; 2.15. (Changed edition, Amendment No. 1).