What is it and why is it needed?
Wastewater treatment is an activity by which pollutants are removed from industrial and domestic wastewater. The complex is carried out before the liquid is discharged into reservoirs .
Each enterprise is obliged to carry out wastewater treatment; this is stipulated in the Water Code of the Russian Federation and the Federal Law of 2011 “On Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal”.
If measures are neglected, pollution will enter the natural reservoir and soil, and poison the local ecosystem. The number of plants and animals will decrease. Hazardous substances accumulate in biota and enter the human body through the food chain.
Industrial and domestic wastewater
can be sent to the same treatment plant .
Mixing them optimizes the ratio of carbon and sodium, carbon and phosphorus, which increases the efficiency of biological treatment.
The process takes place at industrial or municipal wastewater treatment plants.
Reference. If residential buildings are not connected to the central sewer system, domestic local facilities (LOFs) are used to treat wastewater.
Industrial VOCs are required if the effluent contains aggressive or biotoxic contaminants. The bulk of impurities are removed, then the water is supplied to general production facilities.
WASTEWATER RATING: MOVEMENT TOWARDS LIBERALIZATION
The water supply and sewerage complex functions as an ecological shield for the country's water bodies. The state water policy in the field of wastewater disposal in terms of wastewater rationing is changing towards liberalization in relation to water and wastewater utilities.
The activities of water supply and sewerage enterprises (water utilities) are regulated by environmental and water legislation, primarily the Water Code, the Federal Law “On Water Supply and Sanitation” and the Rules for Cold Water Supply and Sanitation; Strict compliance with their requirements is among the priority strategic directions of water utilities.
In other words, water utilities are entrusted with environmental responsibilities by existing legislation, which they carry out within the framework of established powers and approved tariff and tax policies. First of all, this concerns the obligation to reduce the negative impact on the environment from wastewater discharges based on the principle of standardization based on maximum permissible concentrations (MAC) of chemicals.
And it is the system of regulation of pollutant discharges that has become a serious obstacle both to effective environmental protection and to the effective development of water utilities.
MPC is against modernization
The MPC standardization system itself originated in the distant 1960–1970s, during the period of exclusively state ownership and state planned economy, when the issue of payments for environmental violations was not even raised before water utilities. Moreover, the standards themselves, which, by the way, were derived through mathematical modeling and forecasting, were intended largely for research institutes.
30 years later, the situation has changed dramatically. The high tariffs for discharges established by the new Russian legislation and the increasing coefficients for them come into clear contradiction with tariff and budget policies, negatively affect the economic activities of water and utility companies, unreasonably increasing the financial burden and making it difficult to update production assets and introduce innovative technologies in the field of wastewater treatment .
Today, almost none of the water users and specialists from relevant and related departments have any doubt that the system for regulating discharges needs to be reformed, since it has upset the balance of interests of water users and regulatory authorities, primarily in the field of compensation for exceeding MPCs. The Russian Association of Water Supply and Sanitation (RAWV) has been raising these issues for more than ten years and has been consistently working towards liberalizing environmental legislation in relation to water and wastewater utilities.
Last year, there was a serious breakthrough in this direction: issues of the water industry received priority status as affecting the interests of national security and were allocated as a separate area of activity of the Public Council of the Ministry of Natural Resources and Ecology of Russia, whose decisions are directly reflected in legislative activity.
The ice has broken, gentlemen of the jury!
In April, the State Duma Committee on Natural Resources, Environmental Management and Ecology, with the participation of the Russian Association of Water Supply and Sanitation, held an extended meeting on the topic “The impact of the activities of municipal and industrial enterprises on water bodies. State policy in the field of wastewater regulation.” The event was attended by representatives of Russian water management organizations, private operators, the business community, public organizations, federal executive authorities, and State Duma deputies.
At the meeting, it was noted that state and market regulatory instruments in the field of environmental protection are not sufficiently developed, because they do not provide effective protection of water bodies and do not stimulate the environmental activities of water utilities, including the construction and reconstruction of treatment facilities.
A limiting factor for the introduction of innovations in the field of municipal and industrial wastewater treatment technology for many years has been the established system of regulating maximum permissible concentrations of pollutants in wastewater, which is a set of excessive, impossible requirements for their discharge, as well as administrative barriers to obtaining permits. .
Currently, the Russian Federation has established two types of water quality standards in reservoirs: for reservoirs for drinking and cultural and domestic water use and for reservoirs used for fishing purposes. To regulate wastewater when it is discharged into water bodies, fishery standards are widely used, regardless of the actual purpose of the water body, its condition and ability for self-purification processes. This situation has arisen due to the possibility of double interpretation of the accepted wording of legal norms. Thus, in accordance with the Federal Law “On Fisheries and the Conservation of Aquatic Biological Resources,” water bodies for fishery purposes include water bodies that are “used or can be used” for fishing. And although in practice only single objects are used for fishing, the phrase “may be” fixed in the law allows all water bodies in the country to be classified as fisheries. At the same time, there is no methodology for classifying water bodies as fisheries. At the same time, currently used urban wastewater treatment technologies require that they be purified to the standards of fishery reservoirs. However, the standard technological schemes of many Russian water utilities are not able to provide treatment for most indicators at the same time, and even the most modern schemes with additional treatment only bring the quality of treated wastewater closer to this level.
In connection with the above, draft Federal Law No. 386179-6 “On Amendments to the Federal Law “On Water Supply and Sanitation” and Certain Legislative Acts of the Russian Federation” was submitted for discussion. According to a representative of the housing and communal services department of the Ministry of Construction of Russia, amendments to the law “On Water Supply and Water Disposal” will secure for enterprises performing the function of water disposal a transition to rationing wastewater discharge based on technological standards, and not fishery standards, as before. Standards will be established in accordance with the best available technologies (BAT) reference book “Wastewater treatment in the production of products (goods), performance of work and provision of services at large enterprises.” Moreover, water utilities are expected to be responsible for discharging only those substances that they are intended to treat. For other indicators, permissible discharge standards will be established solely for the purpose of calculating standards for subscribers. The new legislation will also be more liberal for subscribers in terms of the construction of local treatment facilities: they will be allowed to choose a method acceptable to them to achieve the established requirements.
Considering the high relevance of the discussed problem of the targeted formation of legislative provisions in ensuring important social activities to provide the population with drinking water and protect water bodies from the negative impact of wastewater, the meeting participants developed recommendations to the relevant federal executive authorities:
• Accelerate work on establishing criteria for classifying surface water bodies as fisheries.
• Consider the possibility of introducing compulsory environmental risk insurance for water supply and sewerage organizations and their subscribers – industrial enterprises.
• Consider the possibility of creating extra-budgetary environmental water funds, targeted accumulation of budget funds coming from water utilities to form an autonomous source of guaranteed support for the water protection activities of water supply and sewerage organizations in Russia, independent of the state budget.
It is clear that environmental legislation must be improved, and these changes must be based on a balance of interests of the population, the environment, water utilities, and the budgetary and technological capabilities of the participants. Moreover, the approach to wastewater regulation issues should ideally create an economic mechanism that will encourage water-using enterprises to modernize existing treatment facilities and build modern treatment facilities.
The material uses information materials from the State Duma of the Russian Federation and the Russian Association of Water Supply and Sanitation
Tweet
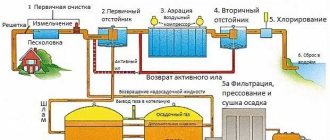
General scheme of operation of treatment facilities
Preparation:
- Averaging is the mixing of waters with different concentrations of pollutants. The stage lasts 18-24 hours;
- Neutralization - lime milk is added to acidic waters, hydrogen chloride, sulfate acid or carbon dioxide is added to alkaline waters;
- Cooling of hot wastewater, extraction of explosive gases.
Mechanical removal of impurities:
- Sedimentation in settling tanks;
- Centrifugation;
- Removal of oils, grease, petroleum products;
- Filtration through neutralizing, absorbent and fabric materials;
- Reagent treatment of wastewater with coagulants;
- Aeration to extract hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide;
- Filtration through membranes.
Destructive cleaning – destruction of contaminants and their breakdown into harmless compounds:
- Oxidation, reduction, transformation, destruction of organic matter by aerobic and anaerobic microorganisms;
- Oxidation with active chlorine or hydrogen peroxide, reduction with hydrogen, photocatalytic and electrochemical oxidation;
- Thermal destruction - combustion.
Post-treatment (deep treatment) – physical, chemical or biological treatment of wastewater:
- Lightening;
- Filtration through granular media;
- Microfiltration;
- Disinfection.
After complete purification, wastewater is discharged into reservoirs or returned to the production cycle. Deep cleaning may not be necessary when discharging a small amount of wastewater into a powerful reservoir.
Difference between cleansing and disinfecting
During cleaning, mechanical and chemical impurities are removed .
Important. The purpose of disinfection is to remove living microorganisms that cause harm to humans.
Harmful microorganisms include pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria, their spores, viruses, fungi, helminths and their eggs.
Disinfection methods:
- Chemical : water treatment with ozone, chlorine dioxide, sodium hypochlorite, polymer antiseptics. These substances kill pathogens or make them unable to reproduce;
- Physical : water treatment with ultraviolet rays, ultrasound;
- Complex : combining chemical and physical methods.
Requirements and regulations
Wastewater must be treated to the level of TAC or MPC , especially if it is returned to fishery water bodies. This rule is prescribed in SanPiN 2.1.5.980-00 “Hygienic requirements for the protection of surface waters.”
After biological treatment, BODp should decrease to 15 mg/l, and suspended solids - to 70 mg/l.
After deep cleaning, the BOD value does not exceed 3-5 mg/l, and the concentration of suspended matter does not exceed 1-2 mg/l.
Other requirements and regulations:
- GN 2.1.5.689-98 “Maximum permissible concentrations (MAC) of chemicals in water of water bodies for domestic, drinking and cultural water use”;
- GN 2.1.5.690-98 “Approximately permissible levels (TAL) of chemical substances in water of water bodies for domestic, drinking and cultural water use.”
2. It is prohibited to discharge industrial wastewater containing:
- substances that can clog pipes, wells, gratings or deposit on the walls of pipes, wells, gratings (scale, lime, sand, gypsum, metal shavings, hide, cane, etc.);
— substances that have a destructive effect on the material of pipes and elements of sewerage structures;
— substances that impair wastewater treatment; — dangerous bacterial contaminants;
— radioactive substances;
— insoluble oils, resins, fuel oil;
— biological difficult-to-oxidize organic substances;
— biological “hard” surfactants;
— only mineral substances (including water from water treatment plants at thermal power plants and boiler houses);
- substances for which maximum limits have not been established
— permissible concentrations (MPC) in water of economic water bodies
— drinking, cultural, domestic and fishery water use. 3. It is strictly prohibited to discharge into the sewerage system:
- acids;
- flammable mixtures;
- toxic and soluble gaseous substances (in particular, solvents, gasoline, diethyl ether, dichloromethane, benzene, etc.) capable of forming toxic gases (hydrogen sulfide, carbon monoxide, hydrocyanic acids, vapors of highly volatile aromatic hydrocarbons, etc.) in sewer networks and structures .);
— explosive and toxic mixtures.
4. Industrial wastewater that has:
— COD is more than 2.5 times higher than BOD5 or total BOD. more than 1.5 times;
— concentrated mother and still solutions;
— volley discharges of industrial wastewater. A salvo discharge is considered to be the discharge of harmful substances into the sewer system of one or more substances regulated by these Rules in concentrations exceeding the MPC by 100 times or more;
— sediments from local treatment facilities, soil, construction and household waste, industrial waste;
— drainage and regulatory
— clean industrial wastewater;
— surface runoff from the territories of industrial sites (rain, melt, irrigation water, etc.).
5. In the water disposal systems of subscribers, it is not allowed to combine industrial wastewater, the interaction of which can lead to the formation of emulsions, toxic or explosive gases, as well as large amounts of insoluble substances (for example, wastewater containing calcium or magnesium salts, or alkaline solutions; soda and acidic waters; sulfates and waters with excessive acid content; sodium sulfide and waters with excessive alkali content; chlorine and phenol, etc.
6. Discharge of industrial wastewater into the sewer system must be carried out through independent outlets with a control well installed outside the territory of the enterprise. Sampling is carried out by employees of the Municipal Unitary Enterprise "UVKH" together with the subscriber's representative.
7. Industrial wastewater can be accepted into the sewer system if the content of harmful substances in it does not exceed the values specified in Appendix No. 1. The MPC of substances not listed in Appendix No. 1 when discharged into the sewer system should be taken as the corresponding MPC in the water of fishery reservoirs water use.
8. Maximum permissible concentrations of harmful substances for industrial wastewater specified in Appendix No. 1 are determined taking into account:
— MPC of pollutants in the water of water bodies used for fishing purposes, according to clause 19 of the “Rules for the Protection of Surface Waters,” 1991;
— conditions for the discharge of treated wastewater into the river. Ryazanka after sewage treatment plants;
— efficiency of removal of pollutants from industrial wastewater at sewage treatment plants;
— the ratio of the volumes of urban and industrial wastewater entering sewerage treatment plants;
— the possibility of using sludge from sewage treatment plants as fertilizer.
According to the requirement of Art. 27 of the Federal Law of December 7, 2011 No. 416-FZ “On Water Supply and Wastewater Disposal” in order to prevent negative impacts on the environment for the facilities of subscribers of the organization engaged in wastewater disposal, the categories of which are determined by Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of March 18, 2013 No. 230, standards for permissible discharges of pollutants, other substances and microorganisms are established (hereinafter referred to as standards for permissible discharges of subscribers), as well as limits for discharges of pollutants, other substances and microorganisms.
Calculation of standards for permissible discharges of pollutants is carried out in accordance with the Methodology for developing standards for permissible discharges of substances and microorganisms into water bodies for water users, approved by Order of the Ministry of Natural Resources of Russia dated December 17, 2007 No. 333.
Information necessary for calculating VAT for subscribers, provided by the organization providing wastewater disposal:
Standards for permissible discharges of substances and microorganisms into the river. Ryazanka (VAT) for the municipal unitary enterprise "UVKH" were approved by the Water Resources Department of the Upper Volga Water Resources Management Institution in the Nizhny Novgorod Region dated July 2, 2014 No. 12-10/1370 for a period of 5 years.
According to the classification, the sewer networks of the municipal unitary enterprise "UVKH" belong to centralized household wastewater systems. Permissible concentrations of pollutants and other substances (Срс) in wastewater entering the wastewater systems of the organization carrying out wastewater disposal are given in Appendix 1. Concentrations of pollutants in wastewater from housing facilities (Szh) are presented in Appendix 2.
The annual consumption of wastewater (Q) entering the treatment facilities of the municipal unitary enterprise "UVKH", necessary for calculating VAT, is 2,355.3 thousand cubic meters. m, of which:
— annual wastewater consumption of subscribers not related to the housing stock (Qpr) — 1,436.7 thousand cubic meters. m.; - annual wastewater consumption from housing facilities, (Ql) - 918.6 thousand cubic meters. m.
Stages of contaminant extraction
There are 3 degrees of extraction of contaminants from wastewater:
- Primary – removal of debris, coarse impurities, surface contaminants and suspended solids.
- Secondary – decomposition of organic waste.
- Tertiary (additional treatment) – extraction of suspended and colloidal particles, pesticides, fungicides, precipitation of phosphorus and nitrogen residues, reduction of COD. Indicators are brought to the standards of ODU or MPC.
At these stages, the following methods are used:
- Mechanical - the use of stationary or mobile filter units: coarse filters, sedimentation tanks, surface contaminant traps. After mechanical cleaning, the amount of contaminants in wastewater is reduced by 30-60%.
- Biological – cleaning using living microorganisms: bacteria, fungi, protozoa. Microorganisms use organic matter as food and convert it into safe biogas, methane and water. Biological methods eliminate 92-96% of contaminants.
- Physico-chemical – purification of wastewater from dissolved impurities and suspended solids using the laws of physics and chemical reagents. 96-98% of fine particles are removed from water.
- Disinfection – destruction of pathogenic bacteria and viruses. According to regulations, wastewater must not contain pathogens, so the efficiency of disinfection reaches 99.9%.
To clean gasoline, fuel oil, kerosene, and petroleum oils, oil traps and porous sorbents are most actively used:
- Activated carbon;
- Clays;
- Coke;
- Peat;
- Ash;
- Silica gels.
Reference. The maximum permissible concentration of petroleum products in wastewater does not exceed 0.01-0.3 mg/l. Such small values are due to the toxicity of the compounds to living organisms.
Question 85: Water statistics
Hydrosphere- this is the totality of waters of internal and territorial seas, lakes, rivers, reservoirs, groundwater, glaciers, ponds, canals and other surface water bodies.
The state of water resources largely depends on the level of treatment of discharged wastewater.
Wastewater
is water that is discharged after use in a process and does not provide any immediate value to that process.
Cleaning of drains
is a wastewater treatment process that ensures it meets established water quality standards.
There are three types of treatment:
1) mechanical wastewater treatment - simple mechanical separation of purified water and solids or sediments in wastewater without biological influences;
2) biological wastewater treatment - purification of filtered wastewater by artificially regulated biological processes using living organisms, usually microorganisms;
3) chemical wastewater treatment - the use of special methods to increase the efficiency of biological treatment to remove nutrients or minerals.
According to the existing sanitary classification, wastewater, depending on the degree of mechanical, chemical and bacterial contamination, is divided into standard-clean, standard-purified and contaminated.
Regulatory (conditionally) – clean wastewater
– these are all types of industrial and municipal wastewater that, entering natural water bodies without treatment, do not deteriorate the standard quality of water in a given area of the reservoir.
Regulatory treated wastewater
– these are those industrial and municipal wastewater that enter surface water bodies after treatment at the appropriate water treatment facilities. At the same time, the content of pollutants in such wastewater should not exceed the established maximum permissible discharges (MPD).
Contaminated wastewater
– these are all industrial, industrial and municipal wastewater (including volley discharges) with a content of pollutants above the approved maximum permissible limits, discharged into natural water sources after insufficient treatment or without treatment at all.
When characterizing the level of water pollution, the actual content of a particular pollutant is compared with its maximum permissible concentration (MAC).
Indicators characterizing the quantitative and qualitative state of water resources and water bodies include:
1) the main quantitative and qualitative indicators that determine the state of water resources and objects available in the area of the economic complex;
2) the volume of water resources involved in the process of use;
3) shortage of water resources (if any) and ways to cover it;
4) establishing a limit for the consumption of fresh water from their source (both surface and underground) and a limit for the discharge of wastewater (both untreated and treated);
5) achievement of temporarily agreed emissions (AT), discharges (VSS), maximum permissible emissions (MPE), discharges (MPD), maximum permissible concentrations (MAC), pollutants in wastewater of enterprises and organizations discharging them into a water body or system sewerage.
Indicators of rational use of water resources and water bodies include:
1) specific water consumption for product creation;
2) specific emissions of harmful pollutants possible with a given production technology;
3) commissioning of facilities for recycling, reuse, and sequential use of water in technological processes;
4) introduction of low-water, water-saving technologies, including the effect of their implementation.
Table of contents
Purification of various wastes
Industrial
Industrial and industrial wastewater needs to be treated to reduce the load on city facilities . The technological scheme differs fundamentally depending on the composition of the wastewater. Some wastewater is saturated with organic matter, others with heavy metal ions.
Indicators of TSP (total suspended particles), BOD5 and COD can reach tens of hundreds of mg/l. The acidity level often exceeds 6-9.
Before discharging wastewater into the city treatment system, BOD5 is adjusted to 400 mg/l, and the pH is reduced to 6-9. The technological scheme is selected depending on the composition of the water.
The above methods are combined in different sequences , some may be eliminated.
Household
This category of wastewater includes water from the bathroom, kitchen, laundry and water that is formed after cleaning the premises. About 58% of pollution is organic, and 42% is mineral. Domestic wastewater contains detergents and pathogens.
Common methods for treating household wastewater are biological. Disinfectants and disinfection reagents must be used .
Superficial
These wastes include:
- rain;
- thawed;
- Irrigation water from populated areas and industrial sites.
Through the drainage system, the liquid enters the sewer, then enters the sump.
Some of the impurities settle out, after which the wastewater is pumped to a flotator, where oil products are removed.
Then purification occurs using mechanical and sorption filters. The wastewater is disinfected and returned to natural bodies of water .
Types of wastewater
Based on the composition of contaminants, wastewater from enterprises is divided into three groups:
- Inorganic waste;
- Wastewater with organic matter;
- A mixture of inorganic and organic contaminants.
The first group includes industrial wastewater from factories that produce soda, sulfates and nitrogen compounds, as well as those using metals, alkalis and acids in their technology.
The second group includes enterprises of the food industry, organic synthesis and oil refineries.
The third group is electroplating and textile production, where acids and alkalis are combined with metals, organic dyes or oils.
Types of structures
The table describes the equipment that is used at different stages of wastewater treatment.
For the mechanical stage:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Sand traps | Horizontal or vertical installations of oblong shape. | Water moves through the equipment at a speed of 0.15-0.3 m/s. At this rate, mineral impurities with a diameter of 0.25 mm or more settle to the bottom, and small particles of organic matter remain in the water. |
| Septic tanks | Reservoirs where water stands still or moves very slowly. | Mechanical impurities settle to the bottom under the force of gravity. |
| Lattices | A filter cloth made of metal rods, which are located at a distance of 2-8 mm from each other. | Water passes through the rods and large debris is retained. |
| Oil traps and oil sand traps | 3-4 separate chambers connected to each other. | In the chambers, the wastewater settles, passes through a grate and a coalescence filter, and sorption materials. |
For the physico-chemical stage:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Flotators | Reservoirs in which gas bubbles form. They are generated by an electric pump / electrolysis process / rotating turbines. | Gas bubbles rise and take with them fine particles. |
| Flocculators | A system of pipes in which the coagulant is mixed with wastewater and a chemical reaction occurs. | Coagulants combine with contaminants, form large flakes and precipitate. |
For the biological stage:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Aero tanks | A rectangular tank through which wastewater mixed with activated sludge flows. | Aerobic bacteria break down organic matter in the presence of oxygen. O2 is supplied by mechanical or pneumatic aerators. |
| Membrane bioreactors | An aeration tank with a membrane that retains activated sludge after processing organic matter. | Aerobic bacteria break down organic matter in the presence of oxygen. O2 is supplied by mechanical or pneumatic aerators. |
| Biofilters | A reservoir with loading material on the surface of which a film of microorganisms forms. | The water passes through a porous filter media. The biological film on the granules breaks down contaminants. |
Filtration systems:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Fixed partitions | Installations with filter fabric of different porosity. | The water passes through the filters and the contaminants remain behind the separating sheet. |
| Grain filters | Granular porous materials that are poured into pipes, tanks, flasks. | Water passes through the absorbent material granules and contaminants accumulate on their surface. |
| Ultrafiltration systems | Filters equipped with membranes - materials with a pore size of up to 0.2 microns. | The membranes allow water to pass through, but retain high-molecular contaminants (99.9% of impurities). |
Disinfection equipment:
| Installation | What is | Principle of operation |
| Ozonizers | Electrical installations with long hoses. The devices generate ozone, which penetrates into the water through tubes. | Ozone oxidizes lipids and lipoproteins of the bacterial cell wall. This leads to structural changes that are incompatible with cell life. |
| UV disinfectants | Devices equipped with several lamps. They are immersed in water and there they emit UV rays. | The lamps generate waves with a length of 200-280 nm. They destroy the genetic apparatus of harmful bacteria and viruses, which prevents them from reproducing. |
Water disposal and wastewater treatment in a private home
With the help of communication systems that serve to drain wastewater, waste and waste liquids are removed from premises and production workshops. Water disposal and wastewater treatment are part of the sewer network, where wastewater is received, passed, and processed using a centralized drainage system.
Liquids, which are wastewater, differ in physical properties and origin. For example, these include precipitation and groundwater. Contaminants are varied in composition and create a favorable environment for the proliferation of microbes. Therefore, they become sources of diseases. When drained, toxic liquid can pollute the surrounding environment.
Drains are:
- atmospheric, which are formed during precipitation. This includes meltwater. They are characterized by a high concentration of contaminants. (garbage, sand, clay particles);
- production, formed as a result of technical processes. In the food industry, a large proportion of contaminants are organic impurities;
- household waste entering the drainage system from residential buildings, medical institutions, and enterprises. Such waters contain organic contaminants up to 58% of the total mass of impurities.
The task of wastewater disposal is to eliminate the negative consequences of contaminated wastewater. These systems provide for purification and disinfection of passing liquid. For this, special devices are used. After purification, the quality of the water becomes suitable for reuse, for example, in an industrial enterprise.
Water disposal and wastewater treatment: standards
There are certain standards for the composition of wastewater. These requirements are designed to protect the drainage system from negative impacts.
Water disposal and wastewater treatment is carried out using: pumping stations that help pump water when gravity flow is not possible;
- mechanical processing stations where sand separators are used;
- grease removal systems;
- aeration tank. In-ground or above-ground biological purifiers;
- chemical cleaning equipment, which is indispensable in production processes;
- membrane purifiers that free wastewater from impurities.
Disposal fluids contain many aggressive chemical compounds. Multi-level filtration is performed to eliminate impurities. The purification methods used are divided into destructive and recuperative groups. In the first case, complex substances are decomposed into simpler ones. Then they either settle to the bottom or escape as a gas mixture. With the recovery method, valuable substances are extracted from the flowing liquid and used for recycling.
To assess the composition of wastewater, chemical analysis is carried out. These measures make it possible to identify the bacteriological and physical qualities of the liquid.
For example, parameters such as:
- pH value;
- remainder (dry, complete);
- coloring;
- temperature;
- settling, suspended elements;
- nitrogen;
- microbial number;
- helminth eggs;
- coli.
After cleaning, a solid phase of impurities called sediments is formed. To remove these contaminants, a special set of measures is used.
Cleaning activities are carried out in 4 stages:
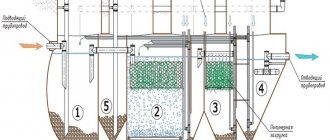
- mechanical stage. The means for this method are grates, sand traps, settling tanks, septic tanks, and filters. At the mechanical stage, preliminary purification of the discharged liquid occurs, retention of coarse inclusions;
- biological treatment. It is considered the main one. Dissolved parts of contaminants are purified through a special biocenosis;
- physico-chemical. This method is used for post-treatment of suspended solids;
- disinfection. Water is disinfected for disposal into a reservoir.
Water disposal and wastewater treatment: gratings
Large impurities are retained during drainage using special gratings. The most common of these products is an inclined type. The gratings are installed at an angle of approximately 70 degrees. This is done for the convenience of freeing them from contamination. If there is a large amount of trapped dirt, mechanical cleaning of the grates is provided.
The width of the slots in this type of mechanical cleaners reaches 16 mm. The gratings help retain debris (organic, mineral). Next, the wastewater penetrates through sand traps. Broken glass and sand settle in them. Grease traps are used to remove hydrophobic components.
Primary settling tanks are then made for the wastewater, where the suspended particles settle. The mechanical stage allows you to create a uniform movement of waste. At the same time, they are cleaned by 60% of mineral debris.
Biological stage
Biological treatment is carried out through anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. This type of cleaning is carried out using different methods. Aerotanks are often used. These systems are implemented in cyclic, flow modes.
After the aeration tank, the wastewater is poured into the next settling tank with suction pumps. There the bottom is cleared of silt, which is returned to the aeration tank.
In biological treatment, activated sludge first comes into contact with contaminated water. Then settling occurs, that is, the active substance is separated from the purified water. To speed up the sludge separation procedure, a membrane separation method is used, which involves ultrafiltration membranes.
Physico-chemical cleaning
Physico-chemical cleaning methods are based on aeration, flotation, hyperfiltration, centrifugation, evaporation, crystallization. An important stage is sludge dewatering. This is done using various technologies. The following are used:
- belt presses;
- disk dehydrators;
- chamber filter presses;
- centrifuges.
To make dehydration more effective, a reagent is used. Of all these methods, centrifuges are considered the most popular, with the help of which it is possible to obtain a high-quality separation of fractions into liquid and solid.
In this case, the process can be performed automatically. It is high speed and efficient. Separation in a centrifugal field is carried out at maximum speed. If the wastewater contains metal salts, then a special technology is used.
Water disposal and wastewater treatment from metal salts
Water disposal and wastewater treatment at an industrial enterprise means that the wastewater contains a huge amount of metal salts. Therefore, deep cleaning is required to reduce the concentration of toxic elements before discharging wastewater into a reservoir. Neutralization is the most popular method of removing salts from liquids during the drainage process. In this case, an increase in the pH of the wastewater is expected. The disadvantage of this technology is the need for additional purification due to the low efficiency of the method. For this purpose, precipitating reagents are used to carry out the necessary reactions.
Disinfection of drains
Final cleaning and disinfection of wastewater occurs thanks to ultraviolet irradiation and treatment with chlorine, which is a reagent used in many treatment plants. However, due to the toxicity of this substance, this reagent is replaced with others.
Drainage system
Drainage and wastewater treatment involves the use of grates, drainage systems, and sand traps. The grate looks like a plate with slits for water to drain. Trays are made from different materials. For example, made of hard plastic. Their length is 50-100 cm, depth – 10-15 centimeters, width – 2-4 cm. The dimensions of these products are chosen taking into account the need for drainage from a particular area. After rain, water flows down the trays. It is sent to sand traps, which are equipped with baskets designed to filter large debris. This basket must be removed during drainage so that it can be cleaned.
Grease traps are important for drainage. It is especially important to install them in public catering establishments, where a large amount of fat that pollutes the drainage system is washed off every day. Grease traps are devices that help clean water from grease.
Autonomous sewers
Local treatment facilities are designed specifically for areas located away from the main public sewer systems. Their introduction into private suburban housing construction helped:
- Reduce the risk and degree of harm to the environment;
- Make country life no less comfortable than in the city.
Unlike cesspools, dangerous insoluble fractions accumulate in a sump-storage tank. This section of the station, like all others, is completely sealed. Access to it is opened only intentionally, during the maintenance process. Also, unlike cesspools, you will not need to regularly turn to cesspools and experience the inconvenience of emitted aromas.
It is worth listing the advantages of using VOCs separately:
- Independence from the general public utility line, and therefore from tariffs in payment documents;
- High degree of reliability. Competition in the field is quite high, so manufacturers have to worry about quality;
- Protection from aggressive climatic conditions;
- Good level of noise reduction;
- Environmental friendliness, allowing the reuse of waste water, the degree of purification of which is about 98%;
- Long service life, accompanied by a warranty;
- No harmful fumes or unpleasant odors.
By the way, about the first point. Central drainage and wastewater treatment are not only monthly expenses, the amount of which grows with enviable frequency from season to season. Ask your neighbors or friends how much it cost them to initially install a public highway to their house. For that amount, you can install either a septic tank with unimaginable performance, or for your family, but several of them at once.
No need to worry about the location on the site. Modern deep biological treatment stations occupy a minimum of space, bringing maximum benefits. The view will only open to a couple of small hatches necessary for servicing the station. The remaining tanks and communications run underground.
How to choose?
The selection of a wastewater treatment device is based on the number of residents, bathrooms and plumbing fixtures located in the room. The performance must be enough for users, otherwise the system is in danger of overflowing, flooding, or failure.
On the contrary, there is no need for excess productivity either. We explain: special bacteria live in the system, due to the vital activity of which water is purified. High performance - large tank. A large reservoir means a lot of bacteria. Insufficient productivity will not allow microorganisms to survive. This means that the quality of the station’s work will have to be forgotten.
The model range of modern manufacturers today is so wide that there is a suitable system for everyone: from a small family (even from one loved one) to an entire townhouse, shopping center or hotel.
The above selection methods are classic. There are unique situations when the determination is made based on:
- The nature of the soil. If the land on the site is particularly absorbent, moisture permeable, has a high level of groundwater, is flooded from season to season, or has other complications, they move from standard models to specialized ones tailored to the problem;
- The nature of the incoming liquid. Is the wastewater characterized by particular contamination, danger, toxicity and requires additional filtration? Selection is carried out individually;
- Regularity of residence. There are models that are best used only on an ongoing basis. Others will survive seasonal appearance and use without any problems, without requiring conservation and re-preservation;
- Cramped conditions. Ideally, take care of the system at the zero stage of construction. But it happens that the sewerage system is connected to a house that has been occupied for a long time, which has already acquired gazebos, garages, summer kitchens and other household and outbuildings. Then the engineer makes a selection depending on the space that the septic tank can occupy;
- Budget. Of course, this is one of the most important criteria. If you initially know that the budget you have set is not flexible, give up famous brands. Most often the price is inflated for the name. Yes, this is a brand reputation, thanks to which you will be more confident in the performance of the station. On the other hand, there are a lot of companies that produce models no worse than Topas and Tanks. It is worth discussing this with an engineer or manager - it is also not in their interests to sell you something that will result in a complaint.
Possible problems
They want to equate the standards for the content of pollutants in treated wastewater to the world standards, and the majority of Russian enterprises use physically outdated equipment .
Purification using technologies developed in the last century does not reduce the level of impurities to the required levels.
Modern equipment is expensive. For example, UV disinfectants are installed only in the capital and several large cities. In most populated areas, the equipment has become so outdated that wastewater is often discharged into water bodies without treatment.
Some private entrepreneurs do not want to invest in the construction of treatment facilities. They dump polluted water into rivers.
Other wastewater treatment problems:
- Selection of an ineffective technological scheme;
- Inability to dispose or bury waste, pollution, and by-products;
- Lack of money for electricity, equipment maintenance and repair, and transportation costs.
Existing problems can only be solved at the legislative level : increase fines for violations, finance city wastewater treatment plants and control the expenditure of money, encourage private owners to introduce new technologies, offering them various discounts and benefits.
Honest inspections should be carried out more often, which can be spontaneous - without warning.
Companies
Mosvodokanal is responsible for cleaning urban wastewater in the capital.
This is a public utility company that operates wastewater treatment plants:
- Kuryanovsky;
- Lyubertsy;
- Yuzhno-Butovskie;
- Zelenogradskie.
Reference. Every day they receive more than 3 million cubic meters. m of domestic and storm water.
All large cities have their own wastewater treatment plants, which are controlled by the local water utility.
Private companies design and build treatment facilities for industrial enterprises and business complexes. A large company in Russia is Ecolos . It produces wastewater treatment plants of various sizes on a turnkey basis, focusing on the needs of customers.
Another large company with similar activities is REATORG . She is engaged in environmental engineering, repair and construction work, design and estimate calculations, etc. The company is focused on industrial facilities.