Scope of application
The first arc furnaces were invented back in the nineteenth century. They were used for smelting metals. Over time, the equipment has been significantly improved. Today, arc furnaces have become indispensable in the metallurgical industry.
The process of remelting steel in arc furnaces is carried out due to the high temperature regime, which is achieved through an electric arc. Thus, the conversion of electrical energy into thermal energy occurs.
Due to their high technical characteristics, arc furnaces are used to create various alloys that are used in defense and aviation structures. Using such thermal equipment, it is possible to obtain homogeneous alloys of any metals.
Some types of arc furnaces are used to determine physical and chemical analyses. Such studies are mainly carried out to identify the quantities of constituents of various materials.
Electric arc furnace design
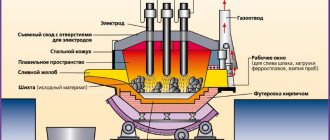
Regardless of design features, all arc furnaces are designed almost identically. Thermal steelmaking units consist of the following basic elements:
- mechanical device;
- electrical department;
- automated system control;
- device for feeding materials into the working part;
- the container in which the melting is carried out;
- waste disposal system;
- gas purification.
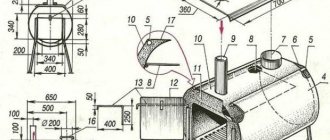
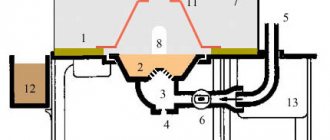
The cylindrical body of the furnace includes detachable parts - a casing and a bottom. The frame is highly resistant to significant temperature influences.
The design has holders in which graphite electrodes are installed. Electricity supply cables are connected to them. During operation of the furnace, a constant arc is formed between the electrodes. Thanks to it, a temperature arises in the device, which ensures the melting of metals.
What does an electric arc furnace look like?
Devices designed for automatic control of the entire system are built into the closed body of the furnace structure. The melting process is controlled using doors. There are several cavities in the frame to remove waste. Through them, various additives are also introduced to adjust the composition of the metal.
The charge can be loaded into the furnace through the working window or from above. Devices that feed material through a special opening are usually small in size. It is fashionable to load scrap metal into such units manually using a wide shovel.
Furnaces with top charge feed are more powerful and larger devices. They have a rather complex design. The mechanism of the device can be of three types:
- rotary vault;
- roll-out housing;
- rollable vault.
The most common are arc units with a rotating mechanism.
Gas furnaces for melting non-ferrous metals
Non-ferrous metals include copper, magnesium, bronze, lead, aluminum, and titanium. Each metal has its own melting characteristics. Any gas furnace for melting non-ferrous metals must have the ability not only to melt, but also to quickly heat up. Depending on the required characteristics of the melt, the configuration of the furnace and gas burners is selected. Gas furnaces quickly melt non-ferrous metals, because they do not have a high melting point: aluminum 660 °C, copper 1083 °C, lead 327 °C, zinc 419 °C.
Non-ferrous metals are melted using a removable refractory graphite crucible. Conventional lining takes a lot of time (stuffing, drying). Crucibles are changed within 15-30 minutes without stopping the work process.
Operating principle of steel-smelting electric arc units
The main function of arc furnaces is to release heat to the arc due to the high accumulation of electricity. Thanks to this, metal is melted at a significant heating rate.
An arc can burn both in the vapor of the processed material and in a normal atmosphere. The most popular in the industrial sector are electric arc steel-smelting furnaces. To produce steel, secondary raw materials – scrap – are consumed. The melting process consists of several stages:
- the vault rises;
- the charge is loaded into the furnace using a special crane;
- the arch is fixed in place;
- electrical power is supplied to the electrodes;
- electrical conductors touch the scrap loaded into the unit;
- an interphase short circuit is formed;
- automatic lifting of holders with electrodes is triggered;
- an electric arc ignites.
Thus, the operation of the furnace begins, which occurs at a high power temperature. It consists of the following main stages:
- Melting scrap metal. The heated charge is covered with a protective film, which blocks the access of harmful gases to the material. At the same time, various substances that have a bad effect on the quality of the metal are absorbed.
- Oxidation process. Harmful elements are corrected. At this time, the temperature in the unit rises. Its value becomes 120 degrees higher than the limit established for metal melting. Phosphorus and sulfur should occupy no more than 0.15 percent in the total composition. Hydrogen and nitrogen levels are also monitored.
- Recovery. Sulfur elements are removed from the material, and the composition of the metal is brought to standard values.
The operating process of a furnace device largely depends on its design and functional features.
Melting gold and silver
A gold smelting furnace is easy to make at home. It is also applicable for smelting silver.
The operating procedure is as follows:
- A fireclay brick is taken and cut into 2 parts. Using a Pobedit drill with a diameter of 48 mm, a through hole is made in one half, in the middle. And in the second hole is drilled to half the height.
- A spiral is drawn through the hole and both halves are tightened with bolts, holes for which are drilled from the sides.
- A graphite crucible is installed on top.
- A metal frame is made and both halves are inserted into it.
- All side gaps are covered with clay.
- Voltage is applied to the removed ends of the spiral.
- Pieces of gold or silver are thrown into the crucible.
- During the heating process, the non-ferrous metal melts.
Making furnaces for melting metal with your own hands is a complex process, but doable. To do this, you need to study the characteristics of the types of equipment. Decide which one is most preferable to the given conditions. Manufacturing costs will quickly pay for themselves.
Types and characteristics of electric arc furnaces
Modern arc furnaces come in a variety of sizes and have a distinctive set of features.
Indirect arc furnaces
Arc combustion in such furnaces occurs between electrodes that are located above the molten mass. Due to this, heat exchange occurs between the material and the source of energy transfer. The radiation emanating from the arc, as well as convection, allows the metal to be heated to the temperature necessary for its melting.
Indirect arc furnaces are equipped with the following electrical equipment:
- electric drive of the feed mechanism for consumable electrodes;
- transformer;
- adjusting device.
Such ovens come in capacities of 0.5 and 0.25 tons. The maximum power of the power transformer can be 600 KV/A.
Current flow from the transformer substation to the electrodes is carried out through flexible cables. Adjustment of the distance between electrical conductors is carried out through automated control.
Indirect electric arc furnaces have a low coefficient of waste emission and metal evaporation. A reduction in the yield of vaporous substances is achieved due to the high location of the eclectic arc from the material to be melted.
Indirect arc furnaces are used for remelting various non-ferrous metals and their alloys. Often such thermal equipment is used in the smelting of certain types of nickel and cast iron.
Indirect arc furnaces are relatively small and it is impossible to carry out all metal remelting processes in them, since some alloys require more power and higher temperatures.
Direct arc furnaces
In such furnace devices, an arc is formed between an electrical conductor and molten metal, which thereby heats up. Due to direct contact between the electrode and the material, high evaporation of the metal occurs.
Direct electric arc furnaces are quite powerful equipment that can operate on three-phase current. They are distinguished by their high productivity and are mainly used for smelting various refractory metals into ingots, including structural and high-alloy steels.
Direct electric arc furnace
The electric furnace is equipped with hydraulic or electromechanical drive mechanisms that allow tilting to drain molten steel, turning and lifting the roof, and moving the electrodes. Current is supplied to the conductor holders by air-cooled copper pipes or busbars.
The process of igniting the electrodes is carried out by lowering them to the molten metal. After this, an electric arc is formed during the lifting of the conductors.
Resistance arc furnaces
A special feature of resistance furnaces is that the arc is formed inside the material being melted. The charge can be directed relative to the electrical discharge in parallel or in series.
Resistance arc furnaces do not have a tilt function. The molten mass passes through a special hole - a tap hole. The electrodes are located vertically in the structure. They are relatively large in size. Thanks to this, the unit can operate with high power and at a significant current.
In furnaces of this type, metals are melted with a high resistivity. Such equipment is used for smelting and reducing ore. Using resistance arc furnaces, it is possible to produce alloys of cast iron, carbide, abrasives, calcium, and nickel matte. Resistance thermal installations, unlike other types of arc furnaces, are capable of raising the temperature to extreme levels.
Vacuum arc furnaces
Such units belong to direct-acting equipment. The arc in vacuum furnaces burns in vapor or inert gas of the metal being melted. The process occurs at low pressure. There are two types of vacuum furnaces:
- With consumable electrode. The arc in such devices burns between the electrical conductor being melted and a bath of liquid metal.
- With non-consumable electrode. An electrical discharge occurs between the graphite electrical conductor and the metal, which is melted.
In both the first and second variants, melting is carried out in a vacuum chamber. All heating elements of such equipment are cooled with water. Thanks to this, various operations can be carried out in vacuum furnaces at fairly high temperatures.
Units with non-consumable electrodes are practically not used in industry. Their main purpose is to smelt small-sized ingots in laboratory conditions. They are a good tool for performing various analyses.
Example of an electric arc furnace
Vacuum arc furnaces with a consumable electrode are widely used for industrial purposes. In such devices, when working with metal, the following processes occur:
- melting;
- recovery;
- deoxidation;
- crystallization.
At the same time, at high temperatures, volatile gas impurities are removed, and unstable compounds decompose. Thanks to this, in vacuum arc furnaces it is possible to obtain material with a low content of non-metallic impurities and gases.
Vacuum furnaces are used for industrial purposes in industries such as rocketry and nuclear energy. Using such equipment it is possible to obtain ingots weighing more than 50 tons.
Plasma arc furnaces
In such installations, the metal is heated by an electric arc passing along with a jet of inert gas plasma. This process ensures the purity of the melted material, and also allows you to significantly increase the productivity of furnace equipment.
In plasma-arc furnaces, metals with a low oxygen content are smelted. The melting process is carried out in a neutral atmosphere, which allows creating all the conditions for maximum gas release. Metal smelting occurs at high speed.
Flame-arc furnaces are used to produce high-quality steel and alloys. Their use is much cheaper than metal smelting in vacuum furnaces.
Gas furnaces for aluminum smelting
Aluminum smelting is carried out in electric, gas, crucible, electric resistance and induction furnaces. To obtain a well-mixed aluminum melt, it is best to use induction melting furnaces. If you want to save money, then you need to use gas ovens. In general, the choice of furnace depends on the purpose of the alloy and the nature of production.
Crucible or rotary furnaces are also used for melting aluminum and its alloys. A gas crucible furnace for aluminum melting has the necessary power and various modifications. In turn, crucible furnaces can be gas or induction. The model is selected depending on the current metal processing needs.
Advantages and disadvantages
The use of electric arc furnaces for steel smelting is widely used in the metallurgical industry. The main advantages of using such equipment are the ability to carry out the following operations:
- melting the charge regardless of its composition;
- rapid heating of metal in a furnace;
- temperature control;
- deoxidation of the metal and resulting in a material with a low content of impurities.
When remelting steel in a furnace unit, all conditions are created to reduce the waste of alloying components. This ensures that metal losses due to oxidation at high temperatures are reduced.
Electric arc units are widely used for industrial purposes for melting various metals. With their help you can obtain high-quality strong steel alloys. The efficiency of an arc furnace largely depends on the quality of the heating device. Therefore, you should purchase reliable equipment from well-known and trusted manufacturers.
Gas consumption of gas melting furnaces
Gas consumption during operation of melting furnaces depends on the gas burner. Low and medium pressure burners are installed on gas thermal furnaces. A correctly selected gas burner should provide:
- supplying the required amount of gas and air to the combustion zone;
- good mixing of the charge;
- complete combustion of gas with a minimum excess air ratio;
- good heat exchange inside the melting unit, eliminating local overheating;
- stable operation within the required range of changes in thermal output.
Gas consumption when melting 1 ton of copper or aluminum charge ranges from 60 to 100 m3/hour.