Characteristics of steel grade 15kp
15KP - High-quality structural carbon steel, welds well, welding is carried out without heating and without subsequent heat treatment, welding methods: manual arc welding, automatic submerged arc welding and gas protection, KTS, ESW.
Not prone to flake sensitivity, no tendency to temper brittleness. Cutting machinability: in the hot-rolled state at in the hot-rolled state at HB 143 and σв=450 MPa, K υ solid. spl = 1.8. It has found its application in elements of pipe connections; fittings, plugs and other parts for boiler and turbine construction are made from it, operating at temperatures from -40 to 425 ° C; after carburization and cyanidation - parts that require high surface hardness and low core strength. Forging is carried out at temperatures from 1300 to 700 0C, cooling is carried out in air.
Characteristics of steel grade 15Х25Т
| Standard | GOST 5582-75 – Rolled thin-sheet corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant and heat-resistant. Specifications | |
| Application | Long products, rods, silver sheets, strips, forgings and forged blanks, pipes | |
| Classification | Corrosion-resistant, heat-resistant steel (old name X25T EI439) | |
The main areas of application of steel 15Х25Т
Steel 15Х25Т
is used in the production of welded structures, assemblies and parts that operate at temperatures
from -20°С to 1100°С
, and which are not subject to shock loads; pipes for heat exchange equipment operating in aggressive environments, equipment, thermocouple covers, spark plug electrodes, heat exchanger parts.
Steel marking 15Х25Т
Decoding steel 15Х25Т
: 15 – percentage of carbon (0.15%), “X25” – the presence of chromium in the alloy in an amount from 24% to 27%. The letter “T” at the end of the marking without a number means the presence of titanium in an amount of up to 1.0%.
Interpretation of steel grade 15kp
Explanation of 15kp steel: Structural high-quality carbon steels are produced in converters or in open-hearth furnaces. The designation of these steel grades begins with the word “Steel”. The next two numbers indicate the average carbon content in hundredths of a percent; numbers 15 indicate a content of about 0.15 percent. The letters after the carbon content indicate the degree of deoxidation: kp - boiling. In terms of price, boiling steels are the cheapest, but their cold brittleness threshold is 30 - 40% higher than calm steels. Steel 15kp – structural steel, low-carbon, high-quality, containing 0.15% carbon from boiling casting.
Steel grade 15: main characteristics and chemical composition
Alloy grade 15 is endowed with relatively high hardness: HB 10-1=149 MPa. At the same time, it can be welded without restrictions and is not prone to temper brittleness and the formation of flakes. The remaining physical and mechanical characteristics of this metal are given in the tables:
As for the chemical composition of steel 15, which ensures its compliance with a high-quality structural carbon alloy, it is represented by the following elements:
- Fe – about 98%
- Mn – 0.35-0.65%
- Si – 0.17-0.37%
- Ni – no more than 0.25%
- Cr – no more than 0.25%
- Cu – no more than 0.25%
- C – 0.12-0.19%
- As – no more than 0.08%
- S – no more than 0.04%
- P – no more than 0.035%
Delivery 15kp
Supplied in the form of long products, including shaped steel according to the regulations of GOST 2590-2006 Hot-rolled round steel , GOST 2591-2006 Hot-rolled square steel , GOST 1133-71 Forged round and square steel, GOST 19771-93 Equal-flange bent steel angles , GOST 8509-93 Hot rolled equal flange steel angles , GOST 8510-86 Hot rolled unequal flange steel angles , GOST 103-2006 long steel strip , GOST 503-81 Cold rolled low carbon steel strip, GOST 103-76 Hot rolled steel strip , GOST 8 2-70 Hot-rolled broadband universal steel, GOST 3282-74 General purpose low-carbon steel wire , GOST 17305-71 Carbon structural steel wire , GOST 3262-75 Steel water and gas pipes .
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 1133-71; GOST 8283-93; GOST 8282-83; GOST 8281-80; GOST 8278-83; GOST 2879-2006; GOST 2591-2006; GOST 2590-2006; GOST 19771-93; GOST 9234-74; GOST 10551-75; GOST 11474-76; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 14918-80; GOST 103-2006; GOST 6765-75; GOST 16523-97; GOST 82-70; GOST 19903-74; GOST 19904-90; |
| Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 1050-88; GOST 8560-78; GOST 1051-73; GOST 8559-75; GOST 10702-78; GOST 7417-75; GOST 14955-77; |
| Sheets and strips | GOST 1577-93; GOST 4405-75; GOST 4041-71; |
| Ribbons | GOST 19851-74; GOST 1530-78; GOST 10234-77; |
| Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 10704-91; GOST 10705-80; GOST 10707-80; GOST 3262-75; |
| Classification, nomenclature and general norms | GOST 2771-81; |
| Low carbon steel wire | GOST 5663-79; GOST 792-67; GOST 1526-81; |
| Medium and high carbon steel wire | GOST 9850-72; GOST 17305-91; GOST 7372-79; GOST 26366-84; GOST 3920-70; |
GOST standards for the production and use of grade 15 steel
Enterprises purchase steel 15 in the form of shaped bars manufactured in accordance with GOST standards:
- GOST 10705-80 and 10704-91 – pipes
- GOST 7417-75, 10702-78, 8559-75, 8560-78 – calibrated rods
- GOST 14955-77 and 10702-78 – ground rods and silver
- GOST 103-2006 and 82-70 – stripes
- GOST 5663-79 and 17305-91 – wire
- GOST 19903-74 and 1577-93 – thick sheets
- GOST 16523-97 – thin sheets
- GOST 6009-74, 10234-77 and 2284-79 – tapes
- GOST 8479-70 – forged blanks and forgings
Grade 15 steel is very popular in industry because it is used for the production of screws, bolts and other parts characterized by high ductility and strength. The operating temperature range for this alloy is very wide: from -40°C to 450°C. Having undergone appropriate heat treatment, grade 15 steel is endowed with high surface hardness, which makes it possible to obtain wear-resistant nuts, levers, cams and other elements of components and mechanisms from it.
Mechanical properties of 15kp steel
| Type of delivery | Size | Eg. | sв | sT | d5 | y | KCU | Heat treatment |
| — | mm | — | MPa | MPa | % | % | kJ/m2 | — |
| Heat treated sheet, GOST 4041-71 | 4-14 | 320-440 | 30 | |||||
| Pipes, GOST 10705-80 | 314 | 196 | 25 | |||||
| Calibrated steel, GOST 10702-78 | 392 | 8 | 50 | |||||
| Strip, GOST 1577-93 | 6-60 | 350 | 205 | 29 | 55 | Normalization |
Mechanical properties of material 15Х25Т
| Rental | Direction | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Short-term strength limit, ST, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % | Relative narrowing, ψ, % | Impact strength KCU at 20°C, J/cm2 |
| Sheet | Transverse | 430 | — | 12 | — | 200 |
| Bar | Longitudinal | 450 | 300 | 20 | 45 | — |
| Thin sheet | — | 530 | — | 17 | — | — |
| Cold-deformed pipes | — | 461 | — | 17 | — | — |
| Hot-deformed pipes | — | 441 | — | 17 | — | — |
Mechanical properties of steel depending on the degree of plastic deformation
| Deformation degree, % | Tensile strength, σв, MPa | Elongation at break, δ5, % |
| 0 | 450 | 32 |
| 10 | 600 | 15 |
| 20 | 700 | 10 |
| 30 | 760 | 8 |
| 40 | 800 | 7 |
| 50 | 840 | 6 |
| 60 | 860 | 5 |
Mechanical properties of steel during long-term strength testing
| Creep limit, MPa | Creep rate, %/hour | Temperature, ºС | Long-term strength limit, MPa | Test duration, hour | Temperature, ºС |
| 12 | 1/1000 | 700 | 18 | 1000 | 700 |
| 8 | 1/10000 | 700 | 8 | 1000 | 800 |
| 3 | 1/1000 | 875 | 4 | 1000 | 875 |
| 2 | 1/10000 | 875 | 3 | 1000 | 1000 |
Heat resistance
| Wednesday | Temperature, °C | Test duration, hour | Depth, mm/year | Strength group or score |
| Air | 850 | — | 0,175 | 6 |
| Air | 950 | — | 0,294 | 6 |
| Air | 1050 | — | 0,490 | 6 |
| Fresh air | 900 | 500 | 0,39 | 6 |
| 1.5% SO2 + clean air | 900 | 500 | 0,54 | Low-resistant |
Corrosion resistance of steel
| Wednesday | Temperature, °C | Test duration, hour | Corrosion depth, mm/year |
| 6% HNO3 solution | 20 | 640 | 0,001 |
| 40% HNO3 solution | 20 | 640 | 0,001 |
| 85% H3PO4 solution | 20 | 480 | 0,01 |
Physical properties of steel 15kp
| Temperature | E 10- 5 | a 10 6 | l | r | C | R 10 9 |
| 0C | MPa | 1/Grad | W/(m deg) | kg/m3 | J/(kg deg) | Ohm m |
| 20 | 2,01 | 7850 | ||||
| 100 | 1.92 | 12.4 | 53 | 7827 | 465 | 233 |
| 200 | 1.85 | 13.2 | 53 | 7794 | 486 | 296 |
| 300 | 1.72 | 13.9 | 49 | 7759 | 515 | 387 |
| 400 | 1.56 | 14.4 | 46 | 7724 | 532 | 487 |
| 500 | 14,8 | 43 | 7687 | 565 | 607 | |
| 600 | 15.1 | 39 | 7648 | 586 | 753 | |
| 700 | 15.3 | 36 | 7611 | 620 | 904 | |
| 800 | 14.1 | 32 | 7599 | 691 | 1092 | |
| 900 | 13.2 | 30 | 7584 | 708 | 1140 | |
| 1000 | 13.3 |
At a temperature of +20 0C, the density of steel is 7850 kg/m3
Structural quality carbon steel 15
Mark 15 – purpose
Structural high-quality carbon steel 15 is used for the manufacture of parts with high ductility, operating in the temperature range -40 +4500C - screws, bolts, hooks; after chemical treatment, products have high surface hardness, the strength of the core remains low - cams, levers, nuts, and other products.
Steel 15 - domestic analogues
| Rolled metal grade | Substitute |
| 15 | 10 |
| 20 |
Characteristics
| Brand | GOST | Foreign analogues | Classification |
| 15 | 4041–71 | There is | Structural high-quality carbon steel |
| 5005–82 | |||
| 1050–88 | |||
| 2284–79 | |||
| 1577–93 | |||
| 10702–78 |
Material 15 – technological properties
| Flock sensitivity | Weldability | Welding methods | Tendency to temper brittleness |
| not sensitive | no limits | KTS, RDS, ADS (flux + shielding gas) | not inclined |
Brand 15 – chemical composition
Mass fraction of elements no more than, %:
| Silicon | Manganese | Copper | Arsenic | Nickel | Sulfur | Carbon | Phosphorus | Chromium |
| 0,17–0,37 | 0,35–0,65 | 0,3 | 0,08 | 0,3 | 0,04 | 0,12–0,19 | 0,035 | 0,25 |
Steel 15 – mechanical properties
| Assortment | GOST | Dimensions – thickness, diameter | Heat treatment | KCU | y | d5 | sT | sв |
| mm | kJ/m2 | % | % | MPa | MPa | |||
| Sheet | 4041–71 | 4–14 | There is | 30 | 320–440 | |||
| Pipes | 5005–82 | 8 | 430 | 510 | ||||
| Rental | 1050–88 | up to 80 | Normalization | 55 | 27 | 225 | 370 | |
| hardened. | 45 | 8 | 440 | |||||
| annealed | 55 | 23 | 340 | |||||
| The tape is annealed. | 2284–79 | 20 | 310–490 | |||||
| hardened. | 440–780 |
Material 15 – hardness, MPa
| Assortment | GOST | HB 10-1 |
| The rental is calibrated. hardened. | 1050–88 | 197 |
| hot rolled | 149 | |
| calibrated I'll anneal | 149 | |
| Sheet after heat treatment | 4041–71 | 121 |
| thick annealed. | 1577–93 | 143 |
| The rod is hot rolled. | 10702–78 | 125 |
Grade 15 – temperature of critical points, 0C
| Critical points | Ac1 | Ac3 | Ar1 | Ar3 |
| Temperature | 735 | 860 | 685 | 840 |
Steel 15 – impact strength, J/cm2
| Heat treatment, delivery condition | KCU at temperatures | |||
| -600WITH | -400WITH | -200WITH | +200WITH | |
| Hot rolled. | 16 | 14–26 | 75–86 | 73–113 |
| Annealed. | 8 | 14–35 | 49–57 | 82–84 |
| Normalized. | 48–65 | 66 | 53–80 | |
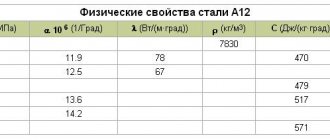
Material 15 – physical properties
| T | R 109 | E 10-5 | l | a 106 | r | C |
| hail | Ohm m | MPa | W/(m deg) | 1/Grad | kg/m3 | J/ (kg deg) |
| 20 | 2.01 | 53 | 7850 | |||
| 100 | 233 | 1.92 | 53 | 12.4 | 7827 | 465 |
| 200 | 296 | 1.85 | 53 | 13.2 | 7794 | 486 |
| 300 | 387 | 1.76 | 49 | 13.9 | 7759 | 515 |
| 400 | 487 | 1.56 | 46 | 14.4 | 7724 | 532 |
| 500 | 607 | 43 | 14.8 | 7687 | 565 | |
| 600 | 753 | 39 | 15.1 | 7648 | 586 | |
| 700 | 904 | 36 | 15.3 | 7611 | 620 | |
| 800 | 1092 | 32 | 14.1 | 7599 | 691 | |
| 900 | 1140 | 30 | 13.2 | 7584 | 708 |
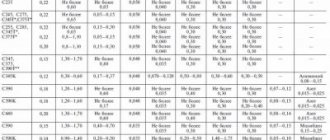
Brand – exact and closest foreign analogues
| Austria | England | Belgium | Bulgaria | Hungary | Germany | European Union | Spain | Italy | China |
| ONORM | B.S. | NBN | BDS | MSZ | DIN, WNR | EN | UNE | UNI | G.B. |
| RC15 |
| 080M15 |
| C15E |
| 1.1141 |
| C15 |
| C15E |
| Ck15 |
| Cq15 |
| RSt42-2 |
| 1.1141 |
| 2C15 |
| C15E2C |
| C15E |
| C15k |
| C16k |
| F.1110 |
| F.1511 |
| C16 |
| H15A |
| ZG200-400 |
| Poland | Romania | USA | France | Czech | Switzerland | Sweden | South Korea | Japan |
| PN | STAS | — | AFNOR | CSN | SNV | SS | KS | JIS |
| 15 |
| OLC15AT |
| OLC15X |
| 1016 |
| 1017 |
| 1018 |
| G10150 |
| G10170 |
| M1015 |
| M1017 |
| XC12 |
| XC15 |
| XC18 |
| 12023 |
| SM15CK |
| S15C |
| S15CK |
| S17C |
Chemical composition
GOST 801 - 78 determines the percentage of substances included in the composition of ShKh15:
- carbon up to 1.05%;
- chromium up to 1.65%;
- silicon up to 0.37%;
- manganese up to 0.4% and many others.
This composition provides high strength indicators, which make it possible to use this material for the manufacture of balls and inner rings for bearings of various types.
Decoding
The name ШХ15 indicates that it contains chromium in an amount of 1.5%. The letter Ш indicates that this brand is used for the manufacture of bearings.
Steel has the following features:
- it is prone to temper brittleness;
- the tensile strength of this material ranges from 590 to 750 MPa;
- at break, the elongation can be 20%;
- impact strength is 440 kJ/sq. M.
To achieve the specified strength parameters, the material is heated to temperatures exceeding the eutectoid transformation point, that is, the point when one solid solution is divided into two. This transformation creates the necessary concentration of substances such as carbon and chromium. In addition, fine, uniform grains are formed.
Analogs
The domestic industry produces the following analogues:
- ШХ9;
- ШХ12;
- SHH15SG.
There are also imported analogues:
- USA - 52100;
- Germany - 100Cr6;
- China - GCr15;
- South Korea - STB4.
GOST
Consumers can purchase the following products made from ШХ15 on the market:
- rental, incl. shaped - GOST 801-78;
- rod, incl. calibrated - GOST 7417-75;
- silver - GOST 14955-77;
- Strip, wire - GOST 103-76, GOST 4727-83.
The main properties include the following:
- homogeneous structure;
- machinability in various ways;
- hardness;
- obtaining a thin edge when sharpening a blade;
The alloy has such disadvantages as difficult sharpening and low resistance to corrosive factors.
Steel ШХ15
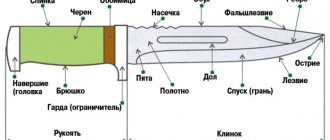
The development of metallurgy has led to the emergence of new types of steels with special performance characteristics. They are used in the production of certain products and parts that have high demands. A similar example is steel ШХ15. Its main purpose is the manufacture of bearings, but its performance indicators are also actively used in knife production.
Steel strips ШХ15.
Steel for quality knives
ShKh15 was first created as a production tool steel, but over time it gained greater versatility and turned into one of the best alloys for making knives.
The metal lends itself well to heat treatment, which allows it to be actively used in the production of cutting tools. After heat treatment, the strength and wear resistance of knives increases significantly.
Blades made of ШХ15 have a long service life , since resistance to external loads allows them to hold an edge for a long time. They withstand the influence of the external environment well.
Blade made of steel ШХ15.
ShKh15 steel for knives is used in the production of tactical, gift, hunting and kitchen models.
Such products cope with cutting meat, chopping bones and branches, cutting thick ropes, and all household tasks without any problems. This knife will be a godsend for an avid cook.
And if you carefully monitor and care for your instrument, it will last a long time.
Characteristic
ShKh15 steel received its wide industrial distribution due to its special performance properties, which are ideal for the manufacture of blades and bearings. Characteristics of ШХ15 consists of the following parameters:
- High hardness index . Bearings and blades are subjected to high loads during use, resulting in rapid wear. To prevent this from happening, the product must have additional hardness.
- Wear resistance , that is, the surface of ShKh15 is not subject to abrasion, which allows it to maintain its original working properties for a long time.
- Poor resistance to corrosion . Due to the small content of such an important element as chromium in the chemical composition, this alloy rusts when exposed to moisture, but this process does not occur very quickly due to other alloying components.
- Resistance to high shock and external mechanical loads . This metal practically does not form dents from precise impacts.
- Plasticity and toughness in the alloy in question are at an average level due to its high hardness.
- The steel structure lends itself well to heat treatment . Quenching and annealing make it possible to improve strength at the molecular level.
- Tendency to temper brittleness, which means that there is a small chance that the metal may become more brittle after quenching due to structural defects. But strict adherence to all technologies allows you to avoid this.
- Poor weldability . The alloy achieves high hardness due to its high carbon content, an element that negatively affects weldability.
pros
Having studied in detail the characteristics of steel grade ШХ15, we can draw intermediate results. Among the advantages of this alloy, the following qualities clearly stand out:
- homogeneity of structure;
- high contact endurance;
- easy to process;
- great hardness;
- excellent wear resistance;
- thin edge when sharpening;
- resistance to crushing;
- plasticity and viscosity.
Minuses
Any steel, no matter how good it is, has drawbacks - it has not yet been possible to obtain a metal that is ideal in all respects. However, the disadvantages of the ShKh15 are not numerous, among them the following can be distinguished:
- above average fragility;
- relatively low corrosion resistance;
- Difficult sharpening of cutting tools.
There are many different grades of steel. Each of them has its own advantages and disadvantages. ShKh 15, in turn, is a very versatile steel, suitable for almost any type of knife. At the moment it is one of the most popular brands with low cost and is used mainly in private forging of blades.
Knife Berkut, steel ШХ15, oxidation coating.
Chemical composition
ShKh15 steel has an unusual chemical composition , which determines its working properties. This brand belongs to low-alloy chromium alloys, which is due to a large number of base additives, which impart the same strength and wear resistance. The composition includes the following elements:
- Carbon (0.95-1%) – its fairly high concentration allows one to achieve increased hardness of the structure.
- Manganese (0.2-0.4%) is present in almost all steels. It is used to remove oxygen and sulfur from steel. It also has a beneficial effect on the ductility and weldability of steels.
- Silicon (0.17-0.37%) - used in steel smelting, has a positive effect on strength and improves the effect of other components. In combination with manganese or molybdenum, silicon provides higher hardenability of steel.
- Chromium (1.35-1.65%) – chromium ensures the alloy’s resistance to rust, but only if its content exceeds 13%. Therefore, ШХ15 is characterized by low corrosion resistance. A small amount of chromium determines that it does not form its own carbides, remains in solid solution and can be part of cementite. The structure is characterized by homogeneity with small carbides. It is this property that leads to increased wear resistance.
Decoding
At first glance, it may seem that the name of the alloy “ShKh15” is a simple set of beech. However, this is not at all true; these letters are abbreviation symbols and carry a semantic load. A person who knows at least a little about metal markings can extract some useful information from this name:
- Ш - according to GOST, all bearing steels are marked with this letter;
- X – means the presence of chromium in the chemical composition of steel;
- 15 – this is the percentage of chromium (1.5%).
GOST
State standards regulate the production stages, characteristics, properties of all steels, ShKh15 is no exception. All detailed information about bearing steels is contained in GOST 801-78.
The permissible limit of elements in the chemical composition, correct hardening, correct labeling, application, etc. are indicated here. Also, for each individual product for the production of which ShKh15 is used, it has its own GOST.
Types of material supply:
| B22 – Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 2590-2006; GOST 2591-2006; |
| B23 – Sheets and strips | GOST 103-2006; |
| B32 – Long and shaped rolled products | GOST 14955-77; GOST 7417-75; GOST 801-78; |
| B62 – Steel pipes and connecting parts for them | GOST 800-78; |
| B73 – Alloy steel wire | GOST 4727-83; |
Specifications
The working properties of ShKh15 steel have already been discussed above. That information is a simple explanation that follows from the following characteristics of this alloy:
- brand: ШХ15;
- class: structural bearing steel;
- specific gravity : 7812 kg/m3
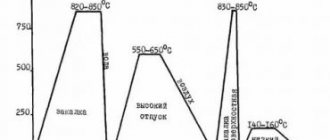
- heat treatment: annealing 800oC, oven, 15 oC/h;
- forging temperature, °C: beginning 1150, end 800. Sections up to 250 mm are cooled in air, 251-350 mm - in a pit;
- hardness : HB 10 -1 = 179 – 207 MPa (61-63 HRC);
- temperature of critical points: Ac1 = 724, Ac3(Acm) = 900, Ar3(Arcm) = 713, Ar1 = 700, Mn = 210;
- machinability by cutting: in the hot-woven state at HB 202 σв=740 MPa, K υ solid. spl=0.9 and Kυ b.st=0.36;
- weldability: welding method KTS;
- flake sensitivity: sensitive;
- tendency to temper brittleness : prone;
- grindability: good.
Analogs
ШХ15 has a large number of analogues around the world . This is due to the fact that bearing steels are subject to the same requirements.
The result is a similar chemical composition, production technology, and characteristics.
Below is a table with similar alloys from different countries of the world, but it is worth considering that their properties, and even more so their cost, are not identical, but simply have many similarities.
| Foreign analogues of steel grade ШХ15 | |
| USA | 52100, G52986, J19965 |
| Germany | 1.3505, 100Cr6, 102Cr6 |
| Japan | SUJ2, SUJ4 |
| France | 100C6, 100Cr6, 100Cr6RR |
| England | 2S135, 534A99, 535A99 |
| China | GCr15 |
Application
The use of ShKh15 is largely due to its high strength indicators and wear resistance - the main advantages of this brand. The scope of application is quite wide , the alloy is used to obtain:
- rollers with a diameter of up to 23 mm;
- discharge valves;
- pusher rollers;
- plungers;
- balls for bearings.
Bearings made of steel ШХ15.
Although this steel is defined as bearing steel, its use is not limited to this. It is actively used in the production of knives and other cutting tools because it has the necessary basic set of useful qualities.
Owner reviews
PreviousNext